Effects of Vitamin B12 Deficiency on Amyloid-β Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C. elegans Strains
2.2. Preparation of B12-Deficient Worms
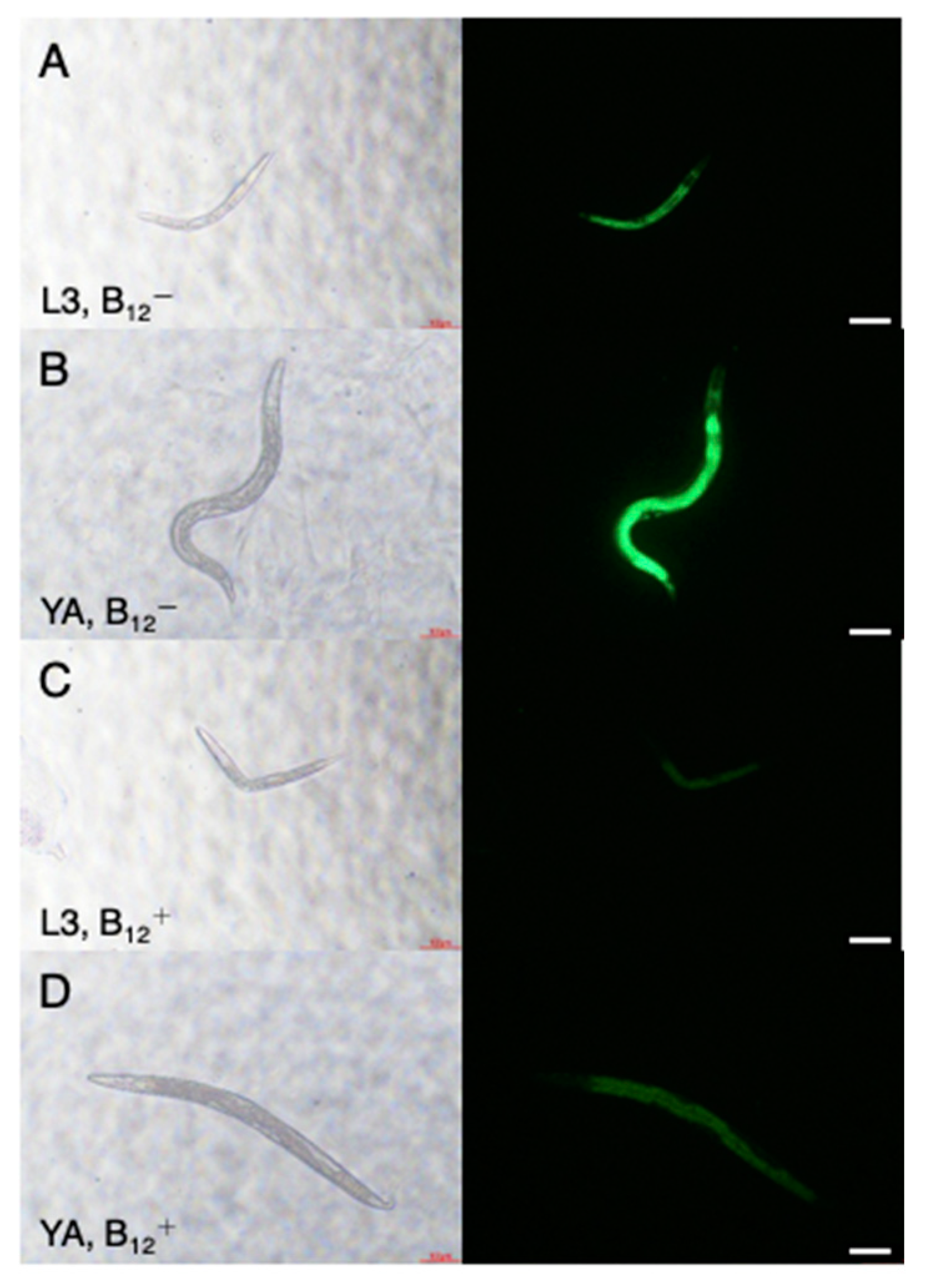
2.3. Fluorescence Imaging of Pacdh: GFP Transgenic Worms
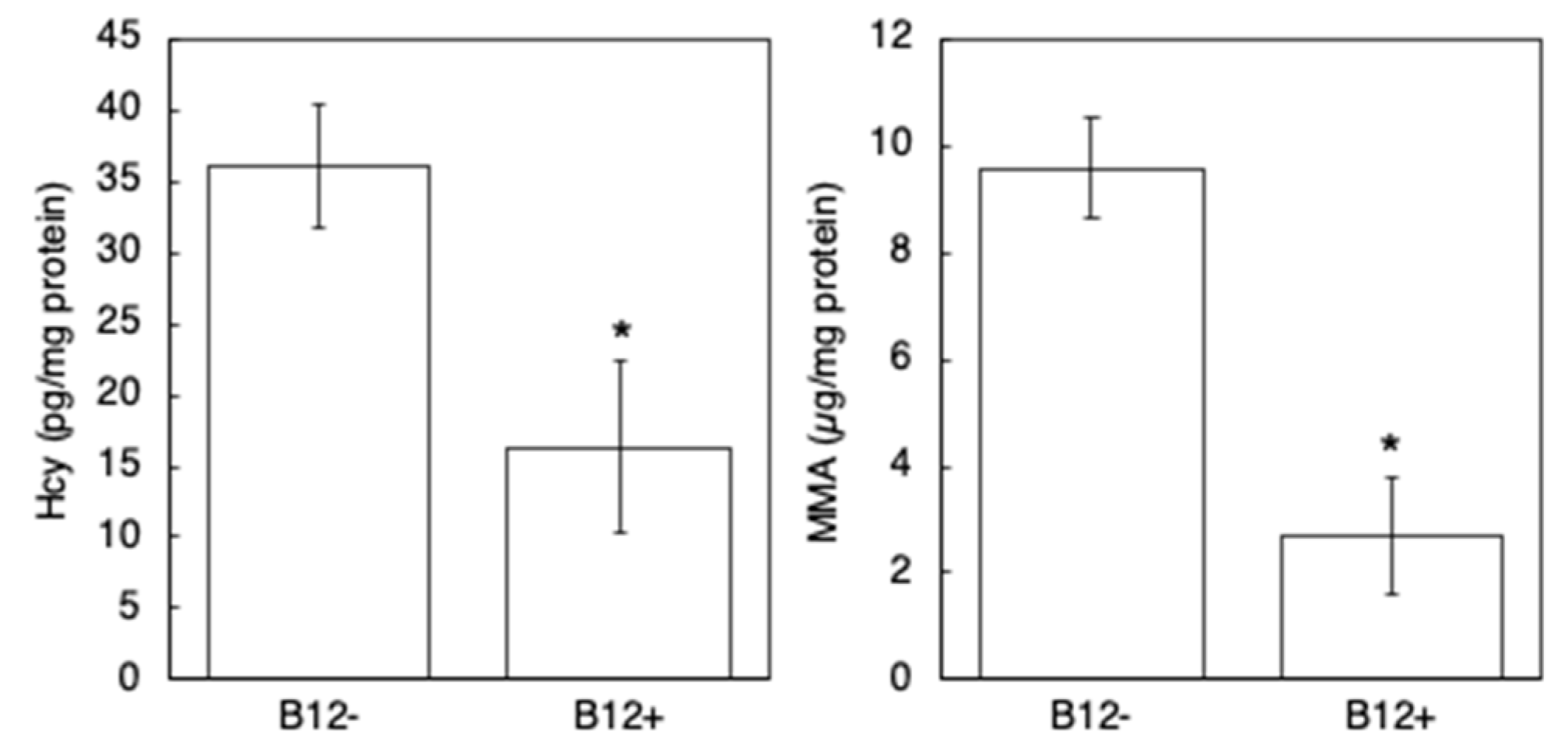
2.4. Measurement of B12-Related Biomarkers Using Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
2.5. Paralysis Assay
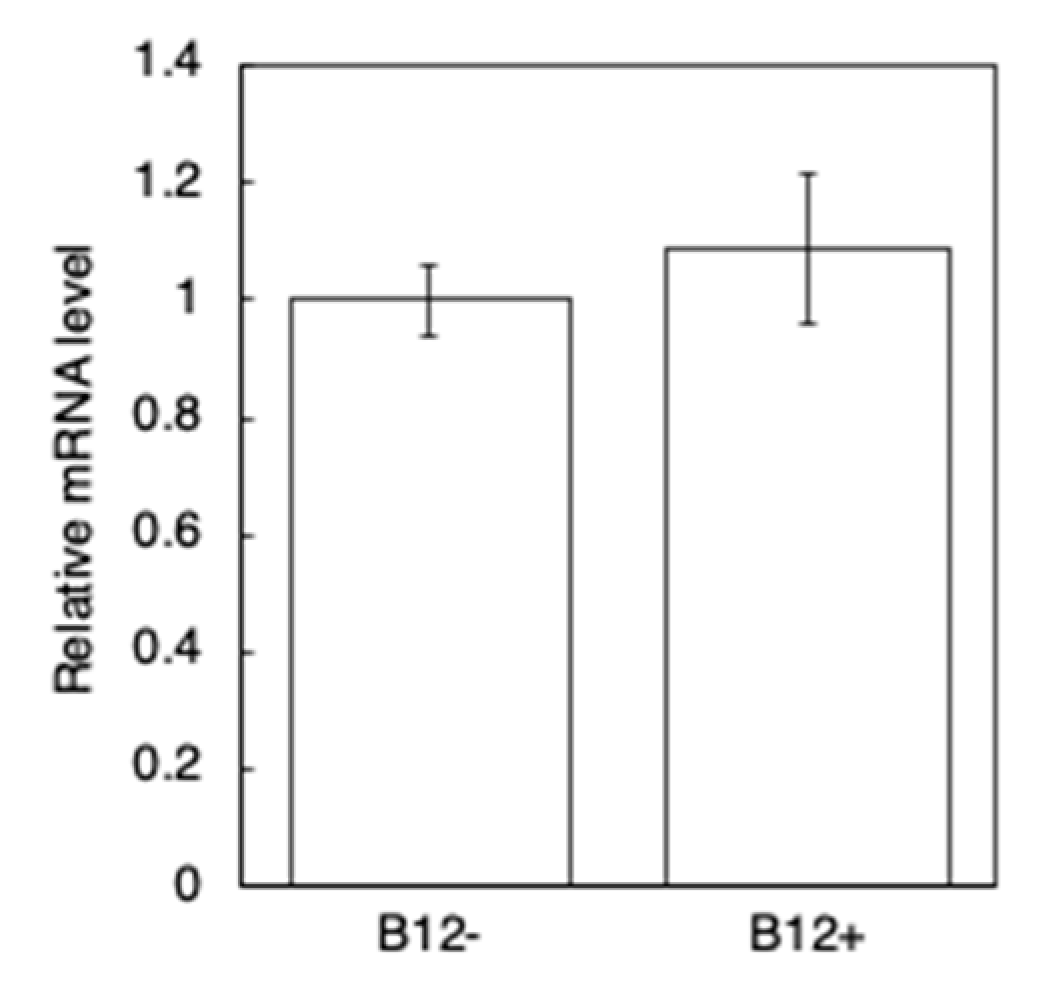
2.6. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
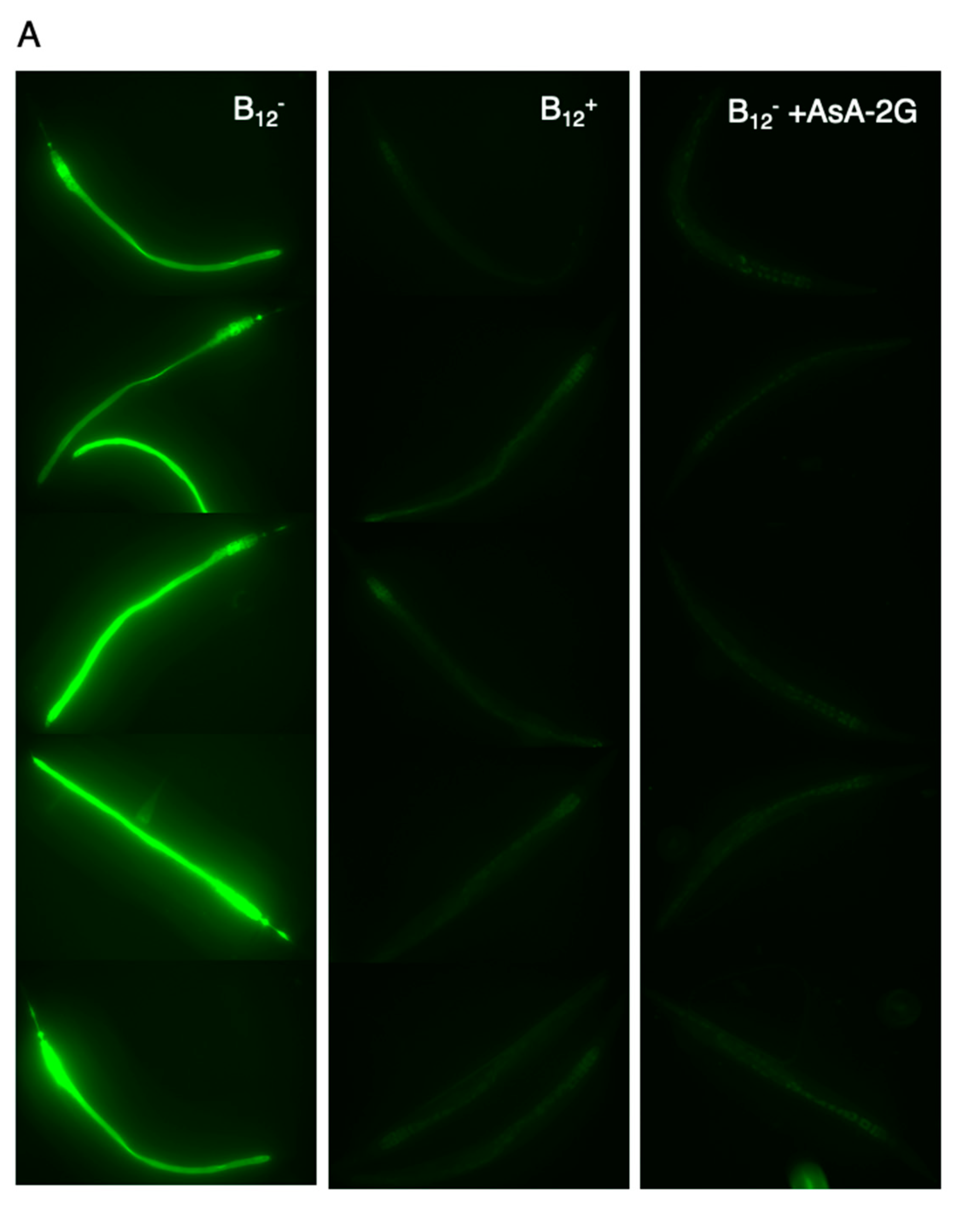
2.7. In Situ Detection of Intracellular ROS
2.8. Immunoblot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Worms Grown on NGM without B12 Supplementation Exhibited B12 Deficiency
3.2. B12 Supplementation Reduced Aβ Toxicity in B12-Deficient GMC101 Worms
3.3. NGM Supplemented with AsA-2G Ameliorated Aβ Toxicity in B12-Deficient GMC101 Worms
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, A.D.; Warren, M.J.; Refsum, H. Vitamin B12. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 83, 215–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, F.; Bito, T. Vitamin B12 sources and microbial interaction. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Asselt, D.Z.; van den Broek, W.J.; Lamers, C.B.; Corstens, F.H.; Hoefnagels, W.H. Free and protein-bound cobalamin absorption in healthy middle-aged and older subjects. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1996, 44, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.; Allen, L.H.; Bjørke-Monsen, A.L.; Brito, A.; Guéant, J.L.; Miller, J.W.; Molloy, A.M.; Nexo, E.; Stabler, S.; Toh, B.H.; et al. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Lagemaat, E.; de Groot, L.; van den Heuvel, E. Vitamin B12 in relation to oxidative stress: A systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s Association 2020 Facts and Figures Report. Alzheimer’s Association. Available online: https://www.alz.org/ (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Masters, C.L.; Bateman, R.; Blennow, K.; Rowe, C.