Glutathione and Glutaredoxin in Redox Regulation and Cell Signaling of the Lens
Abstract
1. Introduction: The Ocular Lens
1.1. The Structure and Function of a Vertebrate Ocular Lens
1.2. Pathology of an Eye Lens: Cataract
2. Sources of Oxidative Stress and the Damage to the Lens
3. The Built-in Reducing System against Oxidative Stress in the Lens: Glutathione (GSH)
4. Hypothesis on the Mechanism of Senile Cataract Formation: The Role of Protein S-S-Glutathione Mixed Disulfides
5. Redox Control in the Lens—Discovery of Thioltransferase (Glutaredoxin 1)
6. Can Thioltransferase (TTase) Regulate Redox Homeostasis in the Lens?
7. Cellular Functions of Thioltransferase (TTase) in Lens Epithelial Cells
7.1. Properties of the Recombinant Human Lens Thioltransferase
7.2. Modulation of Lens Glycolytic Pathway by TTase
7.3. Lens TTase Can Mediate Ascorbate Recycling
8. Mechanism of Lens TTase Adaptive Response to Oxidative Stress and the Presence of Signal Transduction Systems in the Lens
8.1. How Is Thioltransferase in the Lens Being Upregulated under Oxidative Stress and What Is Its Relationship to Cell Signaling Transduction?
8.2. Presence of the Signaling Transduction Systems: The Mitogenic-Response, Stress-Response and the Survival-Response Pathways in the Lens
9. Redox Signaling in the Lens for Cell Proliferation
9.1. Association of ROS with Growth Factor-Stimulated Cell Proliferation
9.2. How Does a Growth Factor Induce ROS Generation In Situ for Cell Signaling in the Lens?
9.3. Regulation of NADPH Oxidase (NOX) and Its Association with Cell Proliferation and Other Cellular Functions
10. Control of Redox Signaling by TTase: A Novel Physiological Function in the Lens
10.1. Low Molecular Weight Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases (LMW-PTP)
10.2. Recombinant Human Lens LMW-PTP
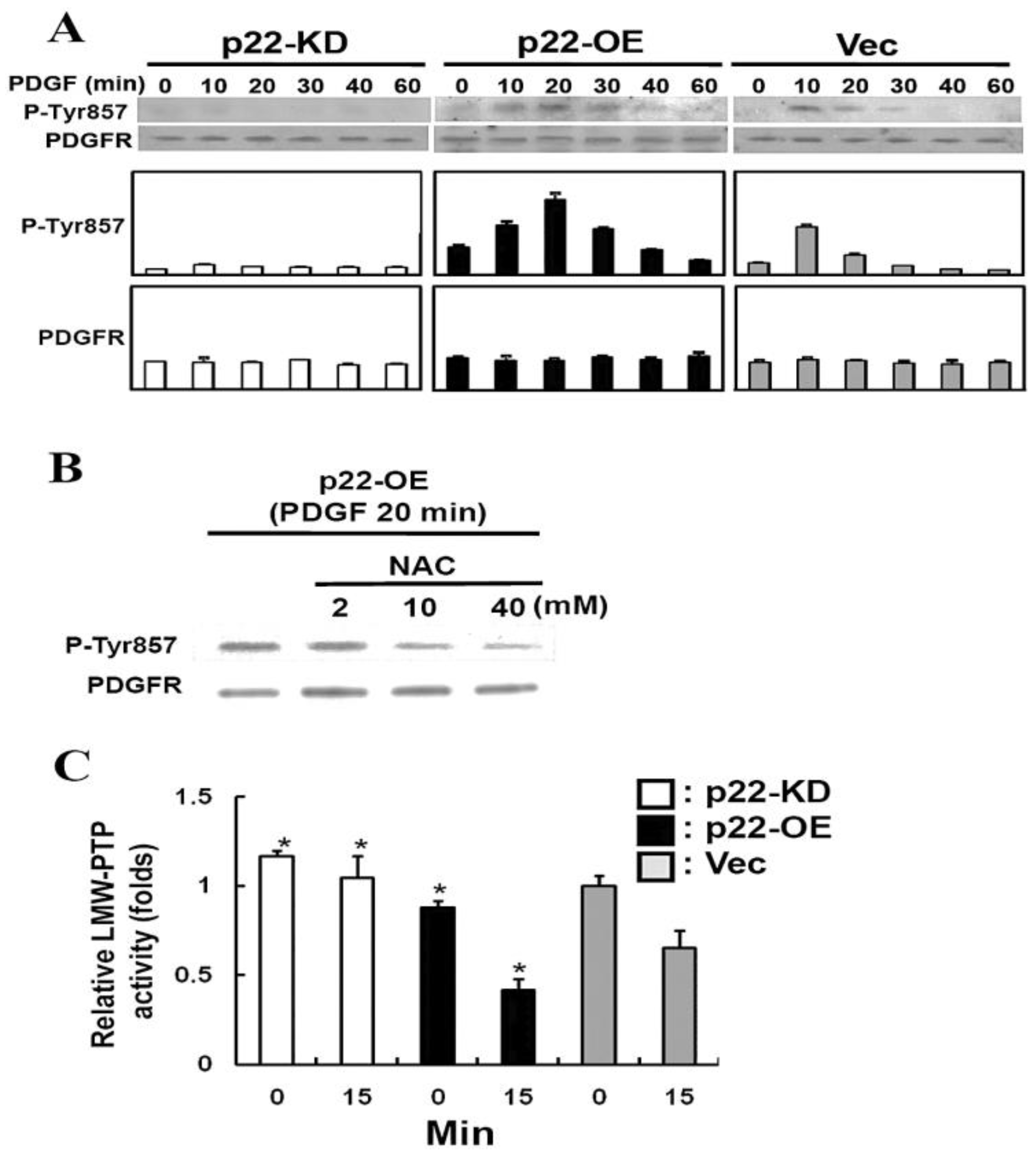
10.3. Regulation of LMW-PTP by TTase in the Lens
11. The Importance of TTase in Cataract Prevention as Demonstrated by a TTase Gene Knockout Mouse Model
12. The Status of TTase in Aging and Cataractous Human Lenses
12.1. Effect of Age on TTase and Other Redox Regulation Systems
12.2. Effect of Lens Opacity on TTase and Other Redox Regulating Systems
13. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berman, E.R. Biochemistry of the Eye; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 201–290. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, J.H. Selected topics in ophthalmic biochemistry. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1964, 72, 554–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datiles, M.B.; Kinoshita, J.H. Pathogenesis of cataracts. In Clinical Ophthalmology; Tasman, W., Jaeger, E., Eds.; Lippincott Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1991; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Augusteyn, R. Protein modification in cataract: Possible oxidative mechanisms. In Mechanisms of Cataract Formation in the Human Lens; Duncan, G., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 72–115. [Google Scholar]
- Spector, A. Oxidative stress-induced cataract: Mechanism of action. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigler, J.S., Jr.; Goosey, J. Aging of protein molecules: Lens crystallins as a model system. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1981, 6, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truscott, R.J.W. Age-related nuclear cataract: A lens transport problem. Ophthalmic Res. 2000, 32, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, M.F. Redox Regulation in the Lens. In Progress in Retina and Eye Research; Osborne, N., Chader, G., Eds.; Pergamon Elsevier Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 22, pp. 657–682. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, M.F. Association of oxidative stress with cataractogenesis. In Redox-Genome Interactions in Health and Disease; Fuchs, J., Podda, M., Packer, L., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 15, pp. 325–349. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, H.R. Ultraviolet radiation and the eye: An epidemiologic study. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1989, 87, 802–853. [Google Scholar]
