Effects of Dietary Supplementation with dl-Methionine and dl-Methionyl-dl-Methionine in Breeding Pigeons on the Carcass Characteristics, Meat Quality and Antioxidant Activity of Squabs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals, Experimental Design and Diets
2.3. Management
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. Carcass Characteristics
2.6. Meat Quality Assay
2.7. Assay of Antioxidant Activities in Muscle
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Carcass Characteristics
3.2. Relative Bioavailability
3.3. Meat Quality
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Finding
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, W.Y.; Fu, Z.; Pan, N.X.; Yan, H.C.; Wang, X.Q.; Gao, C.Q. Leucine promotes the growth of squabs by increasing crop milk protein synthesis through the TOR signaling pathway in the domestic pigeon (Columba livia). Poult. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, D.Y.; Toldra, F. Microbial hazards in food: Food-borne infections and intoxications. In Handbook of Meat Processing; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Ghaly, A.E. Meat spoilage mechanisms and preservation techniques: A critical review. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2011, 6, 486–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.Q.; Wang, X.H.; Hu, X.C.; Yan, H.C.; Wang, X.Q. Effects of dietary crude protein levels on growth performance, carcass characteristics, meat quality of squabs and laying performance of breeding pigeons. J. South China Agric. Univ. 2016, 37, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Zhou, G.L.; Luo, L.H.; Jiang, S.Q.; Chen, F. Effects of Dietary Selenomethionine Supplementation on Growth Performance, Meat Quality and Antioxidant Property in Yellow Broilers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9769–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Xu, R.S.; Min, L.; Ruan, D.; Kim, H.Y.; Hong, Y.G.; Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Xia, W.G.; Luo, X.; et al. Effects of L-methionine on growth performance, carcass quality, feather traits, and small intestinal morphology of Pekin ducks compared with conventional DL-methionine. Poult. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunchasak, C. Role of dietary methionine in poultry production. J. Poul. Sci. 2009, 46, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Anon, M.; Gonzalez-Esquerra, R.; Saleh, E.; Hampton, T.; Ritcher, S.; Firman, J.; Knight, C.D. Evidence for 2-hydroxy-4 (methylthio) butanoic acid and DL-methionine having different dose responses in growing broilers. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Yao, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Z.; Tian, G.; Yu, B.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Jia, G.; et al. Nutrition and health relevant regulation of intestinal sulfur amino acid metabolism. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Błażejak, S. Current knowledge on the importance of selenium in food for living organisms: A review. Molecules 2016, 21, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M. Selenium–Fascinating Microelement, Properties and Sources in Food. Molecules 2019, 24, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.Y.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.M.; Wang, T. Methionine improves breast muscle growth and alters myogenic gene expression in broilers. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.; Pasquetti, T.; Malheiros, R.D.; Ferket, P.R.; Kim, S.W. Effects of supplemental L-methionine on growth performance and redox status of turkey poults compared with the use of DL-methionine. Poult. Sci. 2017, 97, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, P.; Guo, Y.M.; Yang, X.; Long, F.Y. Effects of dietary arginine and methionine levels on broiler carcass traits and meat quality. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2010, 9, 1546–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Kubińska, M.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Czech, A.; Ognik, K.; Zdunczyk, Z. Effect of different dietary methionine levels on the growth performance and tissue redox parameters of turkeys. Poult. Sci. 2016, 96, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissbach, H.; Etienne, F.; Hoshi, T.; Heinemann, S.H.; Lowther, W.T.; Matthews, B.; John, G.S.; Nathan, C.; Brot, N. Peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase: Structure, mechanism of action, and biological function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 397, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. Dipeptide (Methionyl-Methionine) transport and its effect on β-Casein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.J.; Lemme, A.; He, J.Y.; Yin, P.; Figueriredo-Silva, C.; Liu, Y.L.; Xie, S.W.; Niu, J.; Tian, L.X. Fishmeal levels can be successfully reduced in white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) if supplemented with DL-Methionine or DL-Methionyl-DL-Methionine. Aquac. Nutr. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.S.; Htoo, J.K.; Fracaroli, C.; Silva, W.C.; Gobi, J.P.; Veira, A.M.; Barbosa, N.A.A.; Hauschild, L. Bioavailability of di-peptide dl-methionyl-dl-methionine in comparison to dl-methionine in weaned and growing pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 241, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Dai, W.T.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhao, F.Q.; Liu, J.X.; Liu, H.Y. Methionine Partially Replaced by Methionyl-Methionine Dipeptide Improves Reproductive Performance over Methionine Alone in Methionine-Deficient Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, K.G.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.G.; Yue, H.Y.; Sun, L.L.; Qi, G.H. Effects of dietary pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium on growth performance, carcass yield and antioxidant status of broiler chicks. Animal 2015, 9, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, M.; Xu, Y.T.; Hassan, F.; Arain, M.A.; Abd EI-Hack, M.E.; Noreldin, A.E.; Sun, C. Influence of Graded Levels of I-Theanine Dietary Supplementation on Growth Performance, Carcass Traits, Meat Quality, Organs Histomorphometry, Blood Chemistry and Immune Response of Broiler Chickens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.L.; Chen, Y.P.; Cheng, Y.F.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, R.Q.; Wen, C.; Zhou, Y.M. An evaluation of zinc bearing palygorskite inclusion on the growth performance, mineral content, meat quality, and antioxidant status of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Q.; Chen, X.; Tan, H.Z.; Zhang, D.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Wei, S.; Yan, H.C. Nutrient density and slaughter age have differential effects on carcass performance, muscle and meat quality in fast and slow growing broiler genotypes. Br. Poult. Sci. 2013, 54, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.M.; Xu, Y.L.; Yan, H.C.; Li, H.C.; Gao, C.Q.; Wang, X.Q. Dietary Supplementation with Pioglitazone Hydrochloride and Chromium Methionine Improves Growth Performance, Meat Quality, and Antioxidant Ability in Finishing Pigs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4345–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Lemme, A.; He, J.