A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Uric Acid and Allantoin and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
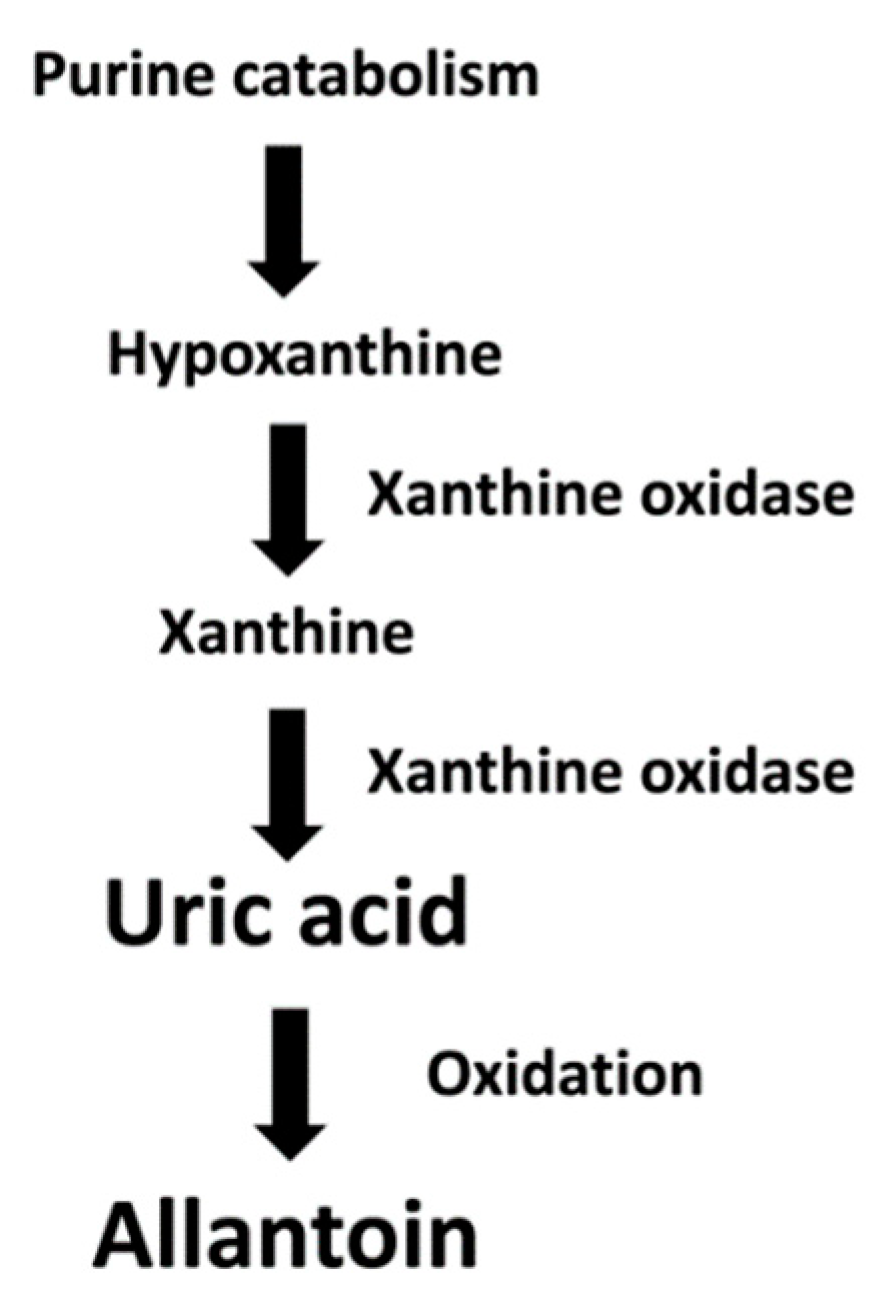
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Systematic Literature Search
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Search
3.2. Uric Acid
3.3. Allantoin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, A.; Koduri, G. Extra-articular manifestations and complications of rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 21, 907–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figus, F.A.; Piga, M.; Azzolin, I.; McConnell, R.; Iagnocco, A. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghdadi, L.R.; Woodman, R.J.; Shanahan, E.M.; Mangoni, A.A. The impact of traditional cardiovascular risk factors on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blum, A.; Adawi, M. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and cardiovascular disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semb, A.G.; Ikdahl, E.; Wibetoe, G.; Crowson, C.; Rollefstad, S. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease prevention in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.N.; Giles, J.T.; Liao, K.P. Shared inflammatory pathways of rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdifield, J.; Paterson, J.M.; Huang, A.; Bernatsky, S. Causes of Death in Rheumatoid Arthritis: How Do They Compare to the General Population? Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Pan, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Song, X.; Ren, Y.; Shan, P.F. Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: An analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.J.; van Halm, V.P.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Smulders, Y.M.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.F.; Visser, M.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; et al. Does rheumatoid arthritis equal diabetes mellitus as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease? A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erre, G.L.; Piga, M.; Fedele, A.L.; Mura, S.; Piras, A.; Cadoni, M.L.; Cangemi, I.; Dessi, M.; Di Sante, G.; Tolusso, B.; et al. Prevalence and Determinants of Peripheral Microvascular Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 6548715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangoni, A.A.; Tommasi, S.; Sotgia, S.; Zinellu, A.; Paliogiannis, P.; Piga, M.; Cauli, A.; Pintus, G.; Carru, C.; Erre, G.L. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine: A Key Player in the Pathophysiology of Endothelial Dysfunction, Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordy, R.; Totoson, P.; Prati, C.; Marie, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erre, G.L.; Mangoni, A.A.; Castagna, F.; Paliogiannis, P.; Carru, C.; Passiu, G.; Zinellu, A. Meta-Analysis of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Concentrations in Rheumatic Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erre, G.L.; Buscetta, G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; Passiu, G.; Zinellu, A. Coronary flow reserve in systemic rheumatic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Guan, S.Y.; Xu, S.Z.; Li, H.M.; Leng, R.X.; Li, X.P.; Pan, H.F. Increased carotid intima-media thickness in rheumatoid arthritis: An update meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Tasso, M.; Lupoli, R.; Di Minno, A.; Baldassarre, D.; Tremoli, E.; Di Minno, M.N. Non-invasive assessment of arterial stiffness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of literature studies. Ann. Med. 2015, 47, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erre, G.L.; Piras, A.; Mura, S.; Mundula, N.; Piras, M.; Taras, L.; Longu, M.G.; Saba, P.S.; Ganau, A.; Carru, C.; et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and arterial stiffness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2016, 44, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiss, A.B.; Silverman, A.; Khalfan, M.; Vernice, N.A.; Kasselman, L.J.; Carsons, S.E.; De Leon, J. Accelerated Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Mechanisms and Treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 969–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoenfeld, Y.; Gerli, R.; Doria, A.; Matsuura, E.; Cerinic, M.M.; Ronda, N.; Jara, L.J.; Abu-Shakra, M.; Meroni, P.L.; Sherer, Y. Accelerated atherosclerosis in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Circulation 2005, 112, 3337–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczuk, E.; Tlustochowicz, W.; Kramarz, E.; Kisiel, B.; Marczak, M.; Tlustochowicz, M.; Malek, L.A. Early