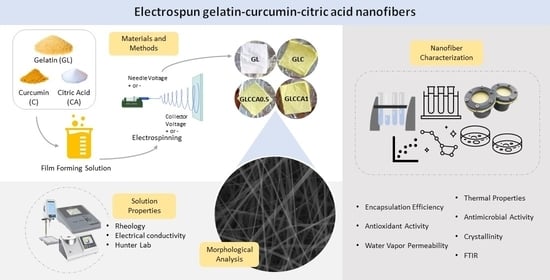
The Effects of Citric Acid Crosslinking on Fabrication and Characterization of Gelatin/Curcumin-Based Electrospun Antioxidant Nanofibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Use of Gelatin
1.2. Curcumin as Functional Agent
1.3. Crosslinking with Citric Acid
1.4. Electrospinning
1.5. Novelty of Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Solution Preparation
2.3. Solution Properties
2.3.1. Rheological Properties
2.3.2. Color
2.3.3. Electrical Conductivity
2.4. Electrospinning
2.5. Nanofiber Film Characterization
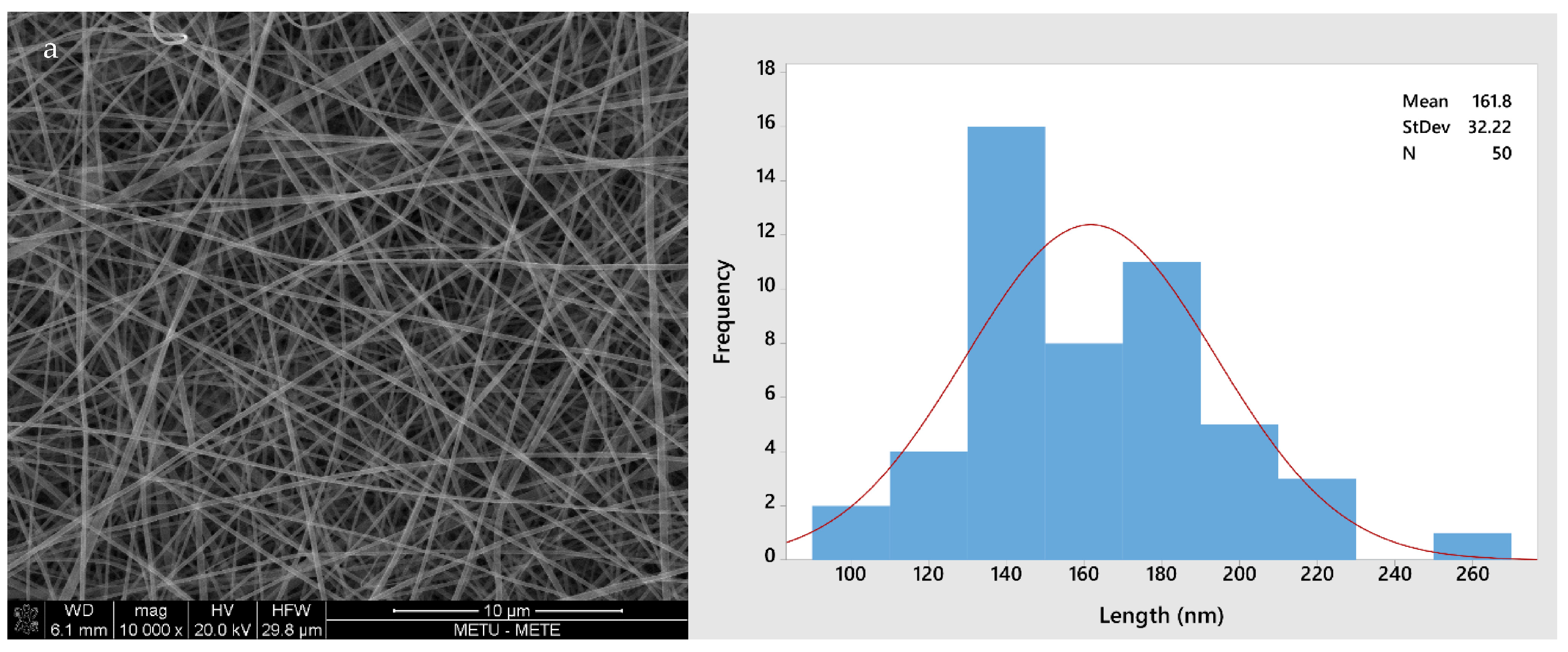
2.5.1. Morphological Analysis
2.5.2. Color
2.5.3. Antioxidant Activity
2.5.4. Thermogravimetric Analyses
2.5.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.5.6. X-ray Diffraction
2.5.7. Water Vapor Permeability
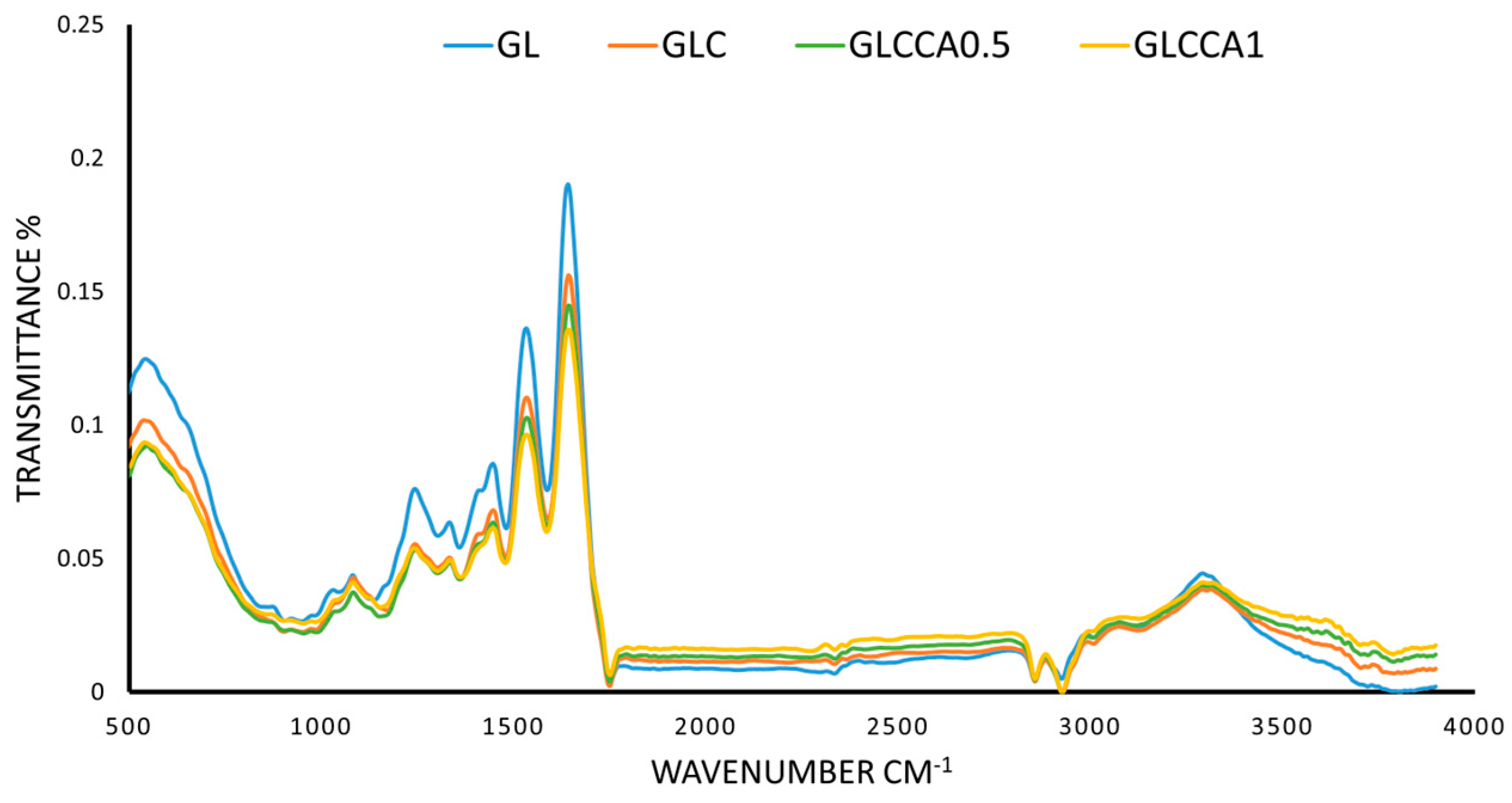
2.5.8. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
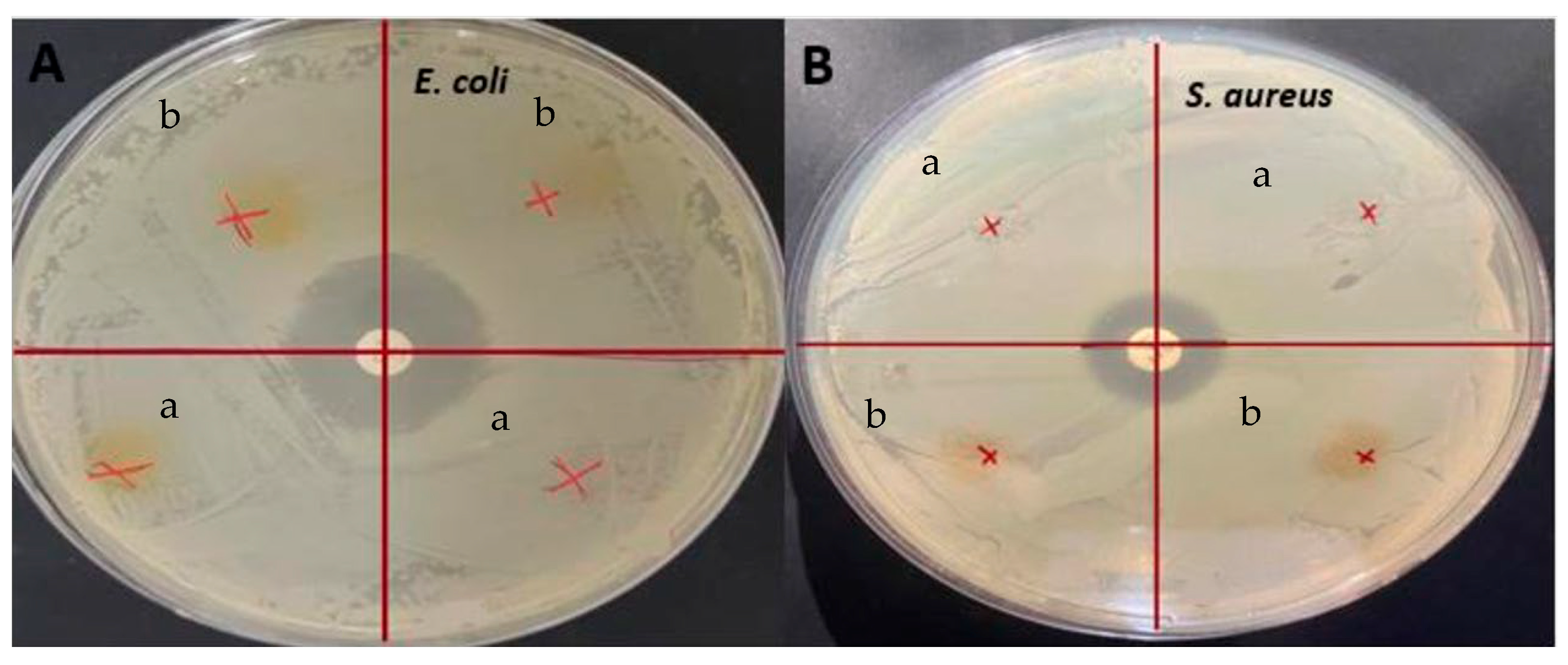
2.5.9. Antimicrobial Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solution Properties, Fiber Morphology, and Color
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.5. Crystallinity Analysis (XRD)
3.6. Water Vapor Permeability
3.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Etxabide, A.; Coma, V.; Guerrero, P.; Gardrat, C.; de la Caba, K. Effect of Cross-Linking in Surface Properties and Antioxidant Activity of Gelatin Films Incorporated with a Curcumin Derivative. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Valdés, A.; Beltrán, A.; Garrigós, M. Gelatin-Based Films and Coatings for Food Packaging Applications. Coatings 2016, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ninan, G.; Joseph, J.; Aliyamveettil, Z.A. A Comparative Study on the Physical, Chemical and Functional Properties of Carp Skin and Mammalian Gelatins. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 51, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Shi, H.; Cao, A.; Jia, J. Characterization of Gelatin/Chitosan Ploymer Films Integrated with Docosahexaenoic Acids Fabricated by Different Methods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, N.; Roriz, C.L.; Morales, P.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Food Colorants: Challenges, Opportunities and Current Desires of Agro-Industries to Ensure Consumer Expectations and Regulatory Practices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.W.; Shin, J.S. Pectin-Coated Curcumin-Chitosan Microparticles Crosslinked with Mg2+ for Delayed Drug Release in the Digestive System. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 2071071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bojorges, H.; Ríos-Corripio, M.A.; Hernández-Cázares, A.S.; Hidalgo-Contreras, J.V.; Contreras-Oliva, A. Effect of the Application of an Edible Film with Turmeric (c Urcuma longa L.) on the Oxidative Stability of Meat. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4308–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla, E.; Koumentakou, I.; Bikiaris, N.; Balla, E.; Lykidou, S.; Nikolaidis, N. Formulation, Characterization and Evaluation of Innovative O/W Emulsions Containing Curcumin Derivatives with Enhanced Antioxidant Properties. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Balaguer, M.P.; López-Carballo, G.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Improving Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Curcumin by Means of Encapsulation in Gelatin through Electrohydrodynamic Atomization. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, J.-S.; Youn, S.J.; Lee, H.; Baik, M.-Y. Enhanced Antioxidant Capacity of Puffed Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) by High Hydrostatic Pressure Extraction (HHPE) of Bioactive Compounds. Foods 2020, 9, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, J.; Nguyen, B.T.; Si, T.T.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. The Effect of Cross-Linking with Citric Acid on the Properties of Agar/Fish Gelatin Films. Polymers 2020, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I. 6-Gelatin. In Handbook of Hydrocolloids; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; ScienceDirect; Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781845694142500060 (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Aydogdu, A.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Fabrication of Gallic Acid Loaded Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Nanofibers by Electrospinning Technique as Active Packaging Material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, N.; Oguz, S.; Aydogdu, A.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. Influence of Solution Properties and PH on the Fabrication of Electrospun Lentil Flour/HPMC Blend Nanofibers. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Duan, G.; Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; He, S.; Jiang, S. Electrospun Functional Materials toward Food Packaging Applications: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López de Dicastillo, C.; Piña, C.; Garrido, L.; Arancibia, C.; Galotto, M.J. Enhancing Thermal Stability and Bioaccesibility of Açaí Fruit Polyphenols through Electrohydrodynamic Encapsulation into Zein Electrosprayed Particles. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydogdu, A.; Yildiz, E.; Aydogdu, Y.