Nutraceutical Strategy to Counteract Eye Neurodegeneration and Oxidative Stress in Drosophila melanogaster Fed with High-Sugar Diet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Fly Husbandry
2.3. Treatments
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Body Weight and Glucose Analysis
2.7. Determination of ROS
2.8. Metabolite Analysis
2.9. Phototaxis Assay
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
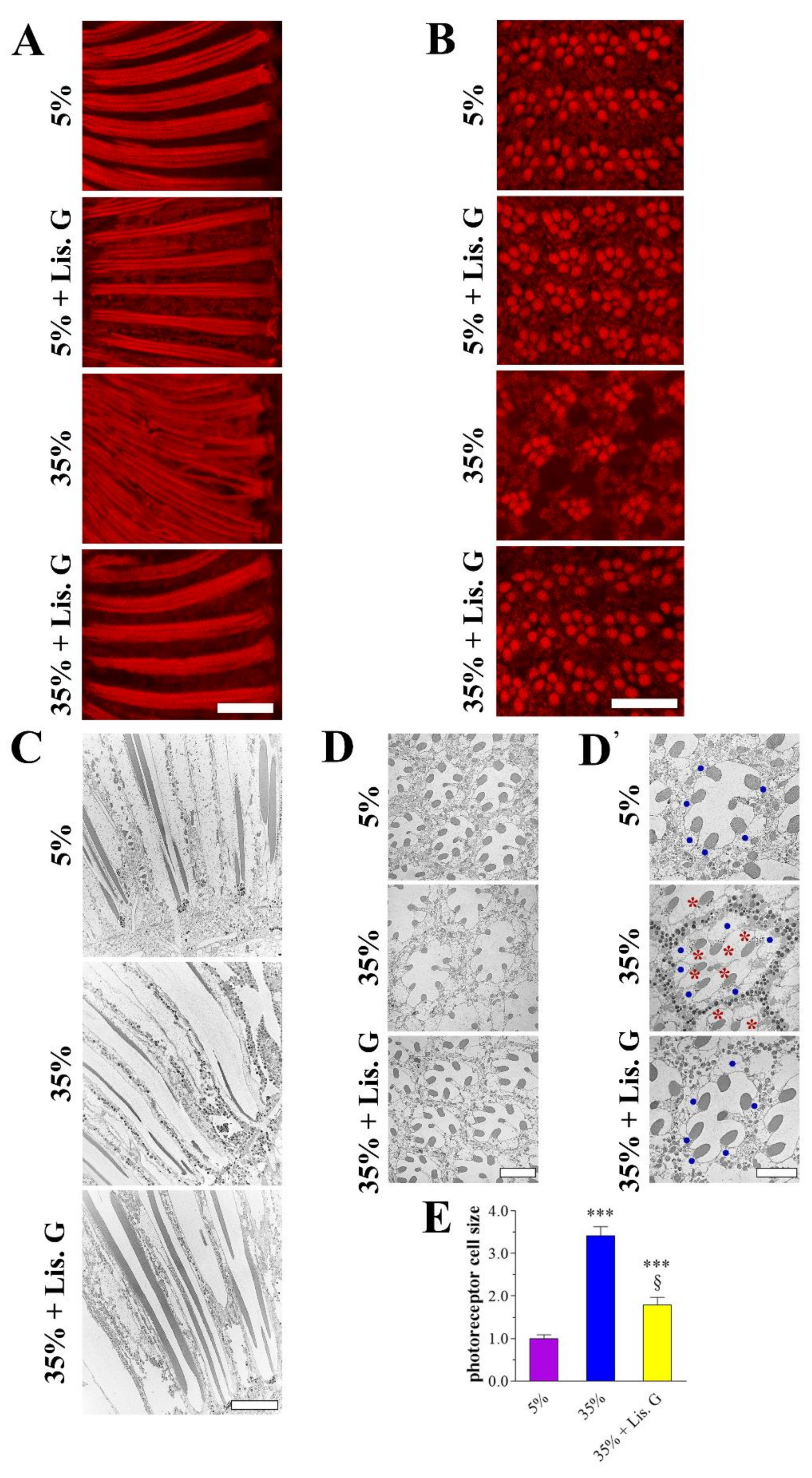
3.1. Eye Organization
3.2. Body Weight and Glycemia
3.3. Oxidative Stress: Peroxynitrite and ROS
3.4. Redox Metabolites
3.5. Vision Behavior
3.6. Apoptosis
3.7. Autophagy
3.8. Combined Effects of Lisosan G and Autophagy Activation
4. Discussion
4.1. Lisosan G and Eye Neurodegeneration
4.2. Antioxidant Activity of Lisosan G
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hass, D.T.; Barnstable, C.J. Uncoupling proteins in the mitochondrial defense against oxidative stress. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 83, 100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.B.; Lindsay, K.J.; Du, J. Glucose, lactate, and shuttling of metabolites in vertebrate retinas. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 1079–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y. Light-Induced Retinal Ganglion Cell Damage and the Relevant Mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chin, E.K.; Almeida, D. Antioxidants for the Treatment of Retinal Disease: Summary of Recent Evidence. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.C.; Wilkinson Berka, J.L.; Deliyanti, D.; Hunter, D.; Fung, A.; Liew, G.; White, A. The role of reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis and treatment of retinal diseases. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 201, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, G.D.; Juarez, O.H.; Hernandez, G.E.; Punzo, S.M.; De la Cruz, Z.D. Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy: Development and treatment. Eye 2017, 31, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Cheung, C.M.; Larsen, M.; Sharma, S.; Simo, R. Diabetic retinopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simo, R.; Stitt, A.W.; Gardner, T.W. Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy: Does it really matter? Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, R.; Hernandez, C.; EUROCONDOR. Neurodegeneration in the diabetic eye: New insights and therapeutic perspectives. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 25, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossino, M.G.; Dal Monte, M.; Casini, G. Relationships Between Neurodegeneration and Vascular Damage in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalani, E.; Cervia, D. Diabetic retinopathy: A matter of retinal ganglion cell homeostasis. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1253–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Xu, G. Autophagy: A Role in the Apoptosis, Survival, Inflammation, and Development of the Retina. Ophthalmic Res. 2019, 61, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boya, P.; Esteban-Martinez, L.; Serrano-Puebla, A.; Gomez-Sintes, R.; Villarejo-Zori, B. Autophagy in the eye: Development, degeneration, and aging. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 55, 206–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Perusek, L.; Maeda, A. Autophagy in light-induced retinal damage. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 144, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, L.S.; Mitchell, C.H.; Boesze-Battaglia, K. Autophagy in the eye: Implications for ocular cell health. