Cereblon Deficiency Contributes to the Development of Elastase-Induced Emphysema by Enhancing NF-κB Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Intratracheal Instillation of Elastase
2.3. Analysis of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF)
2.4. Emphysema Measurement and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Cells and Reagents
2.6. Preparation of Cigarette Smoke Extract (CSE)
2.7. Isolation of RNA and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Measurement of Cytokines
2.9. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Luciferase Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
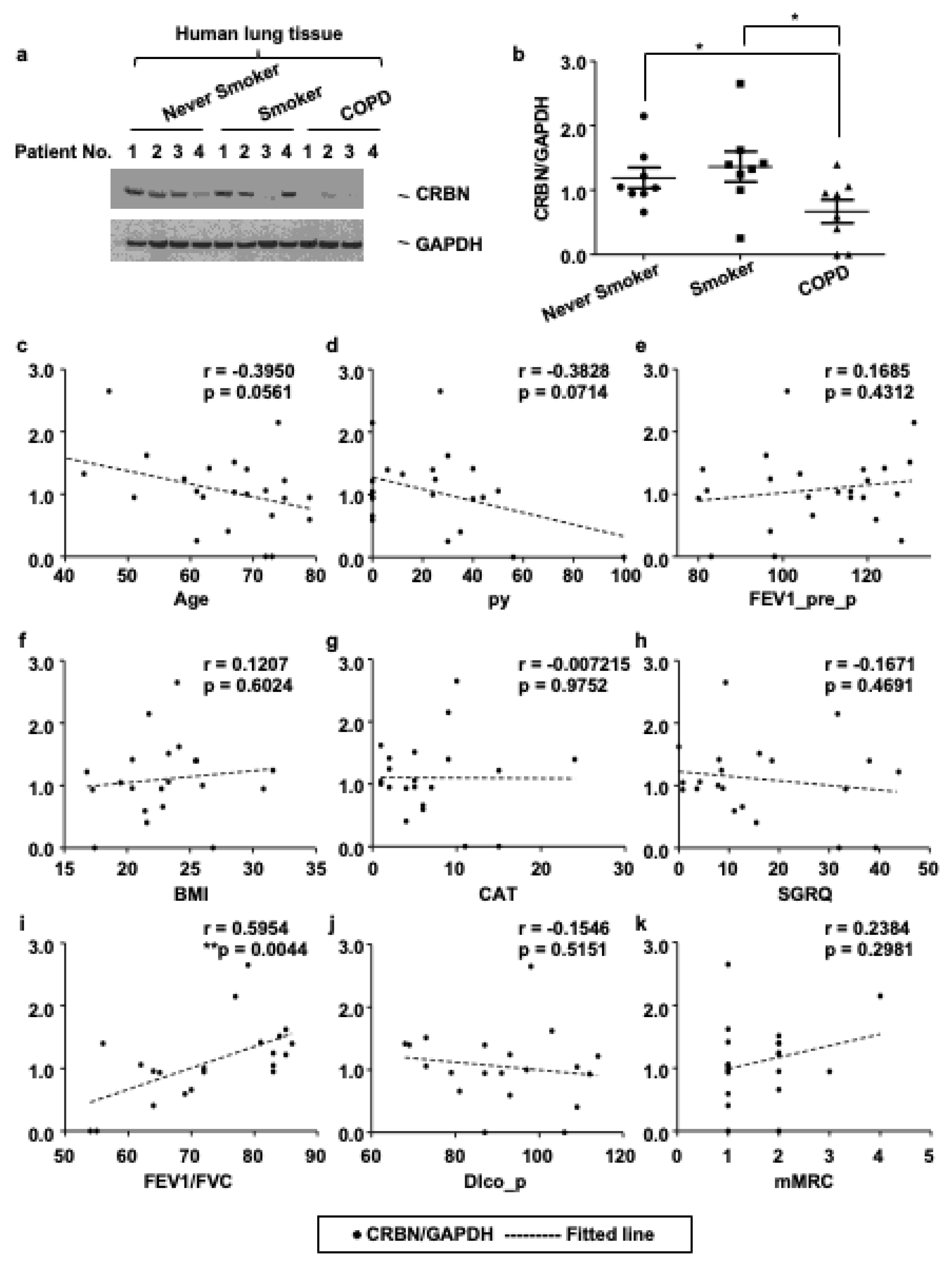
3.1. The Expression Level of CRBN Was Decreased in Lung Tissues of Patients with COPD and Correlated with the Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 s (FEV1)/Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) Ratio
3.2. Crbn KO Exaggerated Elastase-Induced Emphysema in Mice
3.3. Crbn KO Increased Elastase-Induced Inflammation and Cellular Injury
3.4. Crbn KO Enhanced Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines by Increasing NF-κB Activation in Lung Epithelial Cells and Macrophages
3.5. Crbn KO Increased Elastase-Induced Oxidative Damage and MMP9 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, T.; Allen, C.; Arora, M.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brown, A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1545–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Shan, P.; Jiang, G.; Cohn, L.; Lee, P.J. Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency causes pulmonary emphysema. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNee, W. Pulmonary and Systemic Oxidant/Antioxidant Imbalance in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2005, 2, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J.; Hansel, T.T. Prospects for new drugs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feetham, L.; Van Dorn, A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Ko, T.H.; Nyamaa, B.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, N.; Ko, K.S.; Rhee, B.D.; Park, C.-S.; Nilius, B.; Han, J. Cereblon in health and disease. Pflug. Arch. 2016, 468, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Chen, L. Cereblon: A Protein Crucial to the Multiple Functions of Immunomodulatory Drugs as well as Cell Metabolism and Disease Generation. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 9130608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Ye, J.; Zou, X.; Xu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zou, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Cang, Y. CRL4ACRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase restricts BK channel activity and prevents epileptogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, S.; Lee, K.-H.; Song, S.; Jung, Y.-K.; Park, C.-S. Identification and functional characterization of cereblon as a binding protein for large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Peng, Y.-J.; Hu, M.-C.; Huang, J.-J.; Chien, Y.-C.; Wu, J.-T.; Chen, T.-Y.; Tang, C.-Y. The Cullin 4A/B-DDB1-Cereblon E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Complex Mediates the Degradation of CLC-1 Chloride Channels. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhao, C.; Gu, K.; Jiao, Y.; Hao, J.; Sun, G. Thalidomide plus chemotherapy exhibit enhanced efficacy in the clinical treatment of T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A prospective study of 46 cases. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Braggio, E.; Shi, C.-X.; Kortuem, K.M.; Bruins, L.A.; Schmidt, J.E.; Chang, X.-B.; Langlais, P.; Luo, M.; Jedlowski, P.; et al. Identification of cereblon-binding proteins and relationship with response and survival after IMiDs in multiple myeloma. Blood 2014, 124, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Braggio, E.; Shi, C.-X.; Bruins, L.A.; Schmidt, J.E.; Van Wier, S.; Chang, X.-B.; Bjorklund, C.C.; Fonseca, R.; Bergsagel, P.L.; et al. Cereblon expression is required for the antimyeloma activity of lenalidomide and pomalidomide. Blood 2011, 118, 4771–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.; Wi, S.M.; Kang, J.