New Application of the Commercially Available Dye Celestine Blue B as a Sensitive and Selective Fluorescent “Turn-On” Probe for Endogenous Detection of HOCl and Reactive Halogenated Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Human Neutrophils
2.3. Spectrofluorimetry
2.4. Preparation of ROS, RHS, RNS
2.5. Assessing the Limit of Detection (LOD)
2.6. Chlorinating Activity of MPO in Solution and Specific Immuno-Extraction Followed by Enzymatic Detection (SIEFED) Assay
2.7. H2O2 Production by Neutrophils Measured Using Scopoletin
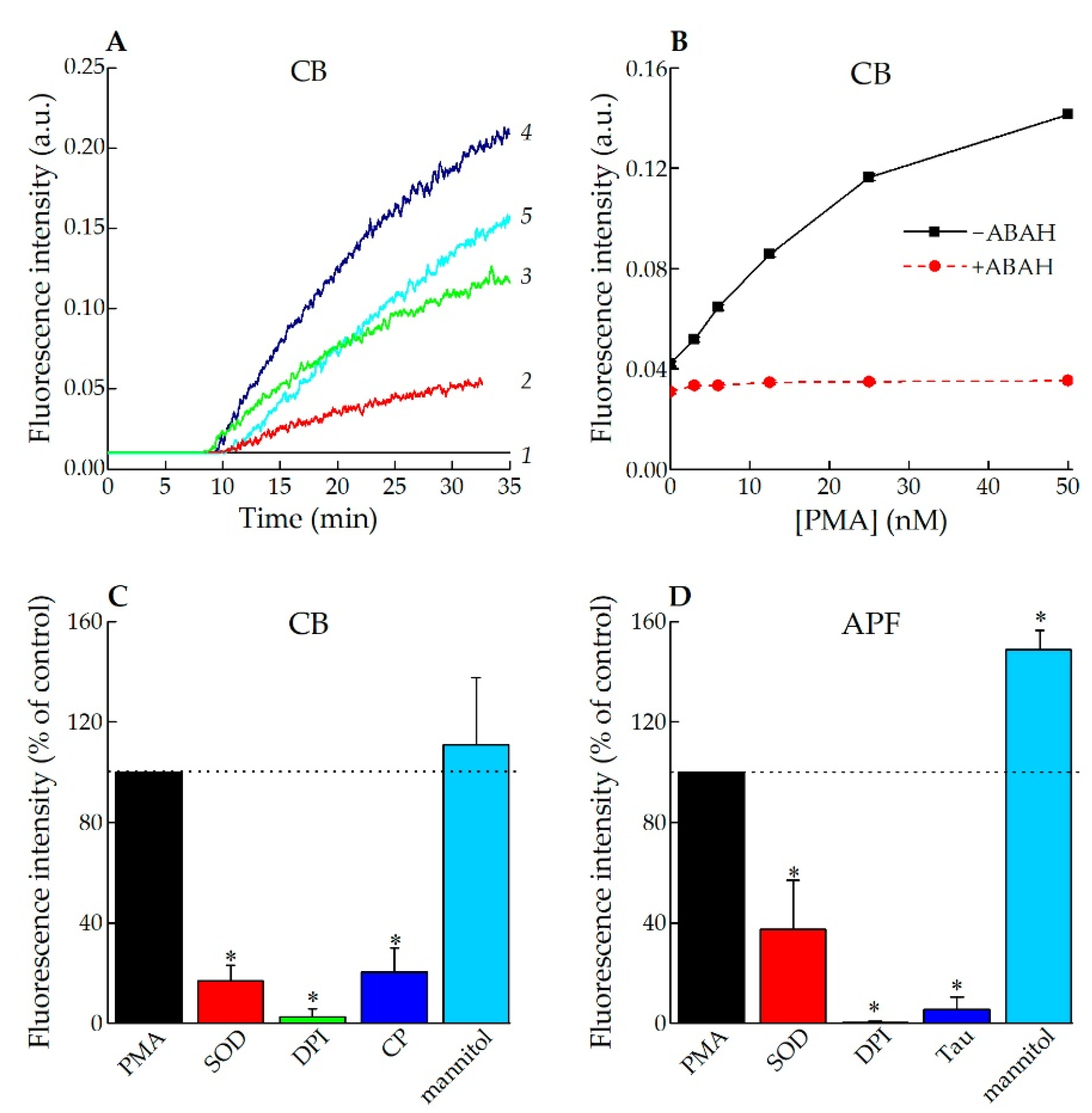
2.8. Registration of HOCl Production by Activated Neutrophils
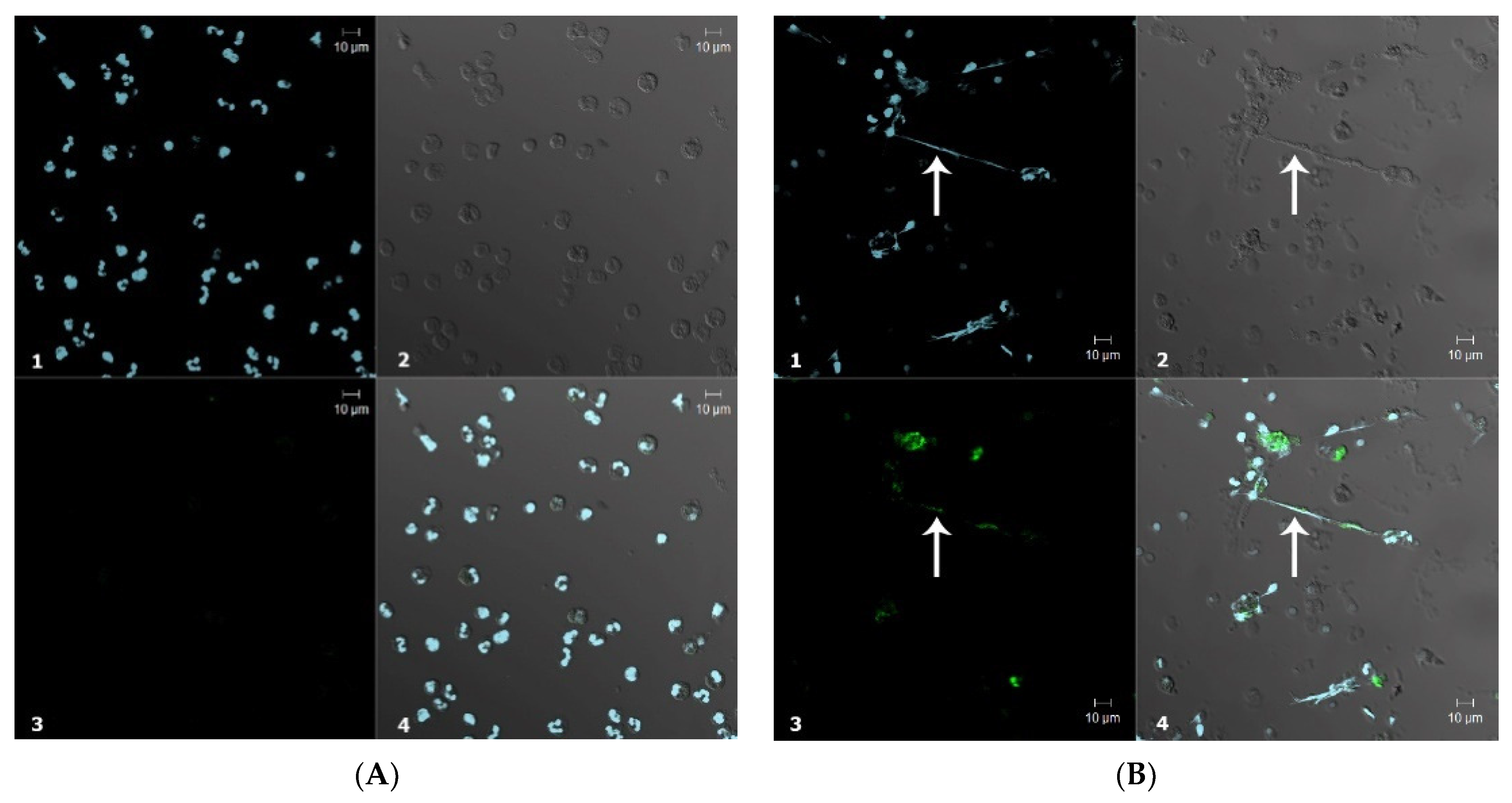
2.9. Confocal Microscopy Assay of Fixed Cells
2.10. Confocal Microscopy Assay of Viable Cells
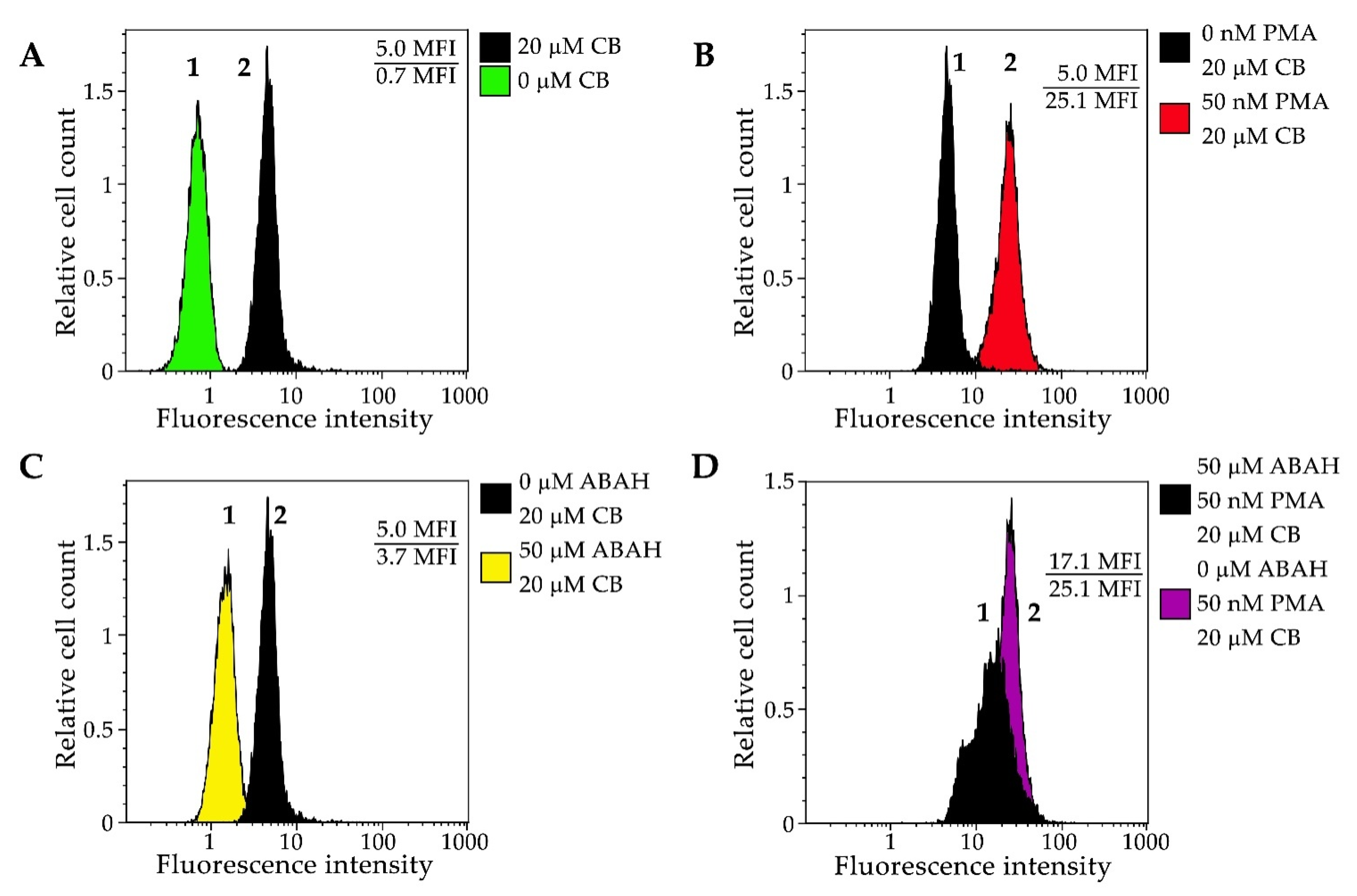
2.11. Flow Cytometry Assay
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
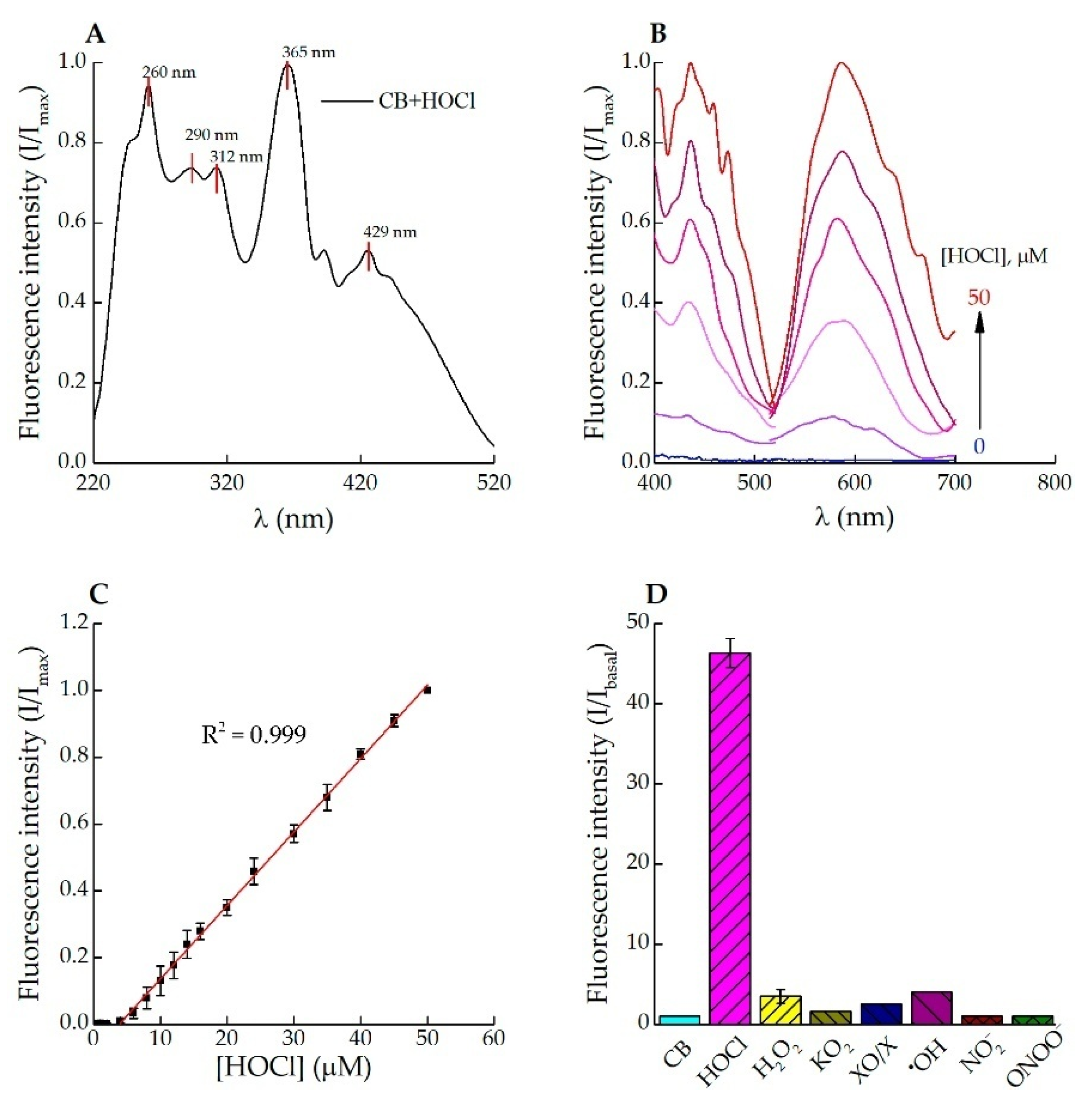
3.1. Fluorescence Response of Celestine Blue B to HOCl
3.2. Application of CB for Endogenous HOCl Detection in Living Cells
3.2.1. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.2.2. Confocal Microscopy
3.2.3. Flow Cytometry
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leliefeld, P.H.C.; Wessels, C.M.; Leenen, L.P.H.; Koenderman, L.; Pillay, J. The Role of Neutrophils in Immune Dysfunction during Severe Inflammation. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 73:1–73:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordenfelt, P.; Tapper, H. Phagosome Dynamics during Phagocytosis by Neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, H.; Albrett, A.M.; Kettle, A.J.; Winterbourn, C.C. Myeloperoxidase Associated with Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Is Active and Mediates Bacterial Killing in the Presence of Hydrogen Peroxide. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnhold, J.; Malle, E. Halogenation Activity of Mammalian Heme Peroxidases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, B.S.; Love, D.T.; Hawkins, C.L. Comparative Reactivity of Myeloperoxidase-Derived Oxidants with Mammalian Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 71, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panasenko, O.M.; Gorudko, I.V.; Sokolov, A.V. Hypochlorous Acid as a Precursor of Free Radicals in Living Systems. Biochem. Mosc. 2013, 78, 1466–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulfig, A.; Leichert, L.I. The Effects of Neutrophil-Generated Hypochlorous Acid and Other Hypohalous Acids on Host and Pathogens. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 385–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Biermann, M.H.; Brauner, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Herrmann, M. New Insights into Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Mechanisms of Formation and Role in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.L.; Davies, M.J. Role of Myeloperoxidase and Oxidant Formation in the Extracellular Environment in Inflammation-Induced Tissue Damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, S.L.; Heinecke, J.W. 3-Chlorotyrosine, a Specific Marker of Myeloperoxidase-Catalyzed Oxidation, Is Markedly Elevated in Low Density Lipoprotein Isolated from Human Atherosclerotic Intima. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, B.; Pennathur, S.; Heinecke, J.W. Myeloperoxidase Targets Apolipoprotein A-I, the Major High Density Lipoprotein Protein, for Site-Specific Oxidation in Human Atherosclerotic Lesions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6375–6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettle, A.J.; Albrett, A.M.; Chapman, A.L.; Dickerhof, N.; Forbes, L.V.; Khalilova, I.; Turner, R. Measuring Chlorine Bleach in Biology and Medicine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacker, B.K.; Albert, C.J.; Ford, B.A.; Ford, D.A. Strategies for the Analysis of Chlorinated Lipids in Biological Systems. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 59, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, G.; Qu, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, P. A HClO-Specific near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe for Determination of Myeloperoxidase Activity and Imaging Mitochondrial HClO in Living Cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.-S.; Thirumalaivasan, N.; Lin, T.-C.; Wu, S.-P. Ultrasensitive and Specific Two-Photon Fluorescence Detection of Hypochlorous Acid by a Lysosome-Targeting Fluorescent Probe for Cell Imaging. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 190, 113545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzi, P.; Nahrendorf, M.; Wildgruber, M.; Waterman, P.; Figueiredo, J.