β3 Relaxant Effect in Human Bladder Involves Cystathionine γ-Lyase-Derived Urothelial Hydrogen Sulfide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Tissue
2.2. Human Bladder Strips
2.3. Human Urothelial T24 Cells
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. H2S Determination
2.6. Determination of cGMP and cAMP in T24 Cells
3. Results
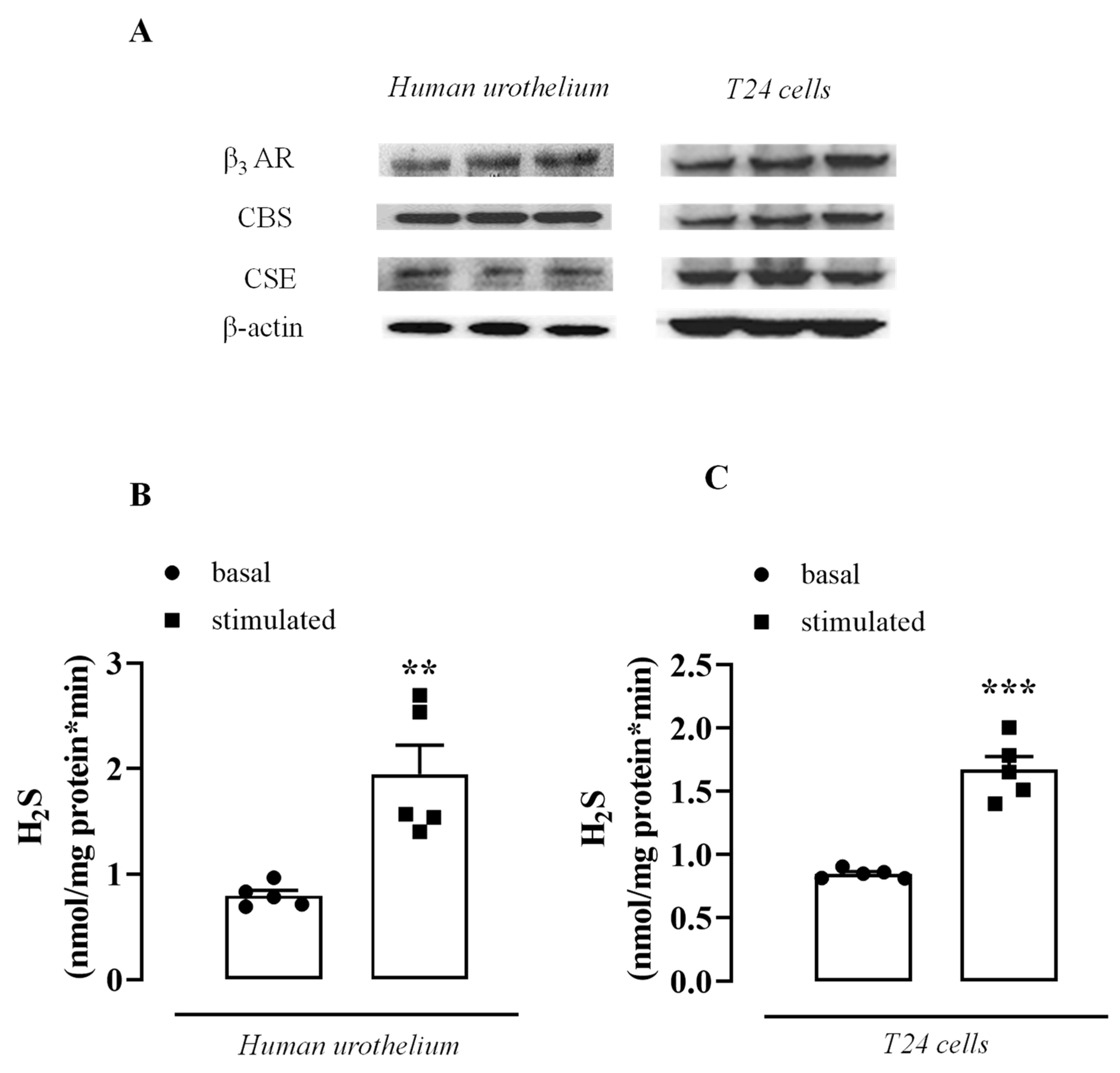
3.1. β3 AR, CBS, and CSE Are Expressed in the Human Urothelium and T24 Cells
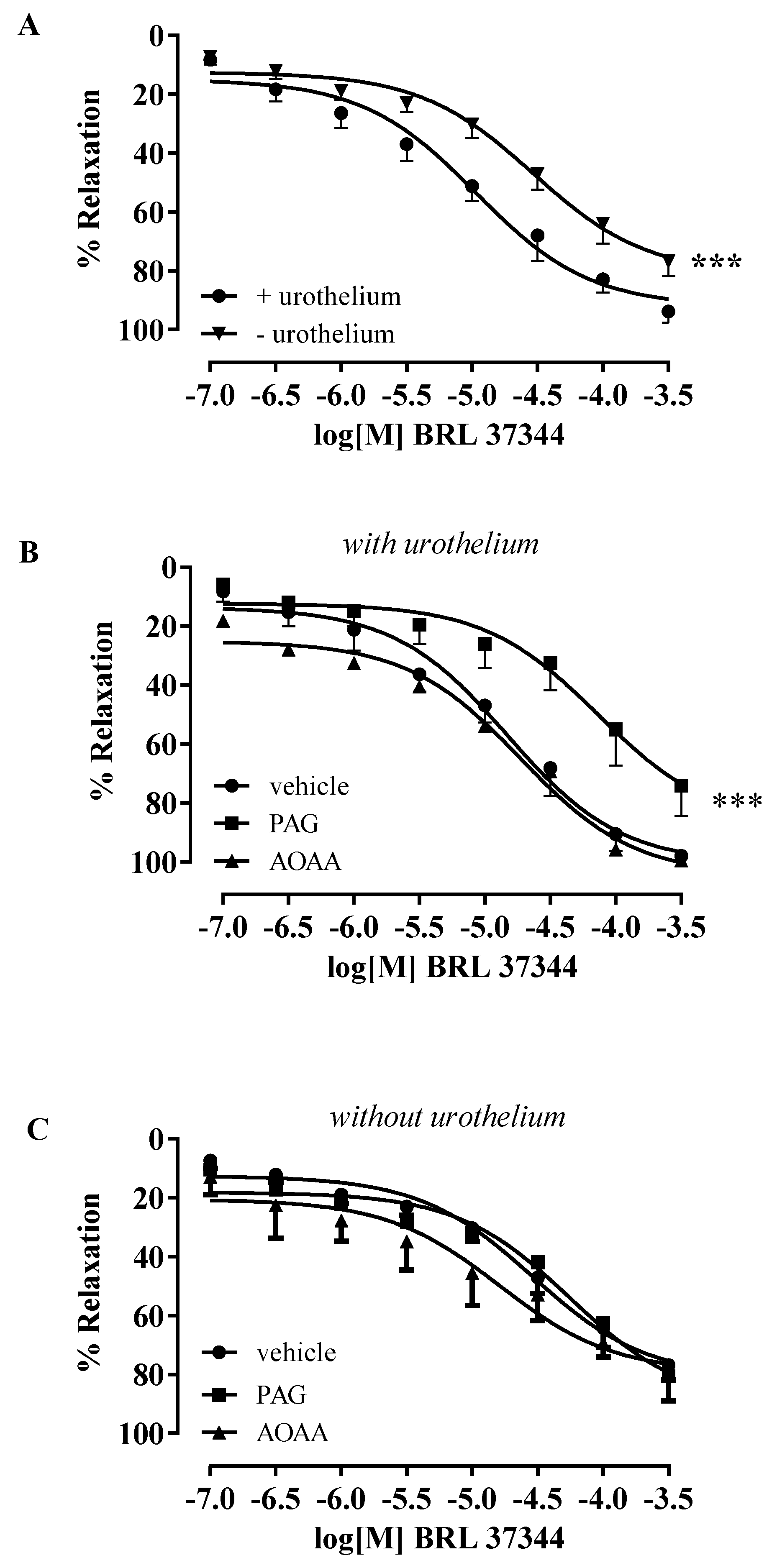
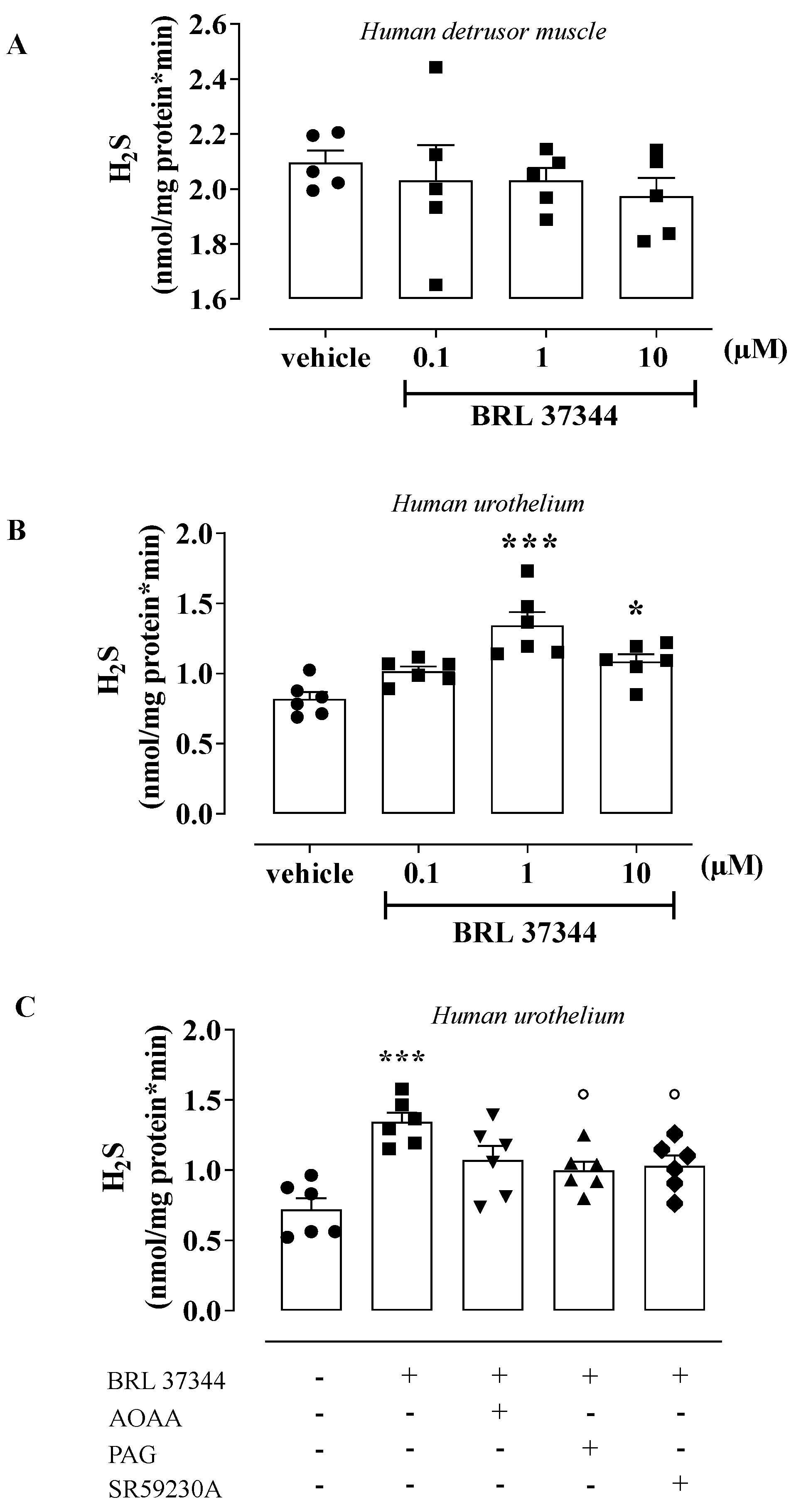
3.2. BRL 37344-Induced Relaxation Involves H2S Production in Human Bladder Strips
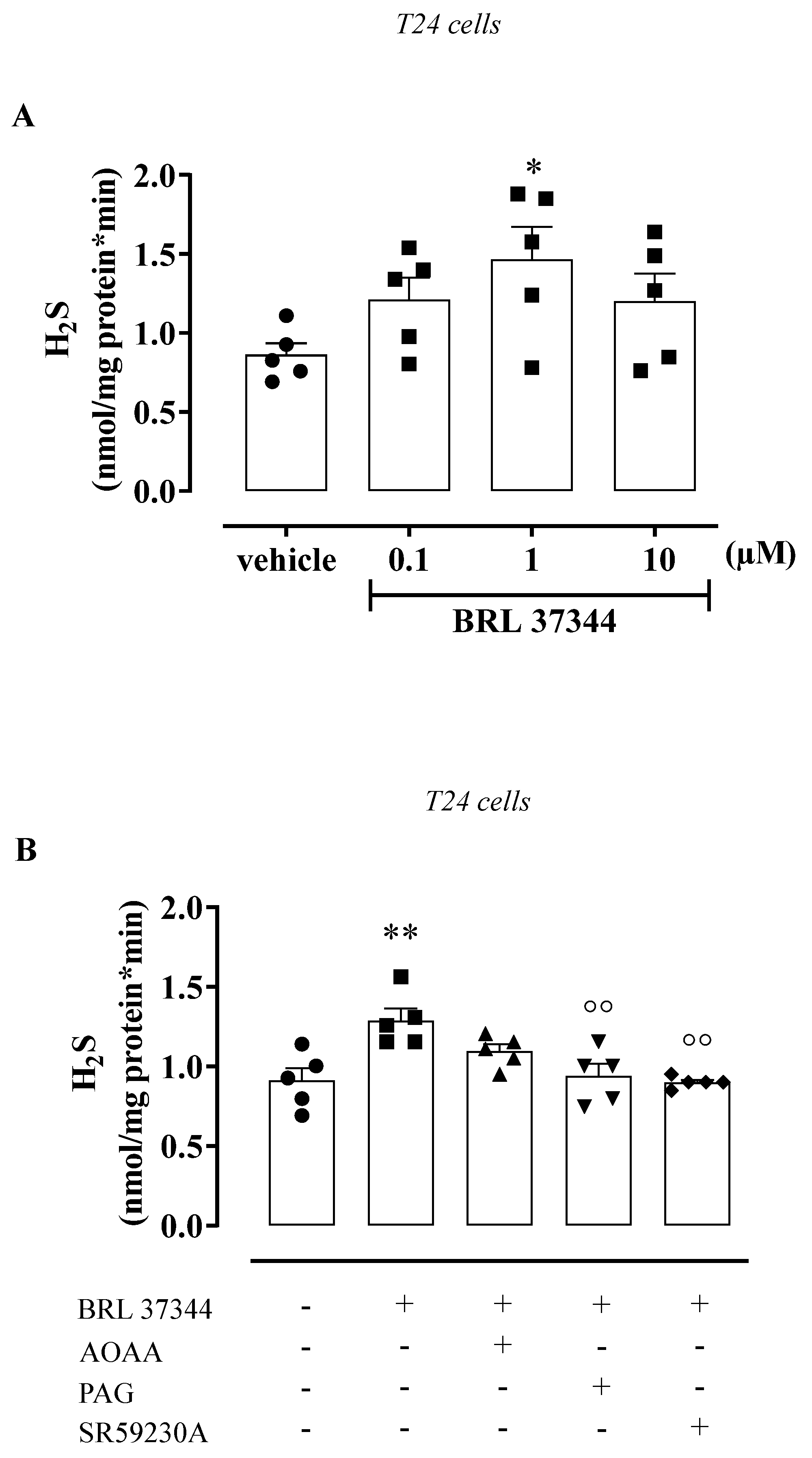
3.3. BRL 37344 Promotes H2S Production in the Human Urothelium and T24 Cells
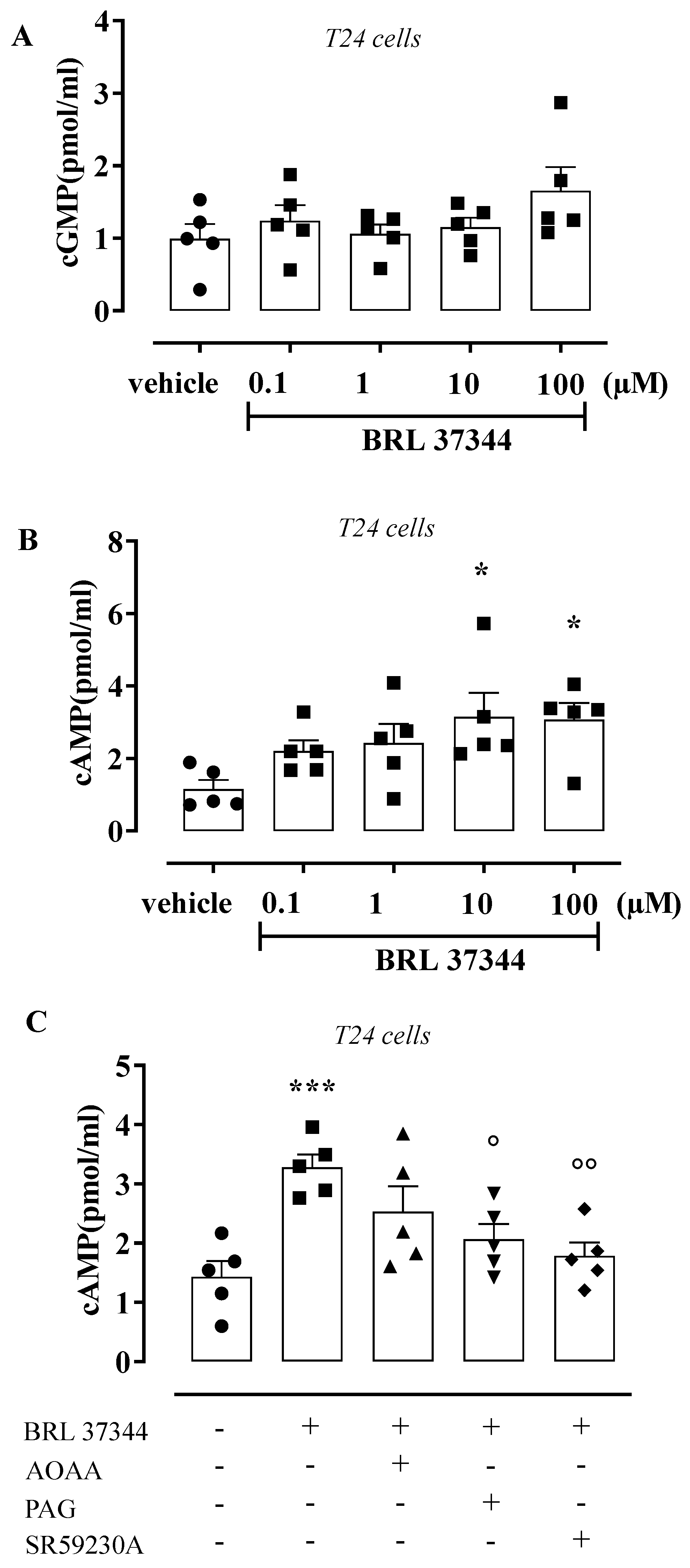
3.4. BRL 37344 Increases cAMP Levels in T24 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazzeri, M. The physiological function of the urothelium--more than a simple barrier. Urol. Int. 2006, 76, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dveksler, G.; Gimeno, M.F.; Gimeno, A.L. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic components of the inotropism evoked by electric field stimulation in the isolated rat urinary bladder. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 1987, 19, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, C.; Caratozzolo, O.; Puglisi, L.A. Possible role for urinary bladder epithelium in bradykinin-induced contraction in diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 214, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, C.A.; Santicioli, P.; Parlani, M.; Astolifi, M.; Patacchini, R.; Meli, A. The presence of the mucosa reduces the contractile response of the guinea-pig urinary bladder to substance P. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawthorn, M.H.; Chapple, C.R.; Cock, M.; Chess-Williams, R. Urothelium-derived inhibitory factor(s) influences on detrusor muscle contractility in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Templeman, L.; Chapple, C.R.; Chess-Williams, R. Urothelium derived inhibitory factor and cross-talk among receptors in the trigone of the bladder of the pig. J. Urol. 2002, 167 Pt 1, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunaga, K.; Chapple, C.R.; McKay, N.G.; Yoshida, M.; Sellers, D.J. The beta3-adrenoceptor mediates the inhibitory effects of beta-adrenoceptor agonists via the urothelium in pig bladder dome. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2010, 29, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, R.M.; Wein, A.J.; Krasnopolsky, L.; Atta, M.A.; Ghoniem, G.M. Effect of mucosal removal on the response of the feline bladder to pharmacological stimulation. J. Urol. 1995, 153, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saban, R.; Keith, I.M.; Nielsen, K.T.; Christensen, M.M.; Rhodes, P.R.; Bruskewitz, C.R. In vitro effects of bladder mucosa and an enkephalinase inhibitor on tachykinin induced contractility of the dog bladder. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyaprasithi, B.; Mang, C.F.; Kilbinger, H.; Hohenfellner, M. Inhibition of human detrusor contraction by a urothelium derived factor. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 1897–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propping, S.; Wuest, M.; Eichhorn, B.; Wirth, M.P.; Kaumann, A.J.; Ravens, U. Mucosa of human detrusor impairs contraction and beta-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation. BJU Int. 2013, 112, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d'Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Mitidieri, E.; Fusco, F.; Russo, A.; Pagliara, V.; Tramontano, T.; Donnarumma, E.; Mirone, V.; Cirino, G.; Russo, G.; et al. Urothelium muscarinic activation phosphorylates CBS (Ser227) via cGMP/PKG pathway causing human bladder relaxation through H2S production. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellers, D.; Chess-Williams, R.; Michel, M.C. Modulation of lower urinary tract smooth muscle contraction and relaxation by the urothelium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2018, 391, 675–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, N.N.; Thor, A.; Hallén, K.; Wiklund, N.P.; Gustafsson, L.E. Cascade bioassay evidence for the existence of urothelium-derived inhibitory factor in Guinea pig urinary bladder. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, N.N.; Gustafsson, L.E.; Svennersten, K. Inhibitory Effects of Urothelium-related Factors. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 121, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, S.; Shimizu, T.; Shimizu, S.; Higashi, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Ono, H.; Aratake, T.; Saito, M. Possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous relaxation factor in the rat bladder and prostate. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombkowski, R.A.; Doellman, M.M.; Head, S.K.; Olson, K.R. Hydrogen sulfide mediates hypoxia-induced relaxation of trout urinary bladder smooth muscle. J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209 Pt 16, 3234–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsunami, M.; Miki, T.; Nishiura, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Okawa, Y.; Nishikawa, H.; Sekiguchi, F.; Kubo, L.; Ozaki, T.; Tsujiuchi, T.; et al. Involvement of the endogenous hydrogen sulfide/Ca(v) 3.2 T-type Ca2+ channel pathway in cystitis-related bladder pain in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gai, J.W.; Wahafu, W.; Guo, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.C.; Xiao, Y.X.; Zhang, L.; Xin, Z.C.; Jin, J. Further evidence of endogenous hydrogen sulphide as a mediator of relaxation in human and rat bladder. Asian J. Androl. 2013, 15, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, V.S.; Ribeiro, A.S.F.; Martínez, M.P.; Orensanz, L.M.; Barahona, M.B.; Martínez-Sáenz, A.; Recio, P.; Benedito, S.; Bustamante, S.; Carballido, J.; et al. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide has a powerful role in inhibitory neurotransmission to the pig bladder neck. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, F.; d’Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Mitidieri, E.; Cirino, G.; Sorrentino, R.; Mirone, V. Sildenafil effect on the human bladder involves the L-cysteine/hydrogen sulfide pathway: A novel mechanism of action of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d'Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Fusco, F.; Mirone, V.; Cirino, G.; Sorrentino, R. The Role of the Hydrogen Sulfide Pathway in Male and