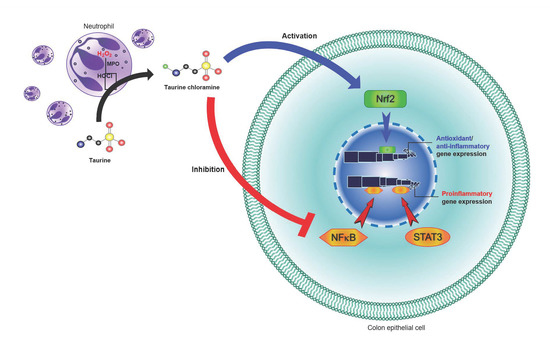
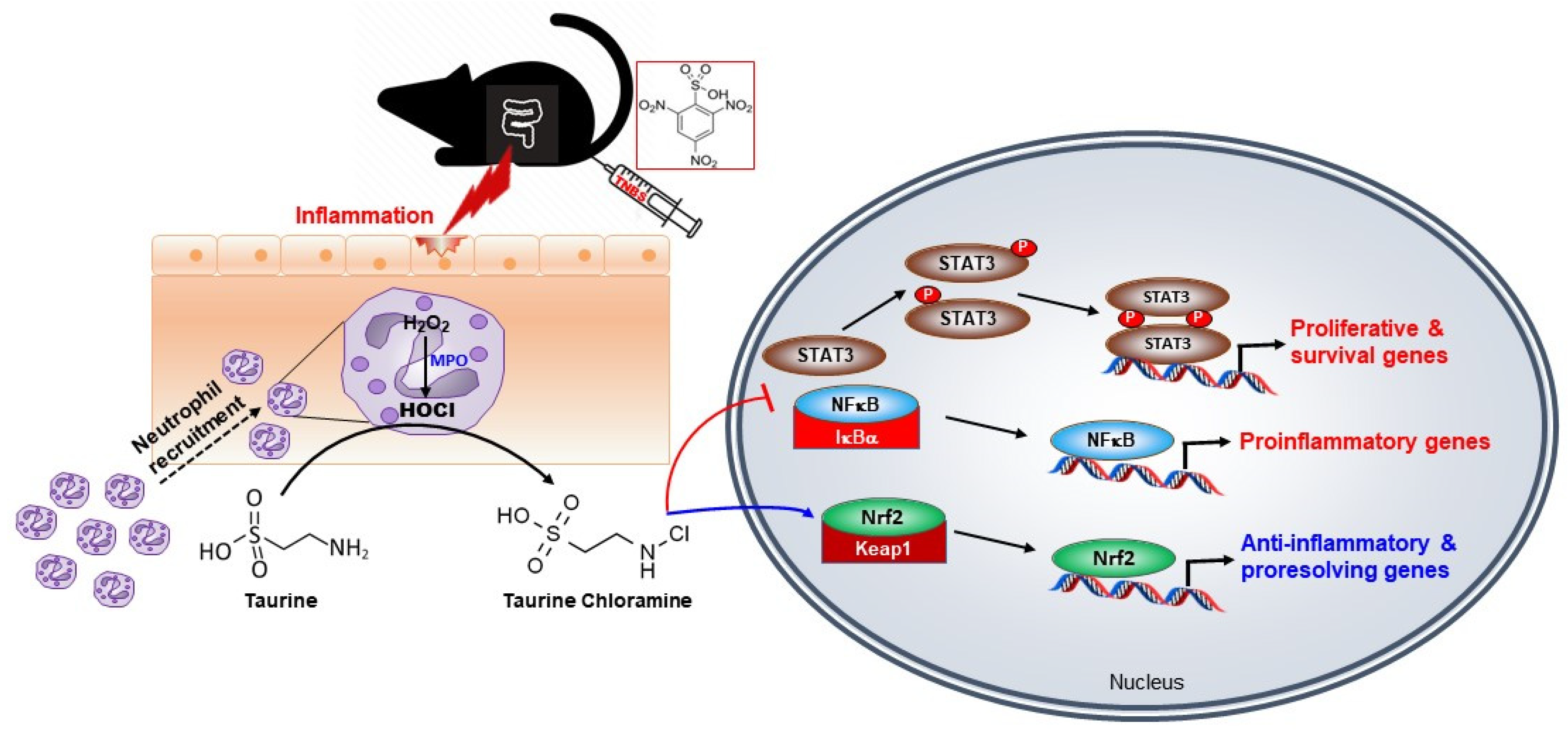
Protective Effects of Taurine Chloramine on Experimentally Induced Colitis: NF?B, STAT3, and Nrf2 as Potential Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice
2.4. Macroscopic Assessment
2.5. Histology
2.6. Measurement of MPO Activity
2.7. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.8. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
