Antioxidants 2021, 10(4), 539; https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10040539 - 30 Mar 2021
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 4897
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the nervous system due to unceasing impairment of dopaminergic neurons situated in the substantia nigra. At present, anti-PD drugs acting on dopamine receptors are mainly symptomatic and have only very limited neuroprotective effects, whereas drugs
[...] Read more.
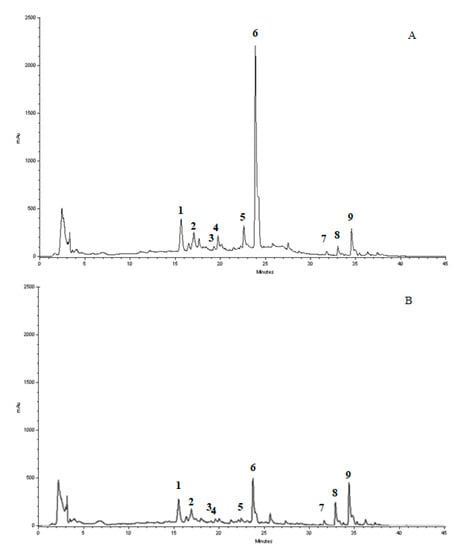
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the nervous system due to unceasing impairment of dopaminergic neurons situated in the substantia nigra. At present, anti-PD drugs acting on dopamine receptors are mainly symptomatic and have only very limited neuroprotective effects, whereas drugs slowing down neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons and deterioration of clinical symptoms are not yet available. Given that, the development of more valuable pharmacological strategies is highly demanded. Comprehensive research on innovative neuroprotective drugs has proven that anti-inflammatory and antioxidant molecules from food sources may prevent and/or counteract neurodegenerative diseases, such as PD. The present study was aimed at the evaluation the protective effect of mandarin juice extract (MJe) against 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell death. Treatment of differentiated SH-SY5Y cells with 6-OHDA brought cell death, and specifically, apoptosis, which was significantly inhibited by the preincubation with MJe through caspase 3 blockage and the modulation of p53, Bax, and Bcl-2 genes. In addition, it showed antioxidant properties in abiotic models as well as in vitro, where it reduced both reactive oxygen and nitrogen species induced by 6-OHDA, along with restored mitochondrial membrane potential, and prevented the oxidative DNA damage evoked by 6-OHDA. Furthermore, MJe restored the impaired balance of SNCA, LRRK2, PINK1, parkin, and DJ-1 gene levels, PD-related factors, caused by 6-OHDA oxidative stress. Overall, these results indicate that MJe exerts neuroprotective effects against 6-OHDA-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells by mechanisms involving both the specific interaction with intracellular pathways and its antioxidant capability. Our study suggests a novel possible strategy to prevent and/or ameliorate neurodegenerative diseases, such as PD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Natural or Synthetic Antioxidants for Neurodegenerative Diseases and Brain Health)
►
Show Figures