Female Urogenital System in Health and Disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2017, 27, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbodio, J.I.; Snyder, S.H.; Paul, B.D. Regulators of the transsulfuration pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R. H2S and polysulfide metabolism: Conventional and unconventional pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, K.E.; Arner, A. Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 935–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petkov, G.V.; Nelson, M.T. Differential regulation of Ca2+-activated K+ channels by beta-adrenoceptors in Guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 288, C1255–C1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, O.; Chapple, C.R. Beta3-adrenoceptors in urinary bladder. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2007, 26, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, T.; Kajioka, S.; Itsumi, M.; Kareman, E.; Lee, K.; Shiota, M.; Eto, M. Mirabegron induces relaxant effects via cAMP signaling-dependent and -independent pathways in detrusor smooth muscle. Low Urin. Tract Symptoms 2019, 11, O209–O217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.E. Antimuscarinic mechanisms and the overactive detrusor: An update. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igawa, Y.; Aizawa, N.; Michel, M.C. β(3)-Adrenoceptors in the normal and diseased urinary bladder-What are the open questions? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 2525–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, A.; Kawasaki, H.; Matsumoto, R.; Shinbo, H.; Kurita, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Ozono, S. Expression of beta-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in Urothelium, Interstitial Cells and Detrusor of the Human Urinary Bladder. Low Urin. Tract Symptoms 2013, 5, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Jin, T.; Ai, J.; Wei, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Jin, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, K. beta-Adrenoceptors regulate matrix metalloproteinase expression in human urothelial cells under hydrostatic pressure. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitidieri, E.; Tramontano, T.; Gurgone, D.; Imbimbo, C.; Mirone, V.; Fusco, F.; Cirino, G.; d'Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Sorrentino, R. β(3) adrenergic receptor activation relaxes human corpus cavernosum and penile artery through a hydrogen sulfide/cGMP-dependent mechanism. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 124, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitidieri, E.; Tramontano, T.; Donnarumma, E.; Brancaleone, V.; Cirino, G.; d’ Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Sorrentino, R. l-Cys/CSE/H2S pathway modulates mouse uterus motility and sildenafil effect. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetik-Anacak, G.; Dikmen, A.; Coletta, C.; Mitidieri, E.; Dereli, M.; Donnarumma, E.; d’Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Sorrentino, R. Hydrogen sulfide compensates nitric oxide deficiency in murine corpus cavernosum. Pharmacol. Res 2016, 2016, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d'Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Mitidieri, E.; Donnarumma, E.; Tramontano, T.; Brancaleone, V.; Cirino, G.; Bucci, M.; Sorrentino, R. Hydrogen sulfide is involved in dexamethasone-induced hypertension in rat. Nitric Oxide 2015, 46, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitidieri, E.; Vanacore, D.; Turnaturi, C.; Sorrentino, R.; d’Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R. Uterine Dysfunction in Diabetic Mice: The Role of Hydrogen Sulfide. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirone, V.; d'Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Mitidieri, E.; Imbimbo, C.; Fusco, F.; Verze, P.; Vitale, D.F.; Sorrentino, R.; Cirino, G. Platelet cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a biomarker of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor efficacy in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A randomized placebo-controlled study. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomiya, M.; Yamaguchi, O. A quantitative analysis of mRNA expression of alpha 1 and beta-adrenoceptor subtypes and their functional roles in human normal and obstructed bladders. J. Urol. 2003, 170 Pt 1, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanishi, T.; Chapple, C.R.; Yasuda, K.; Yoshida, K.; Chess-Williams, R. Identification of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in lower urinary tract of the female pig. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 2706–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, O. Beta3-adrenoceptors in human detrusor muscle. Urology 2002, 59 (Suppl. 1), 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, E.B.; Porter, J.M.; Porter, J.E. Beta-adrenergic receptor activation in immortalized human urothelial cells stimulates inflammatory responses by PKA-independent mechanisms. Cell Commun. Signal 2005, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapple, C.R.; Cardozo, L.; Nitti, V.W.; Siddiqui, E.; Michel, M.C. Mirabegron in overactive bladder: A review of efficacy, safety, and tolerability. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014, 33, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Thiagamoorthy, G.; Cardozo, L. A drug safety evaluation of mirabegron in the management of overactive bladder. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, K.; Burden, H.; Abrams, P. Mirabegron in overactive bladder patients: Efficacy review and update on drug safety. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2016, 7, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Salvo, J.; Nagabukuro, H.; Wickham, L.A.; Abbadie, C.; De Martino, J.A.; Fitzmaurice, A.; Gichuru, L.; Kulick, A.; Donnelly, M.J.; Jochnowitz, N.; et al. Pharmacological Characterization of a Novel Beta 3 Adrenergic Agonist, Vibegron: Evaluation of Antimuscarinic Receptor Selectivity for Combination Therapy for Overactive Bladder. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 360, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nunzio, C.; Presicce, F.; Pirozzi, L.; Castellan, P.; Schips, L.; Cindolo, L.; Lombardo, R.; Tubaro, A. The Current Indications and the Benefits of Combining a β3-Agonist with an Anticholinergic for the Treatment of OAB. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, R.; Hebel, D.; Vouri, S.M.; Pitlick, J.M. Mirabegron: A Beta-3 agonist for overactive bladder. Consult. Pharm. 