Curcumin Modulates Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation, and DNA Damage and Protects against Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats
Abstract
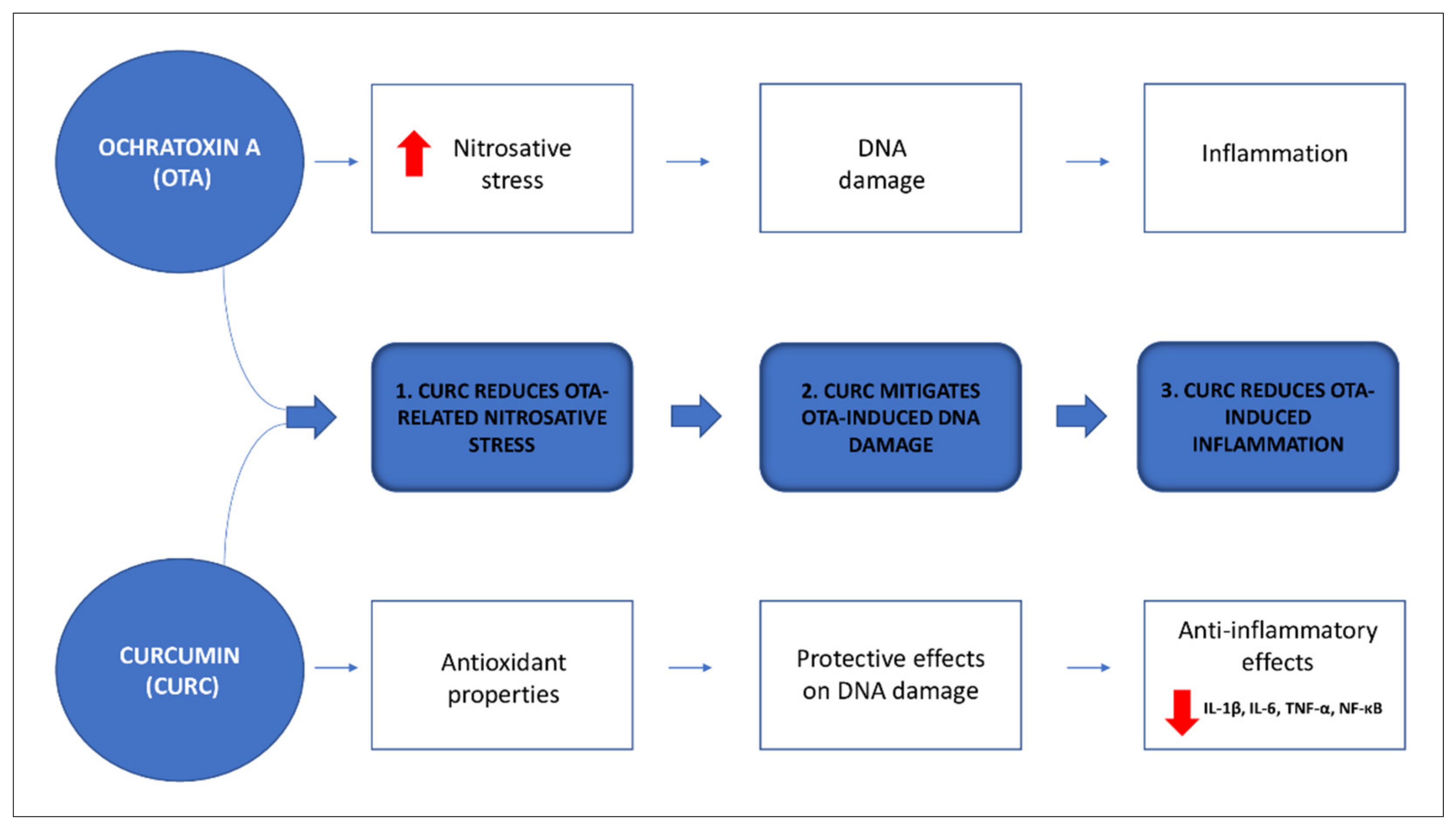
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Ethic Statement
2.3. Experimental Design
- Control group: the rats received 2 mL/kg b.w. of olive oil;
- OTA group: the rats received 0.5 mg/kg b.w. of OTA dissolved in 2 mL/kg b.w. of olive oil;
- CURC group: the rats received 100 mg/kg b.w. of CURC dissolved in 2 mL/kg b.w. of olive oil;
- OTA + CURC group: the rats received 2 mL/kg b.w. of olive oil containing 0.5 mg/kg b.w. of OTA plus 100 mg/kg b.w. of CURC.
