Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance during Single and Repeated Bouts of Short-Duration High-Intensity Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
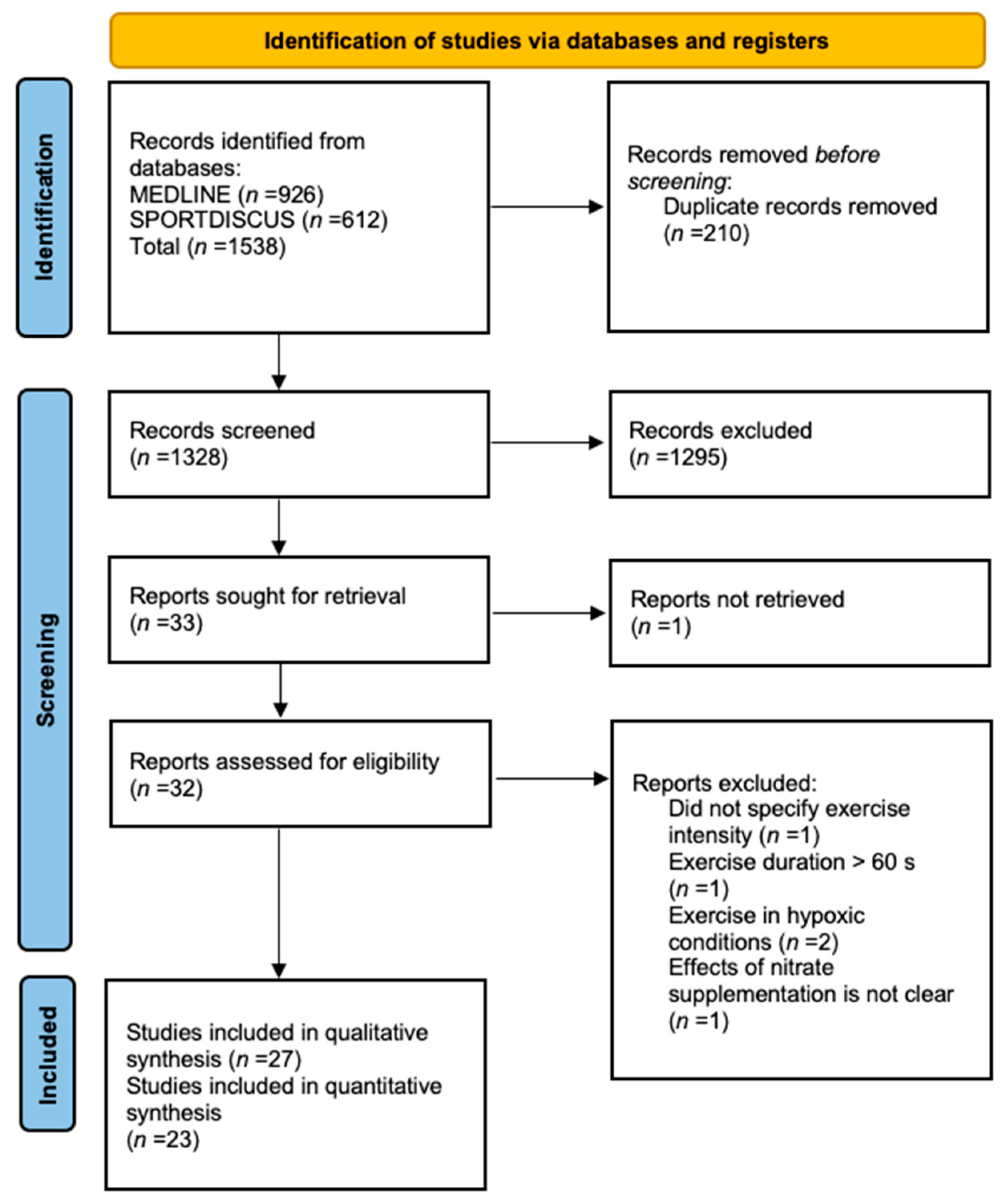
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
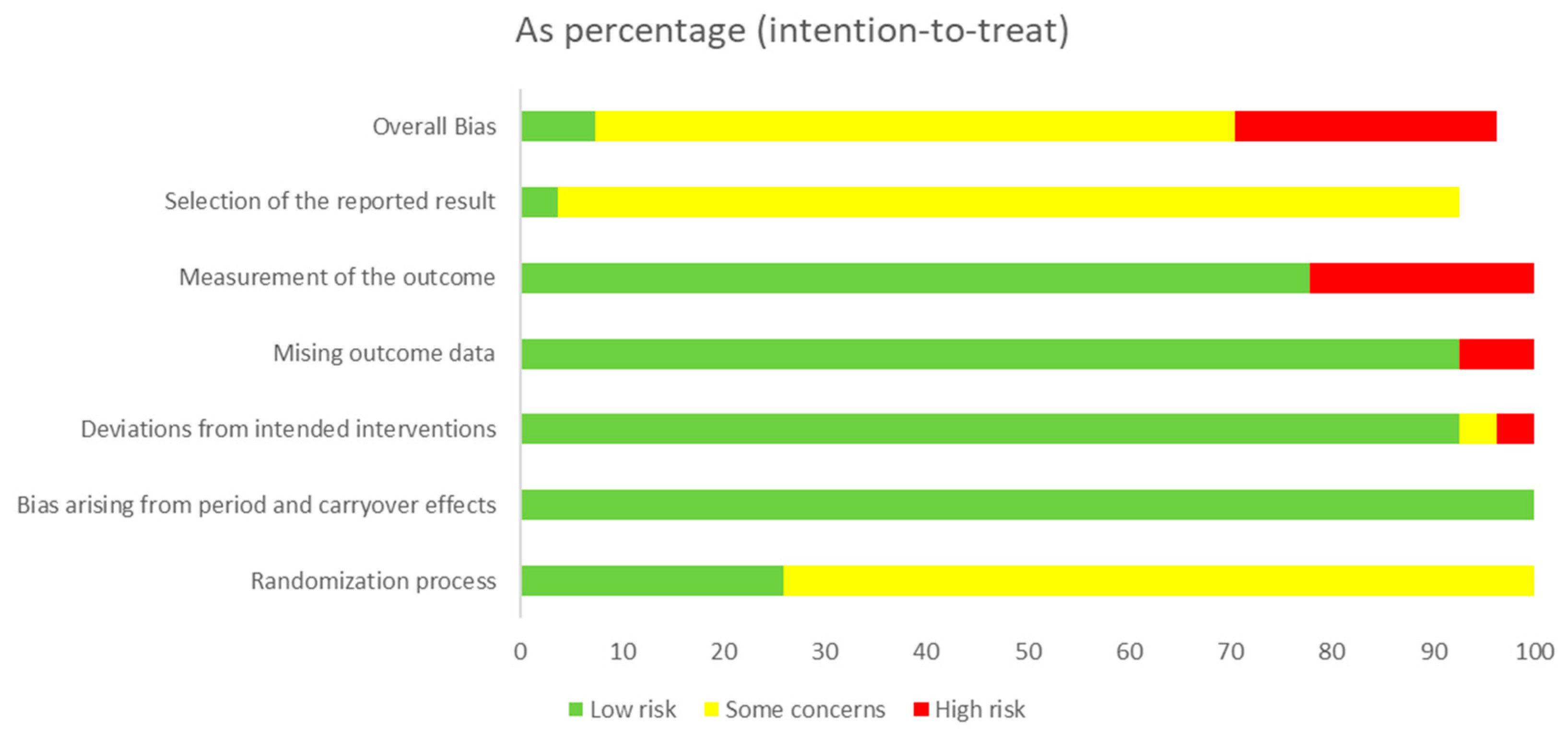
2.5. Quality Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Quality Assessment
3.3. Meta-Analysis
3.3.1. Time to Reach Peak Power
3.3.2. Peak Power
3.3.3. Mean Power
3.3.4. Total Work Done
3.3.5. Total Distance Covered
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Gladwin, M.T. The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway in Physiology and Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapil, V.; Khambata, R.S.; Jones, D.A.; Rathod, K.; Primus, C.; Massimo, G.; Fukuto, J.M.; Ahluwalia, A. The Noncanonical Pathway for in Vivo Nitric Oxide Generation: The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 692–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Burke, L.M.; Dvorak, J.; Larson-Meyer, D.E.; Peeling, P.; Phillips, S.M.; Rawson, E.S.; Walsh, N.P.; Garthe, I.; Geyer, H.; et al. IOC Consensus Statement: Dietary Supplements and the High-Performance Athlete. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 52, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, P.; Binnie, M.J.; Goods, P.S.R.; Sim, M.; Burke, L.M. Evidence-Based Supplements for the Enhancement of Athletic Performance. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Vanhatalo, A.; Seals, D.R.; Rossman, M.J.; Piknova, B.; Jonvik, K.L. Dietary Nitrate and Nitric Oxide Metabolism: Mouth, Circulation, Skeletal Muscle, and Exercise Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignarro, L.J.; Buga, G.M.; Wood, K.S.; Byrns, R.E. Artery and Vein Is Nitric Oxide. Sci. York 1987, 84, 9265–9269. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, Y.; Balke, J.E.; Madorma, D.; Siegel, M.P.; Knowels, G.; Brouckaert, P.; Buys, E.S.; Marcinek, D.J.; Percival, J.M. Nitric Oxide Regulates Skeletal Muscle Fatigue, Fiber Type, Microtubule Organization, and Mitochondrial ATP Synthesis Efficiency Through CGMP-Dependent Mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 966–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.S.; Meissner, G. Physiology of Nitric Oxide in Skeletal Muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, F.; Gehlert, S.; Grau, M.; Bloch, W. Skeletal Muscle Function during Exercise-Fine-Tuning of Diverse Subsystems by Nitric Oxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7109–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.J.; Winyard, P.; Vanhatalo, A.; Blackwell, J.R.; DiMenna, F.J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Tarr, J.; Benjamin, N.; Jones, A.M. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Reduces the O2 Cost of Low-Intensity Exercise and Enhances Tolerance to High-Intensity Exercise in Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.J.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O.; Ekblom, B. Effects of Dietary Nitrate on Oxygen Cost during Exercise. Acta Physiol. 2007, 191, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.; Vanhatalo, A.; Winyard, P.; Jones, A. The Nitrate-Nitrite-Nitric Oxide Pathway: Its Role in Human Exercise Physiology. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2012, 12, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.J.; Fulford, J.; Vanhatalo, A.; Winyard, P.G.; Blackwell, J.R.; DiMenna, F.J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Benjamin, N.; Jones, A.M. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Enhances Muscle Contractile Efficiency during Knee-Extensor Exercise in Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.J.; Schiffer, T.A.; Borniquel, S.; Sahlin, K.; Ekblom, B.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Dietary Inorganic Nitrate Improves Mitochondrial Efficiency in Humans. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betteridge, S.; Bescós, R.; Martorell, M.; Pons, A.; Garnham, A.P.; Stathis, C.C.; McConell, G.K. No Effect of Acute Beetroot Juice Ingestion on Oxygen Consumption, Glucose Kinetics, or Skeletal Muscle Metabolism during Submaximal Exercise in Males. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 120, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, J.; Ludzki, A.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F.; Senden, J.M.G.