- Rathbun, W.B. Lenticular glutathione synthesis: Rate-limiting factors in its regulation and decline. Curr. Eye Res. 1984, 3, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.N. Glutathione and its function in the lens—An Overview. Exp. Eye Res. 1990, 50, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giblin, F.J. Glutathione: A vital lens antioxidant. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 16, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.C.; Lorentzen, K.A.; Kisler, J.; Donaldson, P.J. Molecular identification and characterization of the glycine transporter (GLYT1) and the glutamine/glutamate transporter (ASCT2) in the rat lens. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.C.; Lam, L.; Li, B.; Donaldson, P.J. Molecular identification and cellular localization of a potential transport system involved in cysteine/cysteine uptake in human lenses. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 116, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokovc, B.V.; Mackie, J.B.; McComb, J.G.; Kaplowitz, N.; Weiss, M.H.; Kannan, R. Blood-to lens transport of reduced glutathione in an in situ perfused guinea pig eye. Exp. Eye Res. 1994, 59, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, L.; Donaldson, P.J.; Lim, J.C. Dynamic regulation of GSH synthesis and uptake pathways in the rat lens epithelium. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitson, J.A.; Sell, D.R.; Goodman, M.C.; Monnier, V.M.; Fan, X. Evidence of dual mechanisms of glutathione uptake in the rodent lens: A novel role for vitreous humor in lens glutathione homeostasis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis Sci. 2016, 57, 3914–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, M.F.; Dickerson, J.E., Jr.; Garadi, R. The Role of Protein-thiol Mixed Disulfides in Cataractogenesis. Exp. Eye Res. 1990, 50, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.F.; McKellar, R.; Chyan, O. Quantitation of Protein Mixed Disulfides by Ion-Exchange Chromatography. Exp. Eye Res. 1986, 42, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.F.; Huang, Q.L.; Zigler, J.S., Jr. Normal and Cataractous Human Lenses: Re-evaluation of the Thiol/disulfide and Protein Status. Curr. Eye Res. 1989, 8, 883–890. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, M.F.; Dickerson, J.E., Jr. Protein-thiol Mixed Disulfides in Human Lens. Exp. Eye Res. 1992, 55, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, J.E., Jr.; Lou, M.F. A New Mixed Disulfide Species in Human Cataractous and Aged Lenses. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1157, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.L.; Lou, M.F. The Effect and Recovery of Long Term H2O2 Exposure on Rat Lens Morphology and Biochemistry. Exp. Eye Res. 1993, 57, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.M.; Raghavachari, N.; Lou, M.F. Relationship of protein-GSH and thioltransferase in H2O2-induced cataract in cultured pig lens. Exp. Eye Res. 1997, 64, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.R.A.; Chen, A.A.; Smith, J.B.; Lou, M.F. Modification of γB-crystallins from a hydrogen peroxide treated bovine lens. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 4735–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, M.F.; Dickerson, J.E., Jr.; Wolfe, J.K.; Tung, W.; Chylack, L., Jr. Correlation of protein-thiol mixed disulfide level with the opacity and brunescence in human lens. Exp. Eye Res. 1999, 68, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, L. Increase in the intramolecular disulfide bonding of alpha-crystallin during aging of the human lens. Exp. Eye Res. 1996, 63, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, M.F.; Xu, G.T.; Cui, C.L. Further Studies on the Dynamic Changes of Glutathione and Protein-thiol Mixed Disulfides in H2O2 Induced Cataract in Rat Lenses: Distributions and effect of aging. Curr. Eye Res. 1995, 14, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, J.J. Free and protein bound glutathione in normal and cataractous human lenses. Biochem. J. 1970, 117, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.N.; Han, R.F. Protein-bound glutathione in mammalian lenses and in galactose cataract. Doc. Ophthalmol. 1976, 8, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Truscott, R.J.W.; Augusteyn, R.C. The state of sulphydryl groups in normal and cataractous human lenses. Exp. Eye Res. 1977, 25, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, A.; Roy, D. Disulfide-linked high molecular weight protein associated with human cataract. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 3244–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.F. Protein-thiol mixed disulfides and thioltransferase in the lens- a review. In Advances in Ocular Toxicology; Green, K., Edelhauser, H.F., Hackett, R.B., Hull, D.S., Potter, D.E., Tripathi, R.C., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, M. Thiol regulation in the lens. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 16, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, A. Hydrogen donor system for Escherichia coli ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase dependent upon glutathione. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, K.; Eriksson, S.; Mannervik, B. Purification and characterization of cytoplasmic thioltransferase (glutathione: Disulfide oxidoreductase) from rat liver. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 2978–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.R.; Wells, W.W. The primary structure of pig liver thioltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 6699–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, A.; Martinez-Galisteo, E.; Antonio-Barcena, J.; Spyrou, G.; Holmgren, A. Purification from placenta, amino acid sequence, structure comparisons and cDNA cloning of human Grx (thioltransferase). Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 227, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, T.; Oshida, T.; Nishimura, M.; Maeda, H.; Hara, T.; Hosomi, S.; Mizoguchi, T.; Nishihara, T. Study of human erythrocyte thioltransferase: Comparative characterization with bovine enzyme and its physiological role under oxidative stress. J. Biochem. 1992, 111, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieyal, J.J.; Srinivasa, U.; Starke, D.W. Glutathionyl specificity of thioltransferase: Mechanistic and physiological implications. In Biothiols in Health and Disease; Packer, L., Cadenas, E.P., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA; Basel, Switzerland; Hong Kong, 1995; pp. 302–372. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, E.M.; Mieyal, J.J. Protein-thiol oxidation and cell death: Regulatory role of glutaredoxins. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2012, 17, 1748–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavachari, N.; Lou, M.F. Evidences for the Presence of Thioltransferase in the Lens. Exp. Eye Res. 1996, 63, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.Y.; Xing, K.Y.; Liu, A.; Raghavarchari, N.; Ehlers, N.; Lou, M.F. Recombinant human lens thioltransferase: Purification, characterization and function. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 743–751. [Google Scholar]
- Chrestensen, C.A.; Eckman, C.B.; Starke, D.W.; Mieyal, J.J. Cloning, expression and characterization of human thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) in E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1995, 374, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, C.A.; Spyrou, G.; Holmgren, A. High-level expression of fully active human glutaredoxin (thioltransferase) in E. coli and characterization of Cys 7 to Ser mutant protein. FEBS Lett. 1996, 378, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Levine, M. The human glutaredoxin gene: Determination of its organization, transcription start point, and promoter analysis. Gene 1997, 197, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Raghavachari, N.; Wang, G.M.; Lou, M.F. Distribution of thioltransferase in ocular tissues. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.; Fernando, M.R.; Lou, M.F. Induction of thioltransferase and thiolredoxin/thioredoxin reductase systems in cultured porcine lenses under oxidative stress. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 3783–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegorova, S.; Liu, A.M.; Lou, M.F. Cloning, expression and characterization of human lens thioredoxin. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, W.W.; Yang, Y.; Deits, T.L.; Gan, Z.R. Thioltransferases. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 1993, 66, 149–201. [Google Scholar]
- Gallogly, M.M.; Mieyal, J.J. Mechanisms of reversible protein glutathionylation in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillig, C.H.; Berndt, C.; Holmgren, A. Glutaredoxin systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 1304–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, F.T.; Branco, V.; Vale, F.F.; Coppo, L. Glutaredoxin: Discovery, redox defense and much more. Redox Biol. 2021, 43, 10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.Y.; Lou, M.F. Effect of H2O2 on human lens epithelial cells and the possible mechanism for oxidative damage repair by thioltransferase. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.F.; Wang, G.M.; Wu, F.; Raghavachari, N.; Reddan, J.R. Thioltransferase is present in the lens epithelial cells as a highly oxidative stress-resistant enzyme. Exp. Eye Res. 1998, 66, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavachari, N.; Kryzan, K.; Xing, K.Y.; Lou, M.F. Regulation of thioltransferase expression in human lens epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, H.F. Biological disulfides: The third messenger? Modulation of phosphofructokinase activity by thiol/disulfide exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 12086–12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.M. Role of reversible oxidation-reduction of enzyme thiols-disulfides in metabolic regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1985, 54, 305–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, T.; Hara, T.; Yazawa, H.; Mizoguchi, T. Effect of thioltransferase on the cystamine-activated fructose 1,6-biphosphatase by its redox regulation. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Intl. 1994, 32, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, F.; Xing, K.Y.; Lou, M.F. Modulation of lens glycolytic pathway by thioltransferase. Exp. Eye Res. 2000, 70, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, S.; Nanri, H.; Fernando, M.R.; Minakami, S. Possible differences in the regenerative roles played by thioltransferase and thioredoxin for oxidatively damaged proteins. J. Biochem. 1994, 116, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giblin, F.J.; Nies, D.E.; Reddy, V.N. Stimulation of the hexose monophosphate shunt in rabbit lens in response to the oxidation of glutathione. Exp. Eye Res. 1981, 33, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, W.W.; Xu, D.P.; Yang, Y.; Rocque, P.A. Mammalian thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) and protein disulfide isomerase have dehydroascorbate reductase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 15361–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, M.R.; Satake, M.; Monnior, V.M.; Lou, M.F. Thioltransferase mediated ascorbate recycling in human lens epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, H.; Lofgren, S.; Tian, X.; Lou, M.F. Ultraviolet radiation-induced cataract in mice: The effect of age and the potential biochemical mechanism. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7276–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysan, K.; Lou, M.F. Regulation of Human thioltransferase (hTTase) gene by AP-1 transcription factor under oxidative stress. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Karin, M.; Liu, Z.G.; Zandi, E. AP-1 function and regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, K.; Matsui, M.; Iwata, S.; Nishiyama, A.; Mori, K.; Yodoi, J. AP-1 transcriptional activity is regulated by a direct association between thioredoxin and Ref-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997, 94, 3633–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Schlessinger, J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 1990, 61, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seger, R.; Krebs, E.G. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatechka, D.S., Jr.; Lou, M.F. Studies of the Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases and Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in the Lens: 1. The Mitogenic stress responses. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatechka, D.S., Jr.; Lou, M.F. Studies of the Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases and Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in the Lens: 2. The Intercommunications. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 75, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti, P.A. Prooxidant states and tumor promotion. Science 1985, 227, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.; Tenhaken, R.; Dixon, R.; Lamb, C. H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plants hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell 1994, 79, 583–593. [Google Scholar]
- Burdon, R.H. Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide in relation to mammalian cell proliferation. Free Radic. Bio. Med. 1995, 18, 775–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T. Oxygen radicals and signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998, 10, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, B.; Radeke, H.H.; Selle, S.; Younes, M.; Sies, H.; Resch, K.; Habermehl, G.G. Human fibroblasts release reactive oxygen species in response to interleukin-1 or tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Biochem. J. 1989, 263, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, M.; Shibanuma, M.; Kuroki, T.; Nose, K. Production of hydrogen peroxide by transforming growth factor-beta 1 and its involvement in induction of egr-1 in mouse osteoblastic cells. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 126, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaresan, M.; Yu, Z.X.; Ferrans, V.J.; Irani, K.; Finkel, T. Requirement for generation of H2O2-for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science 1995, 270, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.Y.; Cruz, T.F. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in cytokine and growth factor induction of c-fos expression in chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 11727–11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, J.D.; Bassnett, S.; Kornacker, S.; Beebe, D.C. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptors in the developing chicken lens. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.C.W.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, K.; Krysan, K.; Lou, M.F. Platelet derived growth factor (PDGF)-induced reactive oxygen species in the Lens epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 78, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanock, S.J.; EL Benna, J.; Smith, R.M.; Babior, B.M. The respiratory burst oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 24519–24522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.L.; Douglas, J.G. Arachidonic acid activates c-jun-N-terminal kinase through NADPH oxidase in rabbit proximal tubular epithelial cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3771–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.Y.; Wong, J.M.; Cruz, T.F. Reactive oxygen species mediate cytokine activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 15703–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Maddala, R.; John, F.; Zigler, J.S., Jr. Expression of nonphagocytic NADPH oxidase system in the ocular lens. Mol. Vis. 2004, 10, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piomelli, D. Arachidonic acid in cell signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1993, 5, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.C.W.; Xing, K.; Vivekanandan, S.; Lou, M.F. The positive feedback role of arachidonic acid in platelet derived growth factor-induced cell signaling in lens epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.C.W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lou, M.F. Control of PDGF-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and signal transduction in human lens epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 374–387. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lou, M.F. The Regulation of NADPH Oxidase and its Association with Cell Proliferation in Human Lens Epithelial Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 2291–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, K.Y.; Lou, M.F. Regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2 alpha) and its association with cell proliferation in human lens epithelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8231–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Twamley-Stein, G.M.; Pepperkok, R.; Ansorge, W.; Courtneidge, S.A. The Src family tyrosine kinases are required for platelet-derived growth factor-mediated signal transduction in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1993, 90, 7696–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; Okedli, E.; Woodard, A.; Toms, S.A.; Allen, G.S. Evidence for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt-p7S6K pathway activation and transduction of mitogenic signals by platelet-derived growth factor in meningioma cells. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 97, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, P.T.; Eguinoa, A.; Qiu, R.G.; Stokoe, D.; Cooke, F.T.; Walters, R.; Wennstrom, S.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Evans, T.; Symons, M.; et al. PDGF stimulates an increase in GTP-Rac via activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Curr. Biol. 1995, 5, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babior, B.M. NADPH oxidase: An update. Blood 1999, 93, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griendling, K.K.; Sorescu, D.; Ushio-Fukai, M. NAD(P)H oxidase: Role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T. Redox-dependent signal transduction. FEBS Lett. 2000, 476, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.Y.; Raza, A.; Lofgren, S.; Fernando, M.R.; Ho, Y.S.; Lou, M.F. Low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase (LMW-PTP) and its possible physiological functions in the eye lens. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1774, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauman, E.B.; Saper, M.A. Structure and function of the protein tyrosine phosphatase. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Hertog, J.; Groen, A.; van der Wijk, T. Redox regulation of protein-tyrosine phosphatases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 434, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raugei, G.; Ramponi, G.; Chiarugi, P. Low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase: Small, but smart. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanquet, P.R.; Croquet, F. A high phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity is present in differentiating bovine lens cells. J. Cell Physiol. 1995, 165, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, I.O.; Kashiwa, Y.; Nishigori, H. 18kDa protein tyrosine phosphatase in the ocular lens. Exp. Eye Res. 2001, 73, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson, G.L.; Massa, H.; Trask, B.J.; Van Etten, L. Gene structure, sequence, and chromosomal localization of the human red cell-type low-molecular-weight acid phosphotyrosyl phosphatase gene, ACP1. Genomics 1995, 30, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzocchini, R.; Bucciantini, M.; Stefani, M.; Taddei, N.; Thunnissen, M.G.; Nordlund, P.; Ramponi, G. Expression, purification and preliminary crystal analysis of the human low Mr phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase isoform 1. FEBS Lett. 1998, 426, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.F.; Xing, K.Y.; Fernando, M.R.; Moon, S.; Ho, Y.S. Thioltransferase knockout mouse: A new cataract model. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 1026. [Google Scholar]
- Lofgren, S.; Fernando, M.R.; Xing, K.Y.; Wang, Y.; Kuszynski, C.A.; Ho, Y.S.; Lou, M.F. Effect of thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) deletion on cellular sensitivity to oxidative stress and cell proliferation in lens epithelial cells of thioltransferase knockout mouse. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4497–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, L.M.; Lofgren, S.; Ho, Y.S.; Lou, M.; Wegener, A.; Holz, F.; Soderberg, P. Absence of glutaredoxine1 increases susceptibility to oxidative stress induced by UVR-B. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronschlager, M.; Galichanin, K.; Ekstrom, J.; Lou, M.F.; Soderberg, P.G. Protective effect of the thioltransferase gene on in vivo UVR-300 nm-induced cataract. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, K.Y.; Lou, M.F. Effect of age on thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) and thioredoxin systems in the human lens. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 6598–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xing, K.Y.; Fan, Y.C.; Libondi, T.; Lou, M.F. Loss of thiol repair systems in human cataractous lenses. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Qiu, W.Y.; Pan, Q.; Yao, Y.F.; Xing, K.; Lou, M.F. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are essential mediators in epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated corneal epithelial cell proliferation, adhesion, migration, and wound healing. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Qiu, W.Y.; Huo, Y.N.; Yao, Y.F.; Lou, M.F. Low levels of hydrogen peroxide can stimulate corneal epithelial cell adhesion, migration and wound healing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladyshav, V.; Sun, C.A.; Liu, A.M.; Lou, M.F. Identification and characterization of a new mammalian mitochondrial glutaredoxin (thioltransferase). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30374–30380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.L.; Xing, K.Y.; Lou, M.F. Glutaredoxin2 prevents H2O2-induced cell apoptosis by protecting complex I activity. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1797, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, M.F.; Basu, S.; Yu, Y.; Wu, H.; Menko, A.S. Glutaredoxin2 (Grx2) gene knockout suppresses fiber cell differentiation and delays de-nucleation of the mouse lens. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5592. [Google Scholar]
- Liyanage, N.; Fernando, M.R.; Lou, M.F. Regulation of thioredoxin by a specific thioredoxin-binding protein in the eye lens. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 85, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, M.F. Glutathione and Glutaredoxin in Redox Regulation and Cell Signaling of the Lens. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101973
Lou MF. Glutathione and Glutaredoxin in Redox Regulation and Cell Signaling of the Lens. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(10):1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101973
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Marjorie F. 2022. "Glutathione and Glutaredoxin in Redox Regulation and Cell Signaling of the Lens" Antioxidants 11, no. 10: 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101973
APA StyleLou, M. F. (2022). Glutathione and Glutaredoxin in Redox Regulation and Cell Signaling of the Lens. Antioxidants, 11(10), 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101973