-L.; Aikawa, E.; McCarthy, J.; Weissleder, R.; Hilderbrand, S.A. Oxazine Conjugated Nanoparticle Detects In Vivo Hypochlorous Acid and Peroxynitrite Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15739–15744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.W.; Querol Sans, M.; Bogdanov, A.; Weissleder, R. Imaging of Myeloperoxidase in Mice by Using Novel Amplifiable Paramagnetic Substrates. Radiology 2006, 240, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Milton, A.; Arnold, R.D.; Huang, H.; Smith, F.; Panizzi, J.R.; Panizzi, P. Methods for Measuring Myeloperoxidase Activity toward Assessing Inhibitor Efficacy in Living Systems. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landino, L.M.; Mall, C.B.; Nicklay, J.J.; Dutcher, S.K.; Moynihan, K.L. Oxidation of 5-Thio-2-Nitrobenzoic Acid, by the Biologically Relevant Oxidants Peroxynitrite Anion, Hydrogen Peroxide and Hypochlorous Acid. Nitric Oxide 2008, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.; Jameson, G.N.L.; Winterbourn, C.C. Kinetics and Mechanisms of the Reaction of Hypothiocyanous Acid with 5-Thio-2-Nitrobenzoic Acid and Reduced Glutathione. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemmig, J.; Remmler, J.; Zschaler, J.; Arnhold, J. Detection of the Halogenating Activity of Heme Peroxidases in Leukocytes by Aminophenyl Fluorescein. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, T.; Flemmig, J.; Furtmüller, P.G.; Obinger, C.; Arnhold, J. (−)-Epicatechin Enhances the Chlorinating Activity of Human Myeloperoxidase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 495, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setsukinai, K.; Urano, Y.; Kakinuma, K.; Majima, H.J.; Nagano, T. Development of Novel Fluorescence Probes That Can Reliably Detect Reactive Oxygen Species and Distinguish Specific Species. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3170–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learn, D.B.; Fried, V.A.; Thomas, E.L. Taurine and Hypotaurine Content of Human Leukocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1990, 48, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sze, D.Y.; Jardetzky, O. Determination of Metabolite and Nucleotide Concentrations in Proliferating Lymphocytes by 1H-NMR of Acid Extracts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1054, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.R.; Fellman, J.H.; Eicher, A.L.; Pratt, K.L. Antioxidant Role and Subcellular Location of Hypotaurine and Taurine in Human Neutrophils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Gen. Subj. 1991, 1073, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.J.; Klein, R.; Slivka, A.; Wei, M. Chlorination of Taurine by Human Neutrophils. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 70, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.I.; Davies, M.J. Absolute Rate Constants for the Reaction of Hypochlorous Acid with Protein Side Chains and Peptide Bonds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, D. A Highly Selective Naked-Eye Probe for Hypochlorite with the p-Methoxyphenol-Substituted Aniline Compound. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 6052–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. Highly Selective and Sensitive Colorimetric Probes for Hypochlorite Anion Based on Azo Derivatives. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 77, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Peng, M.; Qin, J.; Li, Z. Simple Triphenylamine-Based Luminophore as a Hypochlorite Chemosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertozo, L.D.C.; Zeraik, M.L.; Ximenes, V.F. Dansylglycine, a Fluorescent Probe for Specific Determination of Halogenating Activity of Myeloperoxidase and Eosinophil Peroxidase. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 532, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Mi, Y.; Guo, L.; Xu, W.; Zou, D.; Li, T.; Wu, Y. A Novel Fluorescent Probe for Imaging the Process of HOCl Oxidation and Cys/Hcy Reduction in Living Cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 9519–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tian, X.; Shin, I.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Detection of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4783–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.J.; Ye, S.; Yang, D. Fluorescent Probes for HOCl Imaging. Isr. J. Chem. 2017, 57, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudhistira, T.; Mulay, S.V.; Kim, Y.; Halle, M.B.; Churchill, D.G. Imaging of Hypochlorous Acid by Fluorescence and Applications in Biological Systems. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 3048–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reut, V.E.; Gorudko, I.V.; Grigorieva, D.V.; Sokolov, A.V.; Panasenko, O.M. Fluorescent Probes for HOCl Detection in Living Cells. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 48, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.V.; Kostevich, V.A.; Kozlov, S.O.; Donskyi, I.S.; Vlasova, I.I.; Rudenko, A.O.; Zakharova, E.T.; Vasilyev, V.B.; Panasenko, O.M. Kinetic Method for Assaying the Halogenating Activity of Myeloperoxidase Based on Reaction of Celestine Blue B with Taurine Halogenamines. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.V.; Kostevich, V.A.; Varfolomeeva, E.Y.; Grigorieva, D.V.; Gorudko, I.V.; Kozlov, S.O.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Mikhalchik, E.V.; Filatov, M.V.; Cherenkevich, S.N.; et al. Capacity of Ceruloplasmin to Scavenge Products of the Respiratory Burst of Neutrophils Is Not Altered by the Products of Reactions Catalyzed by Myeloperoxidase. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorudko, I.V.; Grigorieva, D.V.; Sokolov, A.V.; Shamova, E.V.; Kostevich, V.A.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Syromiatnikova, E.D.; Vasilyev, V.B.; Cherenkevich, S.N.; Panasenko, O.M. Neutrophil Activation in Response to Monomeric Myeloperoxidase. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.; Fernandes, E.; Roleira, F. Progress Towards the Discovery of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.N.; Nicklin, H.G. The Chemistry of Pernitrites. Part I. Kinetics of Decomposition of Pernitrous Acid. J. Chem. Soc. Inorg. Phys. Theor. 1968, 0, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.L.; Winefordner, J.D. Limit of Detection. A Closer Look at the IUPAC Definition. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 712A–724A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churashova, I.A.; Sokolov, A.V.; Kostevich, V.A.; Gorbunov, N.P.; Runova, O.L.; Firova, E.M.; Vasilyev, V.B. Myeloperoxidase/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio in Patients with Arterial Hypertension and Chronic Coronary Heart Disease. Med. Acad. J. 2021, 21, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorudko, I.V.; Mukhortava, A.V.; Caraher, B.; Ren, M.; Cherenkevich, S.N.; Kelly, G.M.; Timoshenko, A.V. Lectin-Induced Activation of Plasma Membrane NADPH Oxidase in Cholesterol-Depleted Human Neutrophils. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 516, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemmig, J.; Zschaler, J.; Remmler, J.; Arnhold, J. The Fluorescein-Derived Dye Aminophenyl Fluorescein Is a Suitable Tool to Detect Hypobromous Acid (HOBr)-Producing Activity in Eosinophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 27913–27923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeChatelet, L.; Shirley, P.; Johnston, R.J. Effect of Phorbol Myristate Acetate on the Oxidative Metabolism of Human Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes. Blood 1976, 47, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, G.P.; Chan, C.K.; Lea, P.; Takai, A.; Grinstein, S. Phorbol Ester-Induced Actin Assembly in Neutrophils: Role of Protein Kinase C. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 116, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldefie-Chézet, F.; Walrand, S.; Moinard, C.; Tridon, A.; Chassagne, J.; Vasson, M.-P. Is the Neutrophil Reactive Oxygen Species Production Measured by Luminol and Lucigenin Chemiluminescence Intra or Extracellular? Comparison with DCFH-DA Flow Cytometry and Cytochrome c Reduction. Clin. Chim. Acta 2002, 319, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.G.; Bralove, D.A.; Gallin, J.I. The Differential Mobilization of Human Neutrophil Granules. Effects of Phorbol Myristate Acetate and Ionophore A23187. Am. J. Pathol. 1977, 87, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, T.; Wilcke, J.; Chilcoat, C.; Eyre, P.; Crisman, M. Functional Characterization of Equine Neutrophils in Response to Calcium Ionophore A23187 and Phorbol Myristate Acetate Ex Vivo. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1997, 56, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettle, A.J.; Gedye, C.A.; Winterbourn, C.C. Mechanism of Inactivation of Myeloperoxidase by 4-Aminobenzoic Acid Hydrazide. Biochem. J. 1997, 321, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.; Lo, A.; Logan, M.R.; Lacy, P.; Eitzen, G. Primary Granule Exocytosis in Human Neutrophils Is Regulated by Rac-Dependent Actin Remodeling. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C1354–C1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkina, S.I.; Fedorova, N.V.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Arifulin, E.A.; Stadnichuk, V.I.; Baratova, L.A.; Sud’ina, G.F. Mold Alkaloid Cytochalasin D Modifies the Morphology and Secretion of FMLP-, LPS-, or PMA-Stimulated Neutrophils upon Adhesion to Fibronectin. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4308684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, F.R.; Kelher, M.R.; Moore, E.E.; McLaughlin, N.J.D.; Banerjee, A.; Silliman, C.C. Structural Organization of the Neutrophil NADPH Oxidase: Phosphorylation and Translocation during Priming and Activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 78, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Kill Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasler, P.; Giaglis, S.; Hahn, S. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Health and Disease. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2016, 146, w14352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A.R.; Foutch, P.G.; Crouch, M.M.; Garanich, P.A. A Routine Celestin Blue B and Eosin Stain for Paraffin Tissue Sections. Lab. Med. 1975, 6, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyer, H.; Babich, E. A Hematoxylin and Eosin-Like Stain for Glycol Methacrylate Embedded Tissue Sections. Stain Technol. 1981, 56, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapson, R.; Horobin, R.; Kiernan, J. Hematoxylin Shortages: Their Causes and Duration, and Other Dyes That Can Replace Hemalum in Routine Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining. Biotech. Histochem. 2010, 85, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshenko, A.V.; Kayser, K.; Drings, P.; André, S.; Dong, X.; Kaltner, H.; Schneller, M.; Gabius, H.-J. Carbohydrate-Binding Proteins (Plant/Human Lectins and Autoantibodies from Human Serum) as Mediators of Release of Lysozyme, Elastase, and Myeloperoxidase from Human Neutrophils. Res. Exp. Med. 1995, 195, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, E.F.; Herzig, A.; Krüger, R.; Muth, A.; Mondal, S.; Thompson, P.R.; Brinkmann, V.; von Bernuth, H.; Zychlinsky, A. Diverse Stimuli Engage Different Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Pathways. eLife 2017, 6, e24437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, A.V.; Kostevich, V.A.; Zakharova, E.T.; Samygina, V.R.; Panasenko, O.M.; Vasilyev, V.B. Interaction of Ceruloplasmin with Eosinophil Peroxidase as Compared to Its Interplay with Myeloperoxidase: Reciprocal Effect on Enzymatic Properties. Free Radic. Res. 2015, 49, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Activation Stimuli | Concentration | Fluorescence Intensity (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|