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 124, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervia, D.; Catalani, E.; Casini, G. Neuroprotective Peptides in Retinal Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, R.; Catalani, E.; Dal Monte, M.; Cammalleri, M.; Di Renzo, I.; Perrotta, C.; Cervia, D.; Casini, G. Autophagy-mediated neuroprotection induced by octreotide in an ex vivo model of early diabetic retinopathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.D.; Distefano, G.; Gagliano, C.; Rusciano, D.; Malaguarnera, L. Autophagy in Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 810–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammalleri, M.; Locri, F.; Catalani, E.; Filippi, L.; Cervia, D.; Dal Monte, M.; Bagnoli, P. The Beta Adrenergic Receptor Blocker Propranolol Counteracts Retinal Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Oxygen Induced Retinopathy: Restoring the Balance between Apoptosis and Autophagy. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalani, E.; Bongiorni, S.; Taddei, A.R.; Mezzetti, M.; Silvestri, F.; Coazzoli, M.; Zecchini, S.; Giovarelli, M.; Perrotta, C.; De Palma, C.; et al. Defects of full-length dystrophin trigger retinal neuron damage and synapse alterations by disrupting functional autophagy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1615–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Wang, H.; Yu, P.; Qian, T.; Xu, X. Protective or Harmful: The Dual Roles of Autophagy in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 644121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalani, E.; Silvestri, F.; Bongiorni, S.; Taddei, A.R.; Fanelli, G.; Rinalducci, S.; De Palma, C.; Perrotta, C.; Prantera, G.; Cervia, D. Retinal damage in a new model of hyperglycemia induced by high-sucrose diets. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 166, 105488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalani, E.; Silvestri, F.; Cervia, D. A Drosophila perspective on retina functions and dysfunctions. Neural. Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mansour, S.E.; Browning, D.J.; Wong, K.; Flynn, H.W., Jr.; Bhavsar, A.R. The Evolving Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 653–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossino, M.G.; Casini, G. Nutraceuticals for the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Rivera, R.R.; Castellanos-Gonzalez, J.A.; Olvera-Montano, C.; Flores-Martin, R.A.; Lopez-Contreras, A.K.; Arevalo-Simental, D.E.; Cardona-Munoz, E.G.; Roman-Pintos, L.M.; Rodriguez-Carrizalez, A.D. Adjuvant Therapies in Diabetic Retinopathy as an Early Approach to Delay Its Progression: The Importance of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3096470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonso-Munoz, E.A.; Burggraaf-Sanchez de Las Matas, R.; Mataix Boronat, J.; Molina Martin, J.C.; Desco, C. Role of Oral Antioxidant Supplementation in the Current Management of Diabetic Retinopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.; Chirulli, V.; Gervasi, P.G.; Nencioni, S.; Pellegrini, M. Lisosan G, a powder of grain, does not interfere with the drug metabolizing enzymes and has a protective role on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, L.; Gabriele, M.; Penno, G.; Garofolo, M.; Longo, V.; Del Prato, S.; Lucchesi, D.; Pucci, L. A Fermented Whole Grain Prevents Lipopolysaccharides-Induced Dysfunction in Human Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1026268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Marca, M.; Beffy, P.; Pugliese, A.; Longo, V. Fermented wheat powder induces the antioxidant and detoxifying system in primary rat hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, M.; Pucci, L.; Arvay, J.; Longo, V. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect of fermented whole wheat on TNF alpha-stimulated HT-29 and NF-kappa B signaling pathway activation. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 45, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassinetti, S.; Della Croce, C.M.; Caltavuturo, L.; Longo, V. Antimutagenic and antioxidant activity of Lisosan G in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchesi, D.; Russo, R.; Gabriele, M.; Longo, V.; Del Prato, S.; Penno, G.; Pucci, L. Grain and bean lysates improve function of endothelial progenitor cells from human peripheral blood: Involvement of the endogenous antioxidant defenses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, R.; Rossino, M.G.; Cammalleri, M.; Locri, F.; Pucci, L.; Dal Monte, M.; Casini, G. Lisosan G Protects the Retina from Neurovascular Damage in Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalani, E.; Buonanno, F.; Lupidi, G.; Bongiorni, S.; Belardi, R.; Zecchini, S.; Giovarelli, M.; Coazzoli, M.; De Palma, C.; Perrotta, C.; et al. The Natural Compound Climacostol as a Prodrug Strategy Based on pH Activation for Efficient Delivery of Cytotoxic Small Agents. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, B.; Fiorini, S.; Dal Monte, M.; Lunghi, L.; Biondi, C.; Bagnoli, P.; Cervia, D. Somatostatin coupling to adenylyl cyclase activity in the mouse retina. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2004, 370, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zecchini, S.; Proietti Serafini, F.; Catalani, E.; Giovarelli, M.; Coazzoli, M.; Di Renzo, I.; De Palma, C.; Perrotta, C.; Clementi, E.; Buonanno, F.; et al. Dysfunctional autophagy induced by the pro-apoptotic natural compound climacostol in tumour cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, C.; Buonanno, F.; Zecchini, S.; Giavazzi, A.; Proietti Serafini, F.; Catalani, E.; Guerra, L.; Belardinelli, M.C.; Picchietti, S.; Fausto, A.M.; et al. Climacostol reduces tumour progression in a mouse model of melanoma via the p53-dependent intrinsic apoptotic programme. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Cervia, D.; Catalani, E.; Gevi, F.; Zolla, L.; Casini, G. Protective effects of the neuropeptides PACAP, substance P and the somatostatin analogue octreotide in retinal ischemia: A metabolomic analysis. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 1290–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalani, E.; Proietti Serafini, F.; Zecchini, S.; Picchietti, S.; Fausto, A.M.; Marcantoni, E.; Buonanno, F.; Ortenzi, C.; Perrotta, C.; Cervia, D. Natural products from aquatic eukaryotic microorganisms for cancer therapy: Perspectives on anti-tumour properties of ciliate bioactive molecules. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervia, D.; Garcia-Gil, M.; Simonetti, E.; Di Giuseppe, G.; Guella, G.; Bagnoli, P.; Dini, F. Molecular mechanisms of euplotin C-induced apoptosis: Involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and proteases. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzato, D.; Assi, E.; Moscheni, C.; Brunelli, S.; De Palma, C.; Cervia, D.; Perrotta, C.; Clementi, E. Nitric oxide drives embryonic myogenesis in chicken through the upregulation of myogenic differentiation factors. Exp. Cell. Res. 2014, 320, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervia, D.; Fiorini, S.; Pavan, B.; Biondi, C.; Bagnoli, P. Somatostatin (SRIF) modulates distinct signaling pathways in rat pituitary tumor cells; negative coupling of SRIF receptor subtypes 1 and 2 to arachidonic acid release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2002, 365, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Munoz, D.; Brucoli, M.; Zecchini, S.; Sandoval-Hernandez, A.; Arboleda, G.; Lopez-Vallejo, F.; Delgado, W.; Giovarelli, M.; Coazzoli, M.; Catalani, E.; et al. XIAP as a Target of New Small Organic Natural Molecules Inducing Human Cancer Cell Death. Cancers 2019, 11, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervia, D.; Catalani, E.; Dal Monte, M.; Casini, G. Vascular endothelial growth factor in the ischemic retina and its regulation by somatostatin. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervia, D.; Assi, E.; De Palma, C.; Giovarelli, M.; Bizzozero, L.; Pambianco, S.; Di Renzo, I.; Zecchini, S.; Moscheni, C.; Vantaggiato, C.; et al. Essential role for acid sphingomyelinase-inhibited autophagy in melanoma response to cisplatin. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24995–25009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poetini, M.R.; Araujo, S.M.; Trindade de Paula, M.; Bortolotto, V.C.; Meichtry, L.B.; Polet de Almeida, F.; Jesse, C.R.; Kunz, S.N.; Prigol, M. Hesperidin attenuates iron-induced oxidative damage and dopamine depletion in Drosophila melanogaster model of Parkinson’s disease. Chem. Biol. Int. 2018, 279, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, P.; Airen, S.; Brown, C.; Liu, Z.; Townsend, J.H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H. Nutritional and medical food therapies for diabetic retinopathy. Eye Vis. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, J.S. Extract of Polygonum cuspidatum Attenuates Diabetic Retinopathy by Inhibiting the High-Mobility Group Box-1 (HMGB1) Signaling Pathway in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucolo, C.; Marrazzo, G.; Platania, C.B.; Drago, F.; Leggio, G.M.; Salomone, S. Fortified extract of red berry, Ginkgo biloba, and white willow bark in experimental early diabetic retinopathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2013, 432695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billes, V.; Kovacs, T.; Manzeger, A.; Lorincz, P.; Szincsak, S.; Regos, A.; Kulcsar, P.I.; Korcsmaros, T.; Lukacsovich, T.; Hoffmann, G.; et al. Developmentally regulated autophagy is required for eye formation in Drosophila. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1499–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midorikawa, R.; Yamamoto-Hino, M.; Awano, W.; Hinohara, Y.; Suzuki, E.; Ueda, R.; Goto, S. Autophagy-dependent rhodopsin degradation prevents retinal degeneration in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 10703–10719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalani, E.; De Palma, C.; Perrotta, C.; Cervia, D. Current Evidence for a Role of Neuropeptides in the Regulation of Autophagy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5856071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowluru, R.A.; Mishra, M. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and diabetic retinopathy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.K.; Matragoon, S.; Pillai, B.A.; Liou, G.I.; El-Remessy, A.B. Peroxynitrite mediates retinal neurodegeneration by inhibiting nerve growth factor survival signaling in experimental and human diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opatrilova, R.; Kubatka, P.; Caprnda, M.; Busselberg, D.; Krasnik, V.; Vesely, P.; Saxena, S.; Ruia, S.; Mozos, I.; Rodrigo, L.; et al. Nitric oxide in the pathophysiology of retinopathy: Evidences from preclinical and clinical researches. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018, 96, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behan, W.M.; McDonald, M.; Darlington, L.G.; Stone, T.W. Oxidative stress as a mechanism for quinolinic acid-induced hippocampal damage: Protection by melatonin and deprenyl. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-De La Cruz, V.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Santamaria, A. Quinolinic Acid, an endogenous molecule combining excitotoxicity, oxidative stress and other toxic mechanisms. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. IJTR 2012, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Fairus, A.K.; Choudhary, B.; Hosahalli, S.; Kavitha, N.; Shatrah, O. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitors affect ATP depletion, endogenous ROS and mediate S-phase arrest in breast cancer cells. Biochimie 2017, 135, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey-Mogensen, M.; Goncalves, R.L.; Orr, A.L.; Brand, M.D. Production of superoxide/H2O2 by dihydroorotate dehydrogenase in rat skeletal muscle mitochondria. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Melnyk, S.; Pavliv, O.; Bai, S.; Nick, T.G.; Frye, R.E.; James, S.J. Evidence of oxidative damage and inflammation associated with low glutathione redox status in the autism brain. Transl. Psy. 2012, 2, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Cabrera, R.; Fernandez-Fernandez, S.; Bobo-Jimenez, V.; Escobar, J.; Sastre, J.; Almeida, A.; Bolanos, J.P. gamma-Glutamylcysteine detoxifies reactive oxygen species by acting as glutathione peroxidase-1 cofactor. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.M.; Jiang, H.; Cunningham, G.R.; Magarik, J.A.; Barge, W.S.; Cato, M.C.; Farina, M.; Rocha, J.B.; Milatovic, D.; Lee, E.; et al. gamma-Glutamylcysteine ameliorates oxidative injury in neurons and astrocytes in vitro and increases brain glutathione in vivo. Neurotoxicology 2011, 32, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dringen, R.; Gutterer, J.M.; Hirrlinger, J. Glutathione metabolism in brain metabolic interaction between astrocytes and neurons in the defense against reactive oxygen species. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 4912–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, J.A.; Khasawneh, M.K. Cancer metabolism and oxidative stress: Insights into carcinogenesis and chemotherapy via the non-dihydrofolate reductase effects of methotrexate. BBA Clinical. 2015, 3, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautin, Y.Y.; Johnson, R.J. Uric acid: The oxidant-antioxidant paradox. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, S.; Hilsabeck, T.A.; Wilson, K.A.; Sharma, A.; Bose, N.; Brackman, D.J.; Beck, J.N.; Chen, L.; Watson, M.A.; Killilea, D.W.; et al. A conserved role of the insulin-like signaling pathway in diet-dependent uric acid pathologies in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinazo-Duran, M.D.; Gallego-Pinazo, R.; Garcia-Medina, J.J.; Zanon-Moreno, V.; Nucci, C.; Dolz-Marco, R.; Martinez-Castillo, S.; Galbis-Estrada, C.; Marco-Ramirez, C.; Lopez-Galvez, M.I.; et al. Oxidative stress and its downstream signaling in aging eyes. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGurk, L.; Berson, A.; Bonini, N.M. Drosophila as an In Vivo Model for Human Neurodegenerative Disease. Genetics 2015, 201, 377–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, P.; Almudi, I.; Nunes, M.D.S.; McGregor, A.P. Human eye conditions: Insights from the fly eye. Hum. Genet. 