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Spriet, L.L.; Holloway, G.P. Beetroot Juice Supplementation Reduces Whole Body Oxygen Consumption but Does Not Improve Indices of Mitochondrial Efficiency in Human Skeletal Muscle. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.; Ferguson, S.K.; Bailey, S.J.; Vanhatalo, A.; Poole, D.C. Fiber Type-Specific Effects of Dietary Nitrate. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2016, 44, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Schiffer, T.A.; Ivarsson, N.; Cheng, A.J.; Bruton, J.D.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Westerblad, H. Dietary Nitrate Increases Tetanic [Ca 2+] i and Contractile Force in Mouse Fast-Twitch Muscle. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 3575–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.K.; Hirai, D.M.; Copp, S.W.; Holdsworth, C.T.; Allen, J.D.; Jones, A.M.; Musch, T.I.; Poole, D.C. Impact of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation via Beetroot Juice on Exercising Muscle Vascular Control in Rats. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breese, B.C.; Mcnarry, M.A.; Marwood, S.; Blackwell, J.R.; Bailey, S.J.; Jones, A.M. Beetroot Juice Supplementation Speeds O2 Uptake Kinetics and Improves Exercise Tolerance during Severe-Intensity Exercise Initiated from an Elevated Metabolic Rate. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R1441–R1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, S.; Ramaglia, M.; Bellistri, G.; Pavei, G.; Pugliese, L.; Montorsi, M.; Rasica, L.; Marzorati, M. Aerobic Fitness Affects the Exercise Performance Responses to Nitrate Supplementation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.M. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation and Exercise Performance. Sport. Med. 2014, 44, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krustrup, P.; Söderlund, K.; Mohr, M.; Bangsbo, J. The Slow Component of Oxygen Uptake during Intense, Sub-Maximal Exercise in Man Is Associated with Additional Fibre Recruitment. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2004, 447, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krustrup, P.; Söderlund, K.; Relu, M.U.; Ferguson, R.A.; Bangsbo, J. Heterogeneous Recruitment of Quadriceps Muscle Portions and Fibre Types during Moderate Intensity Knee-Extensor Exercise: Effect of Thigh Occlusion. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2009, 19, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vøllestad, N.K.; Blom, P.C.S. Effect of Varying Exercise Intensity on Glycogen Depletion in Human Muscle Fibres. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1985, 125, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, P.R.; David, P.S.; McClure, T.; Crook, Z.; Poyton, R.O. Mitochondrial Cytochrome Oxidase Produces Nitric Oxide under Hypoxic Conditions: Implications for Oxygen Sensing and Hypoxic Signaling in Eukaryotes. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, H.; Kundu, T.K.; Alzawahra, W.; Zweier, J.L. Nitric Oxide Production from Nitrite Occurs Primarily in Tissues Not in the Blood: Critical Role of Xanthine Oxidase and Aldehyde Oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17855–17863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modin, A.; Björne, H.; Herulf, M.; Alving, K.; Weitzberg, E.; Lundberg, J.O.N. Nitrite-Derived Nitric Oxide: A Possible Mediator of “acidic-Metabolic” Vasodilation. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2001, 171, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkema, S.J.; Adams, G.R.; Meyer, R.A. Acidosis Has No Effect on the ATP Cost of Contraction in Cat Fast- and Slow-Twitch Skeletal Muscles. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1997, 272, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, P.; Behnke, B.J.; Padilla, D.J.; Musch, T.I.; Poole, D.C. Control of Microvascular Oxygen Pressures in Rat Muscles Comprised of Different Fibre Types. J. Physiol. 2005, 563, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.S.; Noyszewski, E.A.; Kendrick, K.F.; Leigh, J.S.; Wagner, P.D. Myoglobin O2 Desaturation during Exercise: Evidence of Limited O2 Transport. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.J.; Varnham, R.L.; DiMenna, F.J.; Breese, B.C.; Wylie, L.J.; Jones, A.M. Inorganic Nitrate Supplementation Improves Muscle Oxygenation, O2 Uptake Kinetics, and Exercise Tolerance at High but Not Low Pedal Rates. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggan, A.R.; Leibowitz, J.L.; Kadkhodayan, A.; Thomas, D.P.; Ramamurthy, S.; Spearie, C.A.; Waller, S.; Farmer, M.; Peterson, L.R. Effect of Acute Dietary Nitrate Intake on Maximal Knee Extensor Speed and Power in Healthy Men and Women. Nitric. Oxide Biol. Chem. 2015, 48, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimer, E.G.; Peterson, L.R.; Coggan, A.R.; Martin, J.C. Acute Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Increases Maximal Cycling Power in Athletes. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodra, P.; Domínguez, R.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Bailey, S.J. Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Mood, Perceived Exertion, and Performance during a 30-Second Wingate Test. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonvik, K.L.; Nyakayiru, J.; Van Dijk, J.W.; Maase, K.; Ballak, S.B.; Senden, J.M.G.; Van Loon, L.J.C.; Verdijk, L.B. Repeated-Sprint Performance and Plasma Responses Following Beetroot Juice Supplementation Do Not Differ between Recreational, Competitive and Elite Sprint Athletes. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jell, H.; Fulford, J.; Carter, J.; Nyman, L.; Bailey, S.J.; Jones, A.M. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Improves Sprint and High-Intensity Intermittent Running Performance. Nitric. Oxide Biol. Chem. 2016, 61, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, L.J.; Mohr, M.; Krustrup, P.; Jackman, S.R.; Ermιdis, G.; Kelly, J.; Black, M.I.; Bailey, S.J.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Improves Team Sport-Specific Intense Intermittent Exercise Performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, D.; Townsend, J.R.; Vantrease, W.C.; Marshall, A.C.; Henry, R.N.; Heffington, S.H.; Johnson, K.D. Acute Beetroot Juice Administration Improves Peak Isometric Force Production in Adolescent Males. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 43, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Samanes, Á.; Pérez-López, A.; Moreno-Pérez, V.; Nakamura, F.Y.; Acebes-Sánchez, J.; Quintana-Milla, I.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; Moreno-Pérez, D.; Fernández-Elías, V.E.; Domínguez, R. Effects of Beetroot Juice Ingestion on Physical Performance in Highly Competitive Tennis Players. Nutrients 2020, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, L.J.; Bailey, S.J.; Kelly, J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Influence of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Intermittent Exercise Performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvares, T.S.; de Oliveira, G.V.; Volino-Souza, M.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Murias, J.M. Effect of Dietary Nitrate Ingestion on Muscular Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 5284–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggan, A.R.; Baranauskas, M.N.; Hinrichs, R.J.; Liu, Z.; Carter, S.J. Effect of Dietary Nitrate on Human Muscle Power: A Systematic Review and Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Walle, G.P.; VUKOVICH, M.D.; VanDeWalle, G.P.; VUKOVICH, M.D. The Effect of Nitrate Supplementation on Exercise Tolerance and Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Gupta, S.; Adli, T.; Hou, W.; Coolsaet, R.; Hayes, A.; Kim, K.; Pandey, A.; Gordon, J.; Chahil, G.; et al. The Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Endurance Exercise Performance and Cardiorespiratory Measures in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, N.F.; Leveritt, M.D.; Pavey, T.G. The Effect of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Endurance Exercise Performance in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sport. Med. 2017, 47, 735–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, H.O.; Drummond, L.R.; Rodrigues, Q.T.; Machado, F.S.M.; Pires, W.; Wanner, S.P.; Coimbra, C.C. Nitrate Supplementation Improves Physical Performance Specifically in Non-Athletes during Prolonged Open-Ended Tests: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 636–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senefeld, J.W.; Wiggins, C.C.; Regimbal, R.J.; Dominelli, P.B.; Baker, S.E.; Joyner, M.J.; Wiggins, C.C.; Regimbal, R.J.; Dominelli, P.B.; Baker, S.E.; et al. Ergogenic Effect of Nitrate Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2020, 52, 2250–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. BMJ 2009, 339, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan---a Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Wylie, L.J.; Fulford, J.; Kelly, J.; Black, M.I.; McDonagh, S.T.J.; Jeukendrup, A.E.