Relationship between Aspartame-Induced Cerebral Cortex Injury and Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis in Sprague Dawley Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals and Experimental Procedures
2.3. Measurement of Brain Function Biomarkers
2.4. Measurement of Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx), 8-Hydroxy-2-deoxy Guanosine (8-OHdG), and Malondialdehyde (MDA) in Rat Brain
2.5. Histological Preparation and Examination
2.6. Cresyl Violet (Nissl) Staining for Determination of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum in the Cytoplasm of Neurons
2.7. Western Blot Analysis of IL6, IL1β, TNFα, iNOS, NFκB, IκB, SOD2, CAT, Nrf2, Keap1, Sirt1, PGC1α, Nrf1, TFAM, Caspase-3, Bax, Bcl2, GFAP, and GAPDH Expressions
2.8. Mitochondria DNA Copy Number Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Oral Administration of Aspartame on Rats’ Body and Brain Weight
3.2. Effects of Oral Administration of Aspartame on BDNF, COX-2, and PGE2 Levels in the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
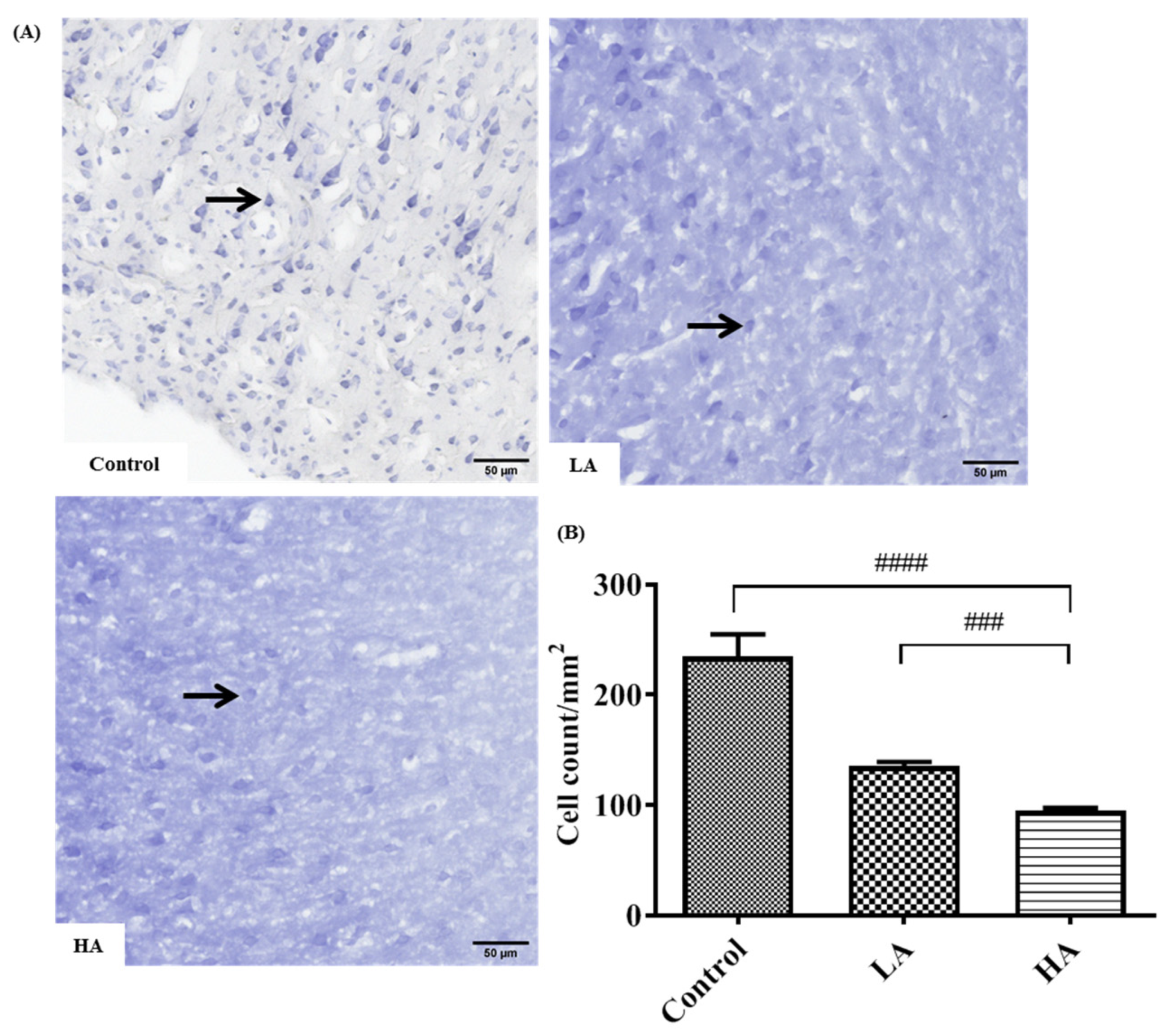
3.3. Effects of Oral Administration of Aspartame on the Histology and Nissl Stain of the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
3.4. Effects of Aspartame Oral Administration on Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Marker Protein Expression of the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
3.5. Effects of Oral Administration of Aspartame on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and Inflammatory Response of the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
3.6. Effects of Oral Administration of Aspartame on Antioxidant Enzymes and Oxidative Biomarkers
3.7. Effects of Oral Administration of Aspartame on Mitochondrial Biogenesis Protein Expression of the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
3.8. Effects of Aspartame Oral Administration on Apoptosis-Related Protein Expression of the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
3.9. Effects of Oral Administration of Aspartame on Mitochondria DNA Copy Number of the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
3.10. Effects of Aspartame Oral Administration on GFAP Expression in the Rats’ Cerebral Cortex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shalaby, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.H.; Aboregela, A.M. Effect of aspartame on the placenta of adult albino rat. A histological and immunohistochemical study. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. Off. Organ. Anat. Ges. 2019, 224, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchko, H.H.; Stargel, W.W.; Comer, C.P.; Mayhew, D.A.; Benninger, C.; Blackburn, G.L.; de Sonneville, L.M.; Geha, R.S.; Hertelendy, Z.; Koestner, A.; et al. Aspartame: Review of safety. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 35, S1–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, P.; Pretorius, E.; Naudé, H. Direct and indirect cellular effects of aspartame on the brain. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebda, M.A.; Sadek, K.M.; El-Sayed, Y.S. Aspartame and Soft Drink-Mediated Neurotoxicity in Rats: Implication of Oxidative Stress, Apoptotic Signaling Pathways, Electrolytes and Hormonal Levels. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, T.; Ab, Q.N.; Shrivastava, V.K. Aspartame: Effects and Awareness. MOJ Toxicol. 2017, 3, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchko, H.H.; Kotsonis, F.N. Acceptable daily intake vs actual intake: The aspartame example. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1991, 10, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.K.; Huang, H.Y.; Tseng, H.F.; Hsuuw, Y.D.; Tso, T.K. Interaction of vitamin E and exercise training on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activities in rat skeletal muscles. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S. Effect of Aspartame on the Frontal Cortex of Adult Male Albino Rats. A Light and Electron Microscopic Study. Egypt. J. Histol. 2009, 32, 346–357. [Google Scholar]
- Young, A.P.; Young, H.P.; Tolbert, L.D. Basic Clinical Neuroscience, 3rd ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 206–208. [Google Scholar]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J.; Nwoha, P.U. Alterations in behavior, cerebral cortical morphology and cerebral oxidative stress markers following aspartame ingestion. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 78, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Lin, Y.F.; Au, H.K.; Hsia, S.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Hsieh, R.H. Aspartame Consumption, Mitochondrial Disorder-Induced Impaired Ovarian Function, and Infertility Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.A. Anti-neuroinflammatory and antioxidant effects of N-acetyl cysteine in long-term consumption of artificial sweetener aspartame in the rat cerebral cortex. J. Basic. Appl. Zool. 2015, 72, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, E.A. Inflammation and neurochemical alterations induced by oral aspartame administration in experimental rats. Indian J. Appl. Res. 2016, 5, 750–753. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.Y.; Kim, W.; Hahn, K.R.; Nam, S.M.; Yi, S.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Kang, M.S.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Yoon, Y.S.; et al. Spatial and temporal changes in the PGE2 EP2 receptor in mice hippocampi during postnatal development and its relationship with cyclooxygenase-2. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 24, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldminz, A.M.; Au, S.C.; Kim, N.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Lizzul, P.F. NF-κB: An essential transcription factor in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 69, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopincová, J.; Púzserová, A.; Bernátová, I. Biochemical aspects of nitric oxide synthase feedback regulation by nitric oxide. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2011, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Salem, N.A.; Hussein, J.S. Effect of aspartame on oxidative stress and monoamine neurotransmitter levels in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. Neurotox. Res. 2012, 21, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, I.; Sheeladevi, R. Neurobehavioral changes and activation of neurodegenerative apoptosis on long-term consumption of aspartame in the rat brain. J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2015, 2, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Abdusalam, S.Z.; Onaolapo, O.J. Silymarin attenuates aspartame-induced variation in mouse behaviour, cerebrocortical morphology and oxidative stress markers. Pathophysiology 2017, 24, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J.; Nwoha, P.U. Aspartame and the hippocampus: Revealing a bi-directional, dose/time-dependent behavioural and morphological shift in mice. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 139, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, A.Y.; Onaolapo, O.J.; Nwoha, P.U. Methyl aspartylphenylalanine, the pons and cerebellum in mice: An evaluation of motor, morphological, biochemical, immunohistochemical and apoptotic effects. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 86, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruszkiewicz, J.; Albrecht, J. Changes in the mitochondrial antioxidant systems in neurodegenerative diseases and acute brain disorders. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 88, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärkkäinen, V.; Pomeshchik, Y.; Savchenko, E.; Dhungana, H.; Kurronen, A.; Lehtonen, S.; Naumenko, N.; Tavi, P.; Levonen, A.L.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Nrf2 regulates neurogenesis and protects neural progenitor cells against Aβ toxicity. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Fekri, H.S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. Therapeutic and biological activities of berberine: The involvement of Nrf2 signaling pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.S.; Wang, L.S.; Chou, T.Y.; Hsu, W.H.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Chang, S.C.; Wei, Y.H. Cigarette smoking and hOGG1 Ser326Cys polymorphism are associated with 8-OHdG accumulation on mitochondrial DNA in thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. S3), S379–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Y.F.; Liu, X.T.; Li, Y.C.; Zhu, H.M.; Sun, M.R.; Li, P.; Liu, B.; Yang, H. Songorine promotes cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2 induction during sepsis. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, K.; Anjaneyulu, M.; Inoue, T.; Choi, J.; Sagi, A.R.; Chen, C.; Ide, T.; Russell, J.W. Mitochondrial transcription factor A regulation of mitochondrial degeneration in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E132–E141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, I.; Sheeladevi, R. Biochemical responses and mitochondrial mediated activation of apoptosis on long-term effect of aspartame in rat brain. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
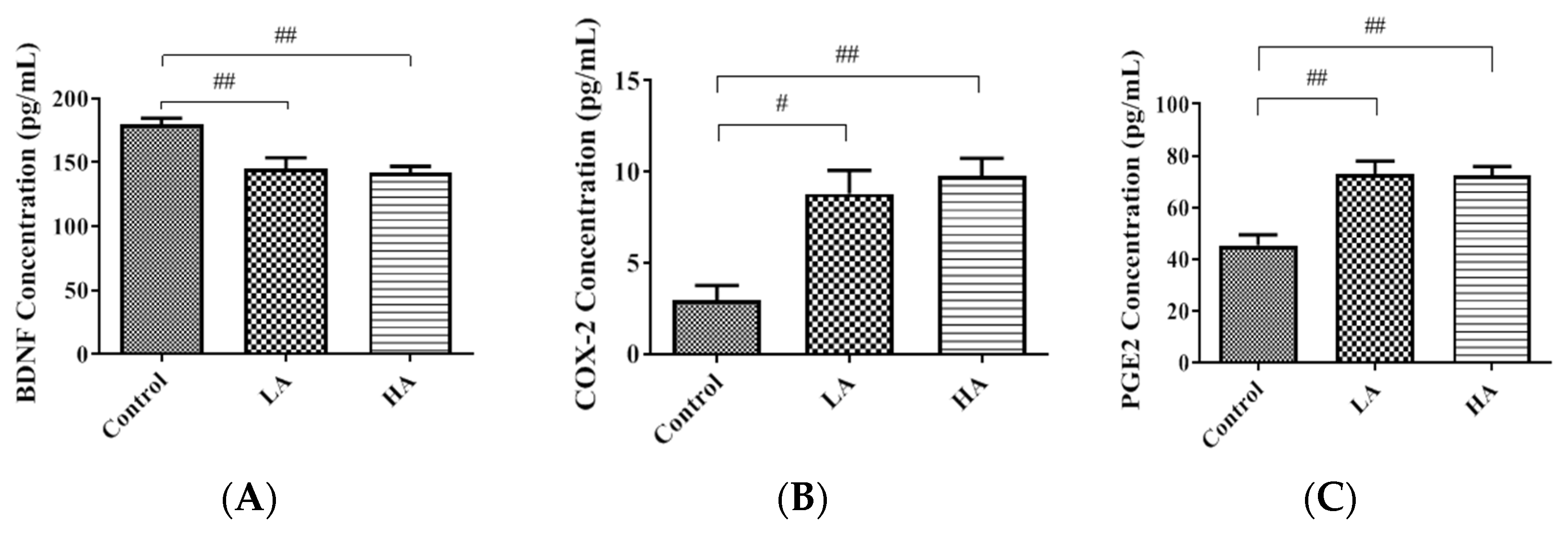
 ). Rat groups: control diet (control), low dose of aspartame (LA), high dose of aspartame (HA).