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Xie, S.W.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, H.J.; Silva, F.; Tian, L.X. Assessing the bioavailability of the Novel Met-Met product (AQUAVI® Met-Met) compared to DL-methionine (DL-Met) in white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2018, 484, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.C.; Wen, W.T.; Deng, Y.; Tian, Y.Y.; Sun, H.H.; Sun, Q. Chinese ethnic meat products: Continuity and development. Meat Sci. 2016, 120, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyayi, E.A.; Aderemi, F.A.; Ladele, O.O.; Popoola, A.S. Effects of low protein diets supplemented with high amino acids (methionine or lysine) on performance of broilers. Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2014, 4, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Peebles, E.D.; Schilling, M.W.; Mercier, Y. Effects of dietary lysine and methionine supplementation on Ross 708 male broilers from 21 to 42 d of age (I): Growth performance, meat yield, and cost effectiveness. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2016, 25, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakangtong, C.; Bunchasak, C. Effects of dietary energy and methionine sources on productive performance and carcass yield in broiler chickens. Kasetsart J. Nat. Sci. 2010, 44, 574–581. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyeh, M.; Gevorgyan, O.K. Influence of excess lysine and methionine on cholesterol, fat and performance of broiler chicks. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2011, 10, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.E.; Abbas, T.E. Effects of dietary levels of methionine on broiler performance and carcass characteristics. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2011, 10, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, M.D.; Van-Kessel, A.G.; Maenz, D.D. Absorption of methionine and 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutoanic acid in conventional and germ-free chickens. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemme, A.; Hoehler, D.; Brennan, J.J.; Mannion, P.F. Relative effectiveness of methionine hydroxy analog compared to DL-methionine in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2002, 81, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hijazeen, M.; Lee, E.J.; Mendonca, A.; Ahn, D.U. Effects of tannic acid on lipid and protein oxidation, color, and volatiles of raw and cooked chicken breast meat during storage. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Jiang, X.Y.; Ding, L.R.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.M. Effects of dietary methionine on growth performance, meat quality and oxidative status of breast muscle in fast-and slow-growing broilers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Nie, S.P.; Qu, Z.; Bi, C.P.; Shan, A.S. The effects of conjugated linoleic acid on growth performance, carcass traits, meat quality, antioxidant capacity, and fatty acid composition of broilers fed corn dried distillers grains with solubles. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.D.; Fletcher, D.L.; Northcutt, J.K.; Russell, S.M. The relationship of broiler breast color to meat quality and shelf-life. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.; Lauridsen, C.; Bertelsen, G. Dietary vitamin E: Quality and storage stability of pork and poultry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.I.; Gomaa, E.A.; Buckley, D.J. Oxidative quality and shelf life of meats. Meat Sci. 1996, 43, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, F.J.; Gray, J.I.; Asghar, A.; Haug, A.; Strasburg, G.M.; Buckley, D.J.; Morrissey, P.A. Influence of diet on lipid oxidation and membrane structure in porcine muscle microsomes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swennen, Q.; Geraert, P.A.; Mercier, Y.; Everaert, N.; Stinckens, A.; Willemsen, H.; Li, Y.; Decuypere, E.; Buyse, J. Effects of dietary protein content and 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutanoic acid or DL-methionine supplementation on performance and oxidative status of broiler chickens. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladikos, D.; Lougovois, V. Lipid oxidation in muscle foods: A review. Food Chem. 1990, 35, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zduńczyk, Z.; Jankowski, J.; Kubińska, M.; Ognik, K.; Czech, A.; Juśkiewicz, J. The effect of different dietary levels of dl-methionine and dl-methionine hydroxy analogue on the antioxidant and immune status of young turkeys. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 71, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkova, A.; Koroleva, O.; Khrameeva, E.; Fedorova, T.; Tsentalovich, M. Structure-functional study of tyrosine and methionine dipeptides: An approach to antioxidant activity prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25353–25376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredient (%) 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| corn | 51.00 | 51.00 | 51.00 | 51.00 | 51.00 | 51.00 | 51.00 | 51.00 | 51.00 |
| soybean meal | 17.50 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 17.50 | 17.50 |
| wheat | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 | 24.00 |
| sorghum | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| dicalcium phosphate | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| shell powder | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| salt | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| vitamin and mineral premix 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| lysine (98.5%) | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| dl-Met | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| dl-Met-Met | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.60 |
| zeolite powder | 0.60 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| formulated nutrient composition (%) | |||||||||
| metabolic energy (ME, MJ/kg) | 12.13 | 12.13 | 12.13 | 12.13 | 12.13 | 12.13 | 12.13 | 12.13 | 12.13 |
| crude protein | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 | 15.00 |
| calcium | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 |
| total phosphorus | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 |
| nonphytate phosphorus | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| dl-Met | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.55 | 0.70 | 0.85 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| dl-Met-Met | - | - | - | - | - | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.60 |
| lysine | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
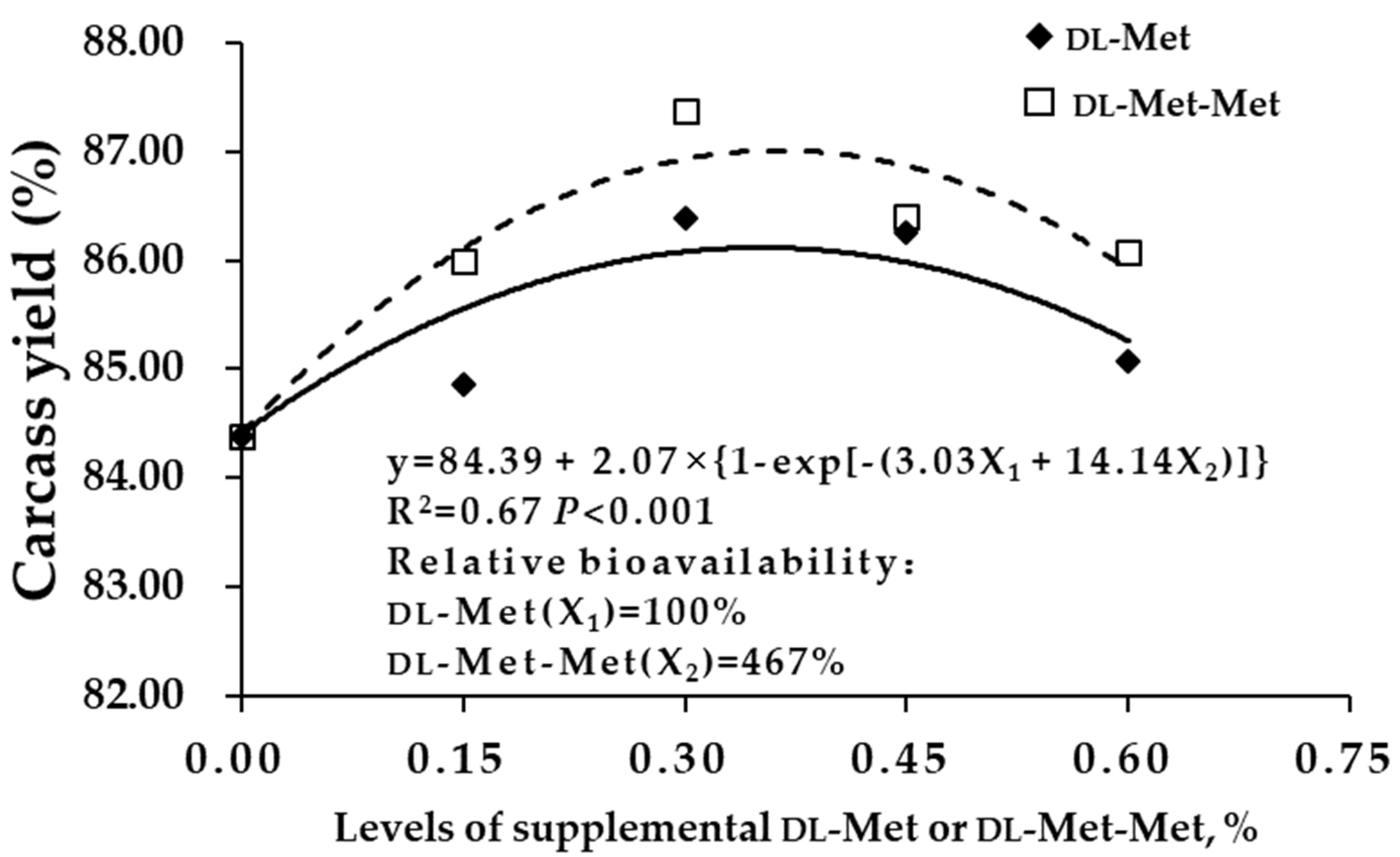
| Items2 | Met Source | Met Dose | Carcass Yield | Semi-Eviscerated Yield | Eviscerated Yield | Breast Muscle Yield | Leg Muscle Yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BD | 0 | 84.38e | 80.83d | 64.41d | 22.60c | 6.83c |
| 2 | dl-Met | 0.15% | 84.86de | 80.92cd | 66.00bc | 23.79bc | 7.13bc |
| 3 | dl-Met | 0.30% | 86.39ab | 82.27a | 66.45bc | 24.86ab | 7.83a |
| 4 | dl-Met | 0.45% | 86.26ab | 81.87ab | 66.68abc | 24.58ab | 7.54ab |
| 5 | dl-Met | 0.60% | 85.07cde | 81.23bcd | 65.23cd | 24.52ab | 7.78a |
| 6 | dl-Met-Met | 0.15% | 85.99bcd | 81.72abc | 67.19ab | 24.74ab | 7.48ab |
| 7 | dl-Met-Met | 0.30% | 87.37a | 82.27a | 68.06a | 26.07a | 7.97a |
