Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Phenanthrenes in Dioscorea batatas Decne Peel, a Discarded Biomass from Postharvest Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Preparation of Standard Phenanthrene Compounds
2.4. Samples and Standard Solutions Preparation
2.5. Quantitative Analysis of Phenanthrenes with HPLC
2.6. Determination of DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.7. ABTS+ Radical Scavenging Activity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calibration, Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
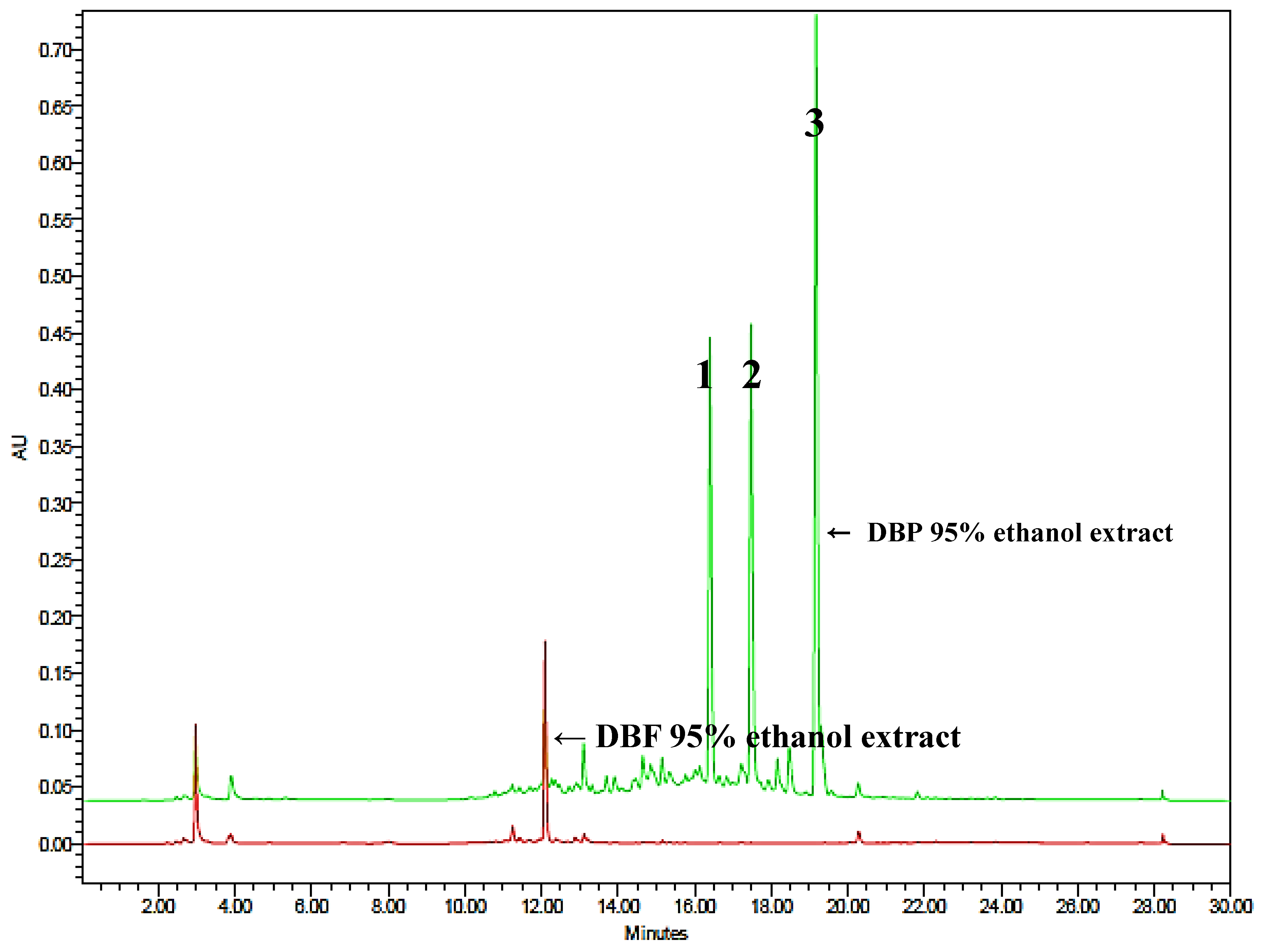
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Phenanthrenes with HPLC
3.3. Antioxidant Activity of Phenanthrenes, DBP and DBF
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryu, H.-Y.; Bae, K.-H.; Kim, E.-J.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Sohn, H.-Y. Evaluation for the Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antithrombosis Activity of Natural Spices for Fresh-cut yam. J. Life Sci. 2007, 17, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhija, S.; Singh, S.; Riar, C.S. Effect of oxidation, cross-linking and dual modification on physicochemical, crystallinity, morphological, pasting and thermal characteristics of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius) starch. Food Hydrocolloid 2016, 55, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.P.; Yu, P. Purification and structural characterization of Chinese yam polysaccharide and its activities. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 117, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.C.; Hsu, F.L.; Lee, M.H. Yam (Dioscorea batatas) tuber mucilage exhibited antioxidant activities in vitro. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.; Houghton, P.; Whang, W.; Cho, J. Screening of Korean herbal medicines used to improve cognitive function for anti-cholinesterase activity. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Jin, M.H.; Park, S.J.; Son, K.H.; Son, J.K.; Chang, H.W. Batatasin I, a Naturally Occurring Phenanthrene Derivative, Isolated from Tuberous Roots of Dioscorea batatas Suppresses Eicosanoids Generation and Degranulation in Bone Marrow Derived-Mast Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, S.; Oh, J.; Lim, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.S. Protective Effects of Dioscorea batatas Flesh and Peel Extracts against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, W.; Wang, R.; Huang, L. Changes in main nutrients and medicinal composition of Chinese yam (Dioscorea opposita) tubers during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Li, X.; Pan, X. A study of promotive and fungistatic actions of steroidal saponin by microcalorimetric method. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 416, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.L.; Poutaraud, A.; Hugueney, P. Metabolism and roles of stilbenes in plants. Plant Sci. 2009, 177, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, B.; Hohmann, J.; Vasas, A. Phenanthrenes: A Promising Group of Plant Secondary Metabolites. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coxon, D.T.; Ogundana, S.K.; Dennis, C. Antifungal phenanthrenes in yam tubers. Phytochemistry 1982, 21, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.R.; Dissanayake, A.A.; Gao, Q.Y.; Nair, M.G. Phenanthrenes in Chinese Yam Peel Exhibit Antiinflammatory Activity, as Shown by Strong in Vitro Cyclooxygenase Enzyme Inhibition. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.H.; Yoon, K.D.; Chin, Y.W.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J. Phenolic compounds with radical scavenging and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitory activities from Dioscorea opposita. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2689–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudjada, A.; Touil, A.; Bensouici, C.; Bendif, H.; Rhouati, S. Phenanthrene and dihydrophenanthrene derivatives from Dioscorea communis with anticholinesterase, and antioxidant activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Zhang, R.; Xing, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, T.; Xia, Q.; Long, D.; Xin, G.; Wang, G. 9, 10-Dihydrophenanthrene derivatives and one 1, 4-anthraquinone firstly isolated from Dioscorea zingiberensis CH Wright and their biological activities. Fitoterapia 2016, 109, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.D.; Yang, M.H.; Nam, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, J.W. Phenanthrene derivatives, 3, 5-dimethoxyphenanthrene-2, 7-diol and batatasin-1, as non-polar standard marker compounds for Dioscorea Rhizoma. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2007, 13, 378–383. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.S.; Hahn, D.; Gu, M.J.; Oh, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.-S. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of 2, 7-dihydroxy-4, 6-dimethoxy phenanthrene isolated from Dioscorea batatas Decne. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Gu, M.J.; Lim, J.S.; Park, E.K.; Baek, M.-C.; Kim, J.-S.; Hahn, D.; Bae, J.-S. Inhibitory effects of compounds isolated from Dioscorea batatas Decne peel on particulate matter-induced pulmonary injury in mice. J. Toxicol. Env. Heal. A 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-B.; Kim, M.-S.; Sohn, H.-Y. Evaluation of antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antithrombin activities of the rhizome of various Dioscorea species. Korean J. Food Preserv. 2010, 17, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Seo, D.-H.; Kim, H.-S. Effect of starch extraction solutions on extraction and physicochemical property of Chinese yam (Dioscorea batatas) starch. Korean J. Food Sci. Techol. 2018, 50, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, E.-J.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Son, K.-H.; Sohn, H.-Y. Antifungal activity of phenanthrene derivatives from aerial bulbils of Dioscorea batatas Decne. J. Life Sci. 2006, 16, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirigaya, N.; Kato, H.; Fujimaki, M. Studies on antioxidant activity of nonenzymic browning reaction products. Part 3. Fractionation of browning reaction solution between ammonia and D-glucose and antioxidant activity of the resulting fractions. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi 1971, 45, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Chiang, B.H.; Wei, J.H.; Wang, C.K.; Chen, P.C.; Hsu, C.K. Effects of blanching, drying and extraction processes on the antioxidant activity of yam (Dioscorea alata). Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2008, 43, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, Y.; Man, S.; Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Wang, T. Antioxidant and Antitumor Activities of the Extracts from Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposite Thunb.) Flesh and Peel and the Effective Compounds. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, H1553–H1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasugi, M.; Kawashima, S.; Monde, K.; Katsui, N.; Masamune, T.; Shirata, A. Antifungal compounds from Dioscorea batatas inoculated with Pseudomonas cichorii. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Chin, Y.-W.; Yoon, K.D.; Kim, J. Phenolic compounds with pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity from Korean yam (Dioscorea opposita). J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | Regression Equation | Range (µg/mL) | R2 | LOD (µg/mL) | LOQ (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Y = 301.34x − 46,588 | 3.125–100 | 0.9994 | 0.44 | 1.47 |
| 2 | Y = 510.71x − 21,040 | 3.125–100 | 0.9990 | 0.58 | 1.94 |
| 3 | Y = 99.155x + 15,3981 | 3.125–100 | 0.9959 | 0.42 | 1.40 |
| Content (mg/100 g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DBP | DBF | ||||
| Dry wt. Basis | Wet wt. Basis | Dry wt. Basis | Wet wt. Basis | ||
| Compound | 1 | 47.35 ± 0.25 | 6.76 ± 0.04 | N.D. | N.D. |
| 2 | 29.29 ± 0.08 | 4.18 ± 0.01 | N.D. | N.D. | |
| 3 | 35.85 ± 0.12 | 5.12 ± 0.02 | N.D. | N.D. | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.; Gu, M.J.; Lee, J.-G.; Chin, J.; Bae, J.-S.; Hahn, D. Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Phenanthrenes in Dioscorea batatas Decne Peel, a Discarded Biomass from Postharvest Processing. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110541
Kim M, Gu MJ, Lee J-G, Chin J, Bae J-S, Hahn D. Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Phenanthrenes in Dioscorea batatas Decne Peel, a Discarded Biomass from Postharvest Processing. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(11):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110541
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Minyoul, Myeong Ju Gu, Joon-Goo Lee, Jungwook Chin, Jong-Sup Bae, and Dongyup Hahn. 2019. "Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Phenanthrenes in Dioscorea batatas Decne Peel, a Discarded Biomass from Postharvest Processing" Antioxidants 8, no. 11: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110541
APA StyleKim, M., Gu, M. J., Lee, J.-G., Chin, J., Bae, J.-S., & Hahn, D. (2019). Quantitative Analysis of Bioactive Phenanthrenes in Dioscorea batatas Decne Peel, a Discarded Biomass from Postharvest Processing. Antioxidants, 8(11), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110541







