Interleukin-4-Mediated Oxidative Stress Is Harmful to Hippocampal Neurons of Prothrombin Kringle-2-Lesioned Rat In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Intrahippocampal Microinjection
2.4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
2.5. In Situ Detection of O2− and O2−-Derived Oxidants
2.6. Quantification of Neurons in Hippocampal CA1 Layer
2.7. Image J Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
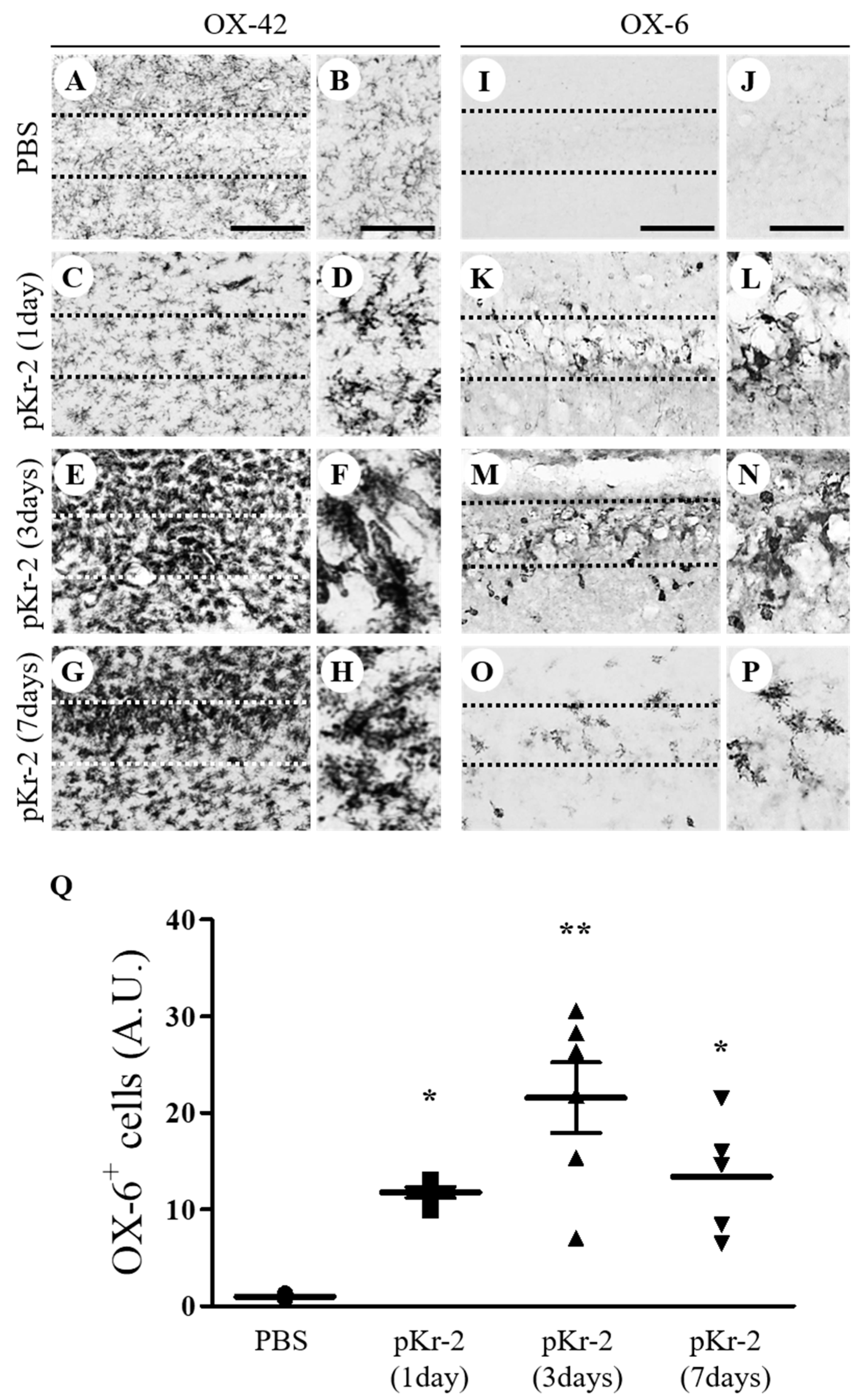
3.1. pKr-2 Induces Activation of Microglia/Macrophages and Neuronal Death in the Hippocampus In Vivo
3.2. Endogenous IL-4 Expressed within Reactive Microglia/Macrophages Contributes to Neurodegeneration in pKr-2-Injected CA1 Layer of Hippocampus In Vivo
3.3. IL-4 Induces Activation of Microglial/Macrophages, ROS Production and Oxidative Damages in pKr-2-Injected CA1 Layer of Hippocampus In Vivo
3.4. IL-4 Induces Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress in pKr-2-Injected CA1 Layer of Hippocampus In Vivo through MPO and iNOS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobb, C.A.; Cole, M.P. Oxidative and nitrative stress in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 84, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasuri, K.; Zhang, L.; Keller, J.N. Oxidative stress, neurodegeneration, and the balance of protein degradation and protein synthesis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 62, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liochev, S.I. Reactive oxygen species and the free radical theory of aging. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 60, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Ko, H.W.; Bok, E.; Park, E.S.; Huh, S.H.; Nam, J.H.; Jin, B.K. The role of neuroinflammation on the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. BMB Rep. 2010, 43, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 443, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.A.; Boddeke, H.W.G.M.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia in Physiology and Disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 619–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, M.; Butovsky, O. Microglia Function in the Central Nervous System During Health and Neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.Y.; Chung, Y.C.; Jin, B.K. Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 Exacerbate Neurotoxicity of Prothrombin Kringle-2 in Cortex In Vivo via Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Chung, E.S.; Bok, E.; Baik, H.H.; Chung, Y.C.; Won, S.Y.; Joe, E.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.S.; Jin, M.Y.; et al. Prothrombin kringle-2 induces death of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in vivo and in vitro via microglial activation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 88, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Jin, B.K. Prothrombin kringle-2-induced oxidative stress contributes to the death of cortical neurons in vivo and in vitro: Role of microglial NADPH oxidase. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 214, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.-H.; Jeon, M.-T.; Leem, E.; Won, S.-Y.; Jeong, K.H.; Park, S.