2.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.10. Tissue Lysis and Protein Extraction
2.11. Preparation of Cytosolic and Nuclear Extracts
2.12. Western Blot Analysis
2.13. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis (RT-PCR)
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TauCl Protects against TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice
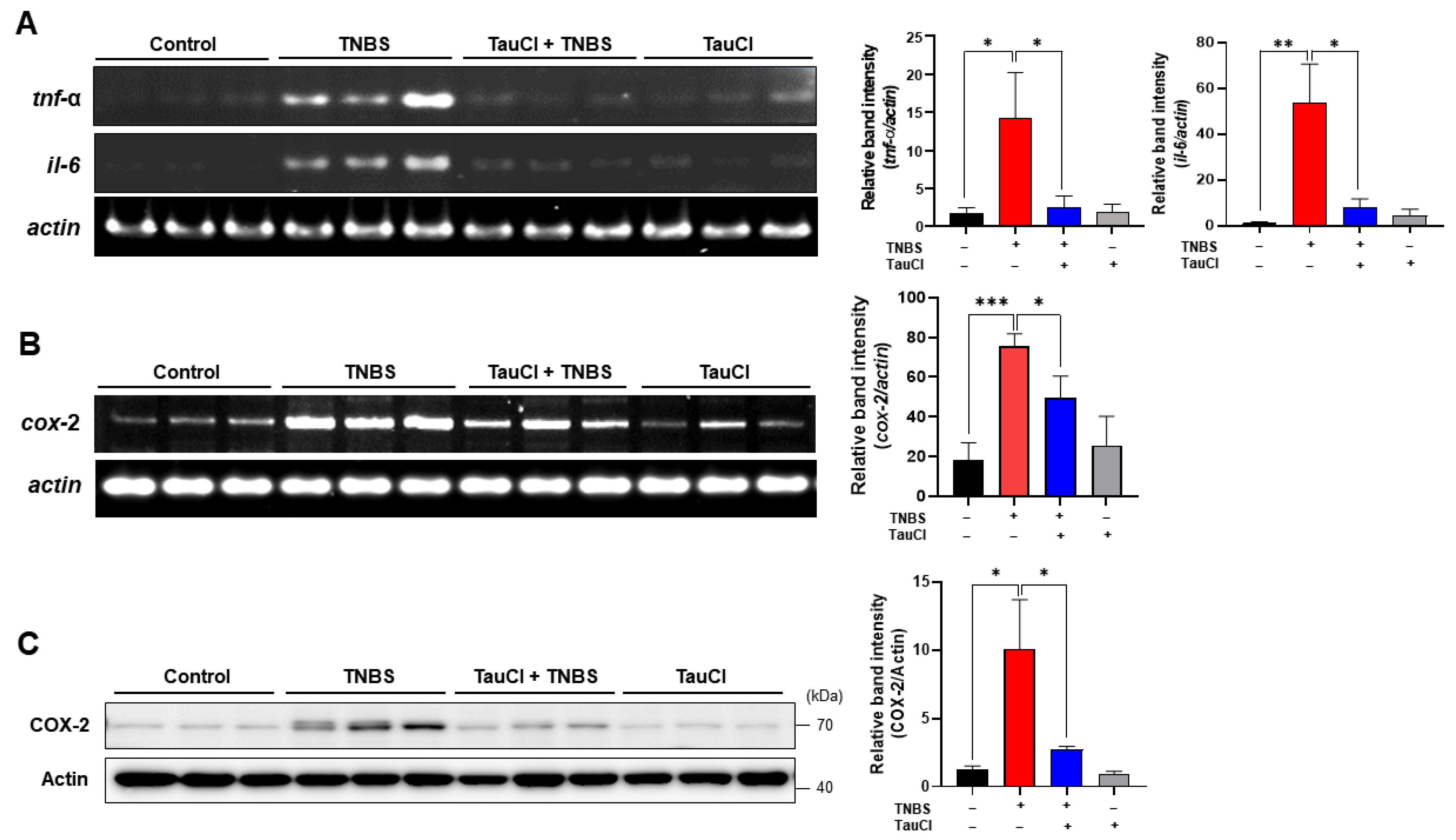
3.2. TauCl Administration Attenuates the Expression