| 8 | dl-Met-Met | 0.45% | 86.40ab | 82.16a | 67.52ab | 25.97a | 7.90a |
| 9 | dl-Met-Met | 0.60% | 86.08bc | 82.14a | 67.22ab | 25.76a | 7.97a |
| SEM | 0.175 | 0.118 | 0.226 | 0.241 | 0.078 | ||
| P-values | |||||||
| treatment effects | <0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.007 | <0.001 | ||
| met source | 0.014 | 0.039 | <0.001 | 0.010 | 0.084 | ||
| main effect of the Met source | |||||||
| dl-Met | 85.64b | 81.58b | 66.09b | 24.43b | 7.57 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 86.46a | 82.07a | 67.50a | 25.64a | 7.83 | ||
| linear effect3 | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.072 | 0.131 | 0.180 | 0.015 | 0.002 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | <0.001 | ||
| quadratic effect3 | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.008 | 0.023 | 0.004 | 0.076 | 0.173 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | <0.001 | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.023 | 0.005 | ||
| Items3 | Met Source | Met Dose | L* | a* | b* | Shear Force (N) | Drip Loss (%) | Cooking Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BD | 0 | 39.22a | 19.40c | 7.65 | 23.11 | 3.75a | 26.86a |
| 2 | dl-Met | 0.15% | 38.67ab | 21.31b | 7.95 | 22.95 | 3.15ab | 26.23ab |
| 3 | dl-Met | 0.30% | 36.33c | 22.22ab | 7.63 | 22.13 | 2.41c | 23.32e |
| 4 | dl-Met | 0.45% | 36.46c | 22.10ab | 7.88 | 22.25 | 2.86bc | 24.62cd |
| 5 | dl-Met | 0.60% | 37.28bc | 22.03ab | 7.97 | 22.49 | 3.17ab | 25.64bc |
| 6 | dl-Met-Met | 0.15% | 37.97abc | 21.69ab | 7.82 | 21.73 | 2.85bc | 25.98ab |
| 7 | dl-Met-Met | 0.30% | 36.89c | 22.73a | 7.66 | 21.61 | 2.37c | 21.93f |
| 8 | dl-Met-Met | 0.45% | 37.03bc | 21.95ab | 7.95 | 22.37 | 2.49c | 24.49d |
| 9 | dl-Met-Met | 0.60% | 37.65abc | 21.32b | 7.79 | 22.98 | 2.71bc | 25.49bcd |
| SEM | 0.214 | 0.214 | 0.103 | 0.434 | 0.082 | 0.167 | ||
| P-values | ||||||||
| treatment effects | 0.009 | <0.001 | 0.993 | 0.996 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Met source | 0.636 | 0.990 | 0.801 | 0.768 | 0.023 | 0.327 | ||
| main effect of the Met source | ||||||||
| dl-Met | 37.18 | 21.91 | 7.86 | 22.45 | 2.90a | 24.95 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 37.39 | 21.92 | 7.80 | 22.17 | 2.60b | 24.47 | ||
| linear effect4) | ||||||||
| dl-Met | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.552 | 0.663 | 0.069 | 0.023 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.010 | 0.004 | 0.725 | 0.929 | 0.003 | 0.253 | ||
| quadratic effect4 | ||||||||
| dl-Met | 0.049 | 0.012 | 0.896 | 0.746 | 0.002 | <0.001 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.008 | <0.001 | 0.876 | 0.314 | 0.004 | <0.001 | ||
| Items3 | Met Source | Met Dose | CAT (U/mg-prot) | T-SOD (U/mg-prot) | GSH-Px (U/mg-prot) | T-AOC (U/mg-prot) | MDA (nmol/mg-prot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BD | 0 | 0.71d | 18.94e | 30.57c | 0.35 | 0.86a |
| 2 | dl-Met | 0.15% | 0.77c | 23.15d | 35.88bc | 0.41 | 0.70b |
| 3 | dl-Met | 0.30% | 0.81abc | 28.43ab | 38.34ab | 0.46 | 0.59b |
| 4 | dl-Met | 0.45% | 0.81abc | 26.68abcd | 37.54ab | 0.45 | 0.61b |
| 5 | dl-Met | 0.60% | 0.80abc | 25.77bcd | 38.01ab | 0.44 | 0.56b |
| 6 | dl-Met-Met | 0.15% | 0.79bc | 24.54cd | 36.18b | 0.41 | 0.64b |
| 7 | dl-Met-Met | 0.30% | 0.85a | 25.77a | 42.66a | 0.44 | 0.59b |
| 8 | dl-Met-Met | 0.45% | 0.84ab | 27.83abc | 39.38ab | 0.42 | 0.64b |
| 9 | dl-Met-Met | 0.60% | 0.84ab | 28.20ab | 40.51ab | 0.44 | 0.65b |
| SEM | 0.009 | 0.641 | 0.765 | 0.012 | 0.021 | ||
| P-values | |||||||
| treatment effects | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.604 | 0.013 | ||
