Aldehyde Dehydrogenase and Aldo-Keto Reductase Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Emerging Roles in Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
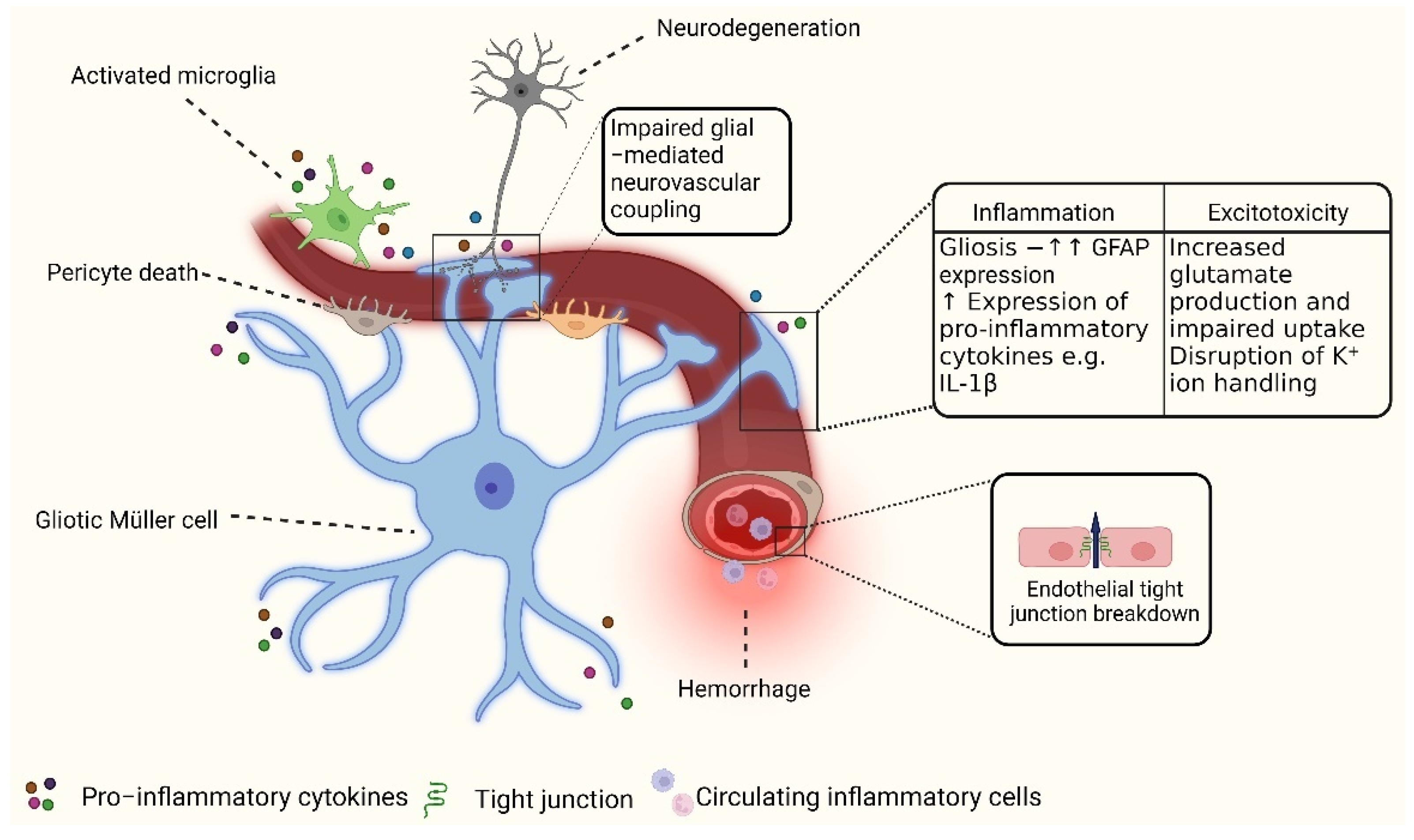
1. Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
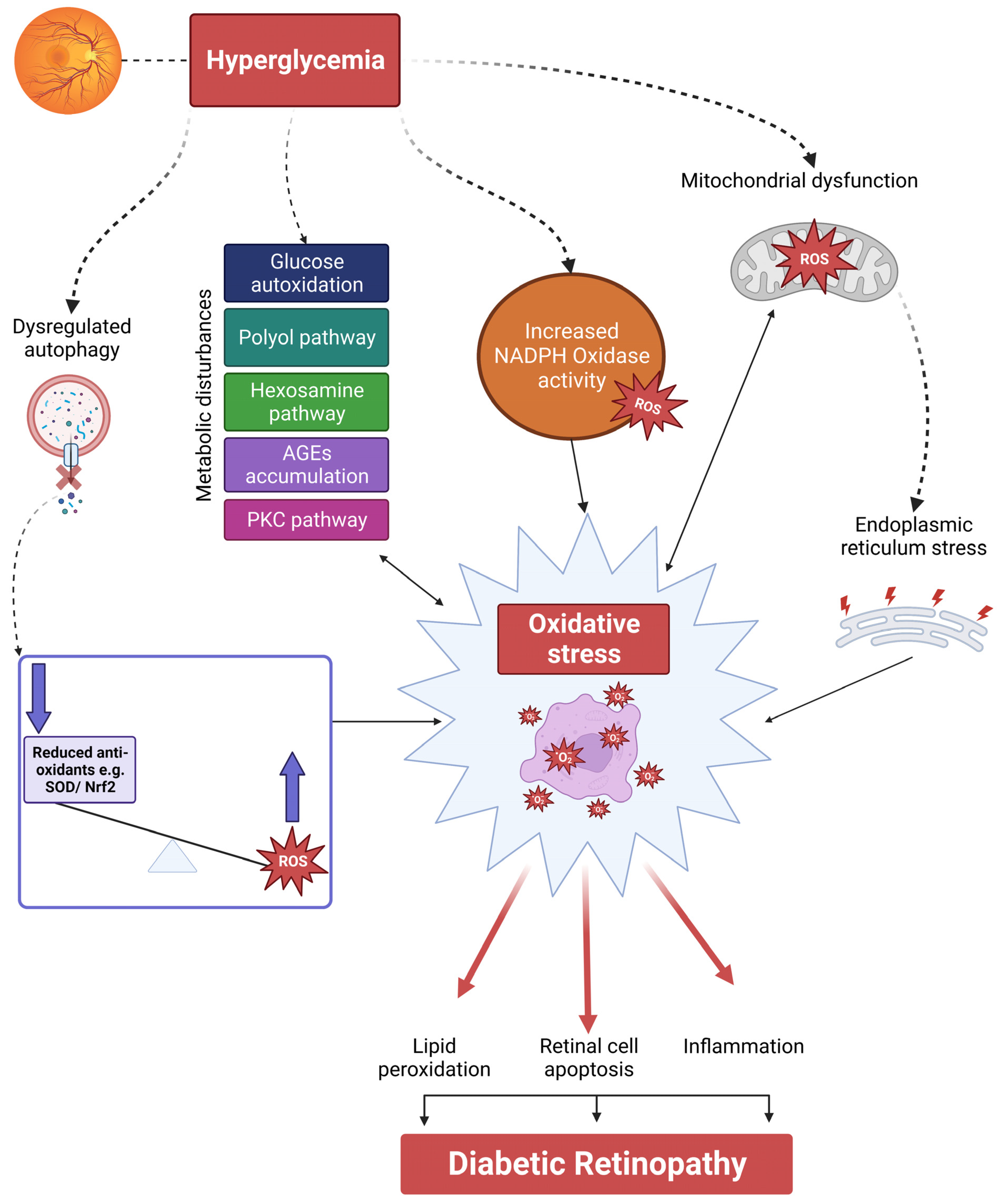
2. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), Lipid Aldehydes and ALEs
2.1. Lipid Peroxidation and ALEs
2.2. α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes
2.2.1. Acrolein
2.2.2. 4-HNE and 4-HHE
2.2.3. Dialdehydes
MDA
Glyoxal
3. Aldehyde Detoxification in the Retina in Health and Diabetes
3.1. ALDH1A1
3.2. ALDH2
3.3. ALDH3a1
3.4. ALDH3a2
3.5. ALDH9a1
3.6. ALDH18a1
3.7. AKR1b1
3.8. AKR1c19
3.9. AKR7a2
4. Therapeutic Approaches Relating to Aldehyde Detoxification
4.1. Gene Therapy
4.2. Pharmacological Approaches
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonetti, D.A.; Silva, P.S.; Stitt, A.W. Current understanding of the molecular and cellular pathology of diabetic retinopathy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, E.J.; Sun, J.K.; Stitt, A.W. Diabetic retinopathy: Current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e93751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M.; Chen, M.; Medina, R.J.; McKay, G.J.; Jenkins, A.; Gardiner, T.A.; Lyons, T.J.; Hammes, H.-P.; Simó, R.; et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 51, 156–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K.; Moss, S.E.; Davis, M.D.; DeMets, D.L. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of Diabetic Retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1989, 107, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-R.; Li, D.; Xie, Z. Association of obesity with diabetic retinopathy in US adults with diabetes in a national survey. Endocr. Connect. 2021, 10, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaxman, S.R.; Bourne, R.R.A.; Resnikoff, S.; Ackland, P.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; et al. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e1221–e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.; Macias, G.L.; Torres, M.; Klein, R.; Peña, F.Y.; Azen, S.P. Biologic Risk Factors Associated with Diabetic Retinopathy: The Los Angeles Latino Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raum, P.; Lamparter, J.; Ponto, K.A.; Peto, T.; Hoehn, R.; Schulz, A.; Schneider, A.; Wild, P.S.; Pfeiffer, N.; Mirshahi, A. Correction: Prevalence and Cardiovascular Associations of Diabetic Retinopathy and Maculopathy: Results from the Gutenberg Health Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, C.-J.; Hsieh, Y.-T.; Yang, C.-M.; Yang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-L.; Wang, I.-J. Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Dyslipidemia: Development and Progression. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2018, 2, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightman, S.; Towler, H.M. Diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Cornerstone 2003, 5, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A.C.Y. Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Sun, J.; Kawasaki, R.; Ruamviboonsuk, P.; Gupta, N.; Lansingh, V.C.; Maia, M.; Mathenge, W.; Moreker, S.; Muqit, M.M.; et al. Guidelines on Diabetic Eye Care: The International Council of Ophthalmology Recommendations for Screening, Follow-up, Referral, and Treatment Based on Resource Settings. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 1608–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, M.; Khamseh, M.E.; Aghili, R.; Emami, Z.; Najafi, L.; Baradaran, H.R. Medical management of diabetic retinopathy: An overview. Arch. Iran. Med. 2012, 15, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simó, R.; Simó-Servat, O.; Bogdanov, P.; Hernández, C. Neurovascular Unit: A New Target for Treating Early Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaadon, P.; Fagan, X.J.; Lifshitz, T.; Levy, J. A review of anti-VEGF agents for proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Eye 2014, 28, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, E.H.; van Dijk, H.W.; Jiao, C.; Kok, P.H.B.; Jeong, W.; Demirkaya, N.; Garmager, A.; Wit, F.; Kucukevcilioglu, M.; van Velthoven, M.E.J.; et al. Retinal neurodegeneration may precede microvascular changes characteristic of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes mellitus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2655–E2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simó, R.; Stitt, A.W.; Gardner, T.W. Neurodegeneration in diabetic retinopathy: Does it really matter? Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, S.; Lo, A.C.Y.; Mi, Y.; Ren, K.; Yang, D. Neurovascular unit in diabetic retinopathy: Pathophysiological roles and potential therapeutical targets. Eye Vis. 2021, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A.J.; Lieth, E.; Khin, S.A.; Antonetti, D.A.; Buchanan, A.G.; Gardner, T.W. Neural apoptosis in the retina during experimental and human diabetes. Early onset and effect of insulin. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.W.; Lin, F.; Fort, P.E. The innate immune system in diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 84, 100940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.M.; Roon, P.; Van Ells, T.K.; Ganapathy, V.; Smith, S.B. Death of Retinal Neurons in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3330–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastinger, M.J.; Singh, R.S.J.; Barber, A.J. Loss of Cholinergic and Dopaminergic Amacrine Cells in Streptozotocin-Diabetic Rat and Ins2Akita-Diabetic Mouse Retinas. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 3143–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-W.