Isatin Counteracts Diethylnitrosamine/2-Acetylaminofluorene-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis in Male Wistar Rats by Upregulating Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Detoxification Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. Animal Grouping
2.4. Blood and Liver Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Estimation of Serum Liver Function Tests Biomarkers
2.6. Detection of Serum Levels of Tumor Markers
2.7. Detection of Liver Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
2.8. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Examination
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isatin Reduced DENA/2-AAF-Induced Increases in Biochemical Markers of Hepatic Dysfunction
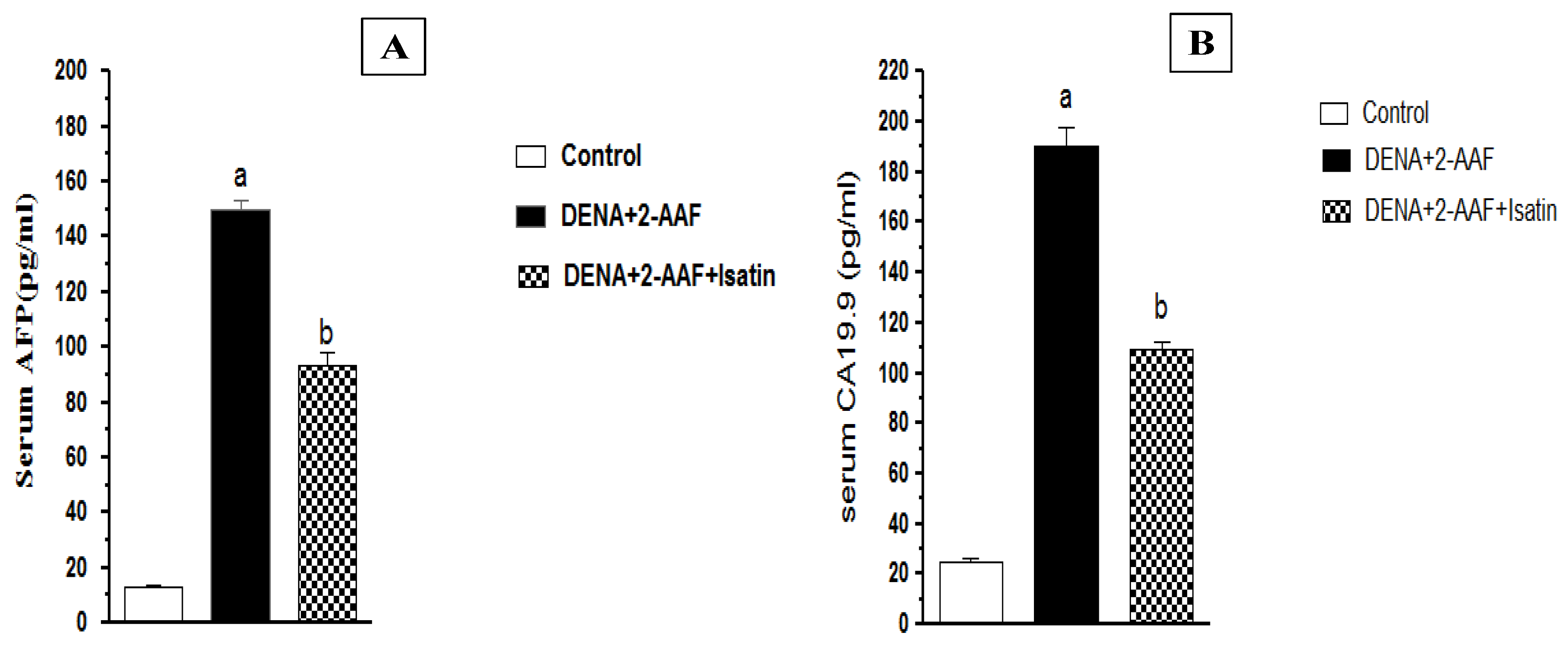
3.2. Isatin Reduced DENA/2-AAF-Induced Increases in Serum Tumor Marker Levels
3.3. Isatin Suppressed Oxidative Stress and Enhanced Antioxidant Defense Capacity in HCC Model Rat Liver
3.4. Isatin Suppressed DENA/2-AAF-Induced Elevations of the Pro-Inflammatory Factors TNF-α, NF-κB p50, and NF-κB p65 in Rat Liver
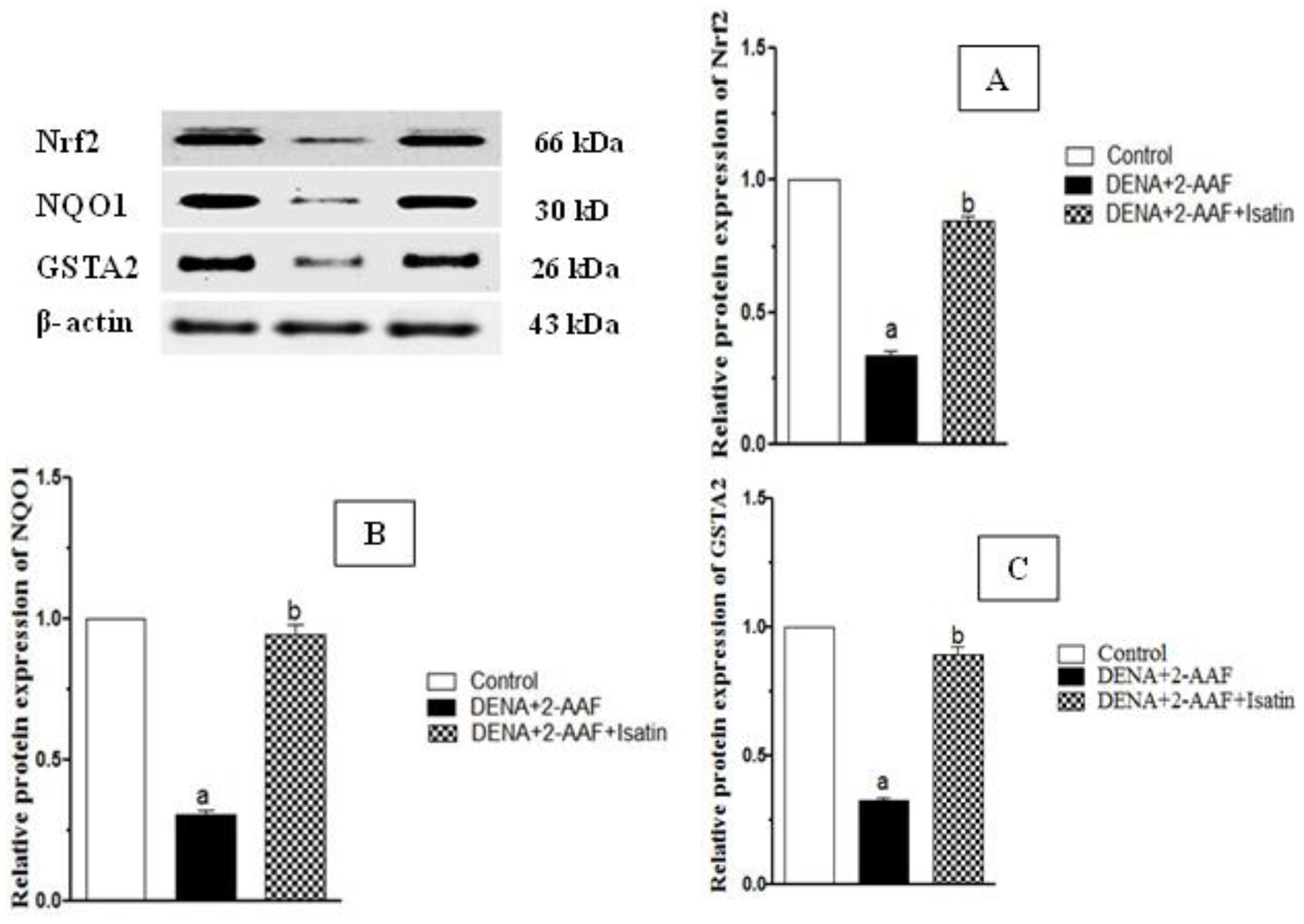