). Rat groups: control diet (control), low dose of aspartame (LA), high dose of aspartame (HA).
 ). Rat groups: control diet (control), low dose of aspartame (LA), high dose of aspartame (HA).
). Rat groups: control diet (control), low dose of aspartame (LA), high dose of aspartame (HA).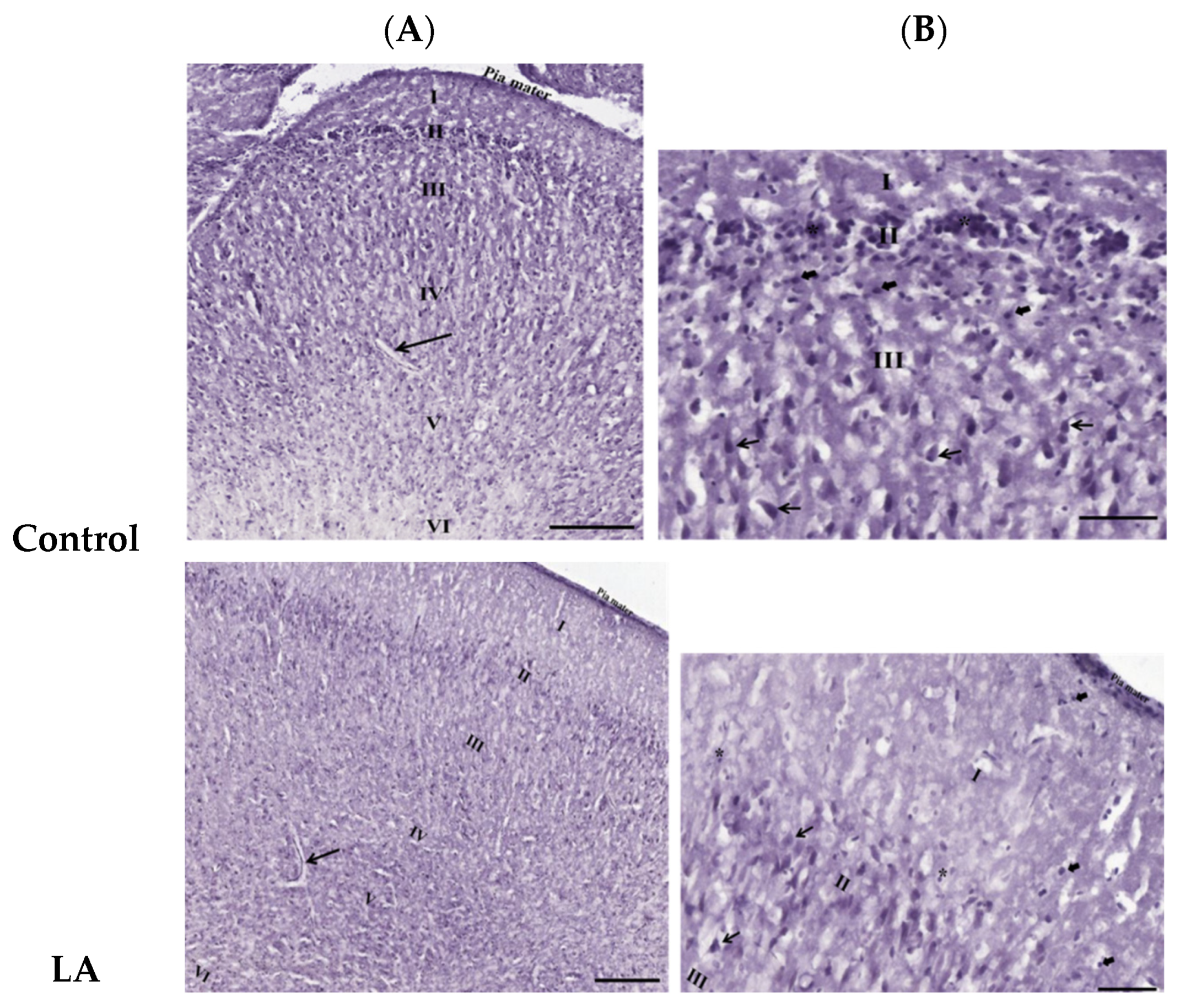










| Primary Antibody | Host | Dilution | Molecular Weight (kD) | Catalog Number | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-IL6 | rabbit | 1:1000 | 24 | DF6087 | Affinity Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA |
| anti-IL1β | rabbit | 1:1000 | 30 | AF5103 | Affinity Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA |
| anti-TNFα | mouse | 1:500 | 26 | 60291-1-Ig | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA |
| anti-iNOS | rabbit | 1:1000 | 130 | AF0199 | Affinity Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA |
| anti-NFκB | rabbit | 1:1000 | 60 | 622601 | Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA |
| anti-IκB | rabbit | 1:1000 | 36 | 10268-1-AP | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA |
| anti-SOD2 | rabbit | 1:1000 | 22 | 13194 | Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA |
| anti-CAT | mouse | 1:1000 | 60 | 863301 | Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA |
| anti-Nrf2 | rabbit | 1:1000 | 68 | 16396-1-AP | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA |
| anti-Keap1 | rabbit | 1:1000 | 70 | 10503-2-AP | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA |
| anti-Sirt1 | mouse | 1:1000 | 120 | 8469 | Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA |
| anti-PGC1ɑ | rabbit | 1:1000 | 91 | NBP1-04676 | Novus Biologicals, Centennial, CO, USA |
| anti-Nrf1 | rabbit | 1:1000 | 54 | AB175932 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK |
| anti-TFAM | rabbit | 1:1000 | 28 | AB131607 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK |
| anti-Caspase-3 | rabbit | 1:1000 | 32 | 19677-1-AP | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA |
| anti-Bax | rabbit | 1:1000 | 21 | 50599-2-Ig | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA |
| anti-Bcl2 | rabbit | 1:1000 | 26 | 26593-1-AP | Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA |
| anti-GFAP | rabbit | 1:1000 | 50 | DF6040 | Affinity Biosciences, Cincinnati, OH, USA |
| anti-GAPDH | rabbit | 1:1000 | 37 | 2118 | Novus Biologicals, Centennial, CO, USA |
| Group | Body Weight (g) | Weight Change (g) | Brain Weight (mg) | Brain Coefficients (mg/100 g BW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | ||||
| Control | 211.90 ± 5.93 | 295.30 ± 13.60 | 83.40 ± 11.48 | 1.90 ± 0.08 | 0.6431 ± 0.0380 |
| LA | 211.21 ± 8.60 | 298.71 ± 20.12 | 87.50 ± 15.57 | 2.00 ± 0.06 | 0.6724 ± 0.0363 |
| HA | 206.43 ± 8.50 | 285.79 ± 20.40 | 79.36 ± 13.56 | 2.08 ± 0.08 | 0.6959 ± 0.0395 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
U-pathi, J.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-W.; Owaga, E.E.; Hsieh, R.-H. Relationship between Aspartame-Induced Cerebral Cortex Injury and Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis in Sprague Dawley Rats. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010002
U-pathi J, Yeh Y-C, Chen C-W, Owaga EE, Hsieh R-H. Relationship between Aspartame-Induced Cerebral Cortex Injury and Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis in Sprague Dawley Rats. Antioxidants. 2024; 13(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleU-pathi, Jureeporn, Yen-Chia Yeh, Chia-Wen Chen, Eddy E. Owaga, and Rong-Hong Hsieh. 2024. "Relationship between Aspartame-Induced Cerebral Cortex Injury and Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis in Sprague Dawley Rats" Antioxidants 13, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010002
APA StyleU-pathi, J., Yeh, Y.-C., Chen, C.-W., Owaga, E. E., & Hsieh, R.-H. (2024). Relationship between Aspartame-Induced Cerebral Cortex Injury and Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Apoptosis in Sprague Dawley Rats. Antioxidants, 13(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13010002