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Chung, J.-W.; Chun, M.-H.; Oh, S.-J. Apoptotic death of photoreceptors in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat retina. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorián-Salvador, M.; Barabas, P.; Byrne, E.M.; Lechner, J.; Augustine, J.; Curtis, T.M.; Chen, M.; Xu, H. VEGF-B Is an Autocrine Gliotrophic Factor for Müller Cells under Pathologic Conditions. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Xia, X.-B.; Xiong, S.-Q. BDNF regulates GLAST and glutamine synthetase in mouse retinal Müller cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, X. Regulation of inflammation by VEGF/BDNF signaling in mouse retinal Müller glial cells exposed to high glucose. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 388, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzel, A.G.T.; Uğurlu, N.; Toklu, Y.; Çiçek, M.; Boral, B.; Şener, B.; Çağil, N. Relationship between stages of diabetic retinopathy and levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in aqueous humor and serum. Retina 2020, 40, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Elliott, M.H.; Zhu, M.; Le, Y.-Z. Müller Cell-Derived VEGF Is Essential for Diabetes-Induced Retinal Inflammation and Vascular Leakage. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.-Z.; Xu, B.; Chucair-Elliott, A.J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M. VEGF Mediates Retinal Müller Cell Viability and Neuroprotection through BDNF in Diabetes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlin, B.A.; Feenstra, D.J.; Mohr, S. Müller cells and diabetic retinopathy. Vis. Res. 2017, 139, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, J.; Troendle, E.P.; Barabas, P.; McAleese, C.A.; Friedel, T.; Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M. The Role of Lipoxidation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 621938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SanGiovanni, J.P.; Chew, E.Y. The role of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in health and disease of the retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2005, 24, 87–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.-H. The NOX Family of ROS-Generating NADPH Oxidases: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, T.P.; Ammendola, R.; Cattaneo, F.; Esposito, G. NOX Dependent ROS Generation and Cell Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataix, J.; Quiles, J.L.; Huertas, J.R.; Battino, M.; Mañas, M. Tissue Specific Interactions of Exercise, Dietary Fatty Acids, and Vitamin E in Lipid Peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 24, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrano, V.; Balzan, S. Enzymatic antioxidant system in vascular inflammation and coronary artery disease. World J. Exp. Med. 2015, 5, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, S.P.; Dean, R.T. Glucose autoxidation and protein modification. The potential role of ‘autoxidative glycosylation’ in diabetes. Biochem. J. 1987, 245, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowluru, R.A.; Abbas, S.N. Diabetes-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Retina. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 5327–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabrawey, M.; Rojas, M.; Sanders, T.; Behzadian, A.; El-Remessy, A.; Bartoli, M.; Parpia, A.K.; Liou, G.; Caldwell, R.B. Role of NADPH Oxidase in Retinal Vascular Inflammation. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, N.M.; Tarr, J.M.; Kohner, E.M.; Chibber, R. NADPH Oxidase versus Mitochondria-Derived ROS in Glucose-Induced Apoptosis of Pericytes in Early Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 2010, 746978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasry, K.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Saleh, H.; Elsherbiny, N.; Elshafey, S.; Hussein, K.A.; Al-Shabrawey, M. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in 12/15-lipoxygenase-induced retinal microvascular dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1220–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitt, A.W. AGEs and Diabetic Retinopathy. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4867–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Yang, C. Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy: Molecular mechanisms, pathogenetic role and therapeutic implications. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Shao, J.; Zhu, L.; Xie, T.-H.; Cai, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, M.-X.; Wang, Z.-L.; Yao, Y.; et al. GRP75 Modulates Endoplasmic Reticulum–Mitochondria Coupling and Accelerates Ca2+-Dependent Endothelial Cell Apoptosis in Diabetic Retinopathy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhou, K.; Zhao, M.; Xiang, L.; Mei, T.; Xu, W.; Shang, B.; Liu, X.; Lai, Y.; Lin, M.; et al. TCF7L2 promotes ER stress signaling in diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 221, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrakhimov, S.B.; Yang, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.W.; Park, T.K. mTOR-dependent dysregulation of autophagy contributes to the retinal ganglion cell loss in streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wei, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, X.; Ding, L.; Xiong, S. Identification and Validation of Autophagy-Related Genes in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 867600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowluru, R.A. Diabetes-induced elevations in retinal oxidative stress, protein kinase C and nitric oxide are interrelated. Acta Diabetol. 2001, 38, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldini, G.