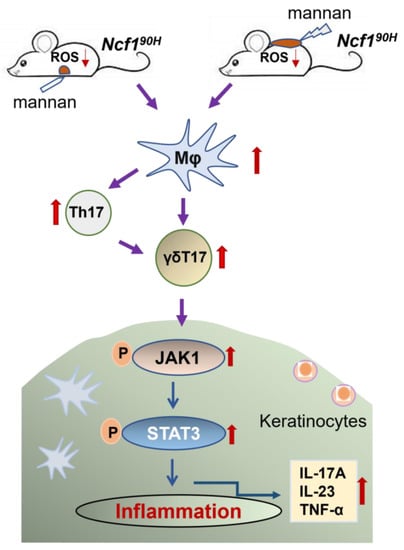
Human NCF190H Variant Promotes IL-23/IL-17—Dependent Mannan-Induced Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Measurement of ROS
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Mannan-Induced Psoriasis (MIP)
2.5. Histology
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ncf190H Mice Express an Intact NOX2 Complex with Deficiency of ROS
3.2. Ncf190H Mice Develop More Severe MIP
3.3. NCF190H Variant Promotes the Expansion of Macrophages and Keratinocytes
3.4. NCF190H Variant Mediates MIP through the IL-23/IL-17 Axis
3.5. NCF190H Variant Upregulates JAK1/STAT3 Pathway in MIP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Holmberg, J.; Tordsson, J.; Lu, S.; Akerstrom, B.; Holmdahl, R. Positional identification of Ncf1 as a gene that regulates arthritis severity in rats. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, L.M.; Nerstedt, A.; Lindqvist, A.K.; Johansson, A.C.; Medstrand, P.; Olofsson, P.; Holmdahl, R. Copy number variation of the gene NCF1 is associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 16, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultqvist, M.; Sareila, O.; Vilhardt, F.; Norin, U.; Olsson, L.M.; Olofsson, P.; Hellman, U.; Holmdahl, R. Positioning of a polymorphic quantitative trait nucleotide in the Ncf1 gene controlling oxidative burst response and arthritis severity in rats. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2373–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, J.; Deng, Y.; Kelly, J.A.; Kim, K.; Bang, S.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Li, Q.Z.; Wakeland, E.K.; Qiu, R.; et al. A missense variant in NCF1 is associated with susceptibility to multiple autoimmune diseases. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olsson, L.M.; Johansson, A.C.; Gullstrand, B.; Jonsen, A.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Ronnblom, L.; Leonard, D.; Wettero, J.; Sjowall, C.; Svenungsson, E.; et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the NCF1 gene leading to reduced oxidative burst is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, S.; Ekici, A.B.; Uebe, S.; Buttner, C.; Kohm, M.; Behrens, F.; Bohm, B.; Sticherling, M.; Schett, G.; Simon, D.; et al. Analyses of association of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis vulgaris with functional NCF1 variants. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultqvist, M.; Olofsson, P.; Holmberg, J.; Bäckström, B.T.; Tordsson, J.; Holmdahl, R. Enhanced autoimmunity, arthritis, and encephalomyelitis in mice with a reduced oxidative burst due to a mutation in the Ncf1 gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12646–12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sareila, O.; Jaakkola, N.; Olofsson, P.; Kelkka, T.; Holmdahl, R. Identification of a region in p47phox/NCF1 crucial for phagocytic NADPH oxidase (NOX2) activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 93, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sareila, O.; Hagert, C.; Kelkka, T.; Linja, M.; Xu, B.; Kihlberg, J.; Holmdahl, R. Reactive Oxygen Species Regulate Both Priming and Established Arthritis, but with Different Mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 1473–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmaladze, I.; Kelkka, T.; Guerard, S.; Wing, K.; Pizzolla, A.; Saxena, A.; Lundqvist, K.; Holmdahl, M.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Mannan induces ROS-regulated, IL-17A-dependent psoriasis arthritis-like disease in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3669–E3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kienhöfer, D.; Hahn, J.; Stoof, J.; Csepregi, J.Z.; Reinwald, C.; Urbonaviciute, V.; Johnsson, C.; Maueroder, C.; Podolska, M.J.; Biermann, M.H.; et al. Experimental lupus is aggravated in mouse strains with impaired induction of neutrophil extracellular traps. JCI Insight 2017, 2, E3669–E3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Ou, J.; Li, K.; Wang, T.; Nandakumar, K.S. Comparative Studies On Mannan and Imiquimod Induced Experimental Plaque Psoriasis Inflammation In Inbred Mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2023, 101, 12646–12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Ma, J.; Yao, C.; Ye, Z.; Ding, H.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Li, G.; He, Y.; Li, J.; et al. The NCF1 variant aggravates autoimmunity by facilitating the activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e153619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Zhao, J.; Deng, Y.; Molano, I.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Ruiz, P.; Li, Q.; Feng, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Human SLE variant NCF1-R90H promotes kidney damage and murine lupus through enhanced Tfh2 responses induced by defective efferocytosis of macrophages. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Urbonaviciute, V.; Saei, A.A.; Lyu, H.; Gaetani, M.; Vegvari, A.; Li, Y.; Zubarev, R.A.; Holmdahl, R. NCF1-dependent production of ROS protects against lupus by regulating plasmacytoid dendritic cell development and functions. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e153619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Li, Q.; Holmdahl, R. Natural loss-of-function mutations in Qa2 and NCF1 cause the spread of mannan-induced psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1765–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Scholz, T.; Yau, A.C.Y.; Guerard, S.; Huffmeier, U.; Burkhardt, H.; Holmdahl, R. Mannan-induced Nos2 in macrophages enhances IL-17-driven psoriatic arthritis by innate lymphocytes. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, B.S.; Brent, L.; Valdimarsson, H.; Powles, A.V.; Alimara, L.; Walker, M.; Fry, L. Is Epidermal-Cell Proliferation in Psoriatic Skin-Grafts on Nude-Mice Driven by T-Cell Derived Cytokines. Br. J. Dermatol. 1992, 126, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Ma, L.; Bai, X.; Miao, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, J. A Scoring Method for Immunohistochemical Staining on Ki67. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 29, e20–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawkes, J.E.; Yan, B.Y.; Chan, T.C.; Krueger, J.G. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 Signaling Pathway and the Treatment of Psoriasis. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papp, K.; Gordon, K.; Thaci, D.; Morita, A.; Gooderham, M.; Foley, P.; Girgis, I.G.; Kundu, S.; Banerjee, S. Phase 2 Trial of Selective Tyrosine Kinase 2 Inhibition in Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, S.L.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Johnson, R.; Estes, L.; Woodworth, T.G.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Krueger, J.G. Response of psoriasis to a lymphocyte-selective toxin (DAB389IL-2) suggests a primary immune, but not keratinocyte, pathogenic basis. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, T.; Riedl, E.; Bangert, C.; Bowman, E.P.; Greisenegger, E.; Horowitz, A.; Kittler, H.; Blumenschein, W.M.; McClanahan, T.K.; Marbury, T.; et al. Clinical improvement in psoriasis with specific targeting of interleukin-23. Nature 2015, 521, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, E.; Maverakis, E.; Sarin, R.; Bouchareychas, L.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Nestle, F.O.; Adamopoulos, I.E. T Cell-Independent Mechanisms Associated with Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation and Selective Autophagy in IL-17A-Mediated Epidermal Hyperplasia. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamata, M.; Tada, Y. Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 941071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Chuang, H.Y.; Ho, J.C.; Lee, C.H.; Hsiao, C.C. Treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitor rectifies M1 macrophage polarization from blood CD14+ monocytes in patients with psoriasis independent of STAT1 and IRF-1 activation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 91, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Lai, C.Y.; Yeh, D.W.; Liu, Y.L.; Su, Y.W.; Hsu, L.C.; Chang, C.H.; Jin, S.L.C.; Chuang, T.C. Involvement of M1 Macrophage Polarization in Endosomal Toll-Like Receptors Activated Psoriatic Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3523642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capon, F.; Di Meglio, P.; Szaub, J.; Prescott, N.J.; Dunster, C.; Baumber, L.; Timms, K.; Gutin, A.; Abkevic, V.; Burden, A.D.; et al. Sequence variants in the genes for the interleukin-23 receptor (IL23R) and its ligand (IL12B) confer protection against psoriasis. Hum. Genet. 2007, 122, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Lai, Y. Keratinocyte: A trigger or an executor of psoriasis? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, E.; Kokolakis, G.; Witte, K.; Philipp, S.; Doecke, W.D.; Babel, N.; Wittig, B.M.; Warszawska, K.; Kurek, A.; Erdmann-Keding, M.; et al. IL-19 is a component of the pathogenetic IL-23/IL-17 cascade in psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cochez, P.M.; Michiels, C.; Hendrickx, E.; Van Belle, A.B.; Lemaire, M.M.; Dauguet, N.; Warnier, G.; de Heusch, M.; Togbe, D.; Ryffel, B.; et al. AhR modulates the IL-22-producing cell proliferation/recruitment in imiquimod-induced psoriasis mouse model. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, T.; Sakai, K.; Sanders, K.M.; Yosipovitch, G.; Akiyama, T. Antipruritic Effects of Janus Kinase Inhibitor Tofacitinib in a Mouse Model of Psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McInnes, I.B.; Kato, K.; Magrey, M.; Merola, J.F.; Kishimoto, M.; Pacheco-Tena, C.; Haaland, D.; Chen, L.; Duan, Y.; Zueger, P.; et al. Upadacitinib in patients with psoriatic arthritis and an inadequate response to non-biological therapy: 56-week data from the phase 3 SELECT-PsA 1 study. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Oh, I.; Kim, J.H.; Jeon, J.E.; Jeon, B.; Shin, J.; Kim, T.Y. Anti-inflammatory activity of compounds isolated from Astragalus sinicus L. in cytokine-induced keratinocytes and skin. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bäckdahl, L.; Aoun, M.; Norin, U.; Holmdahl, R. Identification of Clec4b as a novel regulator of bystander activation of auto-reactive T cells and autoimmune disease. PLoS Genet 2020, 16, e1008788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, P.E.; Nair, R.P.; Ellinghaus, E.; Ding, J.; Tejasvi, T.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Li, Y.; Weidinger, S.; Eberlein, B.; Gieger, C.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies three psoriasis susceptibility loci. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yau, A.C.Y.; Holmdahl, R. Regulation of T Cell Function by Reactive Nitrogen and Oxygen Species in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.; Hultqvist Hopkins, M.; Laulund, F.; Holmdahl, R. A Reduction in Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Due to a Mutation in NCF4 Promotes Autoimmune Arthritis in Mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 25, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Human NCF190H Variant Promotes IL-23/IL-17—Dependent Mannan-Induced Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071348
Li Y, Li Z, Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R. Human NCF190H Variant Promotes IL-23/IL-17—Dependent Mannan-Induced Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(7):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071348
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanpeng, Zhilei Li, Kutty Selva Nandakumar, and Rikard Holmdahl. 2023. "Human NCF190H Variant Promotes IL-23/IL-17—Dependent Mannan-Induced Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis" Antioxidants 12, no. 7: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071348
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, Z., Nandakumar, K. S., & Holmdahl, R. (2023). Human NCF190H Variant Promotes IL-23/IL-17—Dependent Mannan-Induced Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Antioxidants, 12(7), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071348