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Dietary Nitrate Improves Sprint Performance and Cognitive Function during Prolonged Intermittent Exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, S.; Pugliese, L.; Rejc, E.; Pavei, G.; Bonato, M.; Montorsi, M.; La Torre, A.; Rasica, L.; Marzorati, M. Effects of a Short-Term High-Nitrate Diet on Exercise Performance. Nutrients 2016, 8, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muggeridge, D.J.; Howe, C.C.F.; Spendiff, O.; Pedlar, C.; James, P.E.; Easton, C. The Effects of a Single Dose of Concentrated Beetroot Juice on Performance in Trained Flatwater Kayakers. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2013, 23, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, E.; Jodra, P.; Pérez-López, A.; González-Rodríguez, L.G.; da Silva, S.F.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Domínguez, R.; Fernandes da Silva, S.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Domínguez, R. Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Performance and Fatigue in a 30-s All-Out Sprint Exercise: A Randomized, Double-Blind Cross-Over Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakayiru, J.; Jonvik, K.L.; Trommelen, J.; Pinckaers, P.J.M.; Senden, J.M.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Verdijk, L.B. Beetroot Juice Supplementation Improves High-Intensity Intermittent Type Exercise Performance in Trained Soccer Players. Nutrients 2017, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Muggeridge, D.J.; Easton, C.; Ross, M.D. An Acute Dose of Inorganic Dietary Nitrate Does Not Improve High-Intensity, Intermittent Exercise Performance in Temperate or Hot and Humid Conditions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Garnacho-Castaño, M.V.; Cuenca, E.; García-Fernández, P.; Muñoz-González, A.; de Jesús, F.; Lozano-Estevan, M.D.C.; da Silva, S.F.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; et al. Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on a 30-s High-Intensity Inertial Cycle Ergometer Test. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corry, L.R.; Gee, T.I. Dietary Nitrate Enhances Power Output During the Early Phases of Maximal Intensity Sprint Cycling. Int. J. Coach. Sci. 2015, 9, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, S.J.; Baur, D.A.; Spicer, M.T.; Vukovich, M.D.; Ormsbee, M.J. The Effect of Six Days of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance in Trained CrossFit Athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2016, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.M.; Nyberg, M.; Bangsbo, J. Influence of Nitrate Supplementation on VO2 Kinetics and Endurance of Elite Cyclists. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2013, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumar, A.M.; Huntington, A.F.; Rogers, R.R.; Kopec, T.J.; Williams, T.D.; Ballmann, C.G. Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation Attenuates Morning-Associated Decrements in Supramaximal Exercise Performance in Trained Sprinters. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esen, O.; Domínguez, R.; Karayigit, R. Acute Beetroot Juice Supplementation Enhances Intermittent Running Performance but Does Not Reduce Oxygen Cost of Exercise among Recreational Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak-Chaouch, M.; Boissière, J.; Munyaneza, D.; Gamelin, F.X.; Cuvelier, G.; Berthoin, S.; Aucouturier, J. Beetroot Juice Does Not Enhance Supramaximal Intermittent Exercise Performance in Elite Endurance Athletes. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, B.B.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Alves, R.C.; Urbinati, K.S.; McAnulty, S.R.; Junior, T.P.S. Acute Supplementation with Beetroot Juice Does Not Enhance Exercise Performance among Well-Trained Athletes: A Randomized Crossover Study. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 2018, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Aucouturier, J.; Boissière, J.; Pawlak-Chaouch, M.; Cuvelier, G.; Gamelin, F.-X.X. Effect of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Tolerance to Supramaximal Intensity Intermittent Exercise. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2015, 49, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.; Smee, D.; Thompson, K.G.; Rattray, B. No Improvement of Repeated-Sprint Performance with Dietary Nitrate. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, E.J.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Trexler, E.T.; Hirsch, K.R.; Mock, M.G. Effects of Pomegranate Extract on Blood Flow and Vessel Diameter after High-Intensity Exercise in Young, Healthy Adults. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2017, 17, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, 14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring Inconsistency in Meta-Analyses. Br. Med. J. 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager Web (RevMan Web) 5.4 2020. Available online: revman.cochrane.org (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-Analysis in Clinical Trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988; pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Elbourne, D.R.; Altman, D.G.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Curtin, F.; Worthington, H.V.; Vail, A. Meta-Analyses Involving Cross-over Trials: Methodological Issues. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 31, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.L.; Henry, T.; Guelfi, K.; Dawson, B.; McNaughton, L.R.; Wallman, K. Effects of Sodium Phosphate and Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Repeated-Sprint Ability in Females. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.M.E.E.; Evans, M.; Halpenny, C.; Hughes, C.; Jordan, S.; Quinn, A.; Hone, M.; Egan, B. Acute Ingestion of Beetroot Juice Does Not Improve Short-Duration Repeated Sprint Running Performance in Male Team Sport Athletes. J. Sport. Sci. 2020, 38, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegelhalder, B.; Eisenbrand, G.; Preussmann, R. Influence of Dietary Nitrate on Nitrite Content of Human Saliva: Possible Relevance to in Vivo Formation of N-Nitroso Compounds. Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 1976, 14, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Fan, Z.; Xia, D.; Ding, G.; Ong, H.L.; Adams, D.; Gahl, W.A.; Zheng, C.; et al. Sialin (SLC17A5) Functions as a Nitrate Transporter in the Plasma Membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13434–13439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Govoni, M. Inorganic Nitrate Is a Possible Source for Systemic Generation of Nitric Oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, M.C.; Liddle, L.; Monaghan, C.; Muggeridge, D.J.; Sculthorpe, N.; Butcher, J.P.; Henriquez, F.L.; Allen, J.D.; Easton, C. Salivary Nitrite Production Is Elevated in Individuals with a Higher Abundance of Oral Nitrate-Reducing Bacteria. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 120, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, E.R.; Andrade, F.; Vaksman, Z.; Parthasarathy, K.; Jiang, H.; Parthasarathy, D.K.; Torregrossa, A.C.; Tribble, G.; Kaplan, H.B.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Nitrate-Reducing Bacteria in the Oral Cavity: Implications for Nitric Oxide Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhatalo, A.; Blackwell, J.R.; Heureux, J.E.L.; Williams, D.W.; Smith, A.; Van Der Giezen, M.; Winyard, P.G.; Kelly, J.; Jones, A.M. Free Radical Biology and Medicine Nitrate-Responsive Oral Microbiome Modulates Nitric Oxide Homeostasis and Blood Pressure in Humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, L.J.; Kelly, J.; Bailey, S.J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Skiba, P.F.; Winyard, P.G.; Jeukendrup, A.E.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Beetroot Juice and Exercise: Pharmacodynamic and Dose-Response Relationships. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Alghayth, M.; Vanhatalo, A.; Wylie, L.J.; McDonagh, S.T.; Thompson, C.; Kadach, S.; Kerr, P.; Smallwood, M.J.; Jones, A.M.; Winyard, P.G. S-Nitrosothiols, and Other Products of Nitrate Metabolism, Are Increased in Multiple Human Blood Compartments Following Ingestion of Beetroot Juice. Redox Biol. 2021, 43, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, D.; Schwarz, G. Nitrite-Dependent Nitric Oxide Synthesis by Molybdenum Enzymes. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 2126–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Faassen, E.E.; Bahrami, S.; Feelisch, M.; Hogg, N.; Kelm, M.