2.4. Samples Collection and Processing
2.5. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Assay
2.6. Nitric Oxide Determination
2.7. iNOS Activity Assay
2.8. 8-Hydroxy-2′-Deoxy Guanosine (8-OHdG) Analysis
2.9. Hystopathological Examination
2.10. Immunoistochemistry Study
2.11. Statistycal Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of CURC on Kidney and Hepatic Tissue Levels of NO
3.2. Effect of CURC on Liver and Kidney iNOS Activity
3.3. Effect of Curcumin on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Production in Kidney and Liver Tissues
3.4. Effect of Curcumin on OTA-Induced DNA Damage
3.5. Histopayhological Examination
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samson, R.A.; Visagie, C.M.; Houbraken, J.; Hong, S.-B.; Hubka, V.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; Perrone, G.; Seifert, K.A.; Susca, A.; Tanney, J.B.; et al. Phylogeny, identification and nomenclature of the genus Aspergillus. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 78, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pitt, J.I. Penicillium viridicatum, Penicillium verrucosum, and production of ochratoxin A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.D.; Su, P.; Shan, H. Mycotoxin Contamination of Maize in China. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freire, L.; Passamani, F.R.F.; Thomas, A.B.; de Cássia Mirela Resende Nassur, R.; Silva, L.M.; Paschoal, F.N.; Pereira, G.E.; Prado, G.; Batista, L.R. Influence of physical and chemical characteristics of wine grapes on the incidence of Penicillium and Aspergillus fungi in grapes and ochratoxin A in wines. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 241, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Nisar, S.; Asi, M.R.; Jinap, S. Natural incidence of aflatoxins, ochratoxin A and zearalenone in chicken meat and eggs. Food Control 2014, 43, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, B.T.M.; Tuyen, L.D.; Tuan, D.H.; Brimer, L.; Dalsgaard, A. Dietary exposure to aflatoxin B 1, ochratoxin A and fuminisins of adults in Lao Cai province, Viet Nam: A total dietary study approach. Food Chem. Toxicol 2016, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diekman, M.A.; Green, M.L. Mycotoxins and reproduction in domestic livestock. J. Anim. Sci. 1992, 70, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, J.G.; Saraiva, N.; Guerreiro, P.S.; Louro, H.; Silva, M.J.; Miranda, J.P.; Castro, M.; Batinic-Haberle, I.; Fernandes, A.S.; Oliveira, N.G. Ochratoxin A-induced cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and reactive oxygen species in kidney cells: An integrative approach of complementary endpoints. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 87, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Xie, S.; Xu, F.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Huang, L.; Peng, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Ochratoxin A: Toxicity, oxidative stress and metabolism. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer-IARC. Some naturally occurring substances: Food items and constituents, heterocyclic aromatic amines and mycotoxins. In Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 1993; ISBN 978-92-832-1256-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. An update on direct genotoxicity as a molecular mechanism of ochratoxin a carcinogenicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangikar, P.B.; Dwivedi, P.; Sinha, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Telang, A.G. Teratogenic effects in rabbits of simultaneous exposure to ochratoxin A and aflatoxin B1 with special reference to microscopic effects. Toxicology 2005, 215, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliano, N.; Donne, I.D.; Torri, C.; Migliori, M.; Grizzi, F.; Milzani, A.; Filippi, C.; Annoni, G.; Colombo, P.; Costa, F.; et al. Early cytotoxic effects of ochratoxin A in rat liver: A morphological, biochemical and molecular study. Toxicology 2006, 225, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavin, C.; Delatour, T.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Fenaille, F.; Holzhäuser, D.; Guignard, G.; Bezençon, C.; Piguet, D.; Parisod, V.; Richoz-Payot, J.; et al. Ochratoxin A-mediated DNA and protein damage: Roles of nitrosative and oxidative stresses. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 110, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oldreive, C.; Rice-Evans, C. The mechanisms for nitration and nitrotyrosine formation in vitro and in vivo: Impact of diet. Free Radic. Res. 2001, 35, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrenti, V.; Di Giacomo, C.; Acquaviva, R.; Barbagallo, I.; Bognanno, M.; Galvano, F. Toxicity of Ochratoxin A and Its Modulation by Antioxidants: A Review. Toxins 2013, 5, 1742–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagchi, A. Extraction of Curcumin. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2012, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhad, A.; Pilkhwal, S.; Sharma, S.; Tirkey, N.; Chopra, K. Effect of Curcumin on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Cisplatin-Induced Experimental Nephrotoxicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10150–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thresiamma, K.C.; George, J.; Kuttan, R. Protective effect of curcumin, ellagic acid and bixin on radiation induced genotoxicity. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 17, 431–434. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, A.; Eke, D.; Ekinci, S.Y.; Yıldırım, S. The protective role of curcumin on perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced genotoxicity: Single cell gel electrophoresis and micronucleus test. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, S.; Longobardi, C.; Andretta, E.; Prisco, F.; Piegari, G.; Squillacioti, C.; Montagnaro, S.; Pagnini, F.; Badino, P.; Florio, S.; et al. Antioxidative Effects of Curcumin on the Hepatotoxicity Induced by Ochratoxin A in Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, S.; Andretta, E.; Longobardi, C.; Prisco, F.; Paciello, O.; Squillacioti, C.; Mirabella, N.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Effects of curcumin on the renal toxicity induced by ochratoxin a in rats. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strimpakos, A.S.; Sharma, R.A. Curcumin: Preventive and Therapeutic Properties in Laboratory Studies and Clinical Trials. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 511–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, T.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Q.; Ma, C.; Gao, C.; et al. Curcumin Suppresses IL-1β Secretion and Prevents Inflammation through Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 2835–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, R.-Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, H.-L.; Li, J.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Yan, Y.; Lan, H.-Y.; et al. Curcumin relieved cisplatin-induced kidney inflammation through inhibiting Mincle-maintained M1 macrophage phenotype. Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, S.-H.; Ko, E.; Chung, H.-S.; Lee, E.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Shin, M.; Hong, M.; Bae, H. The genome-wide expression profile of Curcuma longa-treated cisplatin-stimulated HEK293 cells. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 70, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, A.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, M.; Loor, J.J.; Wang, H. Melatonin ameliorates ochratoxin A induced liver inflammation, oxidative stress and mitophagy in mice involving in intestinal microbiota and restoring the intestinal barrier function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, G.; Yuan, X.; Hou, L.; Ge, L.; Liu, S.; Muhmood, A.; Liu, K.; Lin, Z.; Liu, D.; Gan, F.; et al. Ochratoxin A induces glomerular injury through activating the ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, S.; Navas, L.; Lombari, P.; Montagnaro, S.; Forte, I.M.; Giordano, A.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Effects of δ-tocotrienol on ochratoxin A-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 8731–8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, S.; Puzio, M.V.; Squillacioti, C.; Mirabella, N.; Zona, E.; Mancini, A.; Borrelli, A.; Astarita, C.; Boffo, S.; Giordano, A.; et al. Effect of rMnSOD on Sodium Reabsorption in Renal Proximal Tubule in Ochratoxin A—Treated Rats. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciarcia, R.; Damiano, S.; Squillacioti, C.; Mirabella, N.; Pagnini, U.; Florio, A.; Severino, L.; Capasso, G.; Borrelli, A.; Mancini, A.; et al. Recombinant Mitochondrial Manganese Containing Superoxide Dismutase Protects Against Ochratoxin A-Induced Nephrotoxicity. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagano, T.B.; Prisco, F.; de Biase, D.; Piegari, G.; Maurelli, M.P.; Rinaldi, L.; Cringoli, G.; Papparella, S.; Paciello, O. Muscular Sarcocystosis in Sheep Associated With Lymphoplasmacytic Myositis and Expression of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I and II. Vet. Pathol. 