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Cummings, J.L. Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, P. Natural Products against Neurodegenerative Diseases: Effects in the Model Organism Caenorhabditis Elegans. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 9 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Chu, J.; Barrero, C.; Merali, S.; Praticò, D. Homocysteine exacerbates β-amyloid pathology, tau pathology, and cognitive deficit in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease with plaques and tangles. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H. Homocysteine, B Vitamins, and Cognitive Impairment. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, A.K.; Wightman, B.; Chalfie, M. A transparent window into biology: A primer on Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2015, 200, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bito, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Yabuta, Y.; Kawano, T.; Watanabe, F. Vitamin B12 deficiency in Caenorhabditis elegans results in loss of fertility, extended life cycle, and reduced lifespan. FEBS Open Bio. 2013, 3, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, E.; Macneil, L.T.; Ritter, A.D.; Yilmaz, L.S.; Rosebrock, A.P.; Caudy, A.A.; Walhout, A.J. Interspecies systems biology uncovers metabolites affecting C. elegans gene expression and life history traits. Cell 2014, 156, 759–770, Erratum in: Cell 2014, 156, 1336–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, P.; Yue, Y.; Zheng, J.; Park, Y. Caenorhabditis elegans: A convenient in vivo model for assessing the impact of food bioactive compounds on obesity, aging, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McColl, G.; Roberts, B.R.; Pukala, T.L.; Kenche, V.B.; Roberts, C.M.; Link, C.D.; Ryan, T.M.; Masters, C.L.; Barnham, K.J.; Bush, A.I.; et