2019, 138, 973–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolus, H.; Crocker, K.; Boekhoff-Falk, G.; Chtarbanova, S. Modeling Neurodegenerative Disorders in Drosophila melanogaster. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Metabolites | f-Value | p-Value | -log10(p) | FDR | Fisher’s LSD * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-aminooctanoic acid | 20.148 | 0.002177 | 2.6622 | 0.0208 | 3-1; 3-2 |
| 3-S-methylthiopropionate | 14.43 | 0.005099 | 2.2925 | 0.0367 | 2-1; 3-1 |
| 5-hydroxykynurenamine | 60.315 | 0.000106 | 3.9732 | 0.0038 | 3-1; 3-2 |
| 7,8-dihydrofolate | 14.479 | 0.005056 | 2.2962 | 0.0367 | 3-1; 3-2 |
| allantoin | 20.855 | 0.001989 | 2.7014 | 0.0204 | 1-2; 3-2 |
| anthranilate | 357.56 | 5.76 × 10−7 | 6.2396 | 4.15 × 10−5 | 2-1; 3-1; 3-2 |
| ascorbic acid | 13.619 | 0.005882 | 2.2305 | 0.0403 | 2-1; 3-1 |
| Cys-Gly | 21.665 | 0.001799 | 2.7449 | 0.0204 | 2-1; 2-3 |
| D-erythrose-4-phosphate | 18.753 | 0.002623 | 2.5812 | 0.0236 | 2-1; 2-3 |
| dihydroorotate | 21.232 | 0.001898 | 2.7218 | 0.0204 | 1-2; 3-2 |
| dTMP | 34.156 | 0.000526 | 3.2787 | 0.0084 | 2-1; 2-3 |
| methylcysteine | 38.627 | 0.000374 | 3.4268 | 0.0074 | 1-2; 3-1;3-2 |
| methylmalonic acid | 37.26 | 0.000414 | 3.3832 | 0.0074 | 1-2; 3-2 |
| myo-inositol | 16.086 | 0.003883 | 2.4108 | 0.0310 | 3-1; 3-2 |
| N-acetyl-L-ornithine | 22.46 | 0.001636 | 2.7862 | 0.0204 | 1-2; 1-3 |
| p-aminobenzoate | 357.56 | 5.76 × 10−7 | 6.2396 | 4.15 × 10−5 | 2-1; 3-1; 3-2 |
| quinolate | 41.163 | 0.000313 | 3.5038 | 0.0074 | 2-1; 2-3 |
| succinate | 37.26 | 0.000414 | 3.3832 | 0.0074 | 1-2; 3-2 |
| uric acid | 16.168 | 0.003834 | 2.4163 | 0.0310 | 2-1; 2-3 |
| xanthine | 32.804 | 0.000588 | 3.2304 | 0.0084 | 2-1; 3-1 |
| γ-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine | 224.41 | 2.30 × 10−6 | 5.639 | 0.0001 | 1-2; 3-1;3-2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Catalani, E.; Fanelli, G.; Silvestri, F.; Cherubini, A.; Del Quondam, S.; Bongiorni, S.; Taddei, A.R.; Ceci, M.; De Palma, C.; Perrotta, C.; et al. Nutraceutical Strategy to Counteract Eye Neurodegeneration and Oxidative Stress in Drosophila melanogaster Fed with High-Sugar Diet. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081197
Catalani E, Fanelli G, Silvestri F, Cherubini A, Del Quondam S, Bongiorni S, Taddei AR, Ceci M, De Palma C, Perrotta C, et al. Nutraceutical Strategy to Counteract Eye Neurodegeneration and Oxidative Stress in Drosophila melanogaster Fed with High-Sugar Diet. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(8):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081197
Chicago/Turabian StyleCatalani, Elisabetta, Giuseppina Fanelli, Federica Silvestri, Agnese Cherubini, Simona Del Quondam, Silvia Bongiorni, Anna Rita Taddei, Marcello Ceci, Clara De Palma, Cristiana Perrotta, and et al. 2021. "Nutraceutical Strategy to Counteract Eye Neurodegeneration and Oxidative Stress in Drosophila melanogaster Fed with High-Sugar Diet" Antioxidants 10, no. 8: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081197
APA StyleCatalani, E., Fanelli, G., Silvestri, F., Cherubini, A., Del Quondam, S., Bongiorni, S., Taddei, A. R., Ceci, M., De Palma, C., Perrotta, C., Rinalducci, S., Prantera, G., & Cervia, D. (2021). Nutraceutical Strategy to Counteract Eye Neurodegeneration and Oxidative Stress in Drosophila melanogaster Fed with High-Sugar Diet. Antioxidants, 10(8), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081197











