Abstract
Helicases function as key enzymes in salinity stress tolerance, and the role and function of PDH45 (pea DNA helicase 45) in stress tolerance have been reported in different crops with selectable markers, raising public and regulatory concerns. In the present study, we developed five lines of marker-free PDH45-overexpressing transgenic lines of rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. IR64). The overexpression of PDH45 driven by CaMV35S promoter in transgenic rice conferred high salinity (200 mM NaCl) tolerance in the T1 generation. Molecular attributes such as PCR, RT-PCR, and Southern and Western blot analyses confirmed stable integration and expression of the PDH45 gene in the PDH45-overexpressing lines. We observed higher endogenous levels of sugars (glucose and fructose) and hormones (GA, zeatin, and IAA) in the transgenic lines in comparison to control plants (empty vector (VC) and wild type (WT)) under salt treatments. Furthermore, photosynthetic characteristics such as net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (gs), intercellular CO2 (Ci), and chlorophyll (Chl) content were significantly higher in transgenic lines under salinity stress as compared to control plants. However, the maximum primary photochemical efficiency of PSII, as an estimated from variable to maximum chlorophyll a fluorescence (Fv/Fm), was identical in the transgenics to that in the control plants. The activities of antioxidant enzymes, such as catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione reductase (GR), and guaiacol peroxidase (GPX), were significantly higher in transgenic lines in comparison to control plants, which helped in keeping the oxidative stress burden (MDA and H2O2) lesser on transgenic lines, thus protecting the growth and photosynthetic efficiency of the plants. Overall, the present research reports the development of marker-free PDH45-overexpressing transgenic lines for salt tolerance that can potentially avoid public and biosafety concerns and facilitate the commercialization of genetically engineered crop plants.
1. Introduction
Rice (Oryza sativa L., family Gramineae (Poaceae)) is an important staple food crop that is produced (518 million tonnes, milled), cultivated, and consumed globally in >122 countries (excluding Antarctica), being susceptible to salt amongst cereal crops [,,]. Major abiotic stresses (salinity, drought, extreme temperatures, heavy metal, etc.) are a significant limitation in rice cultivation globally []. Soil salinity is a major problem that reduces productivity of crops in irrigated as well as in tropical fields, where the deterioration of agricultural lands occur due to salinity [,,]. It brings series of changes at the physiological, biochemical, and molecular levels by affecting the photosynthetic machinery (partial stomatal closure and hampered photosystem II (PSII), reactive oxygen species (ROS)-led molecular injury, restricted water/nutrient availability, and disturbed sodium (Na+)/potassium ion (K+) homeostasis), which ultimately poses serious yield penalty [,,,,,]. Due to rapidly growing global population and urbanization, it is impossible to increase the cultivated land area, and therefore to fulfill the demand of rice consumers, it becomes imperative to discover new techniques for developing salinity-tolerant crop plants by protecting the photosynthetic machinery (net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, chlorophyll content), efficient ROS scavenging, membrane integrity, Na+ exclusion, etc. [,,]. Robust antioxidant machinery consisting of enzymatic (SOD, CAT, APX, GPX, GR, etc.) and non-enzymatic antioxidants (glutathione (GSH) and ascorbic acid (AsA) is efficient enough to protect the photosynthetic machinery, cellular components, and membranes under various abiotic stresses []. Therefore, strong antioxidant machinery can be well correlated with salinity stress tolerance in crop plants []. Nidumukkala et al. [] reviewed the fact that overexpression of helicases in different model and crop plants provides salt tolerance though increased antioxidant capacity, photosynthetic efficiency, and ion homeostasis, as well as by regulating the expression of various stress responsive genes. Therefore, introduction of a stress-tolerant gene in rice is one of the effective ways to develop stress-tolerant cultivars without yield penalty. The presence of selectable marker genes (SMGs, antibiotic or herbicide resistance genes) in genetically engineered crops may arouse public and regulatory concerns due to biosafety issues because the weeds or pathogenic microorganisms present in soil may become resistant to herbicides or antibiotics and can harm public health []. The problem of transgene expression arises due to the sexual crossing, which can lead to homology-dependent gene silencing in the genome []. Due to consumer, environmental, and biosafety concerns, the regulatory bodies also encourage the development of marker-free transgenic crops with an array of different transformation strategies such as homologous recombination, site-specific recombination, co-transformation, transposon-mediated transgene reintegration system, and CRISPR/Cas9 system [,,,]. The tissue culture methods are generally used to understand the mechanisms underlying salt tolerance of transgenic lines [,]. Several techniques have been developed to improve Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of indica rice [,,]. The development of an efficient large-scale transformation system requires a large number of transformants for successful gene transfer []. Previously, many researchers developed a transformation protocol for marker-free transgenic rice plants using anther culture [,], but the unavailability of explants (anther) throughout the year is a major limitation of this method and it is very laborious to screen the transgenic plants by a PCR-based method.