al. Utility of an improved model of amyloid-beta (Aβ1-42) toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans for drug screening for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weaving, G.; Rocks, B.F.; Iversen, S.A.; Titheradge, M.A. Simultaneous quantitation of homocysteine, cysteine and methionine in plasma and urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 43, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineva, E.M.; Zhang, M.; Rabinowitz, D.J.; Phinney, K.W.; Pfeiffer, C.M. An LC-MS/MS method for serum methylmalonic acid suitable for monitoring vitamin B12 status in population surveys. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2955–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.S.; Lee, M.H.; Cha, D.S. Measurement of Intracellular ROS in Caenorhabditis elegans Using 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate. Bio Protoc. 2018, 8, e2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yabuta, Y.; Kamei, Y.; Bito, T.; Arima, J.; Yoneda, K.; Sakuraba, H.; Ohshima, T.; Nakano, Y.; Watanabe, F. Functional and structural characteristics of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revtovich, A.V.; Lee, R.; Kirienko, N.V. Interplay between mitochondria and diet mediates pathogen and stress resistance in caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bito, T.; Misaki, T.; Yabuta, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Kawano, T.; Watanabe, F. Vitamin B12deficiency results in severe oxidative stress, leading to memory retention impairment in Caenorhabditis elegans. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malouf, R.; Evans, J.G. Folic acid with or without vitamin B12 for the prevention and treatment of healthy elderly and demented people. Cochrane. Database Syst. Rev. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.; Almasieh, M.; Catrinescu, M.M.; Levin, L.A. Cobalamin-associated superoxide scavenging in neuronal cells is a potential mechanism for vitamin B12-deprivation optic neuropathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyagi, N.; Sedoris, K.C.; Steed, M.; Ovechkin, A.V.; Moshal, K.S.; Tyagi, S.C. Mechanisms of homocysteine-induced oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H2649–H2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siow, Y.L.; Au-Yeung, K.K.; Woo, C.W.; Karmin, O. Homocysteine stimulates phosphorylation of NADPH oxidase p47phox and p67phox subunits in monocytes via protein kinase Cbeta activation. Biochem. J. 2006, 398, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, C.G.; Borges, C.G.; Seminotti, B.; Amaral, A.U.; Knebel, L.A.; Eichler, P.; de Oliveira, A.B.; Leipnitz, G.; Wajner, M. Experimental evidence that methylmalonic acid provokes oxidative damage and compromises antioxidant defenses in nerve terminal and striatum of young rats. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatin, S.M.; Varadarajan, S.; Link, C.D.; Butterfield, D.A. In vitro and in vivo oxidative stress associated with Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide (1-42). Neurobiol. Aging 1999, 20, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, J.; Link, C.D.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative stress precedes fibrillar deposition of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta-peptide (1-42) in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans model. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Song, W. Oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s disease. In Systems Biology of Free Radicals and Antioxidants; Ismail, L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 2147–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Link, C.D.; Taft, A.; Kapulkin, V.; Duke, K.; Kim, S.; Fei, Q.; Wood, D.E.; Sahagan, B.G. Gene expression analysis in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans Alzheimer’s disease model. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, V.; Romani, M.; Mouchiroud, L.; Beck, J.S.; Zhang, H.; D’Amico, D.; Moullan, N.; Potenza, F.; Schmid, A.W.; Rietsch, S.; et al. Enhancing mitochondrial proteostasis reduces amyloid-β proteotoxicity. Nature 2017, 552, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Beydoun, H.A.; Gamaldo, A.A.; Teel, A.; Zonderman, A.B.; Wang, Y. Epidemiologic studies of modifiable factors associated with cognition and dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solomon, L.R. Functional cobalamin (vitamin B12) deficiency: Role of advanced age and disorders associated with increased oxidative stress. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andra, A.; Tanigawa, S.; Bito, T.; Ishihara, A.; Watanabe, F.; Yabuta, Y. Effects of Vitamin B12 Deficiency on Amyloid-β Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060962
Andra A, Tanigawa S, Bito T, Ishihara A, Watanabe F, Yabuta Y. Effects of Vitamin B12 Deficiency on Amyloid-β Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(6):962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060962
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndra, Arif, Shoko Tanigawa, Tomohiro Bito, Atsushi Ishihara, Fumio Watanabe, and Yukinori Yabuta. 2021. "Effects of Vitamin B12 Deficiency on Amyloid-β Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans" Antioxidants 10, no. 6: 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060962
APA StyleAndra, A., Tanigawa, S., Bito, T., Ishihara, A., Watanabe, F., & Yabuta, Y. (2021). Effects of Vitamin B12 Deficiency on Amyloid-β Toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants, 10(6), 962. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10060962