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S.; Ayhan, Z. Enhancing Oxidative Stability of Walnuts by Using Gallic Acid Loaded Lentil Flour Based Electrospun Nanofibers as Active Packaging Material. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Shang, L.; Deng, L. Influence of the Maillard Reaction on Properties of Air-Assisted Electrospun Gelatin/Zein/Glucose Nanofibers. Foods 2023, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, J.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, H. The Applications of Ferulic-Acid-Loaded Fibrous Films for Fruit Preservation. Polymers 2022, 14, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, C.S.; Baek, D.H.; Gang, K.D.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Characterization of Gelatin Nanofiber Prepared from Gelatin–Formic Acid Solution. Polymer 2005, 46, 5094–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, A.; Cilek, B.; Hasirci, V.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Effect of Degritting of Phenolic Extract from Sour Cherry Pomace on Encapsulation Efficiency—Production of Nano-Suspension. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 6, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, E.; Sumnu, G.; Kahyaoglu, L. Monitoring Freshness of Chicken Breast by Using Natural Halochromic Curcumin Loaded Chitosan/PEO Nanofibers as an Intelligent Package. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, E.; Ilhan, E.; Kahyaoglu, L.N.; Sumnu, G.; Oztop, M.H. The Effects of Crosslinking Agents on Faba Bean Flour–Chitosan-Curcumin Films and Their Characterization. Legume Sci. 2021, 4, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheur, F.B.; Kouidhi, B.; Fdhila, K.; Elabed, H.; Slama, R.B.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A.; Chaieb, K. Anti-bacterial and anti-biofilm activity of probiotic bacteria against oral pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 97, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, R.; Akalın, M. Characterization and Evaluation of Antimicrobial Properties of Electrospun Chitosan/Polyethylene Oxide Based Nanofibrous Scaffolds (With/without Nanosilver). J. Ind. Text. 2013, 44, 553–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassan, A.A.; Norziah, M.H. Starch–Gelatin Edible Films: Water Vapor Permeability and Mechanical Properties as Affected by Plasticizers. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Fiber Fabrication Technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeren, S.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Encapsulation of Caffeic Acid in Carob Bean Flour and Whey Protein-Based Nanofibers via Electrospinning. Foods 2022, 11, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.R.