Myocardial Changes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis without Known Cardiovascular Diseases-A Comprehensive Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, G.D.; Piga, M.; Piga, A.; Falco, O.; Ponti, E.; Cauli, A.; Floris, A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Casu, G.; De Luca, G.; et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of electrocardiographic signs of atrial myopathy in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the EDRA study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houri Levi, E.; Watad, A.; Whitby, A.; Tiosano, S.; Comaneshter, D.; Cohen, A.D.; Amital, H. Coexistence of ischemic heart disease and rheumatoid arthritis patients-A case control study. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungprasert, P.; Srivali, N.; Kittanamongkolchai, W. Risk of incident atrial fibrillation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Zang, C.; et al. Stroke risk in arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.S.; Nicola, P.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Roger, V.L.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Gabriel, S.E. Increased unrecognized coronary heart disease and sudden deaths in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phull, A.R.; Nasir, B.; Haq, I.U.; Kim, S.J. Oxidative stress, consequences and ROS mediated cellular signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 281, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, M.J.; Nissim, A.; Knight, A.R.; Whiteman, M.; Haigh, R.; Winyard, P.G. Oxidative stress in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Sharma, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis: Insights into NRF2-KEAP1 signalling. Autoimmunity 2021, 54, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Armada, M.J.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, J.A.; Blanco, F.J. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaito, A.; Aramouni, K.; Assaf, R.; Parenti, A.; Orekhov, A.; Yazbi, A.E.; Pintus, G.; Eid, A.H. Oxidative Stress-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozos, I.; Luca, C.T. Crosstalk between Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress and Arterial Stiffness. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goette, A.; Lendeckel, U. Atrial Cardiomyopathy: Pathophysiology and Clinical Consequences. Cells 2021, 10, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsaliaris, I.K.; Moschonas, I.C.; Pechlivani, L.M.; Tsouka, A.N.; Tselepis, A.D. Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Vascular Aging and Atherosclerotic Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 5496–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstermann, U.; Xia, N.; Li, H. Roles of Vascular Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassu, S.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Floris, A.; Farina, G.; Passiu, G.; Carru, C.; Erre, G.L. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Peripheral Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Monocentric Cross-Sectional Case-Control Study. Molecules 2020, 25, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinonez-Flores, C.M.; Gonzalez-Chavez, S.A.; Del Rio Najera, D.; Pacheco-Tena, C. Oxidative Stress Relevance in the Pathogenesis of the Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6097417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- da Fonseca, L.J.S.; Nunes-Souza, V.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Rabelo, L.A. Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis: What the Future Might Hold regarding Novel Biomarkers and Add-On Therapies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7536805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Colombo, R.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A. Biomarkers of oxidative damage in human disease. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrocco, I.; Altieri, F.; Peluso, I. Measurement and Clinical Significance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Humans. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 6501046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frijhoff, J.; Winyard, P.G.; Zarkovic, N.; Davies, S.S.; Stocker, R.; Cheng, D.; Knight, A.R.; Taylor, E.L.; Oettrich, J.; Ruskovska, T.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2015, 23, 1144–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sautin, Y.Y.; Johnson, R.J. Uric acid: The oxidant-antioxidant paradox. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glantzounis, G.K.; Tsimoyiannis, E.C.; Kappas, A.M.; Galaris, D.A. Uric acid and oxidative stress. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 4145–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherghina, M.E.; Peride, I.; Tiglis, M.; Neagu, T.P.; Niculae, A.; Checherita, I.A. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Halliwell, B. Action of biologically-relevant oxidizing species upon uric acid. Identification of uric acid oxidation products. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1990, 73, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kand’ar, R.; Zakova, P. Allantoin as a marker of oxidative stress in human erythrocytes. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Moral, M.-P.; Kannan, K. Allantoin as a Marker of Oxidative Stress: Inter- and Intraindividual Variability in Urinary Concentrations in Healthy Individuals. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, T.; Kita, K.; Tomita, S.; Qu, G.J.; Tasaki, Y.; Ito, A. Is allantoin in serum and urine a useful indicator of exercise-induced oxidative stress in humans? Free Radic. Res. 2000, 32, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, L.; Song, M.; Song, Y. Baseline serum uric acid level as a predictor of cardiovascular disease related mortality and all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Song, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z. Elevated serum uric acid and risk of cardiovascular or all-cause mortality in people with suspected or definite coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2016, 254, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M.; Lipid Blood Pressure Meta-Analysis Collaboration, G. Associations of serum uric acid with total and cause-specific mortality: Findings from individuals and pooling prospective studies. Atherosclerosis 2020, 296, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panoulas, V.F.; Milionis, H.J.; Douglas, K.M.; Nightingale, P.; Kita, M.D.; Klocke, R.; Elisaf, M.S.; Kitas, G.D. Association of serum uric acid with cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panoulas, V.F.; Douglas, K.M.; Milionis, H.J.; Nightingale, P.; Kita, M.D.; Klocke, R.; Metsios, G.S.; Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Elisaf, M.S.; Kitas, G.D. Serum uric acid is independently associated with hypertension in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2008, 22, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannawi, S.; AlSalmi, I.; Moller, I.; Naredo, E. Uric acid is independent cardiovascular risk factor, as manifested by increased carotid intima-media thickness in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 1897–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; Johanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tobias, A. Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Tech. Bull. 1999, 47, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootveld, M.; Halliwell, B. Measurement of allantoin and uric acid in human body fluids. A potential index of free-radical reactions in vivo? Biochem. J. 1987, 243, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yardim-Akaydin, S.; Sepici, A.; Ozkan, Y.; Torun, M.; Simsek, B.; Sepici, V. Oxidation of uric acid in rheumatoid arthritis: Is allantoin a marker of oxidative stress? Free Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.J.; Vinagre, F.; Silva, J.J.; Gil, V.; Fonseca, J.E. Cardiovascular risk profile in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis: A comparative study of female patients. Acta Reum. Port. 2010, 35, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.; Singh, A.; Chandra, V.; Negi, M.P.; Tripathy, B.C.; Prakash, J.; Gupta, V. A comparative analysis of serological parameters and oxidative stress in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 2377–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamp, L.K.; Khalilova, I.; Tarr, J.M.; Senthilmohan, R.; Turner, R.; Haigh, R.C.; Winyard, P.G.; Kettle, A.J. Myeloperoxidase and oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, R.; Stamp, L.K.; Kettle, A.J. Detection of allantoin in clinical samples using hydrophilic liquid chromatography with stable isotope dilution negative ion tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 891, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Compan, V.; Melguizo-Madrid, E.; Hernandez-Cruz, B.; Santos-Rey, K.; Leyva-Prado, C.; Gonzalez-Martin, C.; Navarro-Sarabia, F.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, C. Interaction between oxidative stress and smoking is associated with an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilecik, N.A.; Tuna, S.; Samanci, N.; Balci, N.; Akbas, H. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in women with rheumatoid arthritis and effective factors. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 2258–2265. [Google Scholar]