3.5. Isatin Enhanced Expression of Detoxification Pathway Proteins Nrf2, NQO1, and GSTA2 in HCC Model Rat Liver
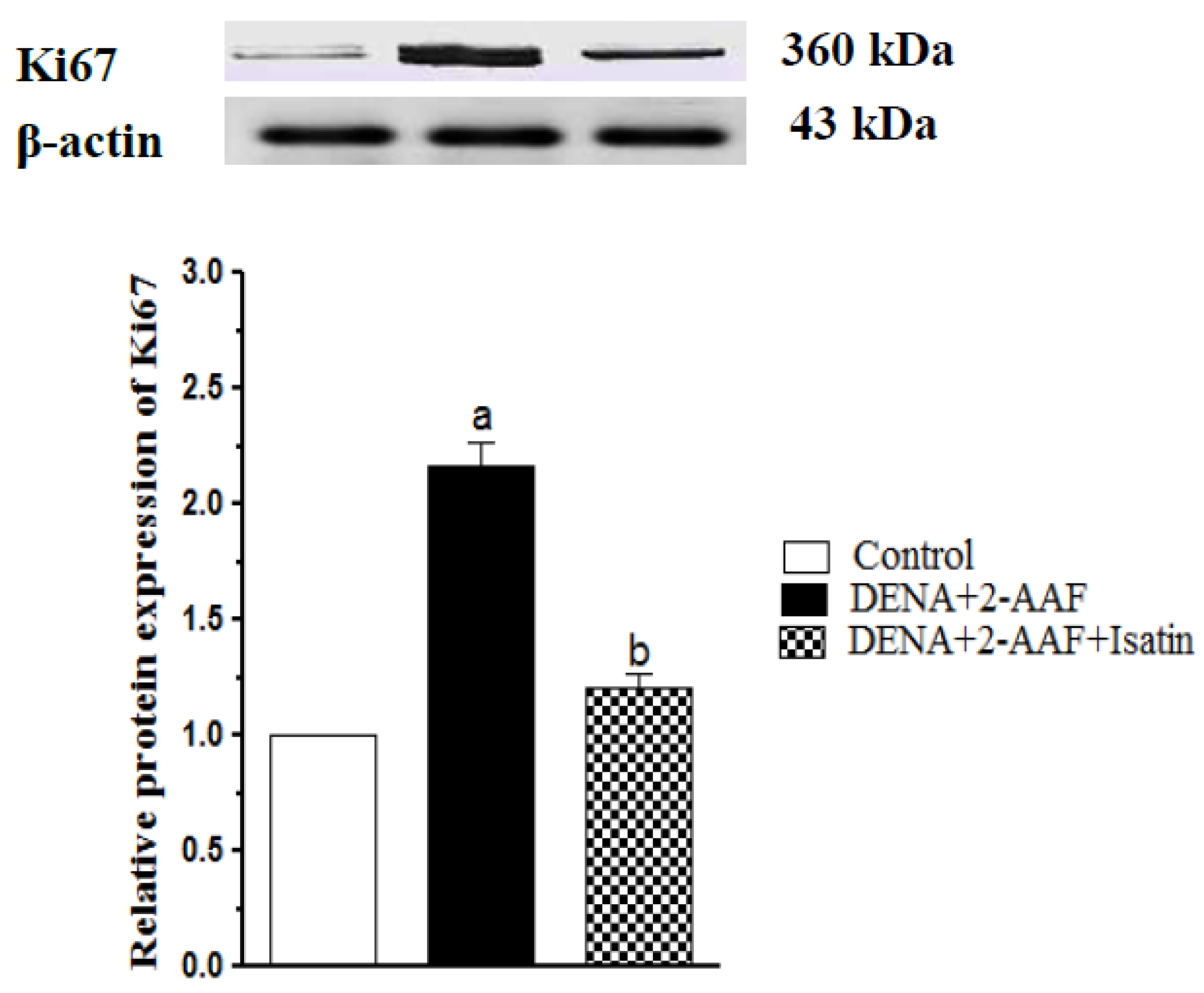
3.6. Isatin Suppressed DENA/2-AAF-Induced Upregulation of Ki67 Protein Expression in Rat Liver
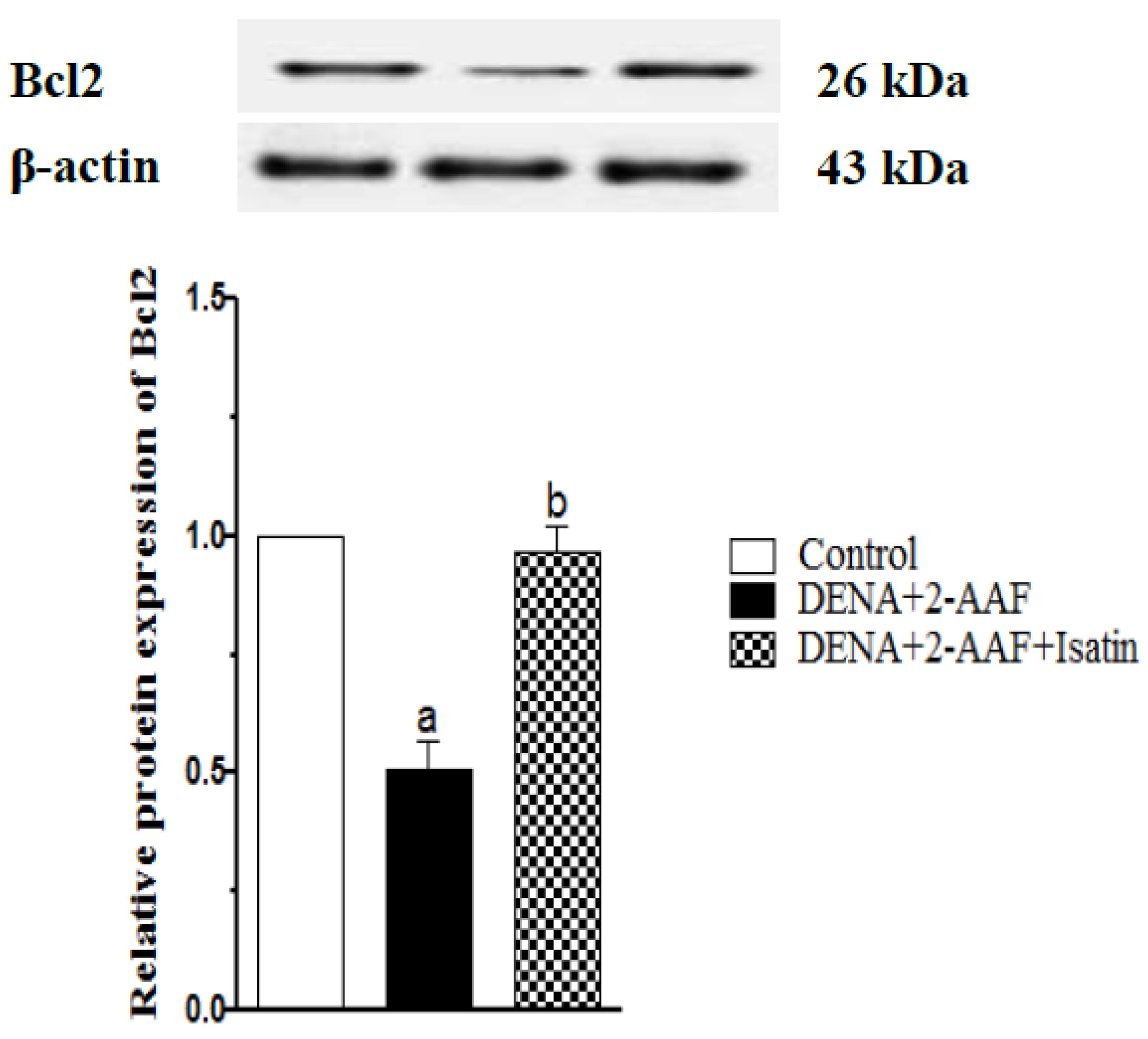
3.7. Isatin Reversed the DENA/2-AAF-Induced Reduction in Liver Bcl2 Expression
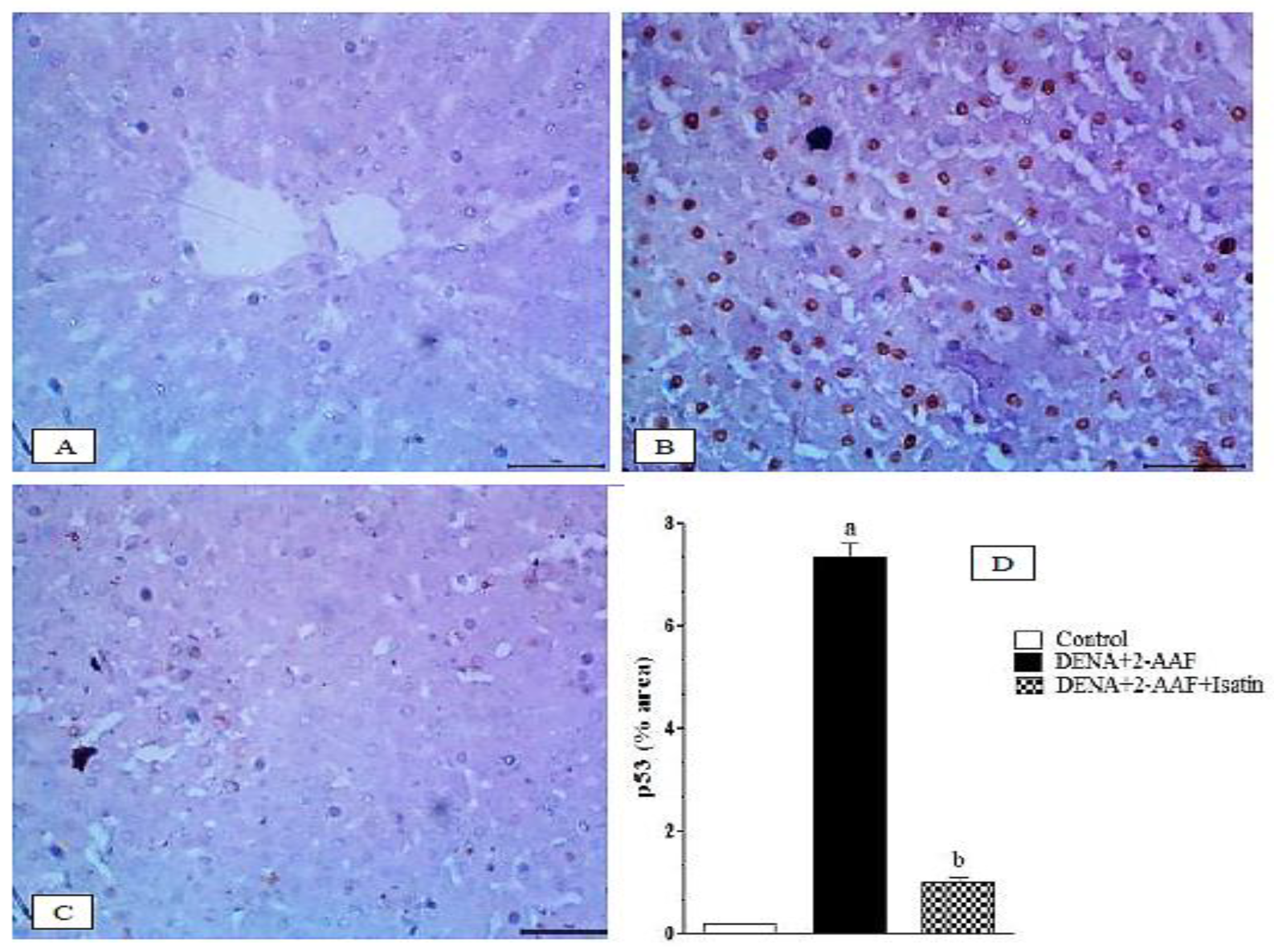
3.8. Isatin Suppressed the DENA/2-AAF-Induced Upregulation of Pro-Apoptotic Factors p53 and Caspase 3 in Rat Liver
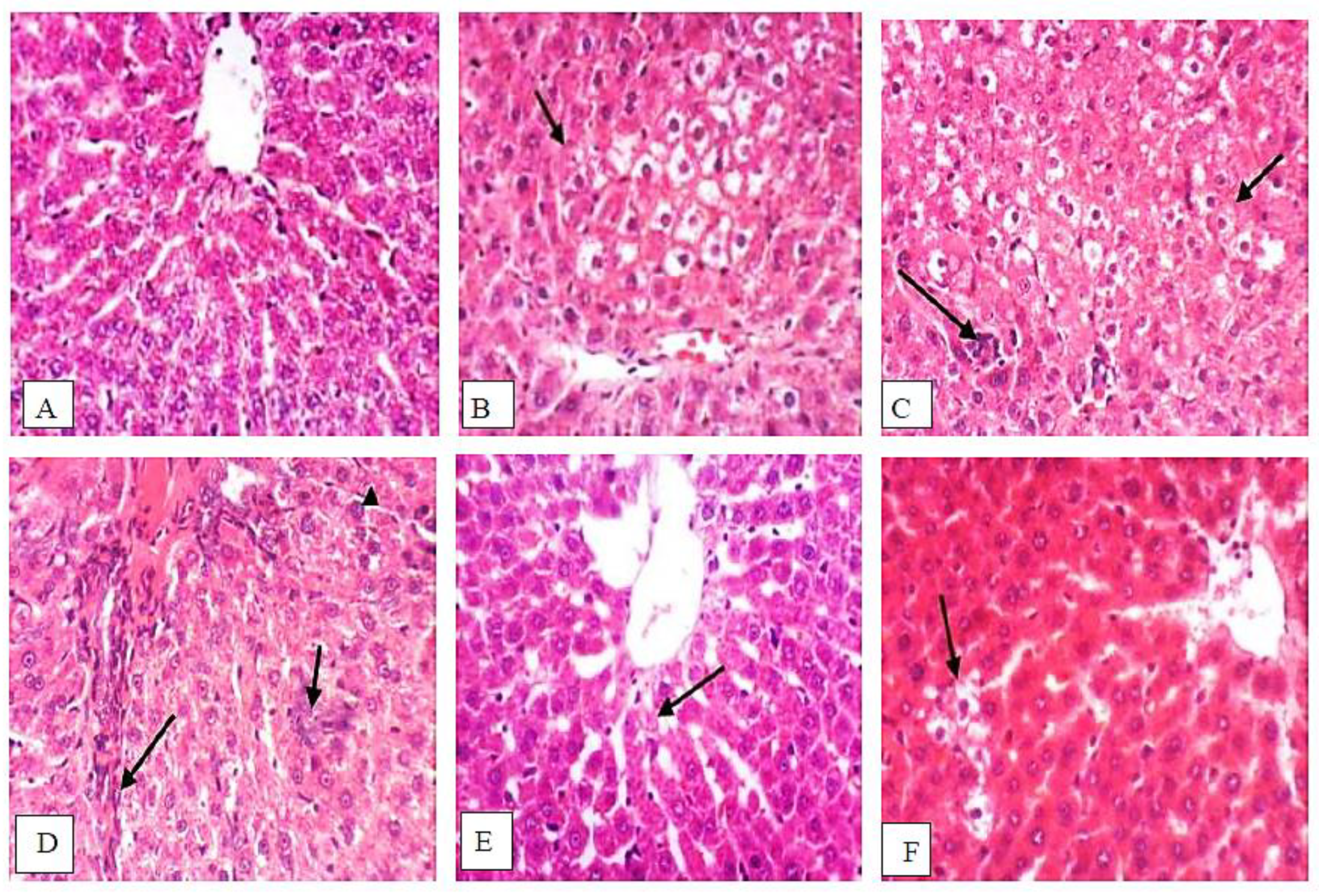
3.9. Isatin Attenuated DENA/2-AAF-Induced Histopathological Changes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seydi, E.; Motallebi, A.; Dastbaz, M.; Dehghan, S.; Salimi, A.; Nazemi, M.; Pourahmad, J. Selective toxicity of Persian Gulf sea cucumber (Holothuria parva) and sponge (Haliclona oculata) methanolic extracts on liver mitochondria isolated from an animal model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e33073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asafo-Agyei, K.O.; Samant, H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma; StatPearls Publishing LLC, National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021.
