Isolation of Biologically Active Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by Using Different Extraction Solvents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
2.2.1. Preparation of Plant Extracts for Total Polyphenolic Compounds, Total Flavonoids, Total Phenolic Acids, Radical Scavenging Activity Analysis and Antimicrobial Testing
2.2.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts for Phytocannabinoids Analysis
2.2.3. Preparation of Plant Extracts for Organic Acids Determination
2.3. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds Content (TPC)
2.4. Determination of Total Flavonoids Content (TFC)
2.5. Determination of Total Amount of Polyphenolic Acids (TPA)
2.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.7. Quantitative Analysis of Phytocannabinoids
2.8. Quantitative Analysis of Organic Acids
2.9. Antimicrobial Activity
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
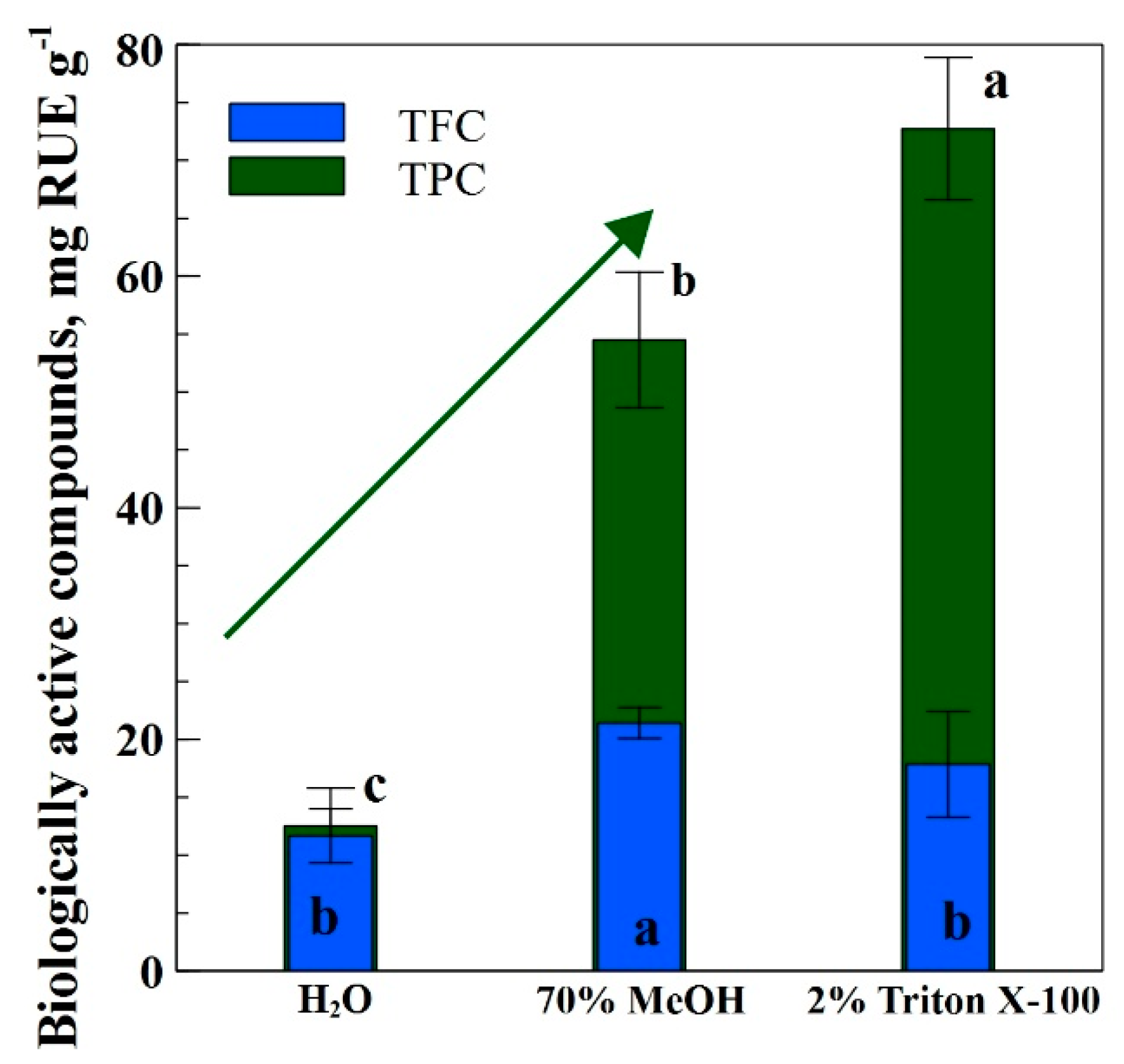
3.1. Spectrophotometric Results
3.2. The Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Hemp Inflorescence
3.3. Organic Acids Composition in Hemp Inflorescence
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karas, J.A.; Wong, L.J.M.; Paulin, O.K.A.; Mazeh, A.C.; Hussein, M.H.; Li, J.; Velkov, T. The Antimicrobial Activity of Cannabinoids. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šain, A.; Matešić, N.; Jurina, T.; Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Benković, M.; Valinger, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. Optimization of ethanol/water solvent extraction of bioactive components originating from industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Hrana u Zdravlju i Bolesti: Znanstveno-Stručni časopis za Nutricionizam i Dijetetiku 2020, 9, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Baldini, M.; Ferfuia, C.; Piani, B.; Sepulcri, A.; Dorigo, G.; Zuliani, F.; Danuso, F.; Cattivello, C. The Performance and Potentiality of Monoecious Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivars as a Multipurpose Crop. Agronomy 2018, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barčauskaitė, K.; Žydelis, R.; Ruzgas, R.; Bakšinskaitė, A.; Tilvikienė, V. The Seeds of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) a Source of Minerals and Biologically Active Compounds. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 13025–13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richins, R.D.; Rodriguez-Uribe, L.; Lowe, K.; Ferral, R.; O’connell, M.A. Accumulation of bioactive metabolites in cultivated medical Cannabis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiago, F.J.; Paiva, A.; Matias, A.A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Flowers and/or Leaves Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 892314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, A.; Leupin, M.; Kneubühl, M.; Pedan, V.; Chetschik, I. Evolution of the Polyphenol and Terpene Content, Antioxidant Activity and Plant Morphology of Eight Different Fiber-Type Cultivars of Cannabis Sativa L. Cultivated at Three Sowing Densities. Plants 2020, 9, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, D.; Molle, A.; Nabissi, M.; Santini, G.; Benelli, G. Valorizing industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-products: Cannabidiol enrichment in the inflorescence essential oil optimizing sample pre-treatment prior to distillation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 128, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väisänen, T.; Kilpeläinen, P.; Kitunen, V.; Lappalainen, R.; Tomppo, L. Effect of steam treatment on the chemical composition of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and identification of the extracted carbohydrates and other compounds. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 131, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, S.; Melzer, R.; Mccabe, P.F. Current Biology Cannabis sativa. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R8–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.-F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis sativa: The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Pan, Z. Cannabidiol and terpenes from hemp—Ingredients for future foods and processing technologies. J. Future Foods 2021, 1, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheljazkov, V.D.; Sikora, V.; Dincheva, I.; Kačániová, M.; Astatkie, T.; Semerdjieva, I.B.; Latkovic, D. Industrial, CBD, and Wild Hemp: How Different Are Their Essential Oil Profile and Antimicrobial Activity? Molecules 2020, 25, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barčauskaitė, K.; Bakšinskaitė, A.; Szumny, A.; Tilvikienė, V. Variation of secondary metabolites in Cannabis sativa L. inflorescences under applied agrotechnological measures. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 188, 115570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, R.A. Plant terpenes: Defense responses, phylogenetic analysis, regulation and clinical applications. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, L.; Castaldo, L.; Narváez, A.; Graziani, G.; Gaspari, A.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ritieni, A. Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Commercial Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences Using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS. Molecules 2020, 25, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, B.R.; Heleno, S.A.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic compounds: Current industrial applications, limitations and future challenges. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gengaihi, S.E.; Hamed, M.A.; Aboubaker, D.H.; Mossa, A.T. Flavonoids from sugar beet leaves as hepatoprotective agent. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 8, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Maravić, N.; Teslić, N.; Nikolić, D.; Dimić, I.; Šereš, Z.; Pavlić, B. From agricultural waste to antioxidant-rich extracts: Green techniques in extraction of polyphenols from sugar beet leaves. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 28, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miłek, M.; Marcinčáková, D.; Legáth, J. Polyphenols Content, Antioxidant Activity, and Cytotoxicity Assessment of Taraxacum officinale Extracts Prepared through the Micelle-Mediated Extraction Method. Molecules 2019, 24, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornpointner, C.; Martinez, A.S.; Marinovic, S.; Haselmair-Gosch, C.; Jamnik, P.; Schröder, K.; Löfke, C.; Halbwirth, H. Chemical composition and antioxidant potential of Cannabis sativa L. roots. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 165, 113422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkpeniet, V.N.; Essien, E.E.; Udoh, I.I. Effect of extraction conditions on total polyphenol contents, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Cannabis sativa L. Electron. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 11, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinzadeh, R.; Khorsandi, K.; Hemmaty, S. Study of the Effect of Surfactants on Extraction and Determination of Polyphenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Fruits Extracts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachura, N.; Kupczyński, R.; Sycz, J.; Kuklińska, A.; Zwyrzykowska-Wodzińska, A.; Wińska, K.; Owczarek, A.; Kuropka, P.; Nowaczyk, R.; Bąbelewski, P.; et al. Biological Potential and Chemical Profile of European Varieties of Ilex. Foods 2022, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Naeem, A.; Calkaite, I.; Hosney, A.; Depar, N.; Barcauskaite, K. Zinc (Zn) mitigates copper (Cu) toxicity and retrieves yield and quality of lettuce irrigated with Cu and Zn-contaminated simulated wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgel, L.; Hartung, J.; Pflugfelder, A.; Graeff-Hönninger, S. Impact of Growth Stage and Biomass Fractions on Cannabinoid Content and Yield of Different Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Genotypes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.N. Essential fatty acids: Biochemistry, physiology and pathology. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 420–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, A.; Nanda, A.; Kumar, P.; Narasimhan, B. Synthesis, antimicrobial evaluation and QSAR studies of gallic acid derivatives. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2870–S2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, A.-M.; Lee, I.-K.; Lee, S.-Y.; Yun, B.-S.; Kang, H.-W. Oxalic Acid from Lentinula edodes Culture Filtrate: Antimicrobial Activity on Phytopathogenic Bacteria and Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses. Mycobiology 2018, 44, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinenghi, L.D.; Jønsson, R.; Lund, T.; Jenssen, H. Isolation, Purification, and Antimicrobial Characterization of Cannabidiolic Acid and Cannabidiol from Cannabis sativa L. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwizhi, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Cinnamic Acid Derivatives and Their Biological Efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, A.; José, H.; Homem, V.; Simões, M. Comparison of Techniques and Solvents on the Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential of Extracts from Acacia dealbata and Olea europaea. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalata, M.; Dreger, M.; Zielińska, A.; Banach, J.; Szalata, M.; Wielgus, K. Simple Extraction of Cannabinoids from Female Inflorescences of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Molecules 2022, 27, 5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čalkaitė, I.; Kundrotaitė, A.; Tilvikienė, V.; Barčauskaitė, K. The effect of sowing rate on the bioaccumulation of biologically active compounds and their radical scavenging activity in Cannabis sativa L. Chemija 2022, 33, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citti, C.; Russo, F.; Sgrò, S.; Gallo, A.; Zanotto, A.; Forni, F.; Vandelli, M.A.; Laganà, A.; Montone, C.M.; Gigli, G.; et al. Pitfalls in the analysis of phytocannabinoids in cannabis inflorescence. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4009–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzorati, S.; Friscione, D.; Picchi, E.; Verotta, L. Cannabidiol from inflorescences of Cannabis sativa L.: Green extraction and purification processes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 155, 112816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Duan, S.; Liu, L. Bioassay-Guided Isolation and Identification of Antibacterial Components against Escherichia coli from Industrial Hemp Leaves. Separations 2023, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostapczuk, K.; Apori, S.O.; Estrada, G.; Tian, F. Hemp Growth Factors and Extraction Methods Effect on Antimicrobial Activity of Hemp Seed Oil: A Systematic Review. Separations 2021, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, A.; Di Simone, S.C.; Canini, A.; Braglia, R.; Di Marco, G.; Campana, C.; Angelini, P.; Flores, G.A.; Venanzoni, R.; Libero, M.L.; et al. Phytochemical and biological investigations on the pollen from industrial hemp male inflorescences. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giselle, F.; Azucena, I.; Dalila, O.; Florencia, F.; Facundo, R.; Giulia, M.; Sandra, F.; Maggi, M.; Ramirez, C.L. Antibacterial activity of cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) female inflorescence and root extract against Paenibacillus larvae, causal agent of American foulbrood. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 47, 102575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| CBDVA | CBL | CBD | CBC | CBN | CBG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemp inflorescences | % | |||||
| 0.094 ± 0.0890 | 0.024 ± 0.0009 | 2.50 ± 0.1048 | 0.330 ± 0.1217 | 0.022 ± 0.0000 | 0.134 ± 0.0093 | |