2014, 29, 823–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paton, D.M. Vibegron: A beta (3)-adrenergic agonist for the treatment of overactive bladder. Drugs Today 2021, 57, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.E. On the site and mechanism of action of β3-adrenoceptor agonists in the bladder. Int. Neurourol. J. 2017, 21, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Igawa, Y.; Aizawa, N. Incontinence: How do β3-adrenoceptor agonists work in the bladder? Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, K.; Gravas, S.; Michel, M.C. Do β3-adrenoceptor agonists cause urinary bladder smooth muscle relaxation by inhibiting acetylcholine release? Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, F859–F861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozveren Adibelli, E.; Aydinoglu, F.; Ogulener, N. The role of l-cysteine/Hydrogen sulfide pathway on β3-Adrenoceptor- induced relaxation in mouse gastric fundus. Nitric Oxide 2022, 119, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa, A.; Velasquez Flores, M.; Nguyen, H.; Cammisotto, P.G.; Campeau, L. Beta-3 Adrenoceptor Signaling Pathways in Urothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells in the Presence of Succinate. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 367, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Vellecco, V.; Zhou, Z.; Pyriochou, A.; Roussos, C.; Roviezzo, F.; Brancaleone, V.; Cirino, G. Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous inhibitor of phosphodiesterase activity. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brancaleone, V.; Mitidieri, E.; Flower, R.J.; Cirino, G.; Perretti, M. Annexin A1 mediates hydrogen sulfide properties in the control of inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 351, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishikawa, H.; Hayashi, H.; Kubo, S.; Tsubota-Matsunami, M.; Sekiguchi, F.; Kawabata, A. Inhibition by hydrogen sulfide of rabbit platelet aggregation and calcium mobilization. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muzaffar, S.; Shukla, N.; Bond, M.; Newby, A.C.; Angelini, G.D.; Sparatore, A.; Del Soldato, P.; Jeremy, J.Y. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide inhibits superoxide formation, NOX-1 expression and Rac1 activity in human vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Vasc. Res. 2008, 45, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njie-Mbye, Y.F.; Kulkarni, M.; Opere, C.A.; Ohia, S.E. Mechanism of action of hydrogen sulfide on cyclic AMP formation in rat retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 98, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untereiner, A.A.; Wang, R.; Ju, Y.; Wu, L. Decreased gluconeogenesis in the absence of cystathionine gamma-lyase and the underlying mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitidieri, E.; Pecoraro, A.; Esposito, E.; Brancaleone, V.; Turnaturi, C.; Napolitano, L.; Mirone, V.; Fusco, F.; Cirino, G.; Sorrentino, R.; et al. β3 Relaxant Effect in Human Bladder Involves Cystathionine γ-Lyase-Derived Urothelial Hydrogen Sulfide. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081480
Mitidieri E, Pecoraro A, Esposito E, Brancaleone V, Turnaturi C, Napolitano L, Mirone V, Fusco F, Cirino G, Sorrentino R, et al. β3 Relaxant Effect in Human Bladder Involves Cystathionine γ-Lyase-Derived Urothelial Hydrogen Sulfide. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(8):1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081480
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitidieri, Emma, Annalisa Pecoraro, Erika Esposito, Vincenzo Brancaleone, Carlotta Turnaturi, Luigi Napolitano, Vincenzo Mirone, Ferdinando Fusco, Giuseppe Cirino, Raffaella Sorrentino, and et al. 2022. "β3 Relaxant Effect in Human Bladder Involves Cystathionine γ-Lyase-Derived Urothelial Hydrogen Sulfide" Antioxidants 11, no. 8: 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081480
APA StyleMitidieri, E., Pecoraro, A., Esposito, E., Brancaleone, V., Turnaturi, C., Napolitano, L., Mirone, V., Fusco, F., Cirino, G., Sorrentino, R., Russo, G., Russo, A., & d’Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R. (2022). β3 Relaxant Effect in Human Bladder Involves Cystathionine γ-Lyase-Derived Urothelial Hydrogen Sulfide. Antioxidants, 11(8), 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081480