2020, 57, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapa, S.F.; Prisco, F.; Popolo, A.; Iovane, V.; Autore, G.; di Iorio, B.R.; Dal Piaz, F.; Paciello, O.; Nishijima, F.; Marzocco, S. Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Indoxyl Sulfate in Mice: Impairment of Intestinal Homeostasis and Immune Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisco, F.; de Biase, D.; Piegari, G.; D’Aquino, I.; Lama, A.; Comella, F.; Mercogliano, R.; Dipineto, L.; Papparella, S.; Paciello, O. Pathologic characterization of white striping myopathy in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gekle, M.; Sauvant, C.; Schwerdt, G. Ochratoxin A at nanomolar concentrations: A signal modulator in renal cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhe, A.; Hildebrand, H.; Bach, U.; Dingermann, T.; Ahr, H.-J. A new approach to studying ochratoxin A (OTA)-induced nephrotoxicity: Expression profiling in vivo and in vitro employing cDNA microarrays. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 73, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhai, S.; Xia, Y.; Wang, H.; Ruan, D.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Ye, H.; et al. Ochratoxin A induces liver inflammation: Involvement of intestinal microbiota. Microbiome 2019, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Malir, J.; Toman, J. Ochratoxin A: 50 Years of Research. Toxins 2016, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palabiyik, S.S.; Erkekoglu, P.; Zeybek, N.D.; Kızılgun, M.; Sahin, G.; Giray, B.K. Ochratoxin A causes oxidative stress and cell death in rat liver. World Mycotoxin J. 2012, 5, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, T.; Gülçin, I. Antioxidant and radical scavenging properties of curcumin. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somparn, P.; Phisalaphong, C.; Nakornchai, S.; Unchern, S.; Morales, N.P. Comparative Antioxidant Activities of Curcumin and Its Demethoxy and Hydrogenated Derivatives. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Priyadarsini, K.I.; Maity, D.K.; Naik, G.H.; Kumar, M.S.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Satav, J.G.; Mohan, H. Role of phenolic O-H and methylene hydrogen on the free radical reactions and antioxidant activity of curcumin. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, A.; Mandrekar, P. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Essential Partners in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachofeiro, V.; Goicochea, M.; de Vinuesa, S.G.; Oubiña, P.; Lahera, V.; Luño, J. Oxidative stress and inflammation, a link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S.S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitiello, M.; D’Isanto, M.; Finamore, E.; Ciarcia, R.; Kampanaraki, A.; Galdiero, M. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the iNOS production and cytokine secretion by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium porins. Cytokine 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, G.; Ulusoy, S.; Orem, A.; Alkanat, M.; Mungan, S.; Yulug, E.; Yucesan, F.B. How Does Colistin-Induced Nephropathy Develop and Can It Be Treated? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3463–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korhonen, R.; Lahti, A.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Nitric Oxide Production and Signaling in Inflammation. Curr. Drug Target. Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, C. 8-hydroxy-2’ -deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Sci. Health. C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2009, 27, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, M.; Nishino, H.; Ohshima, H. Formation of 8-nitroguanosine in cellular RNA as a biomarker of exposure to reactive nitrogen species. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002, 139, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loft, S.; Danielsen, P.; Løhr, M.; Jantzen, K.; Hemmingsen, J.G.; Roursgaard, M.; Karotki, D.G.; Møller, P. Urinary excretion of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine as biomarker of oxidative damage to DNA. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 518, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, H.E.; Weimann, A.; Henriksen, T.; Kjær, L.K.; Larsen, E.L.; Carlsson, E.R.; Christensen, C.K.; Brandslund, I.; Fenger, M. Oxidatively generated modifications to nucleic acids in vivo: Measurement in urine and plasma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 145, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantawy, E.M.; El-Bakly, W.M.; Esmat, A.; Badr, A.M.; El-Demerdash, E. Chrysin alleviates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 728, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farombi, E.O.; Shrotriya, S.; Surh, Y.