-A.; Yang, T.; Park, C.-S.; Park, S.-G.; Chung, S.; Shim, J.-H.; Chun, E.; Lee, K.-Y. Cereblon negatively regulates TLR4 signaling through the attenuation of ubiquitination of TRAF6. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Huang, M.; Zhou, L.; He, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G. Cereblon suppresses the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of c-Jun. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10141–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.M.; Yang, S.-J.; Choi, J.-H.; Park, C.-S. Functional Effects of a Pathogenic Mutation in Cereblon (CRBN) on the Regulation of Protein Synthesis via the AMPK-mTOR Cascade. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 23343–23352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.-J.; Jeon, S.-J.; Van Nguyen, T.; Deshaies, R.J.; Park, C.-S.; Lee, K.M. Ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of AMPK gamma subunit by Cereblon inhibits AMPK activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Res. 2020, 1867, 118729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, E.K.; Chapman, H.A.; Drazen, J.M.; Weiss, S.T.; Rosner, B.; Campbell, E.J.; O’Donnell, W.J.; Reilly, J.J.; Ginns, L.; Mentzer, S.; et al. Genetic Epidemiology of Severe, Early-onset Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Risk to relatives for airflow obstruction and chronic bronchitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, P.D.; Kuhn, C.; Pierce, J.A. The induction of emphysema with elastase. I. The evolution of the lesion and the influence of serum. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1973, 82, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hoenderdos, K.; Condliffe, A. The Neutrophil in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman-Eisenstat, J.B.; Jorens, P.G.; Hebert, C.A.; Ueki, I.; Nadel, J.A. Interleukin-8: An important chemoattractant in sputum of patients with chronic inflammatory airway diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1993, 264, L413–L418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.D. The Macrophage in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, S29–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, K.L.; Camps, M.; Rommel, C.; Mackay, C.R. Targeting dual-specificity phosphatases: Manipulating MAP kinase signalling and immune responses. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkham, P.A.; Barnes, P.J. Oxidative Stress in COPD. Chest 2013, 144, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, A.M. Matrix metalloproteinases in destructive lung disease. Matrix Biol. 2015, 44–46, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.J.; Senior, R.M. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in Lung Remodeling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.; Walton, G.M.; Sapey, E. Neutrophilic Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. COPD 2018, 15, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu, D.; Sanna, A.; Veriter, C.; Kostianev, S.; Calcagni, P.G.; Fabbri, L.M.; Maestrelli, P. Airways obstruction, chronic expectoration, and rapid decline of FEV1 in smokers are associated with increased levels of sputum neutrophils. Thorax 1996, 51, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabral, M.B.; Veiga, J.; Maia, D.; Gonçalves, I.; Mineiro, A.; Coelho, S.; Cravo, P.; Figueiredo, L.; Cardoso, J. Relationship between emphysema extent and pulmonary function test in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1035. [Google Scholar]
