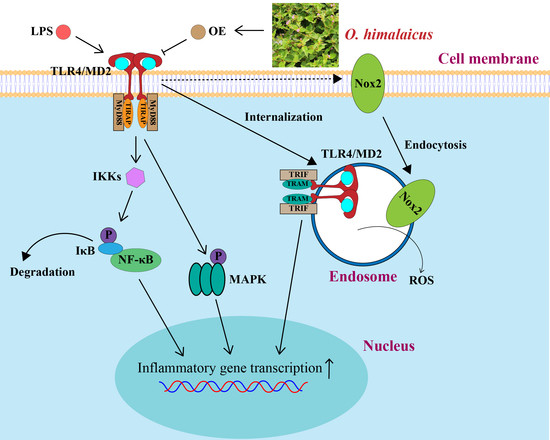
Oxybaphus himalaicus Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/MD2 Complex Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Extraction of O. himalaicus
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. MTT Assay
2.5. Nitric Oxide Measurement
2.6. Reactive Oxygen Species Detection
2.7. Immunofluorescent Staining
2.8. SiRNA Transfection
2.9. Animal Model and Design
2.10. Serum Biochemical Analysis
2.11. Histopathology and Immunochemistry
2.12. Dihydroethidium Staining
2.13. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.14. Western Blotting
2.15. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.16. Analysis of Components in OE
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. OE Dose Dependently Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation in Macrophages
3.2. OE Restrained LPS-Indued NF-κB Activation in Macrophages
3.3. OE Inhibited TLR4/MD2 Complex Formation in Macrophages
3.4. Silencing TLR4 Eliminated Anti-Inflammatory Effect of OE
3.5. OE Alleviated ROS Production by Suppressing NOX2 Endocytosis
3.6. OE Treatment Attenuated LPS-Induced AKI in Mice
3.7. OE Diminished Inflammation in AKI Mice
3.8. OE Inhibited TLR4/MD2 Complex Formation in AKI Mice
3.9. Analysis of Main Constituents in OE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kellum, J.A.; Romagnani, P.; Ashuntantang, G.; Ronco, C.; Zarbock, A.; Anders, H.-J. Acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.J.; Kellum, J.A.; Selby, N.M.; Zarbock, A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Goldstein, S.L.; Cerdá, J.; Chawla, L.S. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterbach, M.A.; Hanke, J.E.; Serefidou, M.; Mangan, M.S.J.; Kolbe, C.C.; Hess, T.; Rothe, M.; Kaiser, R.; Hoss, F.; Gehlen, J.; et al. Toll-like Receptor Signaling Rewires Macrophage Metabolism and Promotes Histone Acetylation via ATP-Citrate Lyase. Immunity 2019, 51, 997–1011.e1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sato, S.; Hemmi, H.; Hoshino, K.; Kaisho, T.; Sanjo, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sugiyama, M.; Okabe, M.; Takeda, K.; et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 2003, 301, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, J.C.; Su, T.; Horng, T.; Chow, A.; Akira, S.; Medzhitov, R. TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimaer, D.P. Jing Zhu Materia Medica; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1986; p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- Pharmacopoeia Committee of the Ministry of Health. Pharmaceutical Standards of the Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Tibet. Med. 1995, 1, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, B.; Li, X. Benzofuran ε-caprolactam glucosides, amides and phenylpropanoid derivatives with anti-inflammatory activity from Oxybaphus himalaicus. Phytochemistry 2021, 191, 112905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Mao, J.; Meng, F.; Lan, X.; Liao, Z.; Chen, M. Evaluation of the Liver Toxicity of Pterocephalus hookeri Extract via Triggering Necrosis. Toxins 2019, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, J.; Zhan, H.; Meng, F.; Wang, G.; Huang, D.; Liao, Z.; Chen, M. Costunolide protects against alcohol-induced liver injury by regulating gut microbiota, oxidative stress and attenuating inflammation in vivo and in vitro. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1268–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Yi, M.; Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M. Protective Effects of Costunolide Against D-Galactosamine and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linghu, L.; Fan, H.; Hu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yang, P.; Lan, X.; Liao, Z.; Chen, M. Mirabijalone E: A novel rotenoid from Mirabilis himalaica inhibited A549 cell growth in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Athamna, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Freudenberg, M.; Yue, T.; Wang, J.; Moresco, E.M.Y.; He, H.; Zor, T.; et al. Sulfatides are endogenous ligands for the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105316118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, F.S.; Hook, J.S.; Hilkin, B.M.; Huber, J.N.; Volk, A.P.; Moreland, J.G. Endotoxin priming of neutrophils requires endocytosis and NADPH oxidase-dependent endosomal reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12395–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonventre, J.V. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): A urinary biomarker and much more. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3265–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, X.; Meng, F.; Qu, S.; Ji, H.; Lan, X.; Chen, M. Himalaflavone A-E, five new flavonoids from Oxybaphus himalaicus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, P.; Fan, H.; Li, S.; Liao, Z.; Lan, X.; Cui, H.; Chen, M. A natural phenylpropionate derivative from Mirabilis himalaica inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5484–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, G.; Gao, X. Flavonoids from Mirabilis himalaica. Fitoterapia 2018, 127, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Wang, G.W.; Zou, Y.L.; Deng, L.Q.; Liu, M.X.; Liao, Z.H.; Lan, X.Z.; Chen, M. A new diphenyl ether derivative from Mirabilis himalaica. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Dan, M.; Han, W.; Ochir, S.; Bao, L.; Liu, L.; Muschin, T.; Baigude, H. Physicochemical properties, immunostimulatory and antioxidant activities of a novel polysaccharide isolated from Mirabilis himalaica (Edgew) Heim. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 17264–17275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.S.; Song, D.H.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, B.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.O. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature 2009, 458, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Bao, X.; Xiao, W.; Chen, G. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) inhibitors: Current research and prospective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 235, 114291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, I.; Ostuni, R.; Marek, L.R.; Barresi, S.; Barbalat, R.; Barton, G.M.; Granucci, F.; Kagan, J.C. CD14 controls the LPS-induced endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4. Cell 2011, 147, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, R.; Huang, L.; Du, L.J.; Feng, J.F.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.Y.; Xu, Q.M.; Yang, S.L.; Gao, H.; Feng, Y.L. Dihydrotanshinone exhibits an anti-inflammatory effect in vitro and in vivo through blocking TLR4 dimerization. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Yang, L.B.; Qian, C.C.; Ma, B.; Manjengwa, G.M.; Miao, X.M.; Wang, J.; Hu, C.H.; Jin, B.; Zhang, L.X.; et al. Flavokawain B alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury via targeting myeloid differentiation factor 2. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 43, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, T.; Pan, Z.; Ge, X.; Sun, C.; Lu, C.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Y.; et al. Shikonin inhibits myeloid differentiation protein 2 to prevent LPS-induced acute lung injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambeth, J.D. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, H.; Dostert, C.; Mak, T.W.; Brenner, D. TNF and ROS Crosstalk in Inflammation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, A.; von Zastrow, M. Endocytosis and signalling: Intertwining molecular networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, W.; Kim, M.H.; Choi, W.M.; Yoo, W.; Lee, J.H.; Shim, Y.R.; Yi, H.S.; et al. Pro-inflammatory hepatic macrophages generate ROS through NADPH oxidase 2 via endocytosis of monomeric TLR4-MD2 complex. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller-Calleja, N.; Manukyan, D.; Canisius, A.; Strand, D.; Lackner, K.J. Hydroxychloroquine inhibits proinflammatory signalling pathways by targeting endosomal NADPH oxidase. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, V.; Tiwari, R.L.; Chandra, T.; Kumar, A.; Dikshit, M.; Barthwal, M.K. The IRAK-ERK-p67phox-Nox-2 axis mediates TLR4, 2-induced ROS production for IL-1β transcription and processing in monocytes. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idelman, G.; Smith, D.L.H.; Zucker, S.D. Bilirubin inhibits the up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase by scavenging reactive oxygen species generated by the toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase. Redox Biol. 2015, 5, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Yin, H.; Wang, X. Small-Molecule Modulators of Toll-like Receptors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wen, J.; Huang, X.; Nie, Q.; Wu, X.; Ma, W.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Interaction between polysaccharides and toll-like receptor 4: Primary structural role, immune balance perspective, and 3D interaction model hypothesis. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, F.; Calabrese, V. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) modulation by synthetic and natural compounds: An update. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3612–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Youn, H.S. Suppression of homodimerization of toll-like receptor 4 by isoliquiritigenin. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.I.; Lee, J.K.; Youn, H.S. Inhibition of homodimerization of toll-like receptor 4 by 6-shogaol. Mol. Cells 2009, 27, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.S.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Saitoh, S.I.; Miyake, K.; Hwang, D.H.; Lee, J.Y. Cinnamaldehyde suppresses toll-like receptor 4 activation mediated through the inhibition of receptor oligomerization. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tan, Y.J.; Wang, M.Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.Y.; Wang, Q.L.; Yao, J.C.; Yue, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.M.; et al. Loganetin protects against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury by modulating the toll-like receptor 4 signalling pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.S.; Acharya, A.; Ray, R.S.; Agrawal, R.; Raghuwanshi, R.; Jain, P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of curcumin in prevention and treatment of disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 887–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gradisar, H.; Keber, M.M.; Pristovsek, P.; Jerala, R. MD-2 as the target of curcumin in the inhibition of response to LPS. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Bai, B.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lum, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. New MD2 inhibitors derived from curcumin with improved anti-inflammatory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 148, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Ying, S.; Chen, G.; Wu, B.; Xu, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Shan, X.; et al. Discovery of new MD2 inhibitor from chalcone derivatives with anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Koo, J.E.; Seo, Y.J.; Tyagi, N.; Jeong, E.; Choi, J.; Lim, K.M.; Park, Z.Y.; Lee, J.Y. Suppression of Toll-like receptor 4 activation by caffeic acid phenethyl ester is mediated by interference of LPS binding to MD2. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Lim, H.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Jung, H.; Kim, M.R.; Moon, D.C.; Kim, K.I.; Lee, M.S.; Ryu, J.H. Carabrol suppresses LPS-induced nitric oxide synthase expression by inactivation of p38 and JNK via inhibition of I-kappaBalpha degradation in RAW 264.7 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, L.; Yao, N.; Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Xia, C. Upregulation of UGT1A1 expression by ursolic acid and oleanolic acid via the inhibition of the PKC/NF-κB signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, L.; Khatoon, S.; Hao, M.; Peng, X.; et al. Abscisic acid ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis by regulating the NF-кB signaling pathway in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 891, 173652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Xu, J.; Xie, Q.M.; Zhang, H.Y.; Fei, G.H.; Wu, H.M. Abscisic acid suppresses the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and oxidative stress in murine allergic airway inflammation. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 3298–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máñez, S.; Recio, M.C.; Gil, I.; Gómez, C.; Giner, R.M.; Waterman, P.G.; Ríos, J.L. A glycosyl analogue of diacylglycerol and other antiinflammatory constituents from Inula viscosa. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, H.; Pu, Q.; Long, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, G.; Meng, F.; Liao, Z.; Lan, X.; Chen, M. Oxybaphus himalaicus Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/MD2 Complex Formation. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122307
Zhan H, Pu Q, Long X, Lu W, Wang G, Meng F, Liao Z, Lan X, Chen M. Oxybaphus himalaicus Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/MD2 Complex Formation. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(12):2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122307
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Honghong, Qingxiu Pu, Xiaoliang Long, Wei Lu, Guowei Wang, Fancheng Meng, Zhihua Liao, Xiaozhong Lan, and Min Chen. 2022. "Oxybaphus himalaicus Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/MD2 Complex Formation" Antioxidants 11, no. 12: 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122307
APA StyleZhan, H., Pu, Q., Long, X., Lu, W., Wang, G., Meng, F., Liao, Z., Lan, X., & Chen, M. (2022). Oxybaphus himalaicus Mitigates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting TLR4/MD2 Complex Formation. Antioxidants, 11(12), 2307. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122307