In the present study, we report that overexpression of PDH45 gene in an elite indica rice variety IR64 (Oryza sativa L., cv. IR64) showed tolerance against salinity stress as well as improved growth, photosynthesis, and better antioxidant machinery in the transgenic rice. We exploited the potential of transgenic technologies for crop improvement through developing marker-free transgenic PDH45 rice. Thus, we also successfully developed a screening technique using 200 mM NaCl salt to screen marker-free PDH45 transgenic rice plants. Development of rice transgenic lines overexpressing the PDH45 gene without the antibiotic marker gene for stable expression of the stress-tolerant trait in a predictable manner avoids the transfer of undesirable transgenic material to non-transgenic crops and related species.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning and Transformation of PDH45 Gene in IR64 Rice
PDH45 gene (accession number: Y17186) was used to establish the tissue culture technique. The coding region of PDH45 gene (1.2 kb) was cloned in reporter gene-free plant transformation vector pCAMBIA1300 in place of hygromycin to generate complete reporter and antibiotic marker-free plasmid pCAMBIA1300-PDH45. An empty vector (pCAMBIA1300) construct, called vector control (VC), was used to compare the function of the gene, and the VC construct comprises all components except the PDH45 gene. The above two constructs (pCAMBIA1300-PDH45 and pCAMBIA1300) were used for the Agrobacterium tumefaciens (LBA4404)-mediated transformation method []. The same conditions were used to generate all the plants.
2.2. Development of Selection Technique for Marker-Free Transgenic Plants
A new selection technique was developed by adding 200 mM NaCl in selection media, shoot induction, and root induction media for the selection of PDH45 marker-free transgenic plants during the plant induction stage. We modified the media described by Sahoo and Tuteja []. Here, we used 200 mM NaCl in place of hygromycin as the gene PDH45 has already been reported as being responsible for salinity tolerance in different plants [,,,,,]. The other compositions of media were the same as described earlier [].
2.3. Molecular Analysis (PCR, Southern Blot, qRT-PCR, and Western Blot) of T1 Transgenic PDH45 Plants
The genomic DNA was extracted from the healthy leaves of marker-free PDH45 transgenic plants and used to check the integration of the gene by PCR and Southern blot analysis. About 25 µg of genomic DNA was used for Southern blot analysis. First, the genomic DNA was digested with XbaI and resolved on 0.8% agarose gel followed by transfer to nylon membrane (Hybond-N, Amersham, Inc., Amersham, UK) as previously described []. The probe was radiolabelled by the gene amplification method using α–[32P] dCTP. Hybridization with the probe was conducted using the method described []. The qRT-PCR experiment was performed to check the transcript levels of the gene using gene-specific primers such as forward 5′-ATGGCGACAACTTCTGTG-3′ and reverse 5′-TATATAAGATCACCAATATTCATTGG-3′. For Western blot analysis, the crude plant extract was denatured and separated by SDS PAGE and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane using the method described []. Polyclonal antibodies (1:1000 dilutions) from rabbit were used as a probe against the PDH45 gene.
2.4. Leaf Disk Senescence Assay and Chlorophyll Content
The chlorophyll content after leaf disk senescence assay was measured using the method described earlier [].
2.5. Biochemical Analysis of Antioxidant Activities of Marker-Free PDH45 Transgenic Lines
The seeds of PDH45 transgenic, WT, and VC plants were kept in hydroponics for germination, and 21-d-old plants were dipped in 200 mM NaCl for 24 h. The experiments were conducted in green houses of the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), New Delhi, where 16 h light photoperiod at 25 °C temperature was maintained. Similar stress treatment and stress conditions as described were also used in the present study []. After 24 h salt stress, the plant tissues were used for biochemical analysis such as catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione reductase (GR), proline, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), lipid peroxidation, relative water content (RWC), and electrolytic leakage. All the parameters were measured using the methods described earlier [].
2.6. Measurement of Photosynthetic Activities and Agronomic Characteristics of PDH45 Transgenic Plants
The different photosynthetic measurements such as photosynthetic yield, rate, intercellular CO2 concentration, CO2 release, stomatal conductance, and transpiration rate were recorded using an infrared gas analyzer (IRGA; LI-COR, http://www.licor.com, (accessed on 2 November 2021), on a sunny day between 11:00 and 12:00 noon. The plants were grown under 200 mM NaCl stress in a large tank, and all the parameters were measured using the expanded leaves of mature plants (60 d old). After 12 d of salt stress, different agronomic characteristics were measured using the method described earlier [].