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Facino, R.M.; Milzani, A.; Carini, M. Intervention strategies to inhibit protein carbonylation by lipoxidation-derived reactive carbonyls. Med. Res. Rev. 2006, 27, 817–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negre-Salvayre, A.; Coatrieux, C.; Ingueneau, C.; Salvayre, R. Advanced lipid peroxidation end products in oxidative damage to proteins. Potential role in diseases and therapeutic prospects for the inhibitors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, N.A. Mechanisms for the autoxidation of polyunsaturated lipids. Acc. Chem. Res. 1986, 19, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalá, A. Lipid peroxidation of membrane phospholipids generates hydroxy-alkenals and oxidized phospholipids active in physiological and/or pathological conditions. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamplona, R. Advanced lipoxidation end-products. Chem. Interact. 2011, 192, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niki, E. Lipid peroxidation: Physiological levels and dual biological effects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Fukuto, J.M.; Miller, T.; Zhang, H.; Rinna, A.; Levy, S. The chemistry of cell signaling by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and 4-hydroxynonenal. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2008, 477, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmijewski, J.W.; Landar, A.; Watanabe, N.; Dickinson, D.A.; Noguchi, N.; Darley-Usmar, V.M. Cell signalling by oxidized lipids and the role of reactive oxygen species in the endothelium. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M. Diabetes-related adduct formation and retinopathy. J. Ocul. Biol. Dis. Inform. 2011, 4, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.E.; McGeown, J.G.; Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M. Therapeutic potential of targeting lipid aldehydes and lipoxidation end-products in the treatment of ocular disease. Futur. Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.; Al-Awadi, F. Lipid peroxidation and retinopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 11, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrosova, I.G.; Fathallah, L.; Greene, D.A. Early changes in lipid peroxidation and antioxidative defense in diabetic rat retina: Effect of dl-α-lipoic acid. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 398, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.K.; Matragoon, S.; Pillai, B.A.; Liou, G.I.; El-Remessy, A.B. Peroxynitrite Mediates Retinal Neurodegeneration by Inhibiting Nerve Growth Factor Survival Signaling in Experimental and Human Diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Bhatnagar, A.; Pierce, W.M. Protein Modification by Acrolein: Formation and Stability of Cysteine Adducts. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Kanematsu, M.; Morimitsu, Y.; Osawa, T.; Noguchi, N.; Niki, E. Acrolein Is a Product of Lipid Peroxidation Reaction: Ormation of acrolein and its conjugate with lysine residues in oxidized low-density lipoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 16058–16066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, K. Current Status of Acrolein as a Lipid Peroxidation Product. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1999, 9, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomitori, H.; Usui, T.; Saeki, N.; Ueda, S.; Kase, H.; Nishimura, K.; Kashiwagi, K.; Igarashi, K. Polyamine Oxidase and Acrolein as Novel Biochemical Markers for Diagnosis of Cerebral Stroke. Stroke 2005, 36, 2609–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Nakamura, M.; Sakamoto, A.; Suzuki, T.; Dohmae, N.; Terui, Y.; Tomitori, H.; Casero, R.A.; Kashiwagi, K.; Igarashi, K. Decrease in acrolein toxicity based on the decline of polyamine oxidases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 79, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.M.; Hazen, S.L.; Hsu, F.F.; Heinecke, J.W. Human neutrophils employ the myeloperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-chloride system to convert hydroxy-amino acids into glycolaldehyde, 2-hydroxypropanal, and acrolein. A mechanism for the generation of highly reactive alpha-hydroxy and alpha,beta-unsaturated. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhata, A.; Honda, K.; Shibata, T.; Chikazawa, M.; Kawai, Y.; Shibata, N.; Uchida, K. Monoclonal Antibody against Protein-Bound Glutathione: Use of Glutathione Conjugate of Acrolein-Modified Proteins as an Immunogen. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, T.M.; Hamilton, R.; Yong, P.-H.; McVicar, C.M.; Berner, A.; Pringle, R.; Uchida, K.; Nagai, R.; Brockbank, S.; Stitt, A.W. Müller glial dysfunction during diabetic retinopathy in rats is linked to accumulation of advanced glycation end-products and advanced lipoxidation end-products. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, P.H.; Zong, H.; Medina, R.J.; Limb, G.A.; Uchida, K.; Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M. Evidence supporting a role for N-(3-formyl-3,4-dehydropiperidino)lysine accumulation in Müller glia dysfunction and death in diabetic retinopathy. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 2524–2538. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Noda, K.; Murata, M.; Yoshida, S.; Saito, W.; Kanda, A.; Ishida, S. Localization of Acrolein-Lysine Adduct in Fibrovascular Tissues of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 42, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.E.; Barabas, P.; Augustine, J.; Chevallier, O.; McCarron, P.; Chen, M.; McGeown, J.G.; Curtis, T.M. Müller glial dysfunction during diabetic retinopathy in rats is reduced by the acrolein-scavenging drug, 2-hydrazino-4,6-dimethylpyrimidine. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2654–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, R.; Venza, I.; Ceci, G.; Visalli, M.; Teti, D.; Reibaldi, A. Vitreous polyamines spermidine, putrescine, and spermine in human proliferative disorders of the retina. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 87, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, S.-S.; Miura, T.; Takao, K.; Sugita, Y.; Samejima, K.; Hiramatsu, K.; Kawakita, M. Development of Irreversible Inactivators of Spermine Oxidase and N1-Acetylpolyamine Oxidase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfarhan, M.; Liu, F.; Shan, S.; Pichavaram, P.; Somanath, P.R.; Narayanan, S.P. Pharmacological Inhibition of Spermine Oxidase Suppresses Excitotoxicity Induced Neuroinflammation in Mouse Retina. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backos, D.S.; Fritz, K.S.; Roede, J.R.; Petersen, D.R.; Franklin, C.C. Posttranslational modification and regulation of glutamate–cysteine ligase by the α,β-unsaturated aldehyde 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, D.R.; Doorn, J.A. Reactions of 4-hydroxynonenal with proteins and cellular targets. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaur, R. Basic aspects of the biochemical reactivity of 4-hydroxynonenal. Mol. Asp. Med. 2003, 24, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.P.; Jung, T.; Grune, T.; Siems, W. 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) modified proteins in metabolic diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 111, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaur, R.J.; Siems, W.; Bresgen, N.; Eckl, P.M. 4-Hydroxy-nonenal—A Bioactive Lipid Peroxidation Product. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2247–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillon, N.J.; Soulère, L.; Vella, R.E.; Croze, M.; Caré, B.R.; Soula, H.A.; Doutheau, A.; Lagarde, M.; Soulage, C.O. Quantitative structure–activity relationship for 4-hydroxy-2-alkenal induced cytotoxicity in L6 muscle cells. Chem. Interact. 2010, 188, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.K.; Murphy, T.C.; Leiphon, L.J.; Watt, J.; Morrow, J.D.; Milne, G.L.; Howard, J.R.H.; Picklo, M.J. Trans-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal is a neurotoxic product of docosahexaenoic (22:6; n − 3) acid oxidation. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubatsch, I.; Ridderström, M.; Mannervik, B. Human glutathione transferase A4-4: An Alpha class enzyme with high catalytic efficiency in the conjugation of 4-hydroxynonenal and other genotoxic products of lipid peroxidation. Biochem. J. 1998, 330, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.H.; Cho, S.; Joo, S.Y.; Ma, S.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.W. 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal-induced apoptosis in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3866–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, E.K.; Picklo, M.J., Sr. Trans-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal, a product of n-3 fatty acid peroxidation: Make some room HNE. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oruç, Y.; Celik, F.; Ozgur, G.; Beyazyildiz, E.; Ugur, K.; Yardim, M.; Sahin, I.; Akkoc, R.F.; Aydin, S. Altered blood and aqueous humor levels of asprosin, 4-hydroxynonenal, and 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine in patients with diabetes mellitus and cataract with and without diabetic retinopathy. Retina 2020, 40, 2410–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés-Blasco, I.; Gallego-Martínez, A.; Machado, X.; Cruz-Espinosa, J.; Di Lauro, S.; Casaroli-Marano, R.; Alegre-Ituarte, V.; Arévalo, J.F.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D. Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory, Angiogenic, and Apoptotic molecules in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydas, G.; Tuzcu, M.; Yasar, A.; Baydas, B. Early changes in glial reactivity and lipid peroxidation in diabetic rat retina: Effects of melatonin. Acta Diabetol. 2004, 41, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, K.K.; Lee, K.; Gao, G.; Lyons, T.J.; Kowluru, R.; Ma, J.-X. The role of lipid peroxidation products and oxidative stress in activation of the canonical wingless-type MMTV integration site (WNT) pathway in a rat model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Takei, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Nakahara, T.; Ishii, K. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal attenuates β2-adrenoceptor-mediated vasodilation of rat retinal arterioles. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Du, M.; Yang, S.; Hammad, S.M.; Wilson, K.; Chen, J.; Lyons, T.J. Mechanisms of modified LDL-induced pericyte loss and retinal injury in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 3128–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Yang, S.; Elliott, M.H.; Fu, D.; Wilson, K.; Zhang, J.; Du, M.; Chen, J.; Lyons, T. Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stresses Mediate Apoptosis Induced by Modified LDL in Human Retinal Müller Cells. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4595–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterbauer, H.; Schaur, R.J.; Zollner, H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 11, 81–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, X.G.; Wang, J. Malondialdehyde regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in murine islets via TCF7L2-dependent Wnt signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas-Bargues, C.; Escrivá, C.; Dromant, M.; Borrás, C.; Viña, J. Lipid peroxidation as measured by chromatographic determination of malondialdehyde. Human plasma reference values in health and disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 709, 108941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoubnasabjafari, M.; Ansarin, K.; Jouyban, A. Reliability of malondialdehyde as a biomarker of oxidative stress in psychological disorders. BioImpacts 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Losada, M.; Alio, J.L. Malondialdehyde serum concentration in type 1 diabetic with and without retinopaty. Doc. Ophthalmol. 1997, 93, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.-Z.; Zhang, H.; Chang, D.; Li, H.; Sui, H. The change of oxidative stress products in diabetes mellitus and diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborti, S. Can Serum MDA: SOD Ratio Predict Risk of Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Res. Rev. 2020, 7, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Grattagliano, I.; Vendemiale, G.; Boscia, F.; Micelli-Ferrari, T.; Cardia, L.; Altomare, E. Oxidative Retinal Products and Ocular Damages in Diabetic Patients. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 25, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altomare, E.; Grattagliano, I.; Vendemaile, G.; Micelli-Ferrari, T.; Signorile, A.; Cardia, L. Oxidative protein damage in human diabetic eye: Evidence of a retinal participation. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 27, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepper, R.E.; Chandler, V.L. Sporicidal Activity of Alkaline Alcoholic Saturated Dialdehyde Solutions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1963, 11, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glomb, M.A.; Lang, G. Isolation and Characterization of Glyoxal−Arginine Modifications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.R.; Baynes, J.W. Maillard reaction products in tissue proteins: New products and new perspectives. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glomb, M.A.; Pfahler, C. Amides Are Novel Protein Modifications Formed by Physiological Sugars. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41638–41647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vistoli, G.; De Maddis, D.; Cipak, A.; Zarkovic, N.; Carini, M.; Aldini, G. Advanced glycoxidation and lipoxidation end products (AGEs and ALEs): An overview of their mechanisms of formation. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47 (Suppl. 1), 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stitt, A.; Gardiner, T.A.; Anderson, N.L.; Canning, P.; Frizzell, N.; Duffy, N.; Boyle, C.; Januszewski, A.S.; Chachich, M.; Baynes, J.W.; et al. The AGE Inhibitor Pyridoxamine Inhibits Development of Retinopathy in Experimental Diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2826–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, B.O.; Schilling, S.; Rosinger, S.; Lang, G.K.; Kientsch-Engel, R.; Stahl, P. Elevated serum levels of N?-carboxymethyl-lysine, an advanced glycation end product, are associated with proliferative diabetic retinopathy and macular oedema. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tsuchida, K.; Okamoto, T.; Matsushita, T.; Higuchi, M.; Matsuda, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Makita, Z.; Koike, T. Increased Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Advanced Glycation End Products in Aqueous Humor of Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. Horm. Metab. Res. 2001, 33, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.V.; Stitt, A.W. The role of advanced glycation end products in retinal ageing and disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, H.-P.; Brownlee, M.; Lin, J.; Schleicher, E.; Bretzel, R.G. Diabetic retinopathy risk correlates with intracellular concentrations of the glycoxidation product N e -(carboxymethyl) lysine independently of glycohaemoglobin concentrations. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuth, S.; Sun, W.; Cleary, P.; Sell, D.R.; Dahms, W.; Malone, J.; Sivitz, W.; Monnier, V.M. Glycation and carboxymethyllysine levels in skin collagen predict the risk of future 10-year progression of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in the diabetes control and complications trial and epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.J.; Siraki, A.G.; Shangari, N. Aldehyde Sources, Metabolism, Molecular Toxicity Mechanisms, and Possible Effects on Human Health. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2005, 35, 609–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliou, V.; Nebert, D.W. Analysis and update of the human aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene family. Hum. Genom. 2005, 2, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penning, T.M. The aldo-keto reductases (AKRs): Overview. Chem. Interact. 2015, 234, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.E.; McGahon, M.K.; Augustine, J.; Chen, M.; McGeown, J.G.; Curtis, T.M. Diabetes Impairs the Aldehyde Detoxifying Capacity of the Retina. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makia, N.L.; Bojang, P.; Falkner, K.C.; Conklin, D.J.; Prough, R.A. Murine hepatic aldehyde dehydrogenase 1a1 is a major contributor to oxidation of aldehydes formed by lipid peroxidation. Chem. Interact. 2011, 191, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvekl, A.; Wang, W.-L. Retinoic acid signaling in mammalian eye development. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 89, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Molotkov, A.; Manabe, S.-I.; Donmoyer, C.M.; Deltour, L.; Foglio, M.H.; Cuenca, A.E.; Blaner, W.S.; Lipton, S.A.; Duester, G. Targeted Disruption of Aldh1a1 (Raldh1) Provides Evidence for a Complex Mechanism of Retinoic Acid Synthesis in the Developing Retina. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Onishi, A.; Misaki, K.; Yonemura, S.; Sugita, S.; Ito, H.; Ohigashi, Y.; Ema, M.; Sakaguchi, H.; Nishida, K.; et al. Neural retina-specific Aldh1a1 controls dorsal choroidal vascular development via Sox9 expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells. eLife 2018, 7, e32358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.-Q.; You, K.S.; Oh, S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Silencing of NRF2 Reduces the Expression of ALDH1A1 and ALDH3A1 and Sensitizes to 5-FU in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and Oxidative Stress: A General Overview of Mechanisms and Implications in Human Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Gong, J.; Cho, H.; Park, J.K.; Sung, E.-R.; Huang, H.; Wu, L.; Eberhart, C.; Handa, J.T.; et al. NRF2 plays a protective role in diabetic retinopathy in mice. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert-Garay, J.S.; Riesgo-Escovar, J.R.; Salceda, R. High glucose concentrations induce oxidative stress by inhibiting Nrf2 expression in rat Müller retinal cells in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyosov, A.A.; Rashkovetsky, L.G.; Tahir, M.K.; Keung, W.-M. Possible Role of Liver Cytosolic and Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenases in Acetaldehyde Metabolism. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 4445–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoval-Sánchez, B.; Rodríguez-Zavala, J.S. Differences in Susceptibility to Inactivation of Human Aldehyde Dehydrogenases by Lipid Peroxidation Byproducts. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Sun, L.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase and cardiac diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 88, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, P.; He, M.; Yan, W.; Chen, W.; Wei, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, W.; Chen, T. ALDH2 protects naturally aged mouse retina via inhibiting oxidative stress-related apoptosis and enhancing unfolded protein response in endoplasmic reticulum. Aging 2020, 13, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Hsiao, J.-R.; Chen, C.-H. ALDH2 polymorphism and alcohol-related cancers in Asians: A public health perspective. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Ferreira, J.C.B.; Gross, E.R.; Mochly-Rosen, D.; Gray, J.P.; Burgos, D.Z.; Yuan, T.; Seeram, N.; Rebar, R.; Follmer, R.; et al. Targeting Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2: New Therapeutic Opportunities. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Saruwatari, J.; Miyagawa, H.; Uchiyashiki, Y.; Oniki, K.; Sakata, M.; Kajiwara, A.; Yoshida, A.; Jinnouchi, H.; Nakagawa, K. Association between aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphisms and the incidence of diabetic retinopathy among Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Long, P.; Chen, T.; Li, K.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wen, A. ALDH2/SIRT1 Contributes to Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes-Induced Retinopathy through Depressing Oxidative Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 1641717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.L. Sirt1 and the Mitochondria. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppaka, V.; Chen, Y.; Mehta, G.; Orlicky, D.J.; Thompson, D.C.; Jester, J.V.; Vasiliou, V. ALDH3A1 Plays a Functional Role in Maintenance of Corneal Epithelial Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nees, D.W.; Wawrousek, E.F.; Robison, W.G.; Piatigorsky, J. Structurally Normal Corneas in Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 3a1-Deficient Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardieu, A. α-Crystallin quaternary structure and interactive properties control eye lens transparency. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1998, 22, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappa, A.; Chen, C.; Koutalos, Y.; Townsend, A.J.; Vasiliou, V. Aldh3a1 protects human corneal epithelial cells from ultraviolet- and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-induced oxidative damage. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Boger, M.; Bennewitz, K.; Sticht, C.; Kopf, S.; Morgenstern, J.; Fleming, T.; Hell, R.; Yuan, Z.; Nawroth, P.P.; et al. Elevated 4-hydroxynonenal induces hyperglycaemia via Aldh3a1 loss in zebrafish and associates with diabetes progression in humans. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Ho, Y.-J.; Chou, H.-C.; Liao, E.-C.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Wei, Y.-S.; Lin, L.-H.; Lin, M.-W.; Wang, Y.-S.; Ko, M.-L.; et al. The Role of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta in Retinal Ganglion Cells with Hyperglycemia and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, P.S. Sjogren-Larsson Syndrome: Mechanisms and Management. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2020, 13, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouzdar-Jain, S.; Suh, D.W.; Rizzo, W.B. Sjögren-Larsson syndrome: A complex metabolic disease with a distinctive ocular phenotype. Ophthalmic Genet. 2019, 40, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.-P.; Chen, J.; Zou, Y.-L. Identification of lncRNAs Associated with the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy: From Sequencing Analysis to Validation via In Vivo and In Vitro Experiments. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 1755945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt, J.W.; Korasick, D.A.; Qureshi, I.A.; Campbell, A.C.; Gates, K.S.; Tanner, J.J. Inhibition, crystal structures, and in-solution oligomeric structure of aldehyde dehydrogenase 9A1. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 691, 108477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, C.; Simó, R. Neuroprotection in Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2012, 12, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Weng, C.; Zeng, Y. Changes in glutamate homeostasis cause retinal degeneration in Royal College of Surgeons rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, H.-J.; Maser, E. Role of human aldo–keto-reductase AKR1B10 in the protection against toxic aldehydes. Chem. Interact. 2009, 178, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccari, R.; Ottanà, R. Targeting Aldose Reductase for the Treatment of Diabetes Complications and Inflammatory Diseases: New Insights and Future Directions. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 58, 2047–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, K.V. Aldose reductase: New insights for an old enzyme. Biomol. Concepts 2011, 2, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pladzyk, A.; Ramana, K.V.; Ansari, N.H.; Srivastava, S.K. Aldose reductase prevents aldehyde toxicity in cultured human lens epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonowal, H.; Ramana, K.V. 4-Hydroxy-Trans-2-Nonenal in the Regulation of Anti-Oxidative and Pro-Inflammatory Signaling Pathways. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5937326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Hara, A. Characterization of aldo-keto reductase 1C subfamily members encoded in two rat genes (akr1c19 and RGD1564865). Relationship to 9-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 700, 108755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Ferrari, M.; Ellis, E.M. Human aldo–keto reductase AKR7A2 protects against the cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of reactive aldehydes and lowers intracellular reactive oxygen species in hamster V79-4 cells. Chem. Interact. 2012, 195, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picklo, M.J.; Olson, S.J.; Hayes, J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Montine, T.J. Elevation of AKR7A2 (succinic semialdehyde reductase) in neurodegenerative disease. Brain Res. 2001, 916, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, M.A.; Xie, C.; Markesbery, W.R. Acrolein is increased in Alzheimer’s disease brain and is toxic to primary hippocampal cultures. Neurobiol. Aging 2001, 22, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, T.; Anderson, H.; Stitt, A. Inhibition of advanced glycation end-products protects against retinal capillary basement membrane expansion during long-term diabetes. J. Pathol. 2003, 201, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, F.; Riedl, E.; Wang, Q.; Hagen, F.V.; Deinzer, M.; Harmsen, M.C.; Molema, G.; Yard, B.; Feng, Y.; Hammes, H.-P. Oral Carnosine Supplementation Prevents Vascular Damage in Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Groppe, M.; Salvetti, A.P.; MacLaren, R.E. Technique of retinal gene therapy: Delivery of viral vector into the subretinal space. Eye 2017, 31, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, B.L.; Davis, J.L.; Gregori, N.Z. Choroideremia Gene Therapy. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2021, 61, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, A.R.; Groppe, M.; MacLaren, R.E. Gene Therapy for Choroideremia Using an Adeno-Associated Viral (AAV) Vector. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 5, a017293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utz, V.M.; Coussa, R.G.; Antaki, F.; Traboulsi, E.I. Gene therapy for RPE65-related retinal disease. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, C.; Tzekov, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, W. The effect of human gene therapy for RPE65-associated Leber’s congenital amaurosis on visual function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, E.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-Associated Virus at 50: A Golden Anniversary of Discovery, Research, and Gene Therapy Success—A Personal Perspective. Hum. Gene Ther. 2015, 26, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, S.B.; Schwartz, J.W.; Bachaboina, L.; Taylor-Blake, B.; Coleman, J.; Ehlers, M.D.; Zylka, M.J.; McCown, T.J.; Samulski, R.J.; Lukashchuk, V.; et al. Optimizing Promoters for Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Gene Expression in the Peripheral and Central Nervous System Using Self-Complementary Vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 22, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, R.R.; Koerber, J.T.; Dalkara, D.; Flannery, J.G.; Schaffer, D.V. A Novel Adeno-Associated Viral Variant for Efficient and Selective Intravitreal Transduction of Rat Müller Cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodyear, M.J.; Crewther, S.G.; Junghans, B.M. A role for aquaporin-4 in fluid regulation in the inner retina. Vis. Neurosci. 2009, 26, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahoon, J.M.; Rai, R.R.; Carroll, L.S.; Uehara, H.; Zhang, X.; O’Neil, C.L.; Medina, R.J.; Das, S.K.; Muddana, S.K.; Olson, P.R.; et al. Intravitreal AAV2.COMP-Ang1 prevents neurovascular degeneration in a murine model of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2015, 64, 4247–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.; Roberts, G.E.; Liu, G.-S. Updates on Gene Therapy for Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2020, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Cha, S.; Lee, K.J.; Woo, H.-N.; Park, K.; Lee, H. mTOR inhibition as a novel gene therapeutic strategy for diabetic retinopathy. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, N. Progress of Nanotechnology in Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah, I.; Ong, C.; Liu, Z.; Su, X. Polymeric biomaterials in the treatment of posterior segment diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 949543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmont-Díaz, J.A.; Calleja-Castañeda, L.F.; Yoval-Sánchez, B.; Rodríguez-Zavala, J.S. Tamoxifen, an anticancer drug, is an activator of human aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2015, 83, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calleja, L.F.; Belmont-Díaz, J.A.; Medina-Contreras, O.; Quezada, H.; Yoval-Sánchez, B.; Campos-García, J.; Rodríguez-Zavala, J.S. Omeprazole as a potent activator of human cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH1A1. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Budas, G.R.; Churchill, E.N.; Disatnik, M.-H.; Hurley, T.D.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Activation of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Reduces Ischemic Damage to the Heart. Science 2008, 321, 1493–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Long, P.; Yan, W.; Chen, T.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. ALDH2 attenuates early-stage STZ-induced aged diabetic rats retinas damage via Sirt1/Nrf2 pathway. Life Sci. 2018, 215, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki, J.P.; Cao, H.; Van Wassenhove, L.D.; Viswanathan, V.; Bloomstein, J.; Nambiar, D.K.; Mattingly, A.J.; Jiang, D.; Chen, C.-H.; Stevens, M.C.; et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3A1 activation prevents radiation-induced xerostomia by protecting salivary stem cells from toxic aldehydes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6279–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Cao, H.; Chen, C.-H.; Kong, C.S.; Ali, R.; Chan, C.; Sirjani, D.; Graves, E.; Koong, A.; Giaccia, A.; et al. A Novel Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-3 Activator (Alda-89) Protects Submandibular Gland Function from Irradiation without Accelerating Tumor Growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4455–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banh, A.; Xiao, N.; Cao, H.; Chen, C.-H.; Kuo, P.; Krakow, T.; Bavan, B.; Khong, B.; Yao, M.; Ha, C.; et al. A Novel Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-3 Activator Leads to Adult Salivary Stem Cell Enrichment In Vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7265–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt-Hyatt, M.; Lickteig, A.J.; Klaassen, C.D. Tissue distribution, ontogeny, and chemical induction of aldo-keto reductases in mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Protein Names (Aliases) | Number of Transcripts | Subcellular Location | Chromosome Localization | Substrate Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALDH1A1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A1 | 4 | Cytosol | 9q21.13 | Retinal, Acrolein, 4-HNE and MDA |
| ALDH2 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 family member | 2 | Mitochondria | 12q24.2 | Acetaldehyde, Acrolein, 4-HNE and MDA |
| ALDH3A1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family member A1 | 10 | Cytosol, Nucleus | 17p11.2 | Aromatic aliphatic, Acrolein. 4-HNE and MDA |
| ALDH3A2 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family member A2 | 22 | Microsomes, peroxisomes | 17p11.2 | Fatty aldehydes |
| ALDH9A1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 9 family member A1 | 1 | Cytosol | 1q23.2 | γ-Aminobutyr-aldehyde, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, betaine aldehyde |
| ALDH18A1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 18 family member A1 | 2 | Mitochondria | 10q24.3 | Glutamic γ-semi-aldehyde, glutamate |
| AKR1A1 | Aldehyde reductase: dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 1 | 6 | Cytosol | 1p33-p32 | DL-glyceraldehyde Melvadate |
| AKR1B1 | Aldose reductase | 1 | Cytosol | 7q35 | Glucose, advanced end glycation products, 4-HNE, GS-HNE, reactive carbonyls |
| AKR1B10 | Small intestine like aldose reductase; 9-cis-retinal reductase | 1 | Cytosol and Plasma Membrane | 7q33 | Retinal; reactive carbonyls |
| AKR7A2 | Aflatoxin aldehyde reductase | 3 | Cytosol | 1p35.1-p36.23 | Reduction of succinic semialdehyde; acrolein 2-carboxybenzlaldehyde; aflatoxin dialdehyde, 4-HNE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karan, B.M.; Little, K.; Augustine, J.; Stitt, A.W.; Curtis, T.M. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase and Aldo-Keto Reductase Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Emerging Roles in Diabetic Retinopathy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071466
Karan BM, Little K, Augustine J, Stitt AW, Curtis TM. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase and Aldo-Keto Reductase Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Emerging Roles in Diabetic Retinopathy. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(7):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071466
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaran, Burak Mugdat, Karis Little, Josy Augustine, Alan W. Stitt, and Tim M. Curtis. 2023. "Aldehyde Dehydrogenase and Aldo-Keto Reductase Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Emerging Roles in Diabetic Retinopathy" Antioxidants 12, no. 7: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071466
APA StyleKaran, B. M., Little, K., Augustine, J., Stitt, A. W., & Curtis, T. M. (2023). Aldehyde Dehydrogenase and Aldo-Keto Reductase Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Emerging Roles in Diabetic Retinopathy. Antioxidants, 12(7), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12071466