| Met source | 0.032 | 0.159 | 0.117 | 0.636 | 0.653 | ||
| main effect of the Met source | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.80b | 26.01 | 37.44 | 0.44 | 0.61 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.83a | 27.54 | 39.69 | 0.43 | 0.63 | ||
| linear effect4 | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.111 | <0.001 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.068 | 0.027 | ||
| quadratic effect4 | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.041 | 0.002 | 0.083 | 0.204 | 0.041 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.276 | 0.017 | ||
| Items3 | Met Source | Met Dose | CAT (U/mg-prot) | T-SOD (U/mg-prot) | GSH-Px (U/mg-prot) | T-AOC (U/mg-prot) | MDA (nmol/mg-prot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BD | 0 | 0.70 | 20.54b | 31.84b | 0.40 | 0.84a |
| 2 | dl-Met | 0.15% | 0.79 | 24.36ab | 37.81ab | 0.44 | 0.78ab |
| 3 | dl-Met | 0.30% | 0.79 | 27.28a | 39.99a | 0.44 | 0.69bc |
| 4 | dl-Met | 0.45% | 0.78 | 26.98a | 39.25a | 0.43 | 0.70bc |
| 5 | dl-Met | 0.60% | 0.81 | 28.29a | 38.96a | 0.46 | 0.66c |
| 6 | dl-Met-Met | 0.15% | 0.77 | 26.20a | 39.01a | 0.45 | 0.72bc |
| 7 | dl-Met-Met | 0.30% | 0.80 | 28.66a | 43.11a | 0.44 | 0.70bc |
| 8 | dl-Met-Met | 0.45% | 0.79 | 28.38a | 41.17a | 0.45 | 0.70bc |
| 9 | dl-Met-Met | 0.60% | 0.84 | 28.36a | 42.43a | 0.44 | 0.66c |
| SEM | 0.010 | 0.643 | 0.808 | 0.008 | 0.013 | ||
| P-values | |||||||
| treatment effects | 0.104 | 0.034 | 0.032 | 0.926 | 0.019 | ||
| Met source | 0.707 | 0.324 | 0.147 | 0.813 | 0.689 | ||
| main effect of the Met source | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.79 | 26.73 | 39.25 | 0.44 | 0.71 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.80 | 27.90 | 41.43 | 0.45 | 0.70 | ||
| linear effect4 | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.025 | 0.004 | 0.048 | 0.296 | 0.005 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.015 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.305 | 0.005 | ||
| quadratic effect4 | |||||||
| dl-Met | 0.163 | 0.216 | 0.061 | 0.668 | 0.202 | ||
| dl-Met-Met | 0.445 | 0.029 | 0.012 | 0.277 | 0.176 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.-G.; Pan, N.-X.; Chen, M.-J.; Wang, X.-Q.; Yan, H.-C.; Gao, C.-Q. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with dl-Methionine and dl-Methionyl-dl-Methionine in Breeding Pigeons on the Carcass Characteristics, Meat Quality and Antioxidant Activity of Squabs. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8100435
Jiang S-G, Pan N-X, Chen M-J, Wang X-Q, Yan H-C, Gao C-Q. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with dl-Methionine and dl-Methionyl-dl-Methionine in Breeding Pigeons on the Carcass Characteristics, Meat Quality and Antioxidant Activity of Squabs. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(10):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8100435
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shi-Guang, Neng-Xia Pan, Meng-Jie Chen, Xiu-Qi Wang, Hui-Chao Yan, and Chun-Qi Gao. 2019. "Effects of Dietary Supplementation with dl-Methionine and dl-Methionyl-dl-Methionine in Breeding Pigeons on the Carcass Characteristics, Meat Quality and Antioxidant Activity of Squabs" Antioxidants 8, no. 10: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8100435
APA StyleJiang, S.-G., Pan, N.-X., Chen, M.-J., Wang, X.-Q., Yan, H.-C., & Gao, C.-Q. (2019). Effects of Dietary Supplementation with dl-Methionine and dl-Methionyl-dl-Methionine in Breeding Pigeons on the Carcass Characteristics, Meat Quality and Antioxidant Activity of Squabs. Antioxidants, 8(10), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8100435