2.7. Chlorophyll a Fluorescence Measurements
Plants were grown in green houses of the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), New Delhi, where 16 h light [photosynthetically active radiation (750 µmol m−2 s−1)] photoperiod at 25 °C temperature was maintained. Minimal fluorescence (Fo), maximal fluorescence (Fm), maximal variable fluorescence (Fv), and Fv/Fm ratio were included, where Fv = Fm − Fo.
Chlorophyll a (Chl a) fluorescence from the leaves of 25-day-old WT, VC, and transgenic rice seedlings was measured with a PAM-2100 fluorometer (Walz, Germany). Before each measurement, the leaf sample was kept in the dark for 20 min []. Optimum quantum efficiency (uPSII, also referred to as Y) of Photosystem II (PSII) was inferred from Fv/Fm = (Fm − Fo)/Fm [].
2.8. Estimation of Sugar, Hormones (GA, Zeatin and IAA), and Ion Contents
Shoots and roots from mature (60 d old) PDH45 T1 transgenic, VC, and WT plants after 12 d of salt stress were used in this study. The sugar content was estimated as described earlier []. The endogenous plant hormones (GA, zeatin and IAA) were estimated as described earlier []. The flame ionization photometer was used for the estimation of potassium, as described by Chapman and Pratt []. The sodium content was estimated as described by Munns et al. [].
2.9. Salinity Tolerance of Transgenic Plant under 200 mM NaCl Stress
The PDH45 transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13) and VC and WT rice plants (60 d old) were grown in one large metal pot filled with soil and dipped in 200 mM NaCl. The plants were allowed to grow up to maturity (harvest), and the phenotypic conditions of these plants were recorded.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
The experimental data were statistically analyzed, and standard error was calculated from three independent observations. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed on the data using SPSS (10.0 Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) to determine the least significant difference (LSD) for the significant data to identify the differences between means and presented as mean ± SE. The means were separated by Duncan’s multiple range tests. Different letters indicate significant difference at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Analysis of Marker-Free PDH45 Transgenic Lines
The marker-free PDH45 transgenic IR64 rice plants were developed using the pCAMBIA1300-PDH45 gene construct (Figure 1a). Phenotypically, the transgenic rice plants were not significantly different from WT and VC plants (Figure 1b). The desired PDH45 gene (1.2 kb) fragment was detected by PCR (Figure 1c). The Southern blot results confirmed the integration of a single-copy PDH45 gene in transgenic rice plants in all the five transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11, and L13) (Figure 1d). The real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) provided ≈8-fold induction in the transcript level of PDH45 in transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13) (Figure 1e). The Western blot results showed that PDH45 protein was expressed to almost similar levels in all the transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13) as compared to WT and VC plants (Figure 1f).
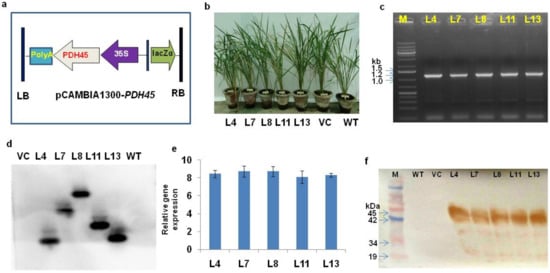
Figure 1.
Screening and analysis of PDH45 marker-free transgenic lines. (a) T-DNA construct of pCAMBIA 1300-PDH45. (b) Transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11, L13, VC, and WT). (c) PCR conformation of the PDH45-overexpressing transgenic (T1) lines showed the amplification of 1.2 Kb fragment. (d) Southern blot analysis showing the integration and copy number of the PDH45 gene. (e) Relative gene expression of PDH45 transgenic lines. (f) Western blot analysis showing the PDH45 protein (≈45 kDa).
3.2. PDH45 Transgenic Lines Showed Salinity Tolerance
The damage caused in the leaf pieces by salt stress was observed in all the plants after 72 h; however, the PDH45-overexpressing lines displayed darker green leaves, in contrast to the yellowish leaves of the WT and VC plants (Figure 2a). In this sense, the reduction of chlorophyll content in leaf tissues was lesser in transgenic lines as compared to WT and VC plants under salt stress (Figure 2b). The lesser chlorophyll content in the leaf tissues of WT and VC plants as compared to transgenic lines provided strong evidence towards tolerance against salinity stress (Figure 2a,b). The transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13) along with WT and VC plants were allowed to grow up to maturity in a metal tank filled with 200 mM NaCl. After 3d, WT and VC plants showed dropping characteristics, whereas PDH45-overexpressing transgenic lines L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13 grew well and produced viable seeds (Figure 2c,d).