- Mansour, D.F.; Abdallah, H.M.; Ibrahim, B.M.; Hegazy, R.R.; Esmail, R.S.; Abdel-Salam, L.O. The carcinogenic agent diethylnitrosamine induces early oxidative stress, inflammation and proliferation in rat liver, stomach and colon: Protective effect of ginger extract. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elbaset, M.; Mansour, A.M.; Ahmed, O.M.; Abo-Youssef, A.M. The potential chemotherapeutic effect of β-ionone and/or sorafenib against hepatocellular carcinoma via its antioxidant effect, PPAR-γ, FOXO-1, Ki-67, Bax, and Bcl-2 signaling pathways. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1611–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arboatti, A.S.; Lambertucci, F.; Sedlmeier, M.G.; Pisani, G.; Monti, J.; Álvarez, M.D.; Frances, D.E.; Ronco, M.T.; Carnovale, C.E. Diethylnitrosamine increases proliferation in early stages of hepatic carcinogenesis in insulin-treated type 1 diabetic mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9472939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bose, P.; Siddique, M.U.; Acharya, R.; Jayaprakash, V.; Sinha, B.N.; Lapenna, A.; Pattanayak, S.P. Quinazolinone derivative BNUA-3 ameliorated [NDEA+2-AAF]-induced liver carcinogenesis in SD rats by modulating AhR-CYP1B1-Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, A.; Sultana, S. Chemoprevention by Butea monosperma of hepatic carcinogenesis and oxidative damage in male Wistar rats. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2006, 7, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Ahmed, A.A.; Fahim, H.I.; Zaky, M.Y. Quercetin and naringenin abate diethylnitrosamine/acetylaminofluorene-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in Wistar rats: The roles of oxidative stress, inflammation and cell apoptosis. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, K.K.; Ali, S.; Ejaz, M.; Nasreen, S.; Ashraf, N.; Gillani, S.F.; Shafi, N.; Safeer, S.; Khan, M.A.; Andleeb, S.; et al. In vivo induction of hepatocellular carcinoma by diethylnitrosoamine and pharmacological intervention in Balb C mice using Bergenia ciliata extracts. Braz. J. Biol. 2019, 79, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tan, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, W.; et al. AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses the in vitro and in vivo proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeena, K.J.; Joy, K.L.; Kuttan, R. Effect of Emblica officinalis, Phyllanthus amarus and Picrorrhiza kurroa on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 1999, 136, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, T.F.; Papendorf, F.; Bleck, J.S.; Kirchhoff, T.; Wohlberedt, T.; Kubicka, S.; Klempnauer, J.; Galanski, M.; Manns, M.P. Survival rate in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective analysis of 389 patients. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokudo, N.; Takemura, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Takayama, T.; Kubo, S.; Shimada, M.; Nagano, H.; Hatano, E.; Izumi, N.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2017 (4th JSH-HCC guidelines) 2019 update. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luján Alvarez, M.; Cerliani, J.P.; Monti, J.; Carnovale, C.; Ronco, M.T.; Pisani, G.; Lugano, M.C.; Carrillo, M.C. The in vivo apoptotic effect of interferon alfa-2b on rat preneoplastic liver involves Bax protein. Hepatology 2002, 35, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hamid, N.M.; Abdel-Ghany, M.I.; Nazmy, M.H.; Amgad, S.W. Can methanolic extract of Nigella sativa seed affect glyco-regulatory enzymes in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma? Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2013, 18, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelloff, G.J. Perspectives on cancer chemoprevention research and drug development. Adv. Cancer Res. 1999, 78, 199–334. [Google Scholar]
- Vine, K.L.; Matesic, L.; Locke, J.M.; Ranson, M.; Skropeta, D. Cytotoxic and anticancer activities of isatin and its derivatives: A comprehensive review from 2000–2008. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, R.P.; Tripathi, R.R. The chemistry and synthesis of 1H-indole-2, 3-dione (Isatin) and its derivatives. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2013, 12, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawat, P.; Verma, S.M. Design and synthesis of chroman derivatives with dual anti-breast cancer and antiepileptic activities. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, M.; Pandeya, S.N.; Singh, K.N.; Stables, J.P. Anticonvulsant activity of Schiff bases of isatin derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2004, 54, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lashgari, N.; Ziarani, G.M. Synthesis of heterocyclic compounds based on isatin through 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions. ARKIVOC Online J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 277–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafder, M.T.; Kasbollah, A.; Saravanan, N.; Crouse, K.A.; Ali, A.M. S-methyldithiocarbazate and its Schiff bases: Evaluation of bondings and biological properties. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Biophys. JBMBB Off. J. Fed. Asian Ocean. Biochem. Mol. Biol. (FAOBMB) 2002, 6, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandeya, S.N.; Sriram, D.; Nath, G.; DeClercq, E. Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-HIV activities of Schiff and Mannich bases derived from isatin derivatives and N-[4-(4′-chlorophenyl) thiazol-2-yl] thiosemicarbazide. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 9, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, H.; Sowa, Y.; Wakada, M.; Yogosawa, M.; Nakanishi, R.; Horinaka, M.; Shimazaki, C.; Taniwaki, M.; Sakai, T. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor SU9516 enhances sensitivity to methotrexate in human T-cell leukemia Jurkat cells. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Khan, M.; Ali, M.; Taha, M.; Rasheed, S.; Perveen, S.; Choudhary, M.I. Synthesis of bis-Schiff bases of isatins and their antiglycation activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7795–7801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.M.; Mughal, U.R.; Khan, A.; Naz, F.; Perveen, S.; Choudhary, M.I. N-Aroylated isatins: Antiglycation activity. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2010, 7, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeya, S.N.; Smitha, S.; Jyoti, M.; Sridhar, S.K. Biological activities of isatin and its derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2005, 55, 27–46. [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev, A.; Buneeva, O.; Glover, V. Biological targets for isatin and its analogues: Implications for therapy. Biologics 2007, 1, 151. [Google Scholar]