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Luo, C.J. Nanofibres in Drug Delivery; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Morota, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Mizukoshi, T.; Konosu, Y.; Minagawa, M.; Tanioka, A.; Yamagata, Y.; Inoue, K. Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Thin Films Produced by Electrospray Deposition: Morphology Control and Additive Effects of Alcohols on Nanostructure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 279, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, K.I.; Maity, D.K.; Naik, G.H.; Kumar, M.S.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Satav, J.G.; Mohan, H. Role of Phenolic O-H and Methylene Hydrogen on the Free Radical Reactions and Antioxidant Activity of Curcumin. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, S.; Naseri, M.; Babaei, S.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Imani, A. Development of Bioactive Composite Films from Chitosan and Carboxymethyl Cellulose Using Glutaraldehyde, Cinnamon Essential Oil and Oleic Acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Peng, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, T. Crystallization Behavior of Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshi, R.; Sauraj; Kumar, B.; Negi, Y.S. Chitosan Film Incorporated with Citric Acid and Glycerol as an Active Packaging Material for Extension of Green Chilli Shelf Life. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loganathan, S.; Ravi Babu, V.R.; Mishra, R.K.; Pugazhenthi, G.; Thomas, S. Thermal and Rheological Measurement Techniques for Nanomaterials Characterization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume iv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. Structure and Properties of Chitosan Films: Effect of the Type of Solvent Acid. LWT 2021, 135, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lei, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, R.; Xiao, D.; Jiao, C.; Xia, R.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Effect of Citric Acid Induced Crosslinking on the Structure and Properties of Potato Starch/Chitosan Composite Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Sharma, H.K.; Saini, C.S. Edible Films Developed from Carboxylic Acid Cross-Linked Sesame Protein Isolate: Barrier, Mechanical, Thermal, Crystalline and Morphological Properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 55, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawdkuen, S.; Sai-Ut, S.; Benjakul, S. Properties of Gelatin Films from Giant Catfish Skin and Bovine Bone: A Comparative Study. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suderman, N.; Isa, M.I.N.; Sarbon, N.M. Characterization on the Mechanical and Physical Properties of Chicken Skin Gelatin Films in Comparison to Mammalian Gelatin Films. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, N.R.; Gaikwad, V.L.; Nair, K.J.; Kadam, H.M. Glass Transition Temperature: Basics and Application in Pharmaceutical Sector. Asian J. Pharm. 2009, 3, e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, J.F.; dos Santos, N.Z.; May, I.C.; Pollo, L.D.; Tessaro, I.C. Impact of Acid Type and Glutaraldehyde Crosslinking in the Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties and Biodegradability of Chitosan Films. Polym. Bull. 2020, 78, 981–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Olsen, C.W.; Olson, D.A.; Chiou, B.; Yee, E.; Bechtel, P.J.; McHugh, T.H. Water Vapor Permeability of Mammalian and Fish Gelatin Films. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, E202–E207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.A.; Martino, M.N.; Zaritzky, N.E. Lipid Addition to Improve Barrier Properties of Edible Starch-Based Films and Coatings. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.; Kalichevsky, M.; Blanshard, J.M.V.; Psomiadou, E. Study of Diffusion and Permeation of Gases in Undrawn and Uniaxially Drawn Films Made from Potato and Rice Starch Conditioned at Different Relative Humidities. Carbohydr. Polym. 1994, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation of Carbohydrate-Based Functional Composite Films Incorporated with Curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prystupa, D.A.; Donald, A.M. Infrared Study of Gelatin Conformations in the Gel and Sol States. Polym. Gels Netw. 1996, 4, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopic Study of Acid Soluble Collagen and Gelatin from Skins and Bones of Young and Adult Nile Perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotatha, D.; Hirata, M.; Ogino, M.; Uchida, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Furuike, T.; Tamura, H. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers for Use as Nonaqueous Electrolyte in Electric Double-Layer Capacitor. J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 2019, e2501039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musso, Y.S.; Salgado, P.R.; Mauri, A.N. Smart edible films based on gelatin and curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 66, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emir, A.A.; Yildiz, E.; Aydogdu, Y.; Sumnu, G. Active Films Based on Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Flour Incorporated with Sumac (Rhus coriaria): Assessment of Antiox-idant and Antimicrobial Performances of Packaging for Shelf Life of Chicken Breast. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 16, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamsa, N.; Sittiwet, C. Antimicrobial activity of Curcuma longa aqueous extract. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 4, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawhavinit, O.A.; Kongkathip, N.; Kongkathip, B. Antimicrobial activity of curcuminoids from Curcuma longa L. on pathogenic bacteria of shrimp and chicken. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2010, 44, 364–371. [Google Scholar]
- Tyagi, P.; Singh, M.; Kumari, H.; Kumari, A.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Bactericidal activity of curcumin I is associated with damaging of bacterial membrane. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aliabbasi, N.; Fathi, M.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Curcumin: A promising bioactive agent for application in food packaging systems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.R.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Mauri, A.N.; Montero, M.P. Exploration of the antioxidant and antimicrobial capacity of two sunflower protein concentrate films with naturally present phenolic compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, S.S.; Perera, Y.; Dunuweera, S.P.; Dunuweera, A.N.; Rajapakse, S.; Rajapakse, R.M.G. Comparison of Antibacterial Activity of Nanocurcumin with Bulk Curcumin. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 46494–46500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Solution/Film Name | Contents |
|---|---|
| GL | 30% gelatin (w/v) solution |
| GLC | 30% GL (w/v) solution mixed with 0.5% curcumin (w/v) in ethanol |
| GLCCA0.5 | 30% GL (w/v) solution mixed with 0.5% curcumin (w/v) in ethanol and 0.5% CA (w/v) |
| GLCCA1 | 30% GL (w/v) solution mixed with 0.5% curcumin (w/v) in ethanol and 1% CA (w/v) |
| Solution/Film | Viscosity (Pa.s) | Electrical Conductivity (mS/cm) | FSD (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GL | 0.41433 ± 0.0083 a | 2.74533 ± 0.0019 a | 162.420 ± 0.916 d |
| GLC | 0.16786 ± 0.0117 b | 1.30757 ± 0.0032 b | 182.246 ± 0.619 c |
| GLCCA0.5 | 0.14931 ± 0.0102 b | 1.29360 ± 0.0048 b | 344.033 ± 0.304 b |
| GLCCA1 | 0.14040 ± 0.0165 b | 1.17300 ± 0.0093 c | 427.417 ± 1.390 a |
| Type | L* | a* | b* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GL | Solution | 90.6350 ± 0.0071 a | −3.980 ± 0.2260 a | 17.330 ± 0.325 c |
| Film | 19.255 ± 0.2900 b | −1.190 ± 0.141 c | 1.200 ±0.226 c | |
| GLC | Solution | 82.0350 ± 0.0778 c | 4.350 ± 0.0283 c | 56.865 ± 0.0495 b |
| Film | 13.915 ± 0.2620 c | 5.330 ± 0.382 a | 8.345 ± 0.304 b | |
| GLCCA0.5 | Solution | 83.120 ± 0.1980 b | 2.430 ± 0.0283 b | 57.790 ± 0.156 ab |
| Film | 20.605 ± 0.4030 a | 3.350 ± 0.382 b | 13.170 ± 0.339 a | |