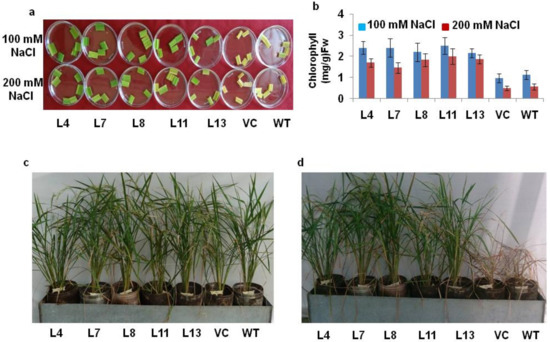
Figure 2.
Salinity tolerance of PDH45-overexpressing transgenic T1 IR64 rice lines. (a) Leaf disk senescence assay under 100 and 200 mM NaCl treatment. (b) Chlorophyll content (mg/g fw) in PDH45 transgenic lines after salt treatment. (c) Third day in 200 mM NaCl treatment. (d) After 15 days of NaCl treatment.
3.3. Agronomic Performance of Marker-Free PDH45 Transgenic Plants under Stress
The agronomic performance of T1 transgenic lines under 200 mM NaCl treatment was compared with WT and VC without NaCl treatment. Better agronomic characteristics were observed in PDH45 transgenic plants as compared to WT and VC plants. Several phenotypic characteristics of transgenic plants were recorded and found to be almost similar to the WT and VC plants grown in 0 mM NaCl. However, under 200 mM NaCl treatment, the WT and VC plants did not survive until flowering stage (Figure 2d).
3.4. Photosynthetic Characteristics and Endogenous Ion Content of Marker-Free PDH45 T1 Transgenic Plants under Stress
The photosynthetic characteristics of transgenic plants were observed and compared to WT and VC plants after 12 d of induction of 200 mM NaCl salt treatment. The photosynthetic rate declined by 33% in WT and 35% in VC plants as compared to PDH45 marker-free transgenic lines. The net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, intracellular CO2, CO2 release, and transpiration rate were also higher in transgenic lines as compared to the WT and VC plants (Figure 3a–e).
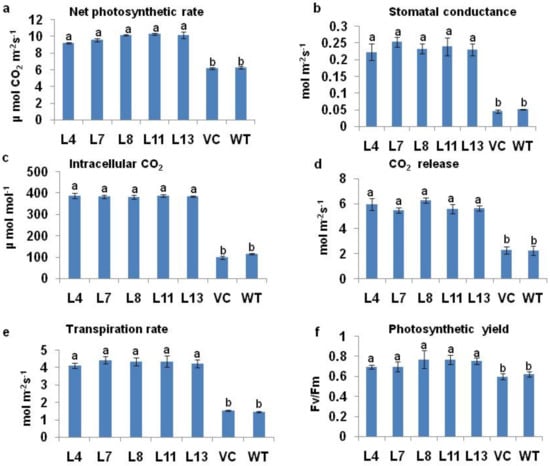
Figure 3.
Measurement of photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll a fluorescence of WT, VC, and PDH45 marker-free transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11, and L13) under 200 mM NaCl treatment. (a) Photosynthetic rate. (b) Stomatal conductance. (c) Intracellular CO2. (d) CO2 release. (e) Transpiration rate. (f) Photosynthetic yield (Fv/Fm). Values are mean ± SE (n = 3). Different letters on the top of bars indicate significant differences at p ≤ 0.05 level as determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (DMRT).
3.5. Chlorophyll a Fluorescence
The chlorophyll fluorescence rose from a low minimum level (‘‘O’’ level or Fo) to a higher maximum level (‘‘P’’ level or Fm) when exposed from dark to light. The maximum primary photochemical efficiency of PSII, estimated from Fv/Fm, was almost identical in the transgenics to that in the VC and WT (Figure 3f).
3.6. Analysis of MDA, H2O2, Ion Leakage, and Antioxidant Response in Marker-Free PDH45 T1 Transgenic Plants
The salt-induced changes in the ion leakage, H2O2, proline content, accumulation of MDA, RWC, and antioxidant machineries in T1 PDH45 transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13) were compared with WT and VC rice seedlings. We observed reduced levels of MDA, H2O2, and ion leakage, alongside an increase in proline content in PDH45 transgenic lines in comparison to the WT and VC plants under salt stress at 200 mM NaCl (Figure 4a–d). The activities of CAT, APX, GPX, GR and RWC were increased in PDH45 transgenic plants as compared to WT and VC plants (Figure 4e–i).