| PMA 1 | 50 nM | 0.139 ± 0.004 * |
| fMLP | 1 μM | 0.130 ± 0.028 * |
| WGA | 50 mg/L | 0.090 ± 0.003 * |
| CAA | 75 mg/L | 0.150 ± 0.045 * |
| PHA-L | 100 mg/L | 0.076 ± 0.020 * |
| Con A | 100 mg/L | 0.083 ± 0.044 * |
| SNA | 75 mg/L | n/d 2 |
| SBA | 100 mg/L | n/d 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reut, V.E.; Kozlov, S.O.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Grudinina, N.A.; Kostevich, V.A.; Gorbunov, N.P.; Grigorieva, D.V.; Kalvinkovskaya, J.A.; Bushuk, S.B.; Varfolomeeva, E.Y.; et al. New Application of the Commercially Available Dye Celestine Blue B as a Sensitive and Selective Fluorescent “Turn-On” Probe for Endogenous Detection of HOCl and Reactive Halogenated Species. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11091719
Reut VE, Kozlov SO, Kudryavtsev IV, Grudinina NA, Kostevich VA, Gorbunov NP, Grigorieva DV, Kalvinkovskaya JA, Bushuk SB, Varfolomeeva EY, et al. New Application of the Commercially Available Dye Celestine Blue B as a Sensitive and Selective Fluorescent “Turn-On” Probe for Endogenous Detection of HOCl and Reactive Halogenated Species. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(9):1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11091719
Chicago/Turabian StyleReut, Veronika E., Stanislav O. Kozlov, Igor V. Kudryavtsev, Natalya A. Grudinina, Valeria A. Kostevich, Nikolay P. Gorbunov, Daria V. Grigorieva, Julia A. Kalvinkovskaya, Sergey B. Bushuk, Elena Yu Varfolomeeva, and et al. 2022. "New Application of the Commercially Available Dye Celestine Blue B as a Sensitive and Selective Fluorescent “Turn-On” Probe for Endogenous Detection of HOCl and Reactive Halogenated Species" Antioxidants 11, no. 9: 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11091719
APA StyleReut, V. E., Kozlov, S. O., Kudryavtsev, I. V., Grudinina, N. A., Kostevich, V. A., Gorbunov, N. P., Grigorieva, D. V., Kalvinkovskaya, J. A., Bushuk, S. B., Varfolomeeva, E. Y., Fedorova, N. D., Gorudko, I. V., Panasenko, O. M., Vasilyev, V. B., & Sokolov, A. V. (2022). New Application of the Commercially Available Dye Celestine Blue B as a Sensitive and Selective Fluorescent “Turn-On” Probe for Endogenous Detection of HOCl and Reactive Halogenated Species. Antioxidants, 11(9), 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11091719