| GLCCA1 | Solution | 83.4800 ± 0.1273 b | 2.205 ± 0.191 b | 57.990 ± 0.311 a |
| Film | 14.540 ± 0.0424 c | 3.845 ± 0.191 b | 9.325 ± 0.460 b |
| Film | AA (%) |
|---|---|
| GLC | 32.01 ± 1.88 a |
| GLCCA0.5 | 22.47 ± 0.63 b |
| GLCCA1 | 27.93 ± 0.78 a |
| Film | Weight Loss 1 (%) | Weight Loss 2 (%) | Crystallinity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GL | 11.110 ± 0.4330 a | 61.430 ± 0.2520 b | 2.220 ± 0.2520 b |
| GLC | 10.200 ± 1.7140 ab | 60.960 ± 0.1153 b | 1.626 ± 0.3150 b |
| GLCCA0.5 | 8.763 ± 0.9120 ab | 60.907 ± 0.5550 b | 6.50 ± 1.5400 a |
| GLCCA1 | 8.047 ± 0.5530 b | 63.180 ± 0.9430 a | 1.5625 ± 0.0898 b |
| Film | Tg (°C) | Tm Start (°C) | Tm Peak (°C) | Tm End (°C) | Tdeg (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GL | 69.16 ± 1.460 c | 55.10 ± 1.57 a | 80.285 ± 0.728 a | 106.36 ± 4.40 b | 231.515 ± 1.068 a |
| GLC | 119.730 ± 1.117 a | 48.98 ± 2.93 a | 73.835 ± 1.308 c | 98.52 ± 8.79 b | 227.745 ± 1.280 a |
| GLCCA0.5 | 112.73 ± 1.640 b | 32.35 ± 2.80 b | 78.055 ± 1.407 ab | 142.69 ± 3.20 a | 230.140 ± 2.570 a |
| GLCCA1 | 110.49 ± 1.440 b | 46.56 ± 2.70 a | 76.010 ± 0.170 bc | 103.25 ± 3.14 b | 226.050 ± 1.004 a |
| Film | WVP (×10−10) gm−1 s−1 Pa−1 Unit | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| GL | 4.395 ± 0.00 a | 0.08763 ± 0.00348 a |
| GLC | 3.590 ± 0.00 bc | 0.05858 ± 0.00813 b |
| GLCCA0.5 | 2.365 ± 0.00 c | 0.04950 ± 0.00337 b |
| GLCCA1 | 4.695 ± 0.00 ab | 0.08225 ± 0.00271 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, R.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S.; Oz, E.; Oz, F. The Effects of Citric Acid Crosslinking on Fabrication and Characterization of Gelatin/Curcumin-Based Electrospun Antioxidant Nanofibers. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071387
Hasan R, Sumnu G, Sahin S, Oz E, Oz F. The Effects of Citric Acid Crosslinking on Fabrication and Characterization of Gelatin/Curcumin-Based Electrospun Antioxidant Nanofibers. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(7):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071387
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Reem, Gulum Sumnu, Serpil Sahin, Emel Oz, and Fatih Oz. 2023. "The Effects of Citric Acid Crosslinking on Fabrication and Characterization of Gelatin/Curcumin-Based Electrospun Antioxidant Nanofibers" Antioxidants 12, no. 7: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071387
APA StyleHasan, R., Sumnu, G., Sahin, S., Oz, E., & Oz, F. (2023). The Effects of Citric Acid Crosslinking on Fabrication and Characterization of Gelatin/Curcumin-Based Electrospun Antioxidant Nanofibers. Antioxidants, 12(7), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071387