-J. Kolaviron inhibits dimethyl nitrosamine-induced liver injury by suppressing COX-2 and iNOS expression via NF-κB and AP-1. Life Sci. 2009, 84, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafees, S.; Rashid, S.; Ali, N.; Hasan, S.K.; Sultana, S. Rutin ameliorates cyclophosphamide induced oxidative stress and inflammation in Wistar rats: Role of NFκB/MAPK pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 231, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, F.M.; Kucukler, S.; Caglayan, C.; Gur, C.; Batil, A.A.; Gülçin, İ. Therapeutic effects of silymarin and naringin on methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: Biochemical evaluation of anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and antiautophagic properties. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.-O.; Kim, M.-O.; Kang, S.-H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, G.-Y. Sulforaphane suppresses TNF-α-mediated activation of NF-κB and induces apoptosis through activation of reactive oxygen species-dependent caspase-3. Cancer Lett. 2009, 274, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vielhauer, V.; Mayadas, T.N. Functions of TNF and its Receptors in Renal Disease: Distinct Roles in Inflammatory Tissue Injury and Immune Regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 286–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in macrophages. Crit Rev. Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S.; Sil, P.C. The beneficial role of curcumin on inflammation, diabetes and neurodegenerative disease: A recent update. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 83, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gupta, S.C.; Sung, B. Curcumin: An orally bioavailable blocker of TNF and other pro-inflammatory biomarkers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1672–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damiano, S.; Iovane, V.; Squillacioti, C.; Mirabella, N.; Prisco, F.; Ariano, A.; Amenta, M.; Giordano, A.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Red orange and lemon extract prevents the renal toxicity induced by ochratoxin A in rats. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, H. Regulation of iNOS on Immune Cells and Its Role in Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, M.; Ericsson, A.C. Function of Macrophages in Disease: Current Understanding on Molecular Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 620510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbon, A.J.; Meli, M.L.; Barker, E.N.; Davidson, A.D.; Tasker, S.; Kipar, A. Inflammatory Mediators in the Mesenteric Lymph Nodes, Site of a Possible Intermediate Phase in the Immune Response to Feline Coronavirus and the Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis? J. Comp. Pathol. 2019, 166, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arend, W.P. Cytokine imbalance in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: The role of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longobardi, C.; Damiano, S.; Andretta, E.; Prisco, F.; Russo, V.; Pagnini, F.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Curcumin Modulates Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation, and DNA Damage and Protects against Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081239
Longobardi C, Damiano S, Andretta E, Prisco F, Russo V, Pagnini F, Florio S, Ciarcia R. Curcumin Modulates Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation, and DNA Damage and Protects against Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(8):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081239
Chicago/Turabian StyleLongobardi, Consiglia, Sara Damiano, Emanuela Andretta, Francesco Prisco, Valeria Russo, Francesco Pagnini, Salvatore Florio, and Roberto Ciarcia. 2021. "Curcumin Modulates Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation, and DNA Damage and Protects against Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats" Antioxidants 10, no. 8: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081239
APA StyleLongobardi, C., Damiano, S., Andretta, E., Prisco, F., Russo, V., Pagnini, F., Florio, S., & Ciarcia, R. (2021). Curcumin Modulates Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation, and DNA Damage and Protects against Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Antioxidants, 10(8), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10081239






