Identification of Lipocalin 2 as a Ferroptosis-Related Key Gene Associated with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage via STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.2. DEGs Screening and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.3. Immune Infiltration Analysis through CIBERSORT
2.4. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.5. Identification of Ferroptosis-HIBD Genes and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.6. ANN for Constructing an HIBD Classification Model
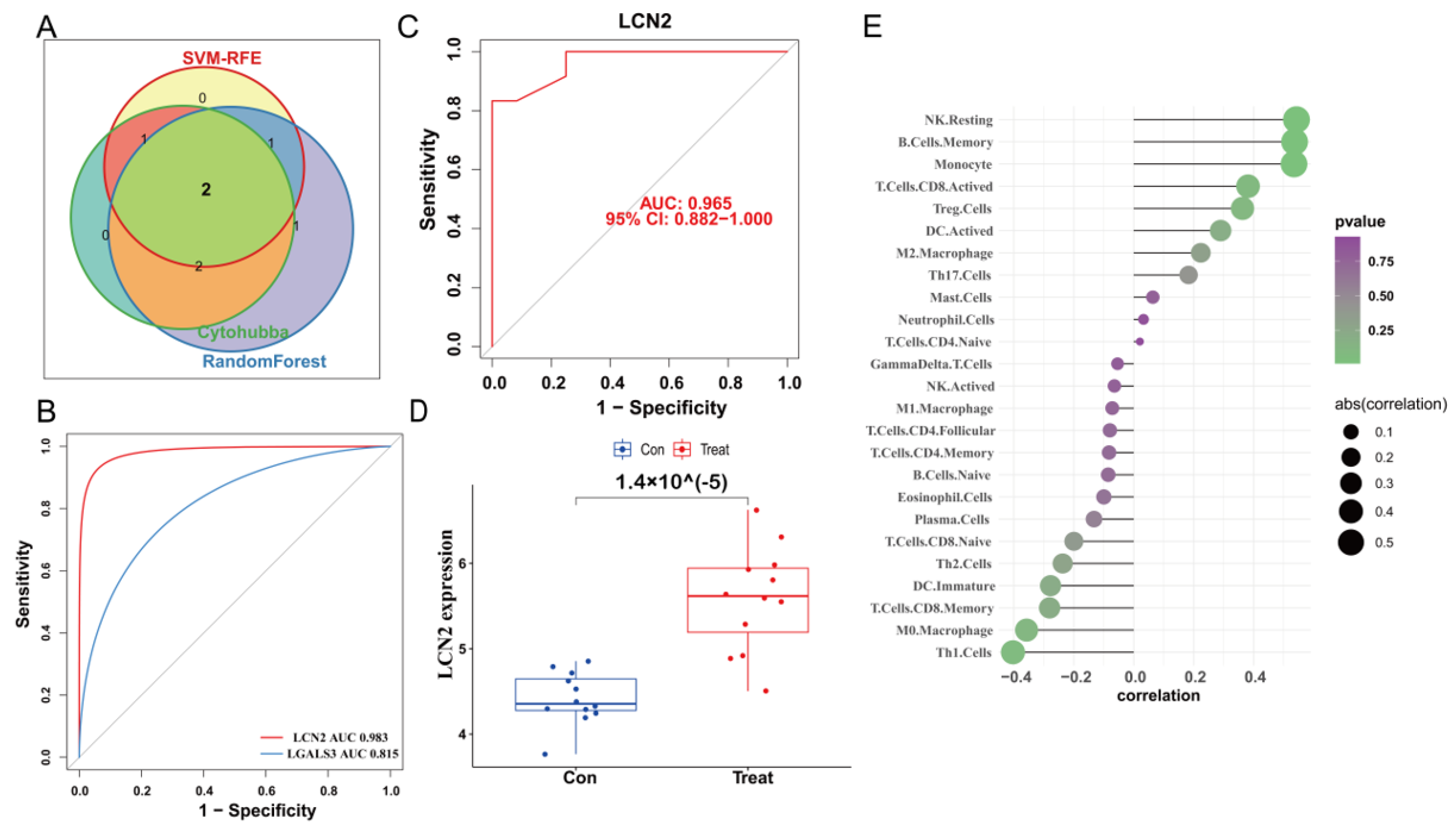
2.7. Construction of PPI Network and Identification of the Hub Genes
2.8. Validation of Expression Levels and the Diagnostic Value of the Core Hub Gene
2.9. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.10. Gene Knockdown by siRNA
- si-NC, sense (5′-3′): UUC UCC GAA CGU GUC ACG UTT, antisense (5′-3′): ACG UGA CAC GUU CGG AGA ATT;
- si-LCN2(1), sense (5′-3′): GGU CCA GAA AGA AAG ACA ATT, antisense (5′-3′): UUG UCU UUC UUU CUG GAC CTT;
- si-LCN2(2), sense (5′-3′): GCU ACU GGA UCA GAA CAU UTT, antisense (5′-3′): AAU GUU CUG AUC CAG UAG CTT;
- si-LCN2(3), sense (5′-3′): CCG ACC AAU GCA UUG ACA ATT, antisense (5′-3′): UUG UCA AUG CAU UGG UCG GTT.