of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Enzymes in the Colon of TNBS-Treated Mice
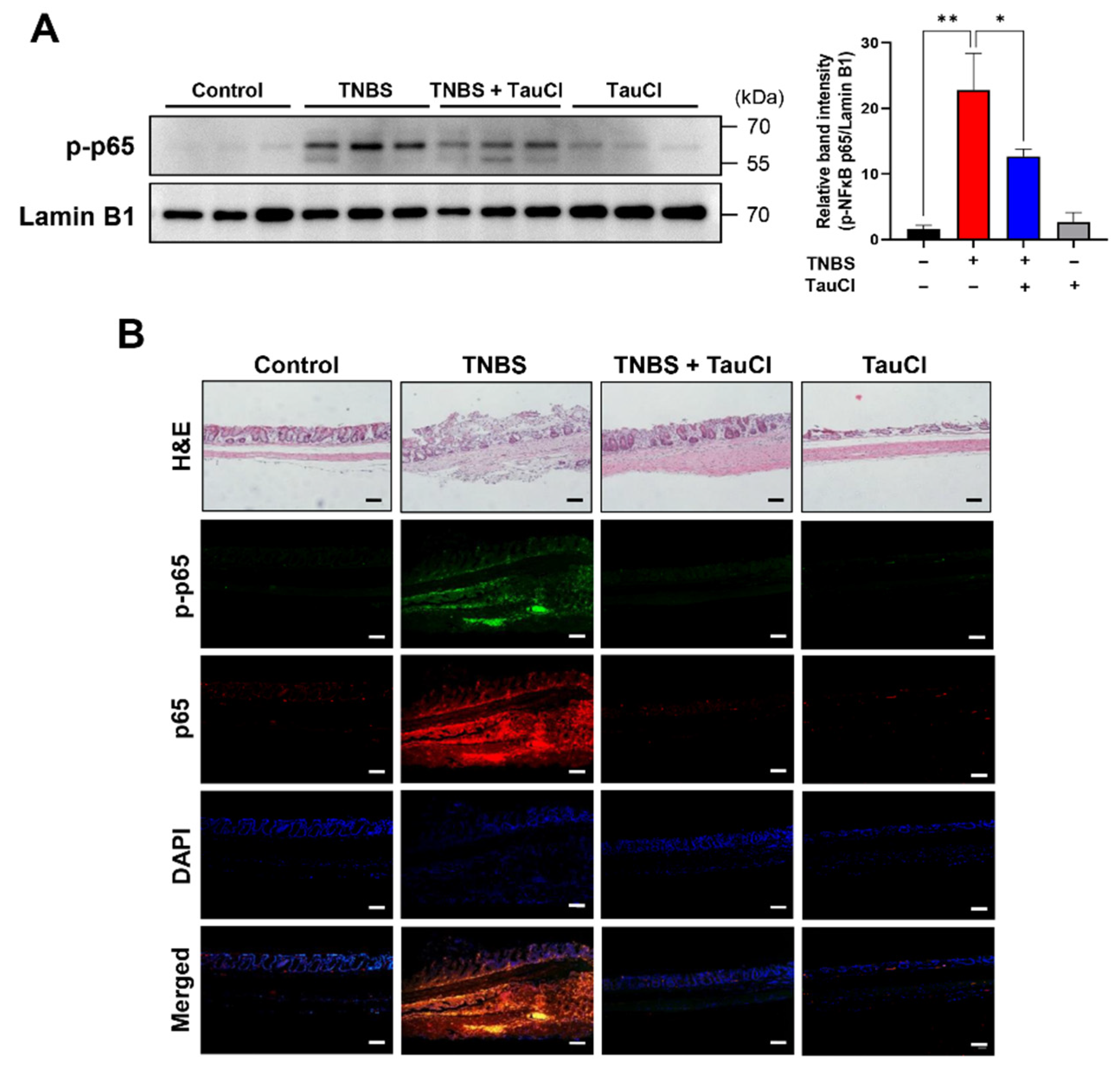
3.3. TNBS-Induced Colonic STAT3 Phosphorylation Was Inhibited by TauCl Administration
3.4. TauCl Administration Upregulates Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Gene Expression
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)? 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/what-is-IBD.htm (accessed on 12 February 2021).
