Resuspendable Powders of Lyophilized Chalcogen Particles with Activity against Microorganisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Chalcogen Nanoparticles
2.2. Lyophilization of Chalcogen Nanoparticles
2.3. Size Characterization of Chalcogen Nanoparticles
2.4. Zeta Potential (ZP) Measurements of Chalcogen Nanoparticles
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of Chalcogen Nanoparticles
2.6. Nematicidal Activity of Chalcogen Nanoparticles
2.7. Antimicrobial Activity of Chalcogen Nanoparticles
3. Results
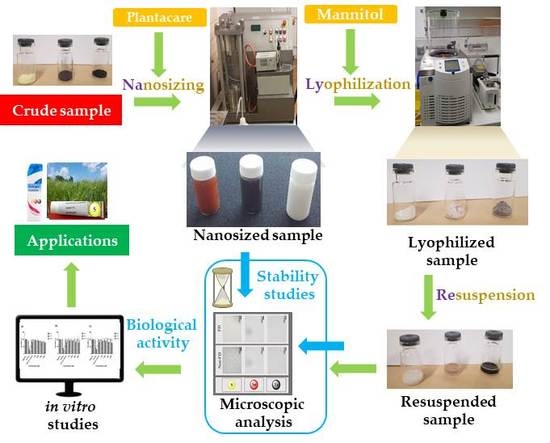
3.1. Nanosizing, Lyophilization and Resuspension (NaLyRe) of Chalcogen Particles
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Resuspended Samples
3.3. Activity against S. Feltiae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacob, C. A scent of therapy: Pharmacological implications of natural products containing redox-active sulfur atoms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, G.K.; Tomar, R.S. Ebselen, a promising antioxidant drug: Mechanisms of action and targets of biological pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4865–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad Nasim, M.; Ali, W.; Dominguez-Alvarez, E.; da Silva Junior, E.N.; Saleem, R.S.Z.; Jacob, C. Chapter 10 reactive selenium species: Redox modulation, antioxidant, antimicrobial and anticancer activities. In Organoselenium Compounds in Biology and Medicine: Synthesis, Biological and Therapeutic Treatments; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2018; pp. 277–302. [Google Scholar]
- Pacula, A.J.; Kaczor, K.B.; Antosiewicz, J.; Janecka, A.; Dlugosz, A.; Janecki, T.; Wojtczak, A.; Scianowski, J. New chiral ebselen analogues with antioxidant and cytotoxic potential. Molecules 2017, 22, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.B.C.; Arrais-Silva, W.W.; Cunha, R.L.O.R.; Giorgio, S. A novel organotellurium compound (RT-01) as a new antileishmanial agent. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachmo, Y.; Kalechman, Y.; Skornick, I.; Gafter, U.; Caspi, R.R.; Sredni, B. The small tellurium compound as101 ameliorates rat crescentic glomerulonephritis: Association with inhibition of macrophage caspase-1 activity via very late antigen-4 inactivation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agata, J.P.; Francesca, M.; Luca, S.; Eder, J.L.; Jacek, Ś.; Claudio, S. An update on “selenium containing compounds from poison to drug candidates: A review on the GPx-like activity”. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2015, 9, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mugesh, G.; du Mont, W.W.; Sies, H. Chemistry of biologically important synthetic organoselenium compounds. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2125–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, J.C.; Loucks, R.J.; Balakrishnan, J.; Varshneya, A.K. Potential energy landscapes of elemental and heterogeneous chalcogen clusters. Phys. Rev. A 2006, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.; Habara, Y. Cross talk between polysulfide and nitric oxide in rat peritoneal mast cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C894–C902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. Signaling molecules: Hydrogen sulfide and polysulfide. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevam, E.C.; Faulstich, L.; Griffin, S.; Burkholz, T.; Jacob, C. Polysulfides in biology: From intricate chemistry to an astonishing yet hidden biological activity. Curr. Org. Chem. 2016, 20, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.C. Colloidal sulphur as a spray material. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1925, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwasniewski, M.T.; Sacks, G.L.; Wilcox, W.F. Persistence of elemental sulfur spray residue on grapes during ripening and vinification. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2014, 65, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevam, E.C.; Griffin, S.; Nasim, M.J.; Denezhkin, P.; Schneider, R.; Lilischkis, R.; Dominguez-Alvarez, E.; Witek, K.; Latacz, G.; Keck, C.; et al. Natural selenium particles from staphylococcus carnosus: Hazards or particles with particular promise? J. Hazard Mater. 2017, 324, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Baldauf, A.; Ba, L.A.; Jamier, V.; Khairan, K.; Sarakbi, M.B.; Reum, N.; Schneider, M.; Roseler, A.; Becker, K.; et al. Selective antimicrobial activity associated with sulfur nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacon, M.; Molpeceres, J.; Berges, L.; Guzman, M.; Aberturas, M.R. Stability and freeze-drying of cyclosporine loaded poly(d,l lactide-glycolide) carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameti, M.; Bohr, G.; Ravi Kumar, M.N.; Kneuer, C.; Bakowsky, U.; Nacken, M.; Schmidt, H.; Lehr, C.M. Stabilisation by freeze-drying of cationically modified silica nanoparticles for gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 266, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, Y.N.; Gurny, R.; Allemann, E. Preparation and characterization of sterile and freeze-dried sub-200 nm nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 233, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Stainmesse, S.; Fessi, H. Freeze-drying of nanoparticles: Formulation, process and storage considerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1688–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sis, H.; Birinci, M. Effect of nonionic and ionic surfactants on zeta potential and dispersion properties of carbon black powders. Colloid Surf. A 2009, 341, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, S.; Meinke, M.; Keck, C.; Müller, R. Rutin—Increased antioxidant activity and skin penetration by nanocrystal technology (smartcrystals). Cosmetics 2016, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.R.; Al Shaal, L.; Muller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Production and characterization of hesperetin nanosuspensions for dermal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Duse, L.; Strehlow, B.; Schafer, J.; Bakowsky, U. Composite liposome-pei/nucleic acid lipopolyplexes for safe and efficient gene delivery and gene knockdown. Colloid Surf. B 2017, 158, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulstich, L.; Griffin, S.; Nasim, M.J.; Masood, M.I.; Ali, W.; Alhamound, S.; Omran, Y.; Kim, H.; Kharma, A.; Schafer, K.H.; et al. Nature’s hat-trick: Can we use sulfur springs as ecological source for materials with agricultural and medical applications? Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, A.V.; Neubert, R.H.H. Characterization of mixtures of alkyl polyglycosides (plantacare) by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 2347–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czepukojc, B.; Viswanathan, U.M.; Raza, A.; Ali, S.; Burkholz, T.; Jacob, C. Tetrasulfanes as selective modulators of the cellular thiolstat. Phosphorus Sulfur 2013, 188, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.; Tittikpina, N.K.; Al-Marby, A.; Alkhayer, R.; Denezhkin, P.; Witek, K.; Gbogbo, K.A.; Batawila, K.; Duval, R.E.; Nasim, M.J.; et al. Turning waste into value: Nanosized natural plant materials of Solanum incanum L. and pterocarpus erinaceus poir with promising antimicrobial activities. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Marby, A.; Ejike, C.E.C.C.; Nasim, M.J.; Awadh-Ali, N.A.; Al-Badani, R.A.; Alghamdi, G.M.A.; Jacob, C. Nematicidal and antimicrobial activities of methanol extracts of 17 plants, of importance in ethnopharmacology, obtained from the arabian peninsula. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 5, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jaeghere, F.; Allemann, E.; Feijen, J.; Kissel, T.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. Freeze-drying and lyopreservation of diblock and triblock poly(lactic acid)-poly(ethylene oxide) (PLA-PEO) copolymer nanoparticles. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2000, 5, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Pikal, M.J. Design of freeze-drying processes for pharmaceuticals: Practical advice. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.D.; Molina, M.C.; Anchordoquy, T.J. Stabilization of lipid/DNA complexes during the freezing step of the lyophilization process: The particle isolation hypothesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1468, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.; Sarfraz, M.; Farida, V.; Nasim, M.J.; Ebokaiwe, A.P.; Keck, C.M.; Jacob, C. No time to waste organic waste: Nanosizing converts remains of food processing into refined materials. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellucci Estevam, E.; Witek, K.; Faulstich, L.; Nasim, M.J.; Latacz, G.; Dominguez-Alvarez, E.; Kiec-Kononowicz, K.; Demasi, M.; Handzlik, J.; Jacob, C. Aspects of a distinct cytotoxicity of selenium salts and organic selenides in living cells with possible implications for drug design. Molecules 2015, 20, 13894–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa-Pureur, R.; Heimfarth, L.; Rocha, J.B. Signaling mechanisms and disrupted cytoskeleton in the diphenyl ditelluride neurotoxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 458601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimfarth, L.; Loureiro, S.O.; Reis, K.P.; de Lima, B.O.; Zamboni, F.; Gandolfi, T.; Narvaes, R.; da Rocha, J.B.T.; Pessoa-Pureur, R. Cross-talk among intracellular signaling pathways mediates the diphenyl ditelluride actions on the hippocampal cytoskeleton of young rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, L.M.; Kimura, E.T. Safety evaluation of selenium sulfide antidandruff shampoos. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1971, 20, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Lir, L.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Han, H.; Wang, Z. Absorption and Raman spectra of Se8-ring clusters in zeolite 5A. Solid State Commun. 1996, 100, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudel, R.; Laitinen, R. Cyclic selenium sulfides. Top. Curr. Chem. 1982, 102, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide and polysulfides as signaling molecules. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2015, 47, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.; Masood, M.I.; Nasim, M.J.; Sarfraz, M.; Ebokaiwe, A.P.; Schafer, K.H.; Keck, C.M.; Jacob, C. Natural nanoparticles: A particular matter inspired by nature. Antioxidants 2017, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Chalogen | In Original Suspension Medium | In Conductivity-Adjusted Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-FD | FD | Non-FD | FD | |
| S | −30 mV | −36 mV | −47 mV | −54 mV |
| Se | −24 mV | −26 mV | −40 mV | −41 mV |
| Te | −27 mV | −30 mV | −31 mV | −36 mV |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Griffin, S.; Sarfraz, M.; Hartmann, S.F.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Nasim, M.J.; Bakowsky, U.; Keck, C.M.; Jacob, C. Resuspendable Powders of Lyophilized Chalcogen Particles with Activity against Microorganisms. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7020023
Griffin S, Sarfraz M, Hartmann SF, Pinnapireddy SR, Nasim MJ, Bakowsky U, Keck CM, Jacob C. Resuspendable Powders of Lyophilized Chalcogen Particles with Activity against Microorganisms. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleGriffin, Sharoon, Muhammad Sarfraz, Steffen F. Hartmann, Shashank Reddy Pinnapireddy, Muhammad Jawad Nasim, Udo Bakowsky, Cornelia M. Keck, and Claus Jacob. 2018. "Resuspendable Powders of Lyophilized Chalcogen Particles with Activity against Microorganisms" Antioxidants 7, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7020023
APA StyleGriffin, S., Sarfraz, M., Hartmann, S. F., Pinnapireddy, S. R., Nasim, M. J., Bakowsky, U., Keck, C. M., & Jacob, C. (2018). Resuspendable Powders of Lyophilized Chalcogen Particles with Activity against Microorganisms. Antioxidants, 7(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7020023