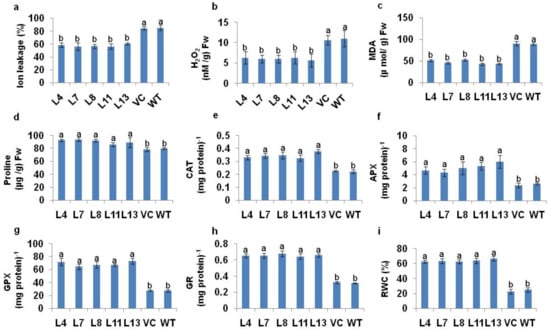
Figure 4.
Biochemical analysis of PDH45-overexpressing T1 transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11, L13, VC) and WT plants exposed to 24 h at 200 mM NaCl treatment. (a) Ion leakage. (b) Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content. (c) Lipid peroxidation expressed in terms of MDA content. (d) Level of proline accumulation. (e) Catalase (CAT) activity; one unit of enzyme activity defined as 1 μmol H2O2 oxidized min−1. (f) Ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity; one unit of enzyme activity defined as 1 μmol of ascorbate oxidized min−1. (g) Guaiacol peroxidase (GPX) activity. (h) Glutathione reductase (GR) activity; one unit of enzyme activity is defined as 1 μmol of GS-TNB formed min−1 due to reduction of DTNB. (i) Percent relative water content (RWC). Values are mean ± SE (n = 3). Different letters on the top of bars indicate significant differences at p ≤ 0.05 level as determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (DMRT).
3.7. The Sugar and Hormone Content of Marker-Free PDH45 T1 Transgenic Plants
The PDH45 L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13 transgenic lines showed higher endogenous sugar (glucose and fructose) content in roots as well as in shoots when compared with WT and VC plants (Figure 5a,b). The endogenous hormones such as GA, zeatin, and IAA content were also higher in roots and shoots of PDH45 transgenics as compared to WT and VC plants (Figure 5c–e). The potassium content in transgenic plants was higher, whereas sodium content was lower in marker-free PDH45 transgenic plant tissues as compared to WT and VC plants (Figure 5f).
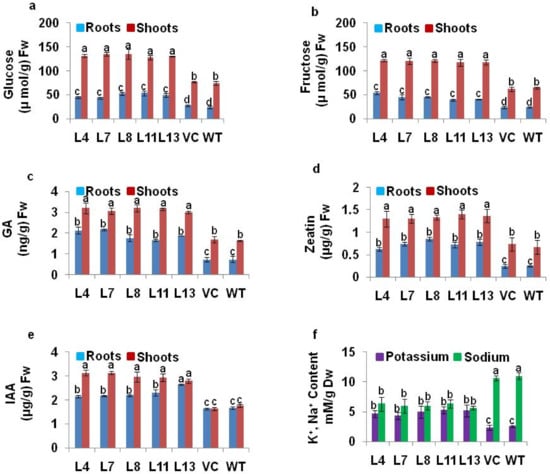
Figure 5.
Soluble sugar, hormones, and K+ and Na+ content in the roots and shoots of PDH45-overexpressing marker-free transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11, L13) as compared to WT and VC plants exposed to 24 h at 200 mM NaCl treatment. (a) Glucose content. (b) Fructose content. (c) Endogenous GA content. (d) Endogenous zeatin content. (e) Endogenous IAA content. (f) Endogenous potassium and sodium content. Values are mean ± SE (n = 3). Different letters on the top of bars indicate significant differences at p ≤ 0.05 level as determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (DMRT).
4. Discussion
In the era of frequently changing global climatic conditions, shortage of irrigation water, reduced agriculturally suitable cultivable land area, degradation and salinization of the agricultural soil, and unpredictable onset of abiotic stresses, agricultural productivity is severely affected, posing a serious threat to food security. Therefore, it is imperative to develop genetically engineered stress-tolerant crops with all the qualifications of global acceptance. It has been reported that overexpression of helicases (PDH45/PDH47) in different model and crop plants provides salt/cold tolerance through increased antioxidant capacity, photosynthetic efficiency, and ion homeostasis, as well as by regulating the expression of various stress responsive genes [,,,,,,]. Genetically engineered transgenic crops with selectable markers (antibiotic or herbicide resistance) have public and regulatory concerns; therefore, development of marker-free transgenic plants is needed in order to avoid public and biosafety concerns and to facilitate the commercialization of genetically engineered crop plants [].