- Krotova, K.; Khodayari, N.; Oshins, R.; Aslanidi, G.; Brantly, M.L. Neutrophil elastase promotes macrophage cell adhesion and cytokine production through the integrin-Src kinases pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-H.; Woo, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Yoo, C.-G. Cigarette smoke extract-induced downregulation of p300 is responsible for the impaired inflammatory cytokine response of macrophages. Cell. Signal. 2021, 85, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawiger, J. Innate Immunity and Inflammation: A Transcriptional Paradigm. Immunol. Res. 2001, 23, 099–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Bellettato, C.M.; Braccioni, F.; Romagnoli, M.; Casolari, P.; Caramori, G.; Fabbri, L.M.; Johnston, S.L. Infections and Airway Inflammation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Severe Exacerbations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanabe, N.; Muro, S.; Hirai, T.; Oguma, T.; Terada, K.; Marumo, S.; Kinose, D.; Ogawa, E.; Hoshino, Y.; Mishima, M. Impact of Exacerbations on Emphysema Progression in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sethi, S.; Murphy, T.F. Infection in the Pathogenesis and Course of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Fujinawa, R.; Ota, F.; Kobayashi, S.; Angata, T.; Ueno, M.; Maeno, T.; Kitazume, S.; Yoshida, K.; Ishii, T.; et al. A Single Dose of Lipopolysaccharide into Mice with Emphysema Mimics Human Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbation as Assessed by Micro-Computed Tomography. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, Y.; Han, S.; Shim, Y.; Yoo, C. Anti-inflammatory effect of adenovirus-mediated IκBα overexpression in respiratory epithelial cells. Eur. Respir. J. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Clin. Respir. Physiol. 2001, 18, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Jeong, J.; Jang, A.-H.; Yoo, C.-G. Neutrophil Elastase Differentially Regulates Interleukin 8 (IL-8) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Production by Cigarette Smoke Extract. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28438–28445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackwell, T.S.; Christman, J.W. The Role of Nuclear Factor- κ B in Cytokine Gene Regulation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 17, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.; Pavlisko, E.; Voynow, J. Pathogenic triad in COPD: Oxidative stress, protease–antiprotease imbalance, and inflammation. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2011, 6, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, I.; Van Schadewijk, A.A.M.; Crowther, A.J.L.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Stolk, J.; MacNee, W.; De Boer, W.I. 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal, a Specific Lipid Peroxidation Product, Is Elevated in Lungs of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Li, Q.; Dong, R.; Zhao, K.; Feng, Y.; Bao, Z.; Zhou, M. Critical regulation of inflammation via class A scavenger receptor. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2018, 13, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohar, J.A.; Hamilton, R.F., Jr.; Zheng, S.; Sadeghnejad, A.; Sterling, D.A.; Xu, J.; Meyers, D.A.; Bleecker, E.R.; Holian, A. COPD Is Associated with a Macrophage Scavenger Receptor-1 Gene Sequence Variation. Chest 2010, 137, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, E.-Y.; Lee, K.-H.; Woo, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, K.-J.; Kim, Y.-K.; Yoo, C.-G. Cereblon Deficiency Contributes to the Development of Elastase-Induced Emphysema by Enhancing NF-κB Activation. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101980
Heo E-Y, Lee K-H, Woo J, Kim J, Lee C-H, Lee K-J, Kim Y-K, Yoo C-G. Cereblon Deficiency Contributes to the Development of Elastase-Induced Emphysema by Enhancing NF-κB Activation. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(10):1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101980
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Eun-Young, Kyoung-Hee Lee, Jisu Woo, Jiyeon Kim, Chang-Hoon Lee, Kyung-Jin Lee, Yun-Kyu Kim, and Chul-Gyu Yoo. 2022. "Cereblon Deficiency Contributes to the Development of Elastase-Induced Emphysema by Enhancing NF-κB Activation" Antioxidants 11, no. 10: 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101980
APA StyleHeo, E.-Y., Lee, K.-H., Woo, J., Kim, J., Lee, C.-H., Lee, K.-J., Kim, Y.-K., & Yoo, C.-G. (2022). Cereblon Deficiency Contributes to the Development of Elastase-Induced Emphysema by Enhancing NF-κB Activation. Antioxidants, 11(10), 1980. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101980