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B.; Kozlov, A.V.; Li, H.; Lundberg, J.O.; Mason, R.; et al. Nitrite as Regulator of Hypoxic Signaling in Mammalian Physiology. Med. Res. Rev. 2009, 29, 683–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggan, A.R.; Broadstreet, S.R.; Mahmood, K.; Mikhalkova, D.; Madigan, M.; Bole, I.; Park, S.; Leibowitz, J.L.; Kadkhodayan, A.; Thomas, D.P.; et al. Dietary Nitrate Increases VO 2 Peak and Performance but Does Not Alter Ventilation or Efficiency in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Card. Fail. 2018, 24, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadach, S.; Won, J.; Zdravko, P.; Matthew, S.; Vanhatalo, A.; Burnley, M.; Walter, P.J.; Cai, H.; Schechter, A.N.; Piknova, B.; et al. 15 N-Labeled Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Increases Human Skeletal Muscle Nitrate Concentration and Improves Muscle Torque Production. Acta Physiol. 2023, 237, e13924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliard, C.N.; Lam, J.K.; Cassel, K.S.; Park, J.W.; Schechter, A.N.; Piknova, B.; Branch, M. Effect of Dietary Nitrate Levels on Nitrate Fluxes in Rat Skeletal Muscle and Liver. Nitric. Oxide 2018, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, L.J.; Park, J.W.; Vanhatalo, A.; Kadach, S.; Black, M.I.; Stoyanov, Z.; Schechter, A.N.; Jones, A.M.; Piknova, B. Human Skeletal Muscle Nitrate Store: Influence of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation and Exercise. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 5565–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srihirun, S.; Park, J.W.; Teng, R.; Sawaengdee, W.; Piknova, B.; Schechter, A.N.; Branch, M.; Diseases, K. Nitrate Uptake and Metabolism in Human Skeletal Muscle Cell Cultures. Nitric. Oxide Biol. Chem. 2020, 94, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Naughton, D.; Winyard, P.G.; Benjamin, N.; Blake, D.R.; Symons, M. Generation of Nitric Oxide by a Nitrite Reductase Activity of Xanthine Oxidase: A Potential Pathway for Nitric Oxide Formation in the Absence of Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 249, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, E.A.; Huang, L.; Malkey, R.; Govoni, M.; Nihlén, C.; Olsson, A.; Stensdotter, M.; Petersson, J.; Holm, L.; Weitzberg, E.; et al. A Mammalian Functional Nitrate Reductase That Regulates Nitrite and Nitric Oxide Homeostasis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piknova, B.; Park, J.W.; Kwan Jeff Lam, K.; Schechter, A. Nitrate as a Source of Nitrite and Nitric Oxide during Exercise Hyperemia in Rat Skeletal Muscle. Nitric. Oxide 2016, 55–56, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsten, Y.; Frandsen, U.; Ørthenblad, N.; Sjødin, B.; Richter, E.A. Xanthine Oxidase in Human Skeletal Muscle Following Eccentric Exercise: A Role in Inflammation. J. Physiol. 1997, 498, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, M.; Christensen, P.M.; Blackwell, J.R.; Hostrup, M.; Jones, A.M.; Bangsbo, J. Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice Ingestion Reduces Skeletal Muscle O2 Uptake and Blood Flow during Exercise in Sedentary Men. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 5203–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.C.; Hill, D.W. Contribution of Energy Systems during a Wingate Power Test. Br. J. Sport. Med. 1991, 25, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanis, G.C.; Nevill, M.E.; Boobis, L.H.; Lakomy, H.K.A. Contribution of Phosphocreatine and Aerobic Metabolism to Energy Supply during Repeated Sprint Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 80, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, J.; Gamu, D.; Heigenhauser, G.J.F.; Van Loon, L.J.C.; Spriet, L.L.; Tupling, A.R.; Holloway, G.P. Beetroot Juice Increases Human Muscle Force without Changing Ca2+-Handling Proteins. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2017, 49, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coggan, A.R.; Peterson, L.R. Dietary Nitrate Enhances the Contractile Properties of Human Skeletal Muscle. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2018, 46, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.J.; Gandra, P.G.; Jones, A.M.; Hogan, M.C.; Nogueira, L. Incubation with Sodium Nitrite Attenuates Fatigue Development in Intact Single Mouse Fibres at Physiological PO2. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 5429–5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillin, N.A.; Moudy, S.; Nourse, K.M.; Tyler, C.J. Nitrate Supplement Benefits Contractile Forces in Fatigued but Not Unfatigued Muscle. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2018, 50, 2122–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study | Participants | Supplementation Protocol | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (♂, ♀) | Health/Training Status | Age (Years) | Type/Volume | NO3− Dose (mmol) | Duration | Time before Trial | Placebo | Exercise Protocol | Performance Variables | Results | |