We developed the method to select marker and reporter free transgenic lines using the previously published reports [,]. In this research, marker-free PDH45 transgenic rice plants were raised using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation followed by screening with 200 mM NaCl in selection, shoot, and root regeneration media to select only the transformed calli for plant regeneration because PDH45 is responsible for salinity tolerance [,,,]. The elevated stress tolerance in PDH45-expressing plants correlated with MH1 (M. sativa helicase 1) transgenic plants, showing that MH1 functions in abiotic stress tolerance by elevating reactive oxygen species (ROS) burden and through osmotic adjustment []. Five independent transgenic lines (L4, L7, L8, L11 and L13) along with empty VC and WT plants were used for functional validation under salt stress. These lines express almost similar levels of PDH45 protein. Similar to previous reports, these PDH45 transgenic rice plants also showed high salinity tolerance. This was indicated by the presence of higher chlorophyll content in the leaf disks of salinity-stressed T1 transgenic plants, whereas VC and WT plant leaves became yellow. Moreover, the transgenic plants were able to grow in the continuous presence of 200 mM NaCl stress. These results indicate that the introduced trait is functional in transgenic plants and that it is also stable. The transgenic lines also maintained higher endogenous nutrient contents as compared to the VC and WT plants under salinity stress, which revealed the salinity tolerance potential of the transgenic lines. Similar findings have been reported earlier [,,,,]. Higher concentration of potassium and lower concentration of sodium were found in leaves of PDH45-overexpressing transgenic lines as compared with VC and WT plants.
PDH45-overexpressing marker-free transgenic lines maintained higher endogenous nutrient contents under salinity stress as compared with WT and VC plants, which proved the salt stress tolerance potential of the marker-free PDH45 transgenic lines, which is in agreement with the previous reports [,,]. The higher potassium and lower sodium concentration in T1 transgenic plants indicates that the lower Na+/K+ ratio in the transgenic lines might be responsible for imparting better stress tolerance to salinity stress in comparison to the VC and WT plants. The better photosynthetic activities such as net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, intercellular CO2 concentration, CO2 release and transpiration rate, and photosynthetic yield (Fv/Fm) were observed in PDH45 transgenic lines as compared to the VC and WT plants. The retention of chlorophyll content in transgenic lines indicates the better control over the photosynthetic apparatus under salt stress. Our data are in agreement with the earlier reports on PDH45-, SUV3-, and BAT1-overexpressing rice plants under stress [,,,].
Sugars such as glucose and fructose may play a key role in salt defense mechanisms through ROS detoxification [,,,,]. The sugar content in PDH45-overexpressing marker-free transgenic lines was higher as compared to VC and WT plants. The PDH45-overexpressing transgenic rice plants showed significantly higher endogenous content of plant hormones in leaf, stem, and root, directing the molecular and biochemical mechanisms to confer increased stress tolerance []. A similar trend of endogenous plant hormone profile was also reflected in OsSUV3 and OsBAT1 transgenic rice under stress conditions [,]. This is a very simple, reproducible, and improved protocol for selection of marker-free transgenic rice plants using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of mature seed-derived callus tissues of indica rice variety, IR64.
5. Conclusions
The present study provides reporter and marker-free transgenic rice plants that has a scope for future commercialization and approval from regulatory agencies as they are focusing on the removal of reporter and marker genes from transgenic plants. We developed a unique successful salt screening method for screening transgenic lines during tissue culture and also utilized the unique function of PDH45 helicase in providing salt tolerance in marker-free transgenic rice cv. IR64. It also provides a good example for the exploitation of helicases for enhanced agricultural production, while withstanding extreme climatic conditions, maintaining biosafety regulations, and ensuring food security.