- Gencer, N.; Sonmez, F.; Demir, D.; Arslan, O.; Kucukislamoglu, M. Synthesis, structure-activity relationships and biological activity of new isatin derivatives as tyrosinase inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Capela, R.; Gonçaves, J.O.; Horton, P.N.; Hursthouse, M.B.; Iley, J.; Casimiro, C.M.; Bom, J.; Moreira, R. Amidomethylation of amodiaquine: Antimalarial N-Mannich base derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7663–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, S.S.; Kulkarni, A.A.; Kumar, S.; Veliyath, S.K.; De Clercq, E.; Balzarini, J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-(5-substituted-1-(diethylamino)methyl)-2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)-N-substituted-hydrazinecarbothioamides. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, P.; Kashanian, S.; Khodaei, M.M.; Harding, F.J. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of isatin and its derivatives: From structure to activity. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premanathan, M.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Kulangiappar, K.; Singaravelu, G.; Thirumalaiarasu, V.; Sivakumar, T.; Kathiresan, K. Antioxidant & anticancer activities of isatin (1H-indole-2,3-dione), isolated from the flowers of Couroupita guianensis. Aubl. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 136, 822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.K.; Chakrabarti, A. Dose-related proconvulsant and anticonvulsant activity of isatin, a putative biological factor, in rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 36, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filomeni, G.; Piccirillo, S.; Graziani, I.; Cardaci, S.; Da Costa Ferreira, A.M.; Rotilio, G.; Ciriolo, M.R. The isatin-Schiff base copper(II) complex Cu(isaepy)2 acts as delocalized lipophilic cation, yields widespread mitochondrial oxidative damage and induces AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, D.; Yogeeswari, P.; Bhat, P.; Thomas, A.; Srividya, M.; Sriram, D. Novel isatinyl thiosemicarbazones derivatives as potential molecule to combat HIV-TB co-infection. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Omar, H.; Hersi, F.; Abo-Youssef, A.; Ahmed, O.; Mohamed, W. The protective role of etoricoxib against diethylnitrosamine/2-acetylaminofluorene-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in Wistar rats: The impact of NF-κB/COX-2/PGE2 signaling. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 15, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socca, E.A.; Luiz-Ferreira, A.; de Faria, F.M.; de Almeida, A.C.; Dunder, R.J.; Manzo, L.P.; Brito, A.R. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and cyclooxigenase-2 by Isatin: A molecular mechanism of protection against TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 209, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeyer, H.U.; Scheibe, P.; Wahlefeld, A.W. Optimization of methods for aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase. Clin. Chem. 1978, 24, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gella, F.J.; Olivella, T.; Pastor, M.C.; Arenas, J.; Moreno, R.; Durban, R.; Gomez, J.A. A simple procedure for the routine determination of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase with pyridoxal phosphate. Clin. Chim. Acta 1985, 153, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruden, E.L.; Tietz, N.W. Clinical Guide to LABORATORY Tests; Finley, P.R., Ed.; Philadelphia WB Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Martinen, K.G. Improved micro-method for determination of serum bilirubin. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1966, 13, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, K. Lipid peroxides and human diseases. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1987, 45, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, E. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar]
- Marklund, S.; Marklund, G. Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1974, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Li, H.B. Dietary natural products for prevention and treatment of liver cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamza, A.A.; Heeba, G.H.; Hamza, S.; Abdalla, A.; Amin, A. Standardized extract of ginger ameliorates liver cancer by reducing proliferation and inducing apoptosis through inhibition oxidative stress/inflammation pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carracedo, A.; Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Rojo, F.; Salmena, L.; Alimonti, A.; Egia, A.; Sasaki, A.T.; Thomas, G.; Kozma, S.C.; et al. Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, V.R.; Hu, C.; Lee, H. Design and synthesis of anti-breast cancer agents from 4-piperazinylquinoline: A hybrid pharmacophore approach. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cândido-Bacani, P.D.; Mori, M.P.; Calvo, T.R.; Vilegas, W.; Varanda, E.A.; de Syllos Cólus, I.M. In vitro assessment of the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and mutagenic potentials of isatin. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2013, 76, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Aleisa, A.M.; Al-Yahya, A.A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alsheikh, A.; Fatani, A.G.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.M. Progression of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic carcinogenesis in carnitine-depleted rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, A. Albumin usage in clinical medicine: Tradition or therapeutic? Transfus. Med. Rev. 2010, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, J.; Wei, W.L.; Husin, N.N.; Alwahaibi, N.Y.; Budin, S.B. Selenium supplementation reduced oxidative stress in diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 14, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaie, A.; Fazlara, A.; Karamolah, M.H.; Shahriari, A.; Zadeh, H.N.; Pashmforosh, M. Effects of Echinacea purpurea on hepatic and renal toxicity induced by diethylnitrosamine in rats. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2013, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, X. Doxorubicin and curcumin co-delivery by lipid nanoparticles for enhanced treatment of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atefipour, N.; Dianat, M.; Badavi, M.; Sarkaki, A. Ameliorative effect of vanillic acid on serum bilirubin, chronotropic and dromotropic properties in the cholestasis-induced model rats. Electron. Physician 2016, 8, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Wen, D.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, G.; Yin, F. Effect of sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, against DENA-induced liver cancer in rats mediated via NF-κB activation and inflammatory cytokines. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westley, C.B.; Benkendorff, K.; McIver, C.M.; Le Leu, R.K.; Abbott, C.A. Gastrointestinal and hepatotoxicity assessment of an anticancer extract from muricid molluscs. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 837370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shizuma, T.; Ishiwata, K.; Nagano, M.; Mori, H.; Fukuyama, N. Protective effects of fermented rice vinegar sediment (Kurozu moromimatsu) in a diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma animal model. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2011, 49, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.K.; Koti, B.C.; Gadad, P.C. Role of Lycopersicon esculentum in diethylnitrosamine-induced and phenobarbital-promoted hepatocellular carcinoma. Indian J. Health Sci. Biomed. Res. (KLEU) 2016, 9, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.Y.; Cai, L.; He, X.D.; Liu, W.; Qu, Q. Comparison of serum tumor markers for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. Surg. 2010, 76, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed-Ahmed, M.M.; Aleisa, A.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Al-Yahya, A.A.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Hafez, M.M.; Nagi, M.N. Thymoquinone attenuates diethylnitrosamine induction of hepatic carcinogenesis through antioxidant signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2010, 3, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.Z.; Shao, X.D.; Liu, M.P.; Xu, J.H.; Ren, L.N.; Zhao, J.J.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, D. Effect of bax, bcl-2 and bcl-xL on regulating apoptosis in tissues of normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, N.; AbouZid, S.F.; El-Kalaawy, A.M.; Ali, T.M.; Elesawy, B.H.; Ahmed, O.M. Tackling of renal carcinogenesis in wistar rats by Silybum marianum total extract, silymarin, and silibinin via modulation of oxidative stress, apoptosis, Nrf2, PPARγ, NF-κB, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 7665169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.; Ahmed, O.M.; El-Twab, A.; Sanaa, M.; Zaky, M.Y.; Bakry, L.N. Prophylactic effects of Cynara scolymus L. leaf and flower hydroethanolic extracts against diethylnitrosamine/acetylaminoflourene-induced lung cancer in Wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43515–43527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Fahim, H.I.; Mohamed, E.E.; Abdel-Moneim, A. Protective effects of Persea americana fruit and seed extracts against chemically induced liver cancer in rats by enhancing their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and apoptotic activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo’men, Y.S.; Hussein, R.M.; Kandeil, M.A. A novel chemoprotective effect of tiopronin against diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats: Role of ASK1/P38 MAPK-P53 signalling cascade. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de La Coste, A.; Mignon, A.; Fabre, M.; Gilbert, E.; Porteu, A.; Van Dyke, T.; Kahn, A.; Perret, C. Paradoxical inhibition of c-myc-induced carcinogenesis by Bcl-2 in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5017–5022. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, A.J.; Ordoñez, R.; Cerski, C.T.; Picada, J.N.; García-Palomo, A.; Marroni, N.P.; Mauriz, J.L.; González-Gallego, J. Melatonin activates endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozpour, L.; Gao, L.; Moghimi, S.; Pasalar, P.; Davoodi, J.; Wang, M.W.; Rezaei, Z.; Dadgar, A.; Yahyavi, H.; Amanlou, M.; et al. Efficient synthesis, biological evaluation, and docking study of isatin based derivatives as caspase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Singh, D.; Anwar, F.; Bhatt, P.C.; Al-Abbasi, F.; Kumar, V. Triterpenoids principle of Wedelia calendulacea attenuated diethynitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma via down-regulating oxidative stress, inflammation and pathology via NF-kB pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.M.; Teixeira, J.C.; Vasconcelos-Nóbrega, C.; Felix, L.M.; Sardão, V.A.; Colaço, A.A.; Oliveira, P.A.; Peixoto, F.P. Mitochondrial and liver oxidative stress alterations induced by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl) nitrosamine: Relevance for hepatotoxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, O.M. Relationships between oxidative stress, cancer development and therapeutic interventions. J. Can. Sci. Res. 2016, 1, 1e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, N.Y.; AbouZid, S.F.; El-Kalaawy, A.M.; Ali, T.M.; Almehmadi, M.M.; Ahmed, O.M. Silybum marianum total extract, silymarin and silibinin abate hepatocarcinogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma growth via modulation of the HGF/c-Met, Wnt/β-catenin, and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileepan, A.B.; Prakash, T.D.; Kumar, A.G.; Rajam, P.S.; Dhayabaran, V.V.; Rajaram, R. Isatin based macrocyclic Schiff base ligands as novel candidates for antimicrobial and antioxidant drug design: In vitro DNA binding and biological studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 183, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.R.; Raja, S.; Saravanan, G.; Dinesh Kumar, P.; Panneer Selvam, T. Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant activities of some novel isatin derivatives and analogs. Asian J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, K.; Ishii, T.; Wakabayashi, N.; Yamamoto, M. Regulatory mechanisms of cellular response to oxidative stress. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guoyin, Z.; Hao, P.; Min, L.; Wei, G.; Zhe, C.; Changquan, L. Antihepatocarcinoma effect of Portulaca oleracea L. in mice by PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 8231358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellezza, I.; Mierla, A.L.; Minelli, A. Nrf2 and NF-κB and their concerted modulation in cancer pathogenesis and progression. Cancers 2010, 2, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswati, S.; Alhaider, A.A.; Agrawal, S.S. Anticarcinogenic effect of brucine in diethylnitrosamine initiated and phenobarbital-promoted hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 206, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Chhimwal, J.; Patial, V.; Sk, U.H. Dendrimer-conjugated podophyllotoxin suppresses DENA-induced HCC progression by modulation of inflammatory and fibrogenic factors. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, A.; Itoh, K.; Nagayoshi, E.; Haruta, J.; Kimura, T.; O’Connor, T.; Harada, T.; Yamamoto, M. High sensitivity of Nrf2 knockout mice to acetaminophen hepatotoxicity associated with decreased expression of ARE-regulated drug metabolizing enzymes and antioxidant genes. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 59, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Matsuura, N.; Sakon, M.; Takeda, T.; Umeshita, K.; Nagano, H.; Nakamori, S.; Dono, K.; Tsujimoto, M.; Nakahara, M.; et al. Both cell proliferation and apoptosis significantly predict shortened disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Youssef, M.I.; Maghraby, H.; Youssef, E.A.; El Sayed, M.M. Expression of Ki 67 in hepatocellular carcinoma induced by diethylnitrosamine in mice and its correlation with histopathological alterations. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Pižem, J.; Marolt, V.F.; Luzar, B.; Cör, A. Proliferative and apoptotic activity in hepatocellular carcinoma and surrounding non-neoplastic liver tissue. Pflugers Arch. 2001, 442, r174–r176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunandhakumar, S.; Paramasivam, A.; Senthilraja, S.; Naveenkumar, C.; Asokkumar, S.; Binuclara, J.; Jagan, S.; Anandakumar, P.; Devaki, T. Thymoquinone inhibits cell proliferation through regulation of G1/S phase cell cycle transition in N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced experimental rat hepatocellular carcinoma. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 223, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, C. Recent advances in isatin hybrids as potential anticancer agents. Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, 1900367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Shang, C.; Wang, H.; Yun, J. Isatin–azole hybrids and their anticancer activities. Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, 1900272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Nikaido, T. In vivo modulation of iNOS pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma by Nigella sativa. Environ. Health. Prev. Med. 2013, 18, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.T.; Jing, Y.Y.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Yang, X.; Pan, X.R.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Hou, X.J.; Zhao, Q.D.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces the differentiation of hepatic progenitor cells into myofibroblasts constitutes the hepatocarcinogenesis-associated microenvironment. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.K.; Balwani, S.; Mathur, D.; Malhotra, S.; Singh, B.K.; Prasad, A.K.; Len, C.; Van der Eycken, E.V.; Ghosh, B.; Richards, N.G.; et al. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity evaluation of novel triazolyl-isatin hybrids. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, G.Y.; He, G.; Ali, S.R.; Holzer, R.G.; Österreicher, C.H.; Takahashi, H.; Karin, M. Dietary and genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell 2010, 140, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Groups | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | Albumin (g/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 19.30 ± 1.44 | 71.50 ± 3.753 | 0.52 ± 0.03 | 3.98 ± 0.15 |
| DENA+2-AAF | 77.50 ± 3.81 a | 152.1 ± 7.17 a | 0.94 ± 0.07 a | 1.92 ± 0.19 a |
| DENA+2-AAF+isatin | 44.50 ± 3.35 b | 125.2 ± 2.03 | 0.45 ± 0.03 b | 3.10 ± 0.02 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tawfik, N.G.; Mohamed, W.R.; Mahmoud, H.S.; Alqarni, M.A.; Naguib, I.A.; Fahmy, A.M.; Ahmed, O.M. Isatin Counteracts Diethylnitrosamine/2-Acetylaminofluorene-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis in Male Wistar Rats by Upregulating Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Detoxification Pathways. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040699
Tawfik NG, Mohamed WR, Mahmoud HS, Alqarni MA, Naguib IA, Fahmy AM, Ahmed OM. Isatin Counteracts Diethylnitrosamine/2-Acetylaminofluorene-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis in Male Wistar Rats by Upregulating Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Detoxification Pathways. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(4):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040699
Chicago/Turabian StyleTawfik, Nagwa G., Wafaa R. Mohamed, Hanan S. Mahmoud, Mohammed A. Alqarni, Ibrahim A. Naguib, Alzhraa M. Fahmy, and Osama M. Ahmed. 2022. "Isatin Counteracts Diethylnitrosamine/2-Acetylaminofluorene-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis in Male Wistar Rats by Upregulating Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Detoxification Pathways" Antioxidants 11, no. 4: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040699
APA StyleTawfik, N. G., Mohamed, W. R., Mahmoud, H. S., Alqarni, M. A., Naguib, I. A., Fahmy, A. M., & Ahmed, O. M. (2022). Isatin Counteracts Diethylnitrosamine/2-Acetylaminofluorene-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis in Male Wistar Rats by Upregulating Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Detoxification Pathways. Antioxidants, 11(4), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040699