| Aucouturier et al. (2015) [65] | 17 ♂ | Healthy, active in team sports | 23 ± 3 | BR juice/500 mL | 10.9 | 3 D | 3 h | Apple-black currant juice | 15 s cycling at 170% of MAP to exhaustion, interspersed with 30 s | MP, TWD, reps, exercise duration | ND in MP, improved TWD, reps and exercise duration |
| Bender et al. (2018) [39] | 16 ♂ | Healthy, recreationally active | 17 ± 1 | BR shot/2 × 70 mL | 12.9 | Single D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR shot | 4 × 20 s all-out WAnT, interspersed with 240 s | PP, MP | ND in PP and MP |
| Bernardi et al. (2018) [64] | 10 ♂ | Well-trained mixed martial arts athletes | 25 ± 5 | BR juice/400 mL | 9.3 | Single D | 2 h | Black current juice | 20 × 6 s all-out cycling interspersed with 24 s | PP, MP, FI | ND in PP, MP, and FI |
| Buck et al. (2015) [74] | 13 ♀ | Team sport players | 26 ± 2 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6 | Single D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR shot | 6 × 20 m all-out effort running, interspersed with 25 s recovery | ST, best ST | ND in ST and best ST |
| Christensen et al. (2013) [60] | 10 ♂ | Elite cyclists | 29 ± 4 | BR juice/500 mL | 8 | 4 D | 3 h | Apple-black currant juice | 6 × 20 s cycling at 0.75 N/kg, interspersed with 100 s | PP, MP | ND in PP and MP |
| Corry et al. (2015) [58] | 10 ♂ | Recreationally active | 20 ± 1 | BR shot/2 × 70 mL | 8 | 2 D | 40 min | Black current juice | 30 s all-out WanT | PP, MP, FI | Improved MP, ND in PP and FI |
| Cuenca et al. (2018) [54] | 15 ♂ | Resistance trained | 22 ± 2 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6 | Single D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR juice | 30 s all-out WAnT | PP, MP, PPTime, PMin, FI | Improved PP, MP and PPTime, ND in FI |
| Domínguez et al. (2017) [57] | 15 ♂ | Healthy trained | 22 ± 2 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 5.6 | Single D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR juice | 30 s all-out WAnT | PP, MP, PPTime, PMin, FI | Improved PP and MP, ND in PPTime, PMin, FI |
| Dumar et al. (2021) [61] | 10 ♂ | National level sprinters | 20.3 ± 2 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6.4 | Single D | 2 h | Black current juice | 3 × 15 s all-out WAnT | MP and TWD | Improved MP and TWD |
| Esen et al. (2022) [62] | 12 ♂ | Recreational active | 27 ± 10 | BR shot/1 × 140 mL | 12.8 | Single D | 3 h | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | Yo-Yo IR1 test | TDC | Longer TDC |
| Jodra et al. (2020) [35] | 15 ♂ | Resistance trained | 23 ± 2 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6.4 | Single D | 2.5-3 h | NR-depleted BR juice | 30 s all-out WAnT | PP, MP, PPTime,PMin | Improved PP and PPTime, ND in MP and PMin |
| Jonvik et al. (2018) [36] | 29 ♂ 23 ♀ | Recreational cyclists (n = 20), national talent speed skaters (n = 23), Olympic- level track cyclists (n = 10) | ♂ = 22 ± 5 ♀ = 26 ± 8 | BR shot/2 × 70 mL | 12.9 | 6 D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR juice | 3 × 30 s all-out WAnT interspersed with 240 s recovery | PP, MP, PPTime | ND in PP and MP, improved PPTime |
| Kramer et al. (2016) [59] | 12 ♂ | CrossFit athletes | 23 ± 5 | KNR/2 capsules | 8 | 6 D | ≥24 h | KCL capsules | 30 s all-out WAnT | PP, MP | Improved PP, ND in MP |
| López-Samanes et al. (2020) [40] | 13 ♂ | Highly competitive tennis players | 25 ± 5 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6.4 | Single D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR juice | 10 m Sprint | ST | ND in ST |
| Martin et al. (2014) [66] | 9 ♂ 7 ♀ | Moderately trained team sport athletes | ♂ = 22 ± 2 ♀ = 21 ± 1 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 4.8 | Single D | 2 h | NR-depleted BR shot | 8 s high intensity cycling to exhaustion interspersed with 30 s | PP, MP, TWD, no of reps | ND in PP, MP, TWD, no of reps |
| Muggeridge et al. (2013) [53] | 8 ♂ | Trained kayakers | 31 ± 15 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 5 | Single D | 3 h | Tomato juice | 5 × 10 s maximum effort kayaking, interspersed with 50 s recovery | PP, FI | ND in PP and FI |