- Luceri, C.; Bigagli, E.; Agostiniani, S.; Giudici, F.; Zambonin, D.; Scaringi, S.; Ficari, F.; Lodovici, M.; Malentacchi, C. Analysis of oxidative stress-related markers in crohn’s disease patients at surgery and correlations with clinical findings. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alemany-Cosme, E.; Sáez-González, E.; Moret, I.; Mateos, B.; Iborra, M.; Nos, P.; Sandoval, J.; Beltrán, B. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease and the interconnection with Immuiological response, microbiota, external environmental factors, and epigenetics. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, C.O.; Sartor, R.B.; Tennyson, G.S.; Riddell, R. Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1344–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, E.; Margonis, G.A.; Angelou, A.; Pikouli, A.; Argiri, P.; Karavokyros, I.; Papalois, A.; Pikoulis, E. The TNBS-induced colitis animal model: An overview. Ann. Med. Surg. 2016, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.; Fuss, I.; Strober, W. TNBS-colitis. Intern. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 19, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxtable, R.J. Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 101–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcinkiewicz, J.; Kontny, E. Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.; Cha, Y.-N. Taurine chloramine produced from taurine under inflammation provides anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.S.; Kim, C. Taurine chloramine administered in vivo increases NRF2-regulated antioxidant enzyme expression in murine peritoneal macrophages. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 775, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.S.; Piao, S.; Cha, Y.N.; Kim, C. Taurine chloramine activates Nrf2, increases HO-1 expression and protects cells from death caused by hydrogen peroxide. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottardi, W.; Nagi, M. Chemical properties of N-chlorotaurine sodium, a key compound in the human defence system. Arch. Pharm. 2002, 335, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chami, B.; Martin, N.J.J.; Dennis, J.M.; Witting, P.K. Myeloperoxidase in the inflamed colon: A novel target for treating inflammatory bowel disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 645, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansberry, D.R.; Shah, K.; Agarwal, P.; Agarwal, N. Fecal myeloperoxidase as a biomarker for inflammatory bowel disease. Cureus 2017, 9, e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lak, S.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Nagili, B.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Beigzali, S.; Salehi, F.; Djafarzadeh, R. Anti-inflammatory effect of taurine in burned patients. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, V.; Mahdavi, R.; Sharafabad, F.H.; Alizadeh, M. The effects of taurine supplementation on oxidative stress indices and infammation biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.W.; Ko, J.I.; Doh, H.M.; Kim, W.B.; Park, T.S.; Shim, M.J.; Kim, B.K. Protective effect of taurine on TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1998, 21, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giriş, M.; Depboylu, B.; Doğru-Abbasoğlu, S.; Erbil, Y.; Olgaç, V.; Alış, H.; Aykaç-Toker, G.; Uysal, M. Effect of taurine on oxidative stress and apoptosis-related protein expression in trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid-induced colitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Satsu, H.; Fujisawa, M.; Hori, M.; Ishimoto, Y.; Totsuka, M.; Nambu, A.; Kakuta, S.; Ozaki, H.; Shimizu, M. Attenuation by dietary taurine of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice and of THP-1-induced damage to intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Ishimoto, Y.; Satsu, H. Dietary taurine attenuates dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced ex perimental colitis in mice. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 643, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ma, N.; He, F.; Kawanishi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Oikawa, S.; Murata, M. Taurine attenuates carcinogenicity in ulcerative colitis-colorectal cancer mouse model. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 7935917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulfig, A.; Leichert, L.I. The effects of neutrophil-generated hypochlorous acid and other hypohalous acids on host and pathogens. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 385–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barua, M.; Liu, Y.; Quinn, M.R. Taurine chloramine inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and TNF-α gene expression in activated alveolar macrophages: Decreased NF-κB activation and IκB kinase activity. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanayama, A.; Inoue, J.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Miyamoto, Y. Oxidation of IκBα at methionine 45 is one cause of taurine chloramine-induced inhibition of NF-κB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 24049–24056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, H.N.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, C.; Cha, Y.N.; Joe, Y.; Chung, H.T.; Jang, J.; Kim, K.; et al. Taurine chloramine stimulates efferocytosis through upregulation of Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase-1 expression in murine macrophages: Possible involvement of carbon monoxide. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Zhong, X.; Kim, W.; Kim, K.; Suh, Y.G.; Kim, C.; Joe, Y.; Chung, H.T.; Cha, Y.N.; Surh, Y.J. Taurine chloramine potentiates phagocytic activity of peritoneal macrophages through up-regulation of dectin-1 mediated by heme oxygenase-1–derived carbon monoxide. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.; Suh, Y.G.; Joe, Y.; Chung, H.T.; Cha, Y.N.; Surh, Y.J. Role of heme oxygenase-1 in potentiation of phagocytic activity of macrophages by taurine chloramine: Implications for the resolution of zymosan A-induced murine peritonitis. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 327, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Ramos, C.; Campos, K.K.D.; de Paula Costa, G.; Cangussú, S.D.; Talvani, A.; Bezerra, F.S. Taurine treatment decreases inflammation and oxidative stress in lungs of adult mice exposed to cigarette smoke. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 98, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Qaradakhi, T.; Gadanec, L.K.; McSweeney, K.R.; Abraham, J.R.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Zulli, A. Inflammatory effect of taurine on cardiovascular disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffer, S.W.; Azuma, J.; Mozaffari, M. Role of antioxidant activity of taurine in diabetes. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 87, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.H.; Yum, H.-W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, C.; Kim, K.; Suh, Y.-G.; Surh, Y.-J. Protective Effects of Taurine Chloramine on Experimentally Induced Colitis: NF?B, STAT3, and Nrf2 as Potential Targets. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030479
Kim SH, Yum H-W, Kim SH, Kim W, Kim S-J, Kim C, Kim K, Suh Y-G, Surh Y-J. Protective Effects of Taurine Chloramine on Experimentally Induced Colitis: NF?B, STAT3, and Nrf2 as Potential Targets. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(3):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030479
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seong Hoon, Hye-Won Yum, Seung Hyeon Kim, Wonki Kim, Su-Jung Kim, Chaekyun Kim, Kyeojin Kim, Young-Ger Suh, and Young-Joon Surh. 2021. "Protective Effects of Taurine Chloramine on Experimentally Induced Colitis: NF?B, STAT3, and Nrf2 as Potential Targets" Antioxidants 10, no. 3: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030479
APA StyleKim, S. H., Yum, H.-W., Kim, S. H., Kim, W., Kim, S.-J., Kim, C., Kim, K., Suh, Y.-G., & Surh, Y.-J. (2021). Protective Effects of Taurine Chloramine on Experimentally Induced Colitis: NF?B, STAT3, and Nrf2 as Potential Targets. Antioxidants, 10(3), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030479