- Chavan, V.U.; Ramavataram, D.; Patel, P.A.; Rupani, M.P. Evaluation of serum magnesium, lipid profile and various biochemical parameters as risk factors of cardiovascular diseases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, BC01–BC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, N.T.; Scavuzzi, B.M.; Iriyoda, T.M.V.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Alfieri, D.F.; de Medeiros, F.A.; de Sa, M.C.; Micheletti, P.L.; Sekiguchi, B.A.; Reiche, E.M.V.; et al. Metabolic syndrome and the decreased levels of uric acid by leflunomide favor redox imbalance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 18, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Z.; Gao, Y.; Fan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Wan, W.; Zhao, D.B. Metabolic abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis patients with comorbid diabetes mellitus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Moustafa, S.R.; Jasem, K.M. Serum Cesium, Rhenium, and Rubidium in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Haro, B.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, S.O.; Gonzalez-Lopez, L.; Espinel-Bermudez, M.C.; Garcia-Benavides, L.; Perez-Guerrero, E.; Vazquez-Villegas, M.L.; Robles-Cervantes, J.A.; Salazar-Paramo, M.; Hernandez-Corona, D.M.; et al. Fasting triglycerides and glucose index: A useful screening test for assessing insulin resistance in patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescha, A.; Zablocka-Slowinska, K.; Placzkowska, S.; Gorczyca, D.; Luczak, A.; Grajeta, H. Silicon intake and plasma level and their relationships with systemic redox and inflammatory markers in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Xu, S.; Lin, H.; Ni, W.; Yang, Q.; Qi, J.; Du, K.; Gu, J.; Lin, Z. Prevalence and risk factors for bone loss in Southern Chinese with rheumatic diseases. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.N.; Kim, A.; Kim, Y.; Kim, G.T.; Sohn, D.H.; Lee, S.G. Higher serum uric acid levels are associated with reduced risk of hip osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.L.; Prakash, J.; Gupta, V. TGF-beta1 +869C/T polymorphism increases susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in North Indian population. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2881–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xu, S.; Lin, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chu, Y. Prevalence and risk factors for bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis patients from South China: Modeled by three methods. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xiang, T.; Gong, B.; Xie, J. Serum Uric Acid as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J.; Oppedisano, F.; Gratteri, S.; Muscoli, C.; Mollace, V. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 213, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriwaki, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Higashino, K. Enzymes involved in purine metabolism--a review of histochemical localization and functional implications. Histol. Histopathol. 1999, 14, 1321–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Yang, F.; Yang, I.; Yin, Y.; Luo, J.J.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.F. Uric acid, hyperuricemia and vascular diseases. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ames, B.N.; Cathcart, R.; Schwiers, E.; Hochstein, P. Uric acid provides an antioxidant defense in humans against oxidant- and radical-caused aging and cancer: A hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6858–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.M.; Morre, J.T.; Beckman, J.S. Triuret: A novel product of peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of urate. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 423, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrini, E.; Serafini, M.; Colic Baric, I.; Hazen, S.L.; Klein, S. Effect of plasma uric acid on antioxidant capacity, oxidative stress, and insulin sensitivity in obese subjects. Diabetes 2014, 63, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurajoh, M.; Fukumoto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Akari, S.; Murase, T.; Nakamura, T.; Ishii, H.; Yoshida, H.; Nagata, Y.; Morioka, T.; et al. Uric acid shown to contribute to increased oxidative stress level independent of xanthine oxidoreductase activity in MedCity21 health examination registry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waring, W.S.; Convery, A.; Mishra, V.; Shenkin, A.; Webb, D.J.; Maxwell, S.R. Uric acid reduces exercise-induced oxidative stress in healthy adults. Clin. Sci. 2003, 105, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gersch, C.; Palii, S.P.; Kim, K.M.; Angerhofer, A.; Johnson, R.J.; Henderson, G.N. Inactivation of nitric oxide by uric acid. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, R.O., 3rd. Role of nitric oxide in cardiovascular disease: Focus on the endothelium. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar]
- Grayson, P.C.; Kim, S.Y.; LaValley, M.; Choi, H.K. Hyperuricemia and incident hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, J.; Lawrence, W.R.; Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Li, C.; Lian, W.; He, J.; Qu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Association between serum uric acid and obesity in Chinese adults: A 9-year longitudinal data analysis. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e041919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Guo, Y.; Tu, H.; Li, S.; Chen, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Wu, X.; Song, Z. Temporal changes in serum uric acid and risk for metabolic syndrome: A longitudinal cohort study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Liu, Y.; Han, L.; Xu, G.; Ran, J.M. Serum uric acid is associated with incident chronic kidney disease in middle-aged populations: A meta-analysis of 15 cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, Q. Association of serum uric acid with mortality and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with hypertension: A meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, L.; Hu, X.; Tan, T.; Yang, J.; Bao, W.; Rong, S. Association of Serum Uric Acid With All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Luo, Q.; Li, B.; Lin, Z.; Yu, X.; Huang, F. Serum uric acid and mortality in chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1326–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.H.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.H. Effect of uric acid-lowering therapy on blood pressure: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. 2017, 49, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Okami, N.; Yamada, T.; Azushima, K.; Yamaji, T.; Kinguchi, S.; Uneda, K.; Kanaoka, T.; Wakui, H.; Tamura, K. Prevention of kidney function decline using uric acid-lowering therapy in chronic kidney disease patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 41, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ge, J.; Zha, M.; Miao, J.J.; Sun, Z.L.; Yu, J.Y. Effects of Uric Acid-Lowering Treatment on Glycemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.X.; Anjos, E.I.; Augusto, O. Uric acid oxidation by peroxynitrite: Multiple reactions, free radical formation, and amplification of lipid oxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 372, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautin, Y.Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Zharikov, S.; Johnson, R.J. Adverse effects of the classic antioxidant uric acid in adipocytes: NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidative/nitrosative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 293, C584–C596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Dubey, P.; Cistola, D.P.; Reddy, S.Y. Association Between Obesity and Cardiovascular Outcomes: Updated Evidence from Meta-analysis Studies. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Burgess, S. Causal role of high body mass index in multiple chronic diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Mendelian randomization studies. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, J.; Ding, N.; He, Y. Correlation of uric acid with body mass index based on NHANES 2013–2018 data: A cross-sectional study. Medicine 2022, 101, e30646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Allan, J.; Gamble, G.D.; Horne, A.; Woodward, O.M.; Stamp, L.K.; Merriman, T.R. Effect of body mass index on serum urate and renal uric acid handling responses to an oral inosine load: Experimental intervention study in healthy volunteers. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlik, P.; Hasikova, L.; Stiburkova, B.; Zavada, J.; Kalikova, K. Rapid and reliable HILIC-MS/MS method for monitoring allantoin as a biomarker of oxidative stress. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 589, 113509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.Y.; Benzie, I.F. Plasma allantoin measurement by isocratic liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry: Method evaluation and application in oxidative stress biomonitoring. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopcil, M.; Kandar, R. Screening method for the simultaneous determination of allantoin and uric acid from dried blood spots. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 225, 115222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, Y.; Yardim-Akaydin, S.; Imren, E.; Torun, M.; Simsek, B. Increased plasma homocysteine and allantoin levels in coronary artery disease: Possible link between homocysteine and uric acid oxidation. Acta Cardiol. 2006, 61, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.; Pakkiri, L.S.; Lim, J.; Chia, S.C.; Ponnalagu, S.; Drum, C.L.; Henry, C.J. Reductions in Postprandial Plasma Allantoin Concentrations With Increasing Doses of Polyphenol Rich Curry Intake—A Randomized Crossover Trial. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Healthy Controls | Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | n | Age (Years) | M/F | Uric Acid Mean ± SD (mg/dL, µmol/L, or mmol/L) | Allantoin Mean ± SD (µmol/L) | n | Age (Years) | M/F | Uric Acid Mean ± SD (mg/dL, µmol/L, or mmol/L) | Allantoin Mean ± SD (µmol/L) |
| Grootveld et al., 1987, UK [63] | 7 | NR | 4/3 | 432 ± 121 * | 18.6 ± 3.8 | 4 | NR | 2/2 | 375 ± 102 * | 36.1 ± 63 |
| Yardim-Akaydin et al., 2004, Turkey [64] | 15 | 55 | 3/12 | 278 ± 54 * | 13.6 ± 63 | 21 | 55 | 4/17 | 281 ± 65 * | 22.1 ± 11.3 |
| Santos et al., 2010, Portugal [65] | 102 | 48 | 0/102 | 3.8 ± 1.0 | NR | 98 | 49 | 0/98 | 4.1 ± 1.1 | NR |
| Mishra et al., 2012, India [66] | 36 | 50 | 11/25 | 5.05 ± 1.74 | NR | 36 | 50 | 14/22 | 4.00 ± 1.26 | NR |
| Stamp et al., 2012, UK [67] | 120 | 68 | 87/33 | NR | 2.22 ± 1.38 | 77 | 55 | 22/55 | NR | 4.01 ± 1.88 |
| Turner et al., 2012, New Zealand [68] | 35 | NR | NR | NR | 2.47 ± 1.63 | 43 | NR | NR | NR | 4.10 ± 1.93 |
| Navarro-Compan et al., 2013, Spain [69] | 65 | 50 | 14/51 | 4.83 ± 1.26 | NR | 65 | 50 | 14/51 | 4.47 ± 1.04 | NR |
| Bilecik et al., 2014, Turkey [70] | 100 | 51 | 0/100 | 4.08 ± 0.97 | NR | 100 | 52 | 0/100 | 4.09 ± 1.13 | NR |
| Chavan et al., 2015, India [71] | 50 | NR | 20/30 | 3.73 ± 1.45 | NR | 50 | NR | 19/31 | 4.46 ± 1.74 | NR |
| Costa et al., 2018, Brazil [72] | 150 | 45 | 42/108 | 4.42 ± 1.43 | NR | 177 | 55 | 33/144 | 4.0 ± 1.5 | NR |
| Liu et al., 2018, China [73] (a) | 100 | 62 | 31/69 | 0.25 ± 0.12 ° | NR | 104 | 62 | 35/65 | 0.28 ± 0.10 ° | NR |
| Liu et al., 2018, China [73] (b) | 100 | 62 | 31/69 | 0.25 ± 0.12 ° | NR | 104 | 64 | 34/70 | 0.27 ± 0.12 ° | NR |
| Al-Hakeim et al., 2019, Iraq [74] | 60 | NR | 30/30 | 5.93 ± 1.78 | NR | 126 | NR | 66/60 | 6.32 ± 2.41 | NR |
| Contreras-Haro et al., 2019, Mexico [75] | 50 | 51 | NR | 4.07 ± 0.9 | NR | 95 | 54 | NR | 4.4 ± 1.2 | NR |
| Prescha et al., 2019, Poland [76] | 129 | 54 | 47/82 | 5.7 ± 4.3 | NR | 115 | 52 | 24/51 | 5.0 ± 5.6 | NR |
| Hu et al., 2020, China [77] | 302 | 63 | 73/229 | 326 ± 102 * | NR | 556 | 58 | 106/450 | 328 ± 117 * | NR |
| Lee et al., 2020, Republic of Korea [78] | 200 | 61 | 0/200 | 4.17 ± 0.89 | NR | 447 | 61 | 0/447 | 4.03 ± 1.11 | NR |
| Patel et al., 2020, India [79] | 87 | 41 | 29/58 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | NR | 76 | 44 | 17/59 | 4.09 ± 1.6 | NR |
| Hu et al., 2021, China [80] | 198 | 60 | 52/146 | 327 ± 101 * | NR | 405 | 59 | 85/317 | 314 ± 104 * | NR |
| Wang et al., 2022, China [81] | 138 | 66 | 26/112 | 235 ± 55 * | NR | 266 | 55 | 28/238 | 262 ± 92 * | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zinellu, A.; Mangoni, A.A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Uric Acid and Allantoin and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081569
Zinellu A, Mangoni AA. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Uric Acid and Allantoin and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants. 2023; 12(8):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081569
Chicago/Turabian StyleZinellu, Angelo, and Arduino A. Mangoni. 2023. "A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Uric Acid and Allantoin and Rheumatoid Arthritis" Antioxidants 12, no. 8: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081569
APA StyleZinellu, A., & Mangoni, A. A. (2023). A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Uric Acid and Allantoin and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants, 12(8), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081569