| Nyakayiru et al. (2017) [55] | 32 ♂ | Soccer players | 23 ± 1 | BR shot/2 × 70 mL | 12.9 | 6 D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR shot | Yo-Yo IR1 test | TDC | Longer TDC |
| Pawlak-Chaouch et al. (2019) [63] | 11 ♂ | Elite endurance athletes | 22 ± 4 | BR juice/500 mL | 5.5 | 3 D | 3 h | Apple-black currant juice | 15 s cycling at 170% of MAP to exhaustion interspersed with 30 s | MP, TWD and no of reps | ND in MP, TWD and no of reps |
| Porcelli et al. (2016) [52] | 7 ♂ | Healthy recreationally active | 25 ± 2 | High NR diet | 8.2 | 6 D | 3 h | Control diet ~2.9 mmol NR/day | 5 × 6 s all-out cycling, interspersed with 24 s recovery | PP | Improved PP |
| Reynolds et al. (2020) [75] | 16 ♂ | Team sport athletes | 21 ± 2 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6 | Single D | 3 h | NR-depleted BR shot | 10 × 40 m all-out running interspersed with 30 s recovery | ST, fastest ST, slowest ST | ND in ST, fastest ST and slowest ST |
| Rimer et al. (2017) [34] | 11 ♂ 2 ♀ | Competitively trained athletes | 26 ± 8 | BR shot/2 × 70 mL | 11.2 | Single D | 2.5 h | NR-depleted BR shot | 4 × 3–4 s all-out cycling interspersed with 120 s. Followed by 30 s WAnT after 300 s rest. | PP, TW, optimal pedalling rate, FI | Improved PP and optimal pedalling rate during 4 × 3–4 s test. ND in PP, TW, and FI during 30 s Wingate test |
| Roelofs et al. (2017) [67] | 10 ♂ 11 ♀ | Recreationally resistance-trained | 22 ± 2 | Pomegranate extract/capsule | 6.8 | Single D | - | Maltodextrin capsule | 10 × 6 s all-out, interspersed with 30 s | PP, MP | Improved PP and MP |
| Smith et al. (2019) [56] | 12 ♂ | Recreationally trained, team sport athletes | 22 ± 4 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6.2 | Single D | 2.5 h | NR-depleted BR shot | 2 halves of 20 × 6 s all out cycling interspersed with 114 s recovery | PP, MP, TWD | ND in PP, MP, TW |
| Thompson et al. (2016) [37] | 32 ♂ | Team-sport players | 24 ± 4 | BR shot/1 × 70 mL | 6.4 | 5 D | 2.5 h | NR-depleted BR shot | Yo-Yo IR1 | TDC, 20 m sprint time, 5, 10, 5–10, 10–20 m split time | Longer TDC, improved 5, 10, 5–10 m split time, ND in 10-20 m split time |
| Thompson et al. (2015) [51] | 16 ♂ | Recreational team-sport players | 24 ± 5 | BR shot/2 × 70 mL | 12.8 | 7 D | 2.5 h | NR-depleted BR shot | 2 halves of 20 × 6 s all out cycling interspersed with 114 s recovery | TWD | Improved TWD |
| Wylie et al. (2016) [41] | 10 ♂ | Recreational team-sport players | 21 ± 1 | BR shot/2 × 70 mL | 8.2 | 3 D | 2.5 h | NR-depleted BR shot | D3: 24 × 6 s all out cycling interspersed with 24 s D4: 7 × 30 s all-out cycling interspersed with 240 s D5: 6 × 60 s interspersed with 60 s | PP, MP | Improved PP and MP during 24 × 6 s. ND in PP and MP during 7 × 30 s and 6 × 60 s |
| Wylie et al. (2013) [38] | 14 ♂ | Recreational team-sport players | 22 ± 2 | Day 1, BR shot/4 × 70 mL Day 2, BR shot/3 × 70 mL | D1:16.4 D2:12. 3 | 2 D | 1.5 h | NR-depleted BR shot | Yo-Yo IR1 | TDC | Longer TDC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsharif, N.S.; Clifford, T.; Alhebshi, A.; Rowland, S.N.; Bailey, S.J. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance during Single and Repeated Bouts of Short-Duration High-Intensity Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12061194
Alsharif NS, Clifford T, Alhebshi A, Rowland SN, Bailey SJ. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance during Single and Repeated Bouts of Short-Duration High-Intensity Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(6):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12061194
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsharif, Nehal S., Tom Clifford, Abrar Alhebshi, Samantha N. Rowland, and Stephen J. Bailey. 2023. "Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance during Single and Repeated Bouts of Short-Duration High-Intensity Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials" Antioxidants 12, no. 6: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12061194
APA StyleAlsharif, N. S., Clifford, T., Alhebshi, A., Rowland, S. N., & Bailey, S. J. (2023). Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance during Single and Repeated Bouts of Short-Duration High-Intensity Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Antioxidants, 12(6), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12061194