Author Contributions
R.T. and N.T. designed the research; R.K.S. performed the experiments; R.K.S., R.T. and N.T. analyzed the data; R.K.S., R.G., S.S.G., J.F.J.B. and N.T. wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The APC was funded by JFJB.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
Work on plant abiotic stress tolerance in N.T.’s laboratory was partially supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, and Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India. S.S.G. & R.G. acknowledges partial support from DBT-BUILDER grant, Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India (BT/INF/22/SP43043/2021). JFJB acknowledges funding support by CONACYT (Ciencia Básica A1-S-25233). The authors gratefully acknowledge the help of Govindjee for his critical review and suggestions for the improvement of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bandumula, N. Rice Production in Asia: Key to Global Food Security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sec. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 88, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, R.S.; Adams, A. The relevance of rice. Rice 2008, 1, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FAO. Crop Prospects and Food Situation—Quarterly Global Report No. 4; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Tuteja, N. Cold, salinity and drought stresses: An overview. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 444, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Ann. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cushman, J.C.; Denby, K.; Mittler, R. Plant responses and adaptations to a changing climate. Plant J. 2022, 109, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.K.; Ansari, M.W.; Tuteja, R.; Tuteja, N. OsSUV3 transgenic rice maintains higher endogenous levels of plant hormones that mitigates adverse effects of salinity and sustains crop productivity. Rice 2014, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerchev, P.I.; Van Breusegem, F. Improving oxidative stress resilience in plants. Plant J. 2022, 109, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, B.; Yun, P.; Shabala, L.; Zhou, M.; Sellamuthu, G.; Venkataraman, G.; Chen, Z.-H.; Shabala, S. Unravelling the physiological basis of salinity stress tolerance in cultivated and wild rice species. Funct. Plant Biol. 2022, 49, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mao, B.; Yuan, D.; Chu, C.; Duan, M. Salt tolerance in rice: Physiological responses and molecular mechanisms. Crop J. 2022, 10, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hill, C.B.; Stefano, G.; Bose, J. Editorial: New Insights Into Salinity Sensing, Signaling and Adaptation in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 604139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuteja, N.; Sahoo, R.K.; Garg, B.; Tuteja, R. OsSUV3 dual helicase functions in salinity stress tolerance by maintaining photosynthesis and antioxidant machinery in rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. IR64). Plant J. 2013, 76, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, R.M.; Mittler, R.; Blumwald, E.; Zandalinas, S.I. Developing climate-resilient crops: Improving plant tolerance to stress combination. Plant J. 2022, 109, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannachi, S.; Steppe, K.; Eloudi, M.; Mechi, L.; Bahrini, I.; Van Labeke, M.-C. Salt Stress Induced Changes in Photosynthesis and Metabolic Profiles of One Tolerant (‘Bonica’) and One Sensitive (‘Black Beauty’) Eggplant Cultivars (Solanum melongena L.). Plants 2022, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidumukkala, S.; Tayi, L.; Chittela, R.K.; Vudem, D.R.; Khareedu, V.R. DEAD box helicases as promising molecular tools for engineering abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019, 39, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuteja, N.; Verma, S.; Sahoo, R.K.; Raveendar, S.; Reddy, I.N.B.L. Recent advances in development of marker-free transgenic plants: Regulation and biosafety concern. J. Biosci. 2012, 37, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Roy, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Development of marker-free transgenic pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) expressing a pod borer insecticidal protein. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, L.; Bi, D.; Tian, X.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zou, X.; Gao, X.; Yang, H.; et al. Generation of Marker-Free Transgenic Rice Resistant to Rice Blast Disease Using Ac/Ds Transposon-Mediated Transgene Reintegration System. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 644437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.J. Generation of marker-free transgenic rice using CRISPR/Cas9 system controlled by floral specific promoters. J. Genet. Genom. 2019, 46, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataiah, P.; Christopher, T.; Subhash, K. Selection and characterization of sodium chloride and mannitol tolerant callus lines of red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Plant Physiol. 2012, 9, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Jiménez, M.; Olaya Pérez-Tornero, O. In Vitro Plant Evaluation Trial: Reliability Test of Salinity Assays in Citrus Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Mao, D.; Chen, L. Agrobacterium-Mediated High-Efficiency Genetic Transformation and Genome Editing of Chaling Common Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) Using Scutellum Tissue of Embryos in Mature Seeds. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 849666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, R.; Asao, H.; Iida, S. A large-scale Agrobacterium-mediated transformation procedure with a strong positive-negative selection for gene targeting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2004, 22, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, M.S.A.; Ahmed, B.; Parveen, S.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Huda, K.M.K. Agrobacterium-mediated Genetic Transformation of Rice var. BRRI Dhan 58. Plant Tissue Cult. Biotech. 2021, 31, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Pu, Y.-P.; Liu, W.-Z.; Hu, G.-C.; Si, H.-M.; Tang, K.-X.; Sun, Z.-X. Rapid Generation of Selectable Marker-Free Transgenic Rice with Three Target Genes by Co-Transformation and Anther Culture. Rice Sci. 2007, 14, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.-J.; Qin, Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, S.K.; Cho, Y.-G.; Shin, K.S.; Lim, M.H.; Cho, H.-S. Development of Selectable Marker-Free Transgenic Rice Plants with Enhanced Seed Tocopherol Content through FLP/FRT-Mediated Spontaneous Auto-Excision. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.K.; Tuteja, N. Development of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation technology for mature seed-derived callus tissues of indica rice cultivar IR64. GM Crops Food 2012, 3, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, X.H.; Reddy, M.K.; Ehtesham, N.Z.; Matta, B.; Tuteja, N. A DNA helicase from Pisum sativum is homologous to translation initiation factor and stimulates topoisomerase I activity. Plant J. 2000, 24, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vashisht, A.A.; Tuteja, N. Stress responsive DEAD-box helicases: A new pathway to engineer plant stress tolerance. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2006, 84, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.K.; Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Pea DNA helicase 45 promotes salinity stress tolerance in IR64 rice with improved yield. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, S.S.; Tajrishi, M.; Madan, M.; Tuteja, N. A DESD-box helicase functions in salinity stress tolerance by improving photosynthesis and antioxidant machinery in rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. PB1). Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, B.; Gill, S.S.; Biswas, D.K.; Sahoo, R.K.; Kunchge, N.S.; Tuteja, R.; Tuteja, N. Simultaneous Expression of PDH45 with EPSPS Gene Improves Salinity and Herbicide Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shivakumara, T.N.; Sreevathsa, R.; Dash, P.K.; Sheshshayee, M.S.; Papolu, P.K.; Tuteja, N.; UdayaKumar, M. Overexpression of Pea DNA Helicase 45 (PDH45) imparts tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in chili (Capsicum annuum L.). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman, W.; Tanaka, C. Solubilization of plant membrane proteins for analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986, 81, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanan-Mishra, N.; Pham, X.H.; Sopory, S.K.; Tuteja, N. Pea DNA helicase 45 overexpression in tobacco confers high salinity tolerance without affecting yield. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garg, B.; Jaiswal, J.P.; Misra, S.; Tripathi, B.N.; Prasad, M.A. A comprehensive study on dehydration-induced antioxidative responses during germination of Indian bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L. Em Thell) cultivars collected from different agroclimatic zones. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2012, 18, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmig, B.; Winter, K.; Kruger, A.; Czygan, F.C. Photoinhibition and zeaxanthin formation in intact leaves: A possible role of the xanthophyll cycle in the dissipation of excess light energy. Plant Physiol. 1987, 84, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreiber, U.; Armond, P.A. Heat-induced changes of chlorophyll fluorescence in isolated chloroplasts and related heat-damage at the pigment level. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1978, 502, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkacier, M.; Erbas, M.; Uslu, M.K.; Aksu, M. Comparison of different extraction and detection methods for sugars using amino-bonded phase HPLC. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2003, 41, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.G.; Du, X.M.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zhou, X. Fluctuation in levels of endogenous plant hormones in ovules of normal and mutant cotton during flowering and their relation to fiber development. J. Plant Growth Regul. 1996, 15, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.D.; Pratt, P.F. Method of Analysis of Soils, Plants and Waters, 2nd ed.; California University Agricultural Division: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1982; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Wallace, P.A.; Teakle, N.L.; Colmer, T.D. Measuring soluble ion concentrations (Na+, K+, Cl-) in salt-treated plants. In Plant Stress Tolerance. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols); Sunkar, R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 371–382. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.; Elias, S.M.; Hossain, A.; Ferdousi, A.; Rahman, M.S.; Tuteja, N.; Seraj, Z.I. Overexpression of a DEAD box helicase, PDH45, confers both seedling and reproductive stage salinity tolerance to rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol. Breed. 2012, 30, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, P.; Jebaraj, S.; Geetha, S. In vitro screening for salt tolerance in Rice (Oryza sativa). Electronic. J. Plant Breed. 2010, 1, 1208–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Zinnah, K.M.A.; Zobayer, N.; Sikdar, S.U.; Liza, L.N.; Chowdhury, M.A.N.; Ashrafuzzaman, M. In vitro regeneration and screening for salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. Res. J. Biological Sci. 2013, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Dong, Y.X.; Gao, X.-Q.; Zhang, X.S. Expression of a putative alfalfa helicase increases tolerance to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis by enhancing the capacities for ROS scavenging and osmotic adjustment. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuteja, N.; Sahoo, R.K.; Huda, K.M.K.; Tula, S.; Tuteja, R. OsBAT1 augments salinity stress tolerance by enhancing detoxification of ROS and expression of stress-responsive genes in transgenic rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, H.J.; Jensen, R.G. Strategies for engineering water stress tolerance in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 1996, 14, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentsink, L.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Vreugdenhil, D.; Tesnier, K.; Groot, S.P.C.; Koornneef, M. Genetic analysis of seed soluble oligosaccharides in relation to seed storability of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, P.; Niyogi, K.; Sengupta, D.N.; Ghosh, B. Spermidine treatment to rice seedlings recovers salinity stress-induced damage of plasma membrane and PM-bound H+-ATPase in salt-tolerant and salt sensitive rice cultivars. Plant Sci. 2005, 168, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanagul, W.; Thitisaksakul, M. Effect of salinity stress on growth and carbohydrate metabolism in three rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity tolerance. Indian. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 46, 736–742. [Google Scholar]
- Osakabe, Y.; Arinaga, N.; Umezawa, T.; Katsura, S.; Nagamachi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Ohiraki, H.; Yamada, K.; Seo, S.U.; Abo, M.; et al. Osmotic stress responses and plant growth controlled by potassium transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).