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Lipid Peroxidation
2.13. Fe2+ Content
2.14. mtROS
2.15. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
2.16. Immunofluorescence (IF)
2.17. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.18. Percentage of Cell Death
2.19. Cell Viability Assay
2.20. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
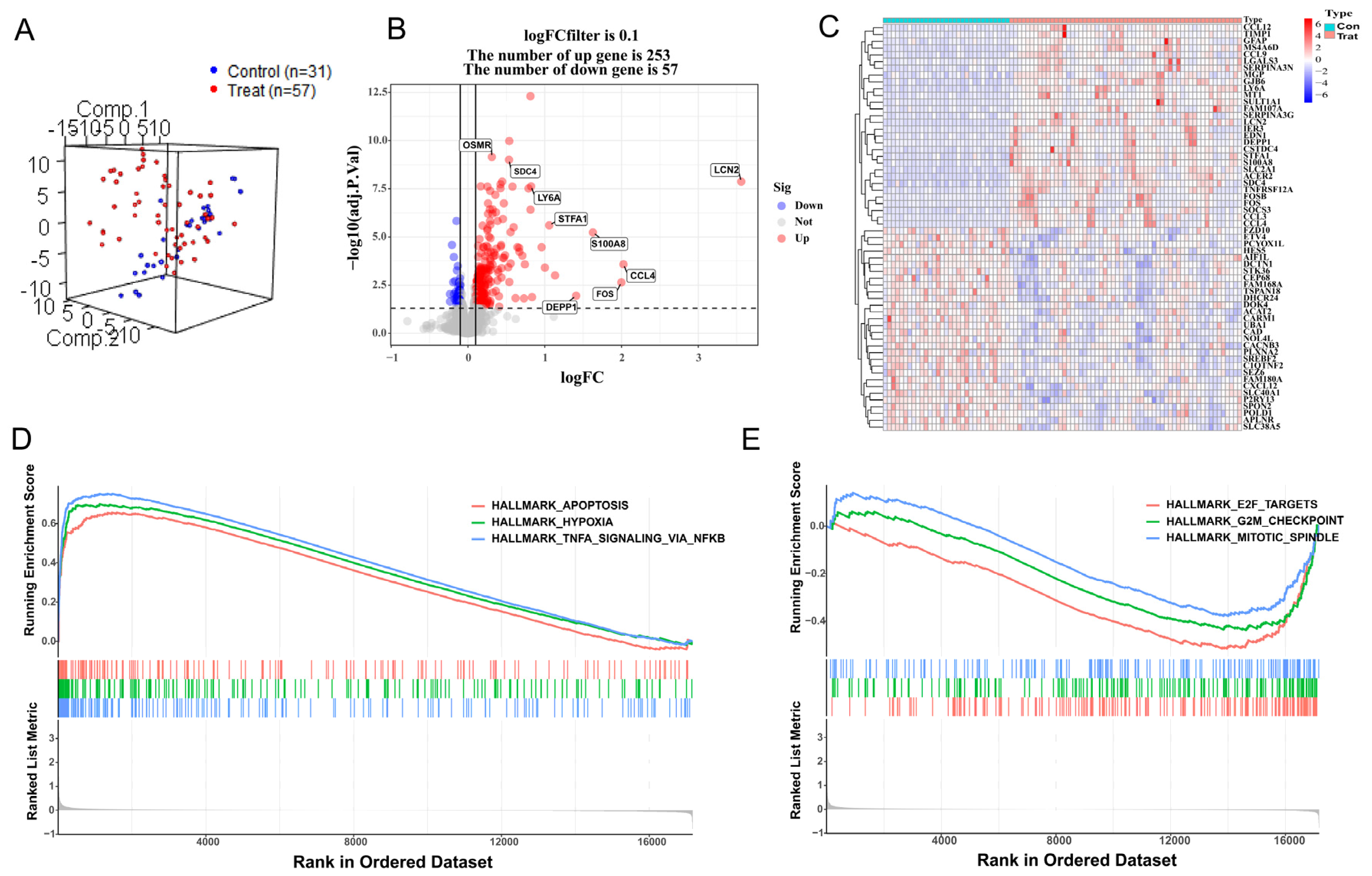
3.1. DEG Analysis and GSEA
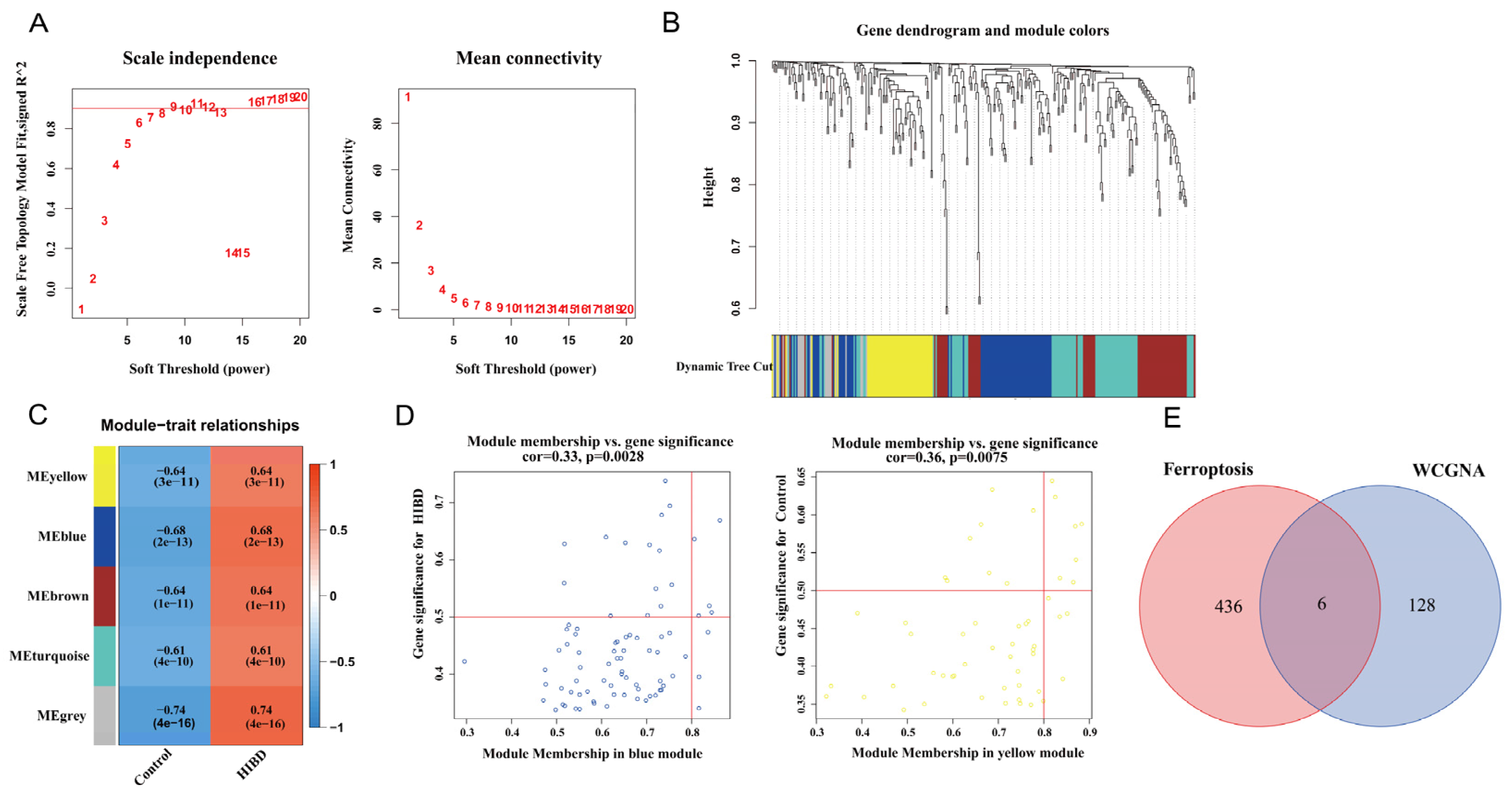
3.2. Construction of Weighted Co-Expression Network and Screening of Significant Modules
3.3. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
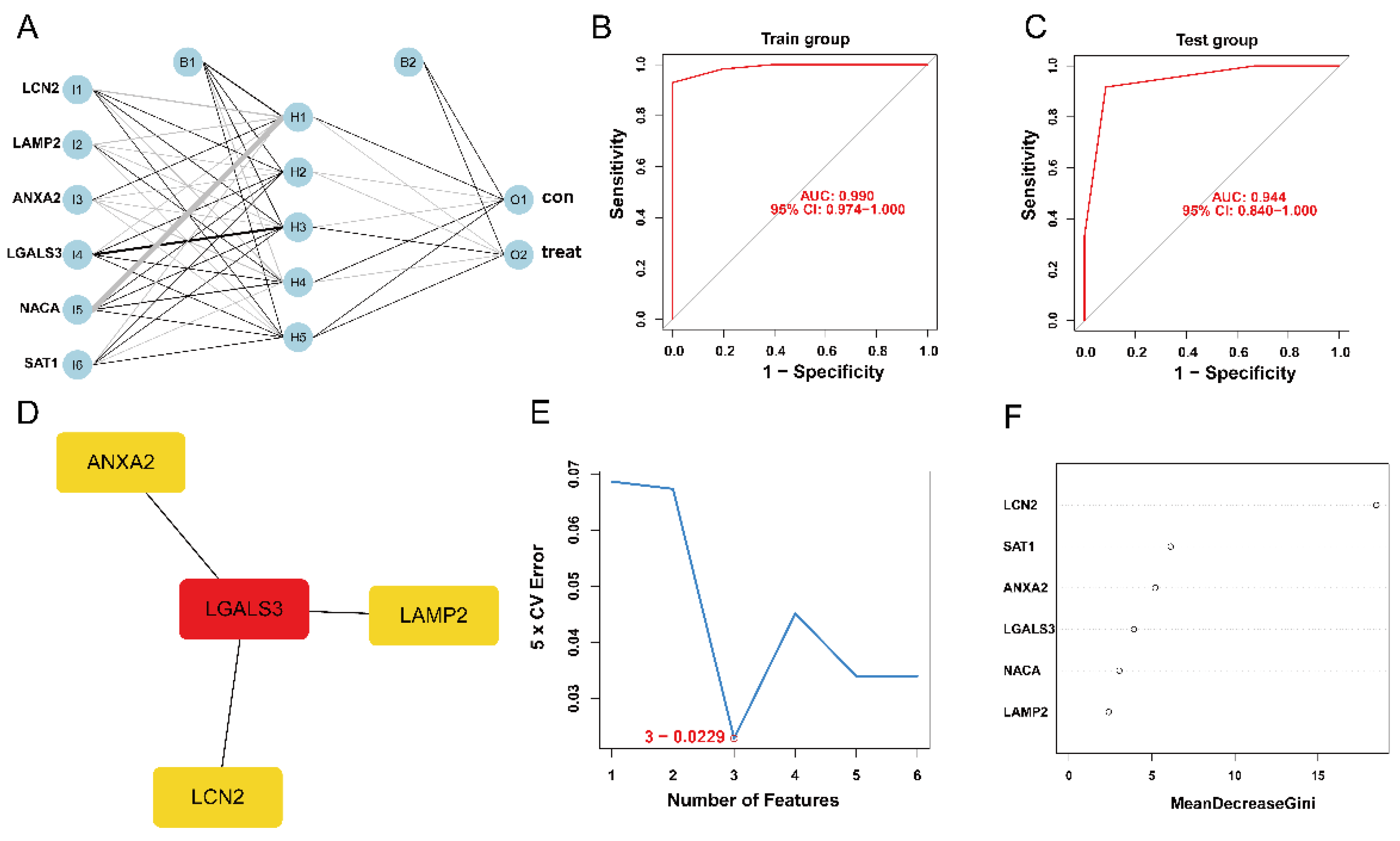
3.4. Establishment and Validation of ANN Model
3.5. Construction of PPI Network and Identification of the Hub Genes
3.6. Validation of LCN2 and Correlation Analysis between LCN2 and Immune Cell Infiltration
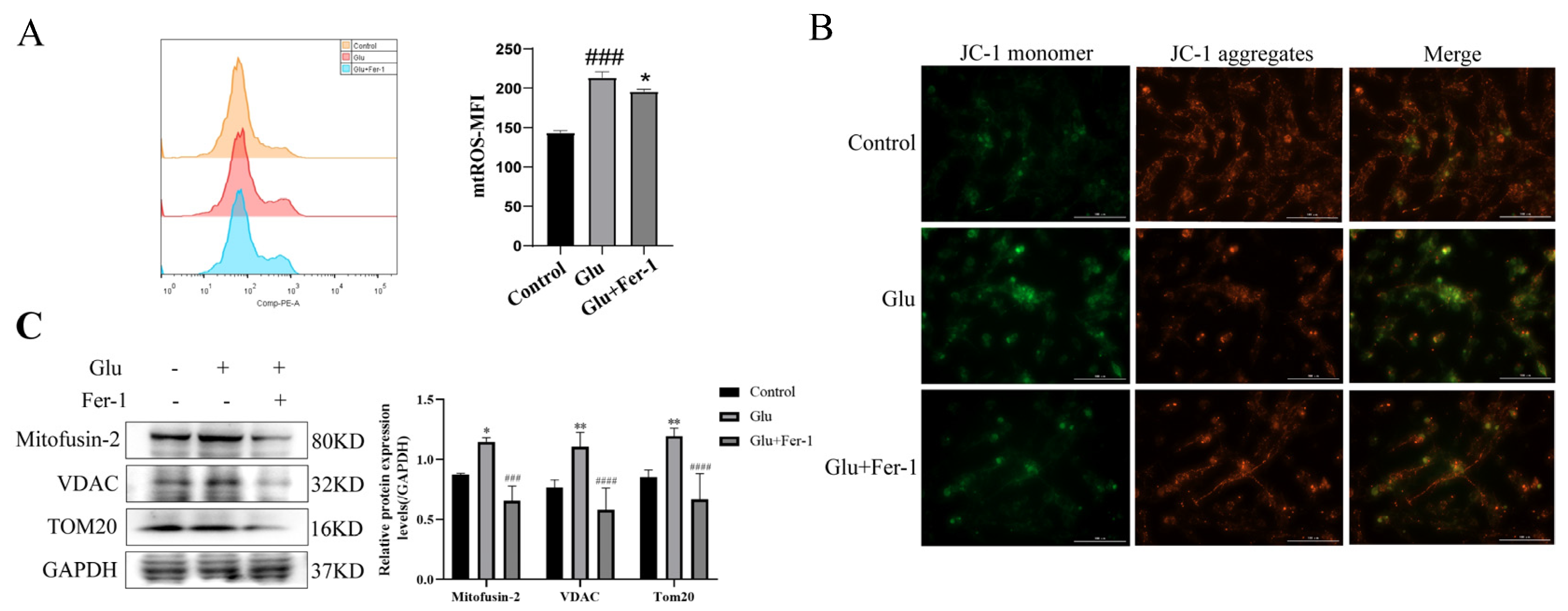
3.7. LCN2 Is Highly Expressed in Glutamate-Induced HT22 Cell Model, Which Can Be Reversed by Ferroptosis Inhibition
3.8. Glutamate Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in HT22 Cells
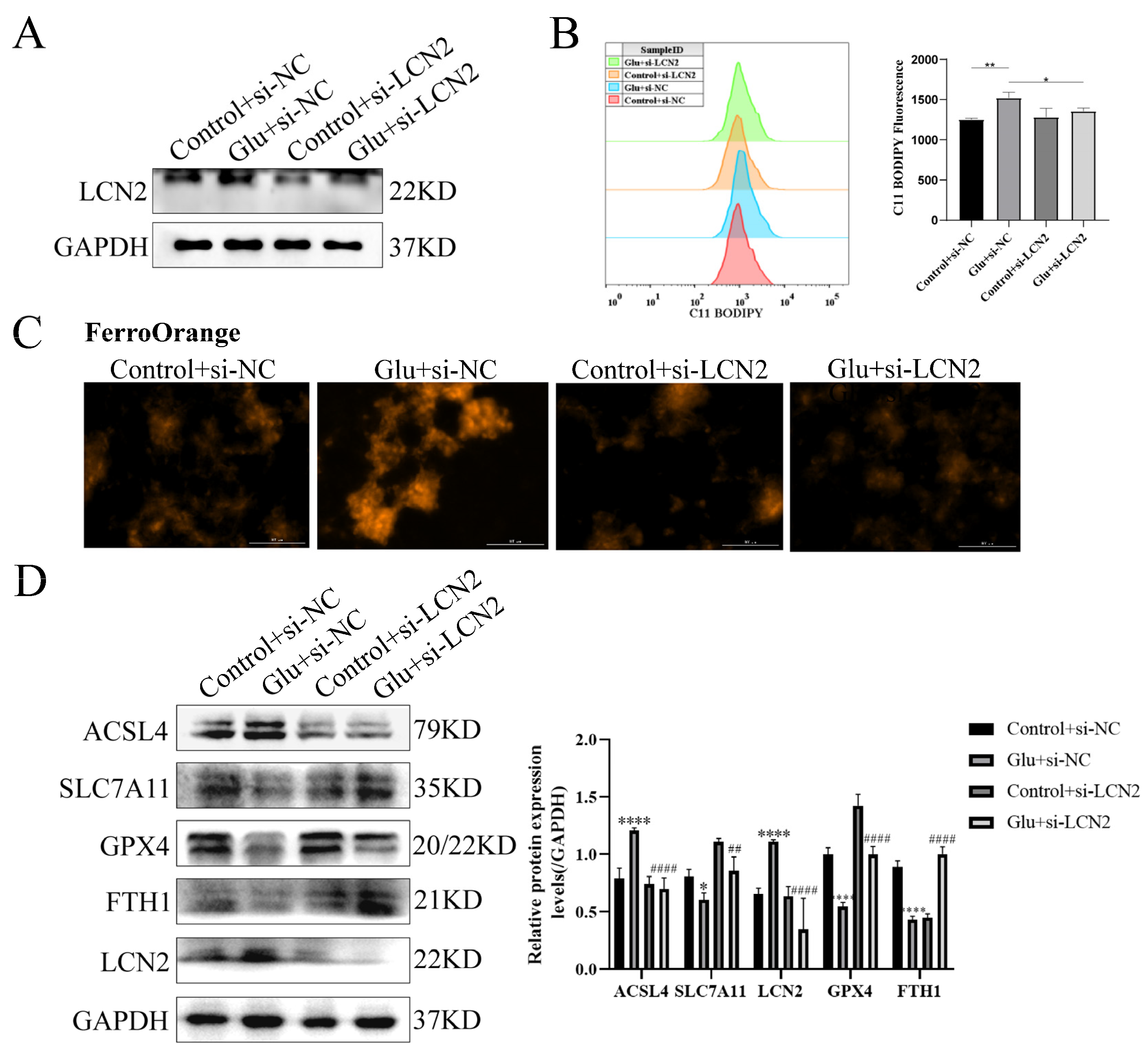
3.9. Knockdown of LCN2 Rescues Glutamate-Induced Mitochondria-Mediated Ferroptosis in HT22 Cells
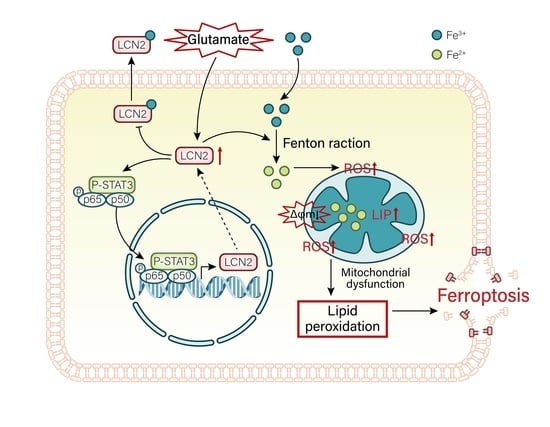
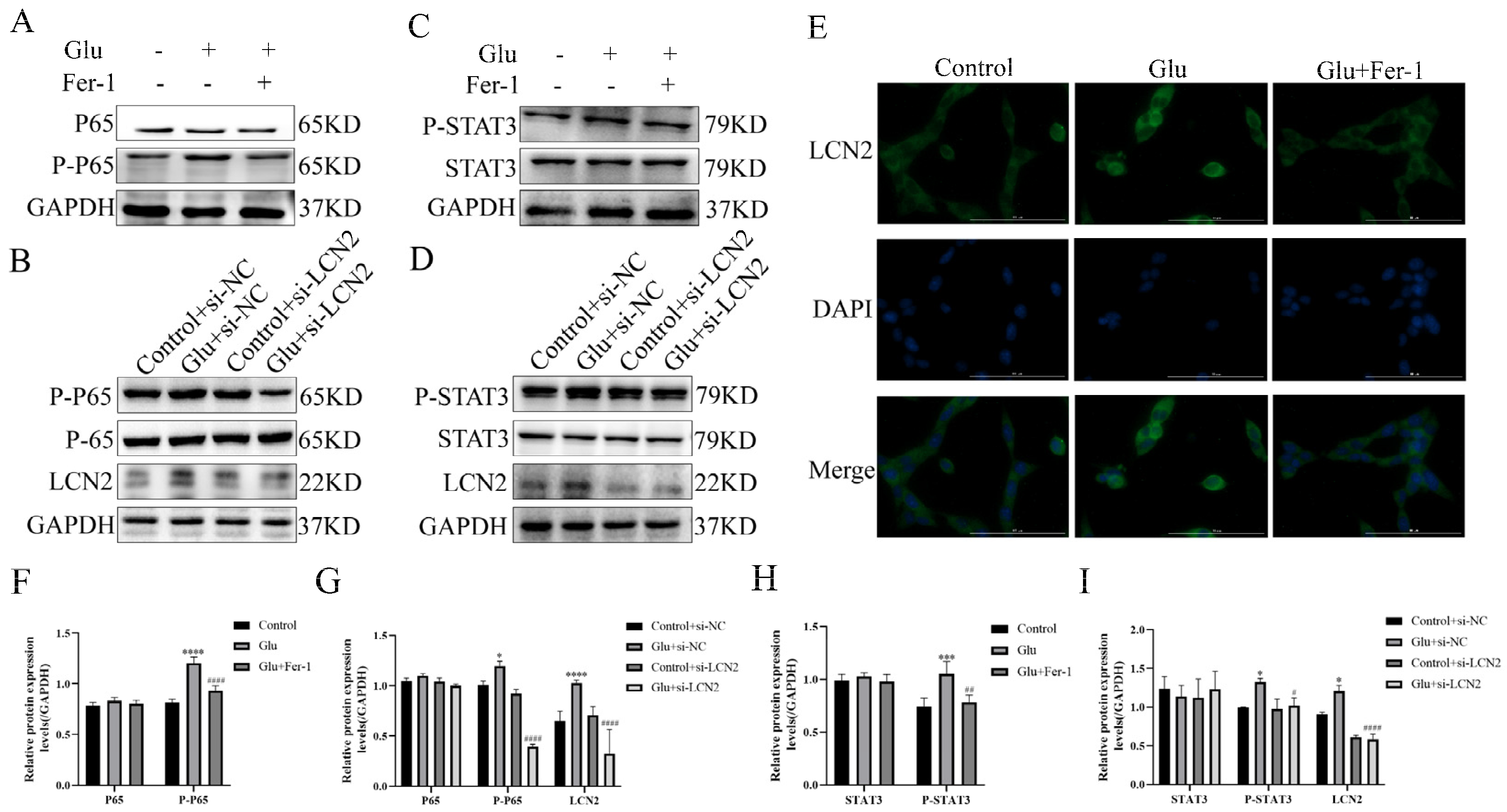
3.10. LCN2 Inhibits Glutamate-Induced Mitochondria-Mediated Ferroptosis in HT22 Cells through NF-κB/STAT3 Axis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobs, S.; Hunt, R.; Tarnow-Mordi, W.; Inder, T.; Davis, P. Cooling for newborns with hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, Cd003311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzopardi, D.; Strohm, B.; Marlow, N.; Brocklehurst, P.; Deierl, A.; Eddama, O.; Goodwin, J.; Halliday, H.L.; Juszczak, E.; Kapellou, O.; et