| Phenolic Acids | Min | Max | Mean | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cinnamic acid, TMS derivative | 0.48 | 2.19 | 1.06 | 82.33 |
| Gallic acid, 4 TMS derivative | 0.88 | 1.13 | 1.03 | 11.75 |
| Other Organic Acids | ||||
| Monoamidomalonic acid, 3 TMS derivative | 1.00 | 5.11 | 2.85 | 68.63 |
| Palmitic acid, TMS derivative | 8.79 | 11.88 | 10.31 | 10.54 |
| Arachidonic acid, TMS derivative | 0.24 | 1.56 | 0.77 | 83.96 |
| Arachidic acid, TMS derivative | 0.64 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 16.49 |
| Linoleic acid, TMS derivative | 13.01 | 24.91 | 18.89 | 24.16 |
| Alfa-linolenic acid, TMS derivative | 9.47 | 17.13 | 12.92 | 25.13 |
| Oleic acid, TMS derivative | 1.71 | 3.25 | 2.76 | 21.84 |
| Stearic acid, TMS derivative | 3.24 | 5.14 | 4.36 | 15.78 |
| Cannabidivarinic acid, TMS derivative | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.56 | 7.14 |
| Cannabidiolic acid, TMS derivative | 15.43 | 24.99 | 19.82 | 21.63 |
| Oxalic acid, TMS derivative | 0.38 | 1.18 | 0.70 | 62.60 |
| Malonic acid, TMS derivative | 0.11 | 1.46 | 1.04 | 50.89 |
| No | Microorganism Strain | Strain Identification Number | Width of Growth Inhibition Zone, mm (Mean ± Standard Deviation) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | 70% MeOH | 2% Triton X-100 | |||
| 1 | S. aureus | ATCC 25923 | 4.0 ± 1.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 12.0 ± 3.0 |
| 2 | B. cereus | ATCC 11778 | 4.5 ± 1.5 | 19.5 ± 0.5 | 14.5 ± 1.0 |
| 3 | B. subtilis | ATCC 6633 | 7.0 ± 2.0 | 14.5 ± 0.5 | 19.5 ± 1.5 |
| 4 | L. monocytogenes | ATCC 13932 | 5.5 ± 1.5 | 14.5 ± 1.0 | 14.5 ± 0.5 |
| 5 | B. megaterium | ATCC 33085 | 3.0 ± 1.5 | 14.5 ± 0.5 | 15.0 ± 4.7 |
| 6 | E. faecalis | ATCC 19433 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 14.5 ± 2.0 | 4.5 ± 0.5 |
| 7 | M. luteus | ATCC 9341 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 14.5 ± 1.0 | 9.5 ± 1.0 |
| 8 | S. enteritidis | ATCC 13076 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 14.5 ± 0.5 | 4.5 ± 0.5 |
| 9 | E. coli | ATCC 8739 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 10.0 ± 2.5 |
| 10 | P. aeruginosa | ATCC 10145 | 7.0 ± 1.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 22.0 ± 1.5 |
| 11 | S. typhymurium | ATCC 14028 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 2.5 ± 2.0 |
| 12 | C. albicans | ATCC 10231 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 3.5 ± 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motiejauskaitė, D.; Ullah, S.; Kundrotaitė, A.; Žvirdauskienė, R.; Bakšinskaitė, A.; Barčauskaitė, K. Isolation of Biologically Active Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by Using Different Extraction Solvents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050998
Motiejauskaitė D, Ullah S, Kundrotaitė A, Žvirdauskienė R, Bakšinskaitė A, Barčauskaitė K. Isolation of Biologically Active Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by Using Different Extraction Solvents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(5):998. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050998
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotiejauskaitė, Dovilė, Sana Ullah, Algimanta Kundrotaitė, Renata Žvirdauskienė, Aušra Bakšinskaitė, and Karolina Barčauskaitė. 2023. "Isolation of Biologically Active Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by Using Different Extraction Solvents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity" Antioxidants 12, no. 5: 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050998
APA StyleMotiejauskaitė, D., Ullah, S., Kundrotaitė, A., Žvirdauskienė, R., Bakšinskaitė, A., & Barčauskaitė, K. (2023). Isolation of Biologically Active Compounds from Cannabis sativa L. Inflorescences by Using Different Extraction Solvents and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity. Antioxidants, 12(5), 998. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12050998