al. Effects of hypothermia for perinatal asphyxia on childhood outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, G.; Zhuang, L.; Gan, B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, C.O.; de Freitas, F.A.; Sampaio-Silva, J.; Rokita-Rosa, L.; Barros, P.L.; Levy, D.; Bydlowski, S.P. Ferroptosis Mechanisms Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Zhu, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Wu, S.; Hei, M. Glycyrrhizin Attenuates Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage by Inhibiting Ferroptosis and Neuroinflammation in Neonatal Rats via the HMGB1/GPX4 Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8438528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Z.; Fu, X. Ferroptosis is Involved in Hypoxic-ischemic Brain Damage in Neonatal Rats. Neuroscience 2022, 487, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekens, D.W.; Eisel, U.L.M.; Gouweleeuw, L.; Schoemaker, R.G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Naudé, P.J.W. Lipocalin 2 as a link between ageing, risk factor conditions and age-related brain diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Jeong, J.H.; Song, J. Lipocalin 2 regulates iron homeostasis, neuroinflammation, and insulin resistance in the brains of patients with dementia: Evidence from the current literature. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.C.; Santos, T.; Sampaio-Marques, B.; Novais, A.; Mesquita, S.D.; Ludovico, P.; Bernardino, L.; Correia-Neves, M.; Sousa, N.; Palha, J.A.; et al. Lipocalin-2 regulates adult neurogenesis and contextual discriminative behaviours. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, B.; Zhu, X.; Norgard, M.A.; Diba, P.; Levasseur, P.R.; Buenafe, A.C.; Huisman, C.; Burfeind, K.G.; Michaelis, K.A.; Kong, G.; et al. Chronic cerebral lipocalin 2 exposure elicits hippocampal neuronal dysfunction and cognitive impairment. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 97, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Fang, P. Asiaticoside attenuates neonatal hypoxic–ischemic brain damage through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/STAT3 pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebhan, M.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Prilusky, J.; Lancet, D. GeneCards: Integrating information about genes, proteins and diseases. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Horvath, S. Network neighborhood analysis with the multi-node topological overlap measure. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasz, E.; Somera, A.L.; Mongru, D.A.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabási, A.L. Hierarchical organization of modularity in metabolic networks. Science 2002, 297, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. Eigengene networks for studying the relationships between co-expression modules. BMC Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, M.W. NeuralNetTools: Visualization and Analysis Tools for Neural Networks. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D447–D452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. S4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.L.; Hung, Y.H.; Lee, W.M.; Li, R.K.; Jiang, B.R. SVM-RFE based feature selection and Taguchi parameters optimization for multiclass SVM classifier. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 795624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, H.; Valim, C.; Vegas, E.; Oller, J.M.; Reverter, F. SVM-RFE: Selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, G.; Rossetto, M.; Di Paolo, M.L.; Orian, L.; Venerando, R.; Roveri, A.; Vučkovi, A.M.; Bosello Travain, V.; Zaccarin, M.; Zennaro, L.; et al. Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, V.E.; Mao, G.; Qu, F.; Angeli, J.P.; Doll, S.; Croix, C.S.; Dar, H.H.; Liu, B.; Tyurin, V.A.; Ritov, V.B.; et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2054–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H. Identification of Potential Prognostic Genes for Neuroblastoma. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Peng, H.; Wu, Z. Establishment and Analysis of a Combined Diagnostic Model of Alzheimer’s Disease with Random Forest and Artificial Neural Network. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 921906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Dai, K.; Wen, T.; Peng, J.; Peng, X.; Zheng, Z.; Jiang, T.; et al. Construction of Novel Gene Signature-Based Predictive Model for the Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction by Combining Random Forest with Artificial Neural Network. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 876543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Zhang, X. Identification and validation of a classifier based on hub aging-related genes and aging subtypes correlation with immune microenvironment for periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1042484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.C.; Dá Mesquita, S.; Sousa, J.C.; Correia-Neves, M.; Sousa, N.; Palha, J.A.; Marques, F. From the periphery to the brain: Lipocalin-2, a friend or foe? Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 131, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nimer, F.; Elliott, C.; Bergman, J.; Khademi, M.; Dring, A.M.; Aeinehband, S.; Bergenheim, T.; Romme Christensen, J.; Sellebjerg, F.; Svenningsson, A.; et al. Lipocalin-2 is increased in progressive multiple sclerosis and inhibits remyelination. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F. Age-Associated Dopaminergic Neuron Loss and Midbrain Glia Cell Phenotypic Polarization. Neuroscience 2019, 415, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mike, E.V.; Makinde, H.M.; Gulinello, M.; Vanarsa, K.; Herlitz, L.; Gadhvi, G.; Winter, D.R.; Mohan, C.; Hanly, J.G.; Mok, C.C.; et al. Lipocalin-2 is a pathogenic determinant and biomarker of neuropsychiatric lupus. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 96, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, H.W.; Suk, K. Increased plasma levels of lipocalin 2 in mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 305, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekens, D.W.; Naudé, P.J.; Engelborghs, S.; Vermeiren, Y.; Van Dam, D.; Oude Voshaar, R.C.; Eisel, U.L.; De Deyn, P.P. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and its Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Brain Regions: Differential Findings in AD with and without Depression. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 55, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudé, P.J.; Eisel, U.L.; Comijs, H.C.; Groenewold, N.A.; De Deyn, P.P.; Bosker, F.J.; Luiten, P.G.; den Boer, J.A.; Oude Voshaar, R.C. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: A novel inflammatory marker associated with late-life depression. J. Psychosom. Res. 2013, 75, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naudé, P.J.; Nyakas, C.; Eiden, L.E.; Ait-Ali, D.; van der Heide, R.; Engelborghs, S.; Luiten, P.G.; De Deyn, P.P.; den Boer, J.A.; Eisel, U.L. Lipocalin 2: Novel component of proinflammatory signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Martinez, C.; Su, X.; Rosato, R.R.; Teng, H.; et al. A targetable LIFR-NF-κB-LCN2 axis controls liver tumorigenesis and vulnerability to ferroptosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, N.; Choudhary, B.S.; Shah, S.G.; Khapare, N.; Dwivedi, N.; Gaikwad, A.; Joshi, N.; Raichanna, J.; Basu, S.; Gurjar, M.; et al. Lipocalin 2 expression promotes tumor progression and therapy resistance by inhibiting ferroptosis in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1495–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschhorn, T.; Stockwell, B.R. The development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis: Death by Lipid Peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Jiang, X. The Chemistry and Biology of Ferroptosis. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Zhu, X.; Sun, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Shen, T.; Hei, M. Inhibition of TLR4 prevents hippocampal hypoxic-ischemic injury by regulating ferroptosis in neonatal rats. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 345, 113828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Li, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y. Vitamin D suppresses ferroptosis and protects against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Transl. Pediatr. 2022, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.J.; Xu, Z.X.; Wu, M.F.; Dong, G.Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Gao, J.Y.; Feng, C.X.; Feng, X. Resatorvid protects against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Neural. Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, R.; Jin, T.; Hu, K.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Vitamin D promotes the cisplatin sensitivity of oral squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting LCN2-modulated NF-κB pathway activation through RPS3. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Deng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ding, R.; Li, X. Identification of Lipocalin 2 as a Ferroptosis-Related Key Gene Associated with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage via STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010186
Luo L, Deng L, Chen Y, Ding R, Li X. Identification of Lipocalin 2 as a Ferroptosis-Related Key Gene Associated with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage via STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(1):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010186
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Lianxiang, Liyan Deng, Yongtong Chen, Rui Ding, and Xiaoling Li. 2023. "Identification of Lipocalin 2 as a Ferroptosis-Related Key Gene Associated with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage via STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway" Antioxidants 12, no. 1: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010186
APA StyleLuo, L., Deng, L., Chen, Y., Ding, R., & Li, X. (2023). Identification of Lipocalin 2 as a Ferroptosis-Related Key Gene Associated with Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage via STAT3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants, 12(1), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12010186