-J.; McLean, C.; Lee, S.J.; Jin, B.K.; Jung, U.J.; et al. Induction of microglial toll-like receptor 4 by prothrombin kringle-2: A potential pathogenic mechanism in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzin, T.M.; Zipser, B.D.; Rafii, M.S.; Kuo-Leblanc, V.; Yancopouloš, G.D.; Glass, D.J.; Fallon, J.R.; Stopa, E.G. Agrin and microvascular damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2000, 21, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, A.; Berneman, Z.; Ponsaerts, P. Neuroprotective modulation of microglia effector functions following priming with interleukin 4 and 13: Current limitations in understanding their mode-of-action. BrainBehav. Immun. 2020, 88, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholl-Franco, A.; Da Silva, A.G.L.S.; Adão-Novaes, J. Interleukin-4 as a Neuromodulatory Cytokine: Roles and signaling in the nervous system. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1153, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, K.G.; Santos, G.D.; Dos Santos, N.B.; Munhoz, C.D.; Azzi-Nogueira, D.; Campos, A.C.; Pagano, R.L.; Britto, L.R.; Hernandes, M.S. Nox2-dependent neuroinflammation in an EAE model of multiple sclerosis. Transl. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-S.; Park, E.J.; Sohn, S.; Kwon, H.J.; Shin, W.-H.; Pyo, H.K.; Jin, B.; Choi, K.S.; Jou, I.; Joe, E.-H. Interleukin-13 and -4 induce death of activated microglia. Glia 2002, 38, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.H.; Park, K.W.; Park, E.S.; Lee, Y.B.; Lee, H.G.; Baik, H.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Maeng, S.; Park, J.; Jin, B.K. Interleukin-13/-4-induced oxidative stress contributes to death of hippocampal neurons in abeta1-42-treated hippocampus in vivo. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2012, 16, 1369–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, K.I.; Won, S.-Y.; Chung, Y.C.; Nam, J.H.; Cho, E.J.; Ahn, T.-B.; Bok, E.; Shin, W.-H.; et al. Inhibition of Microglia-Derived Oxidative Stress by Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor Protects Dopamine Neurons In Vivo from MPP+ Neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, S.U.; Jin, B.K. Thrombin-Induced Oxidative Stress Contributes to the Death of Hippocampal Neurons In Vivo: Role of Microglial NADPH Oxidase. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W.; Baik, H.H.; Jin, B.K. Interleukin-4-induced oxidative stress via microglial NADPH oxidase contributes to the death of hippocampal neurons in vivo. Curr. Aging Sci. 2008, 1, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, E.; Cho, E.J.; Chung, E.S.; Shin, W.-H.; Jin, B.K. Interleukin-4 Contributes to Degeneration of Dopamine Neurons in the Lipopolysaccharide-treated Substantia Nigra in vivo. Exp. Neurobiol. 2018, 27, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, E.; Chung, Y.C.; Kim, K.S.; Baik, H.H.; Shin, W.H.; Jin, B.K. Modulation of M1/M2 polarization by capsaicin contributes to the survival of dopaminergic neurons in the lipopolysaccharide-lesioned substantia nigra in vivo. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.-A.; Yang, M.-S.; Jeong, H.-K.; Min, K.-J.; Kang, S.-H.; Jou, I.; Joe, E.-H. Resident microglia die and infiltrated neutrophils and monocytes become major inflammatory cells in lipopolysaccharide-injected brain. Glia 2007, 55, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.K.; Pennathur, S.; Perier, C.; Tieu, K.; Teismann, P.; Wu, D.C.; Jackson-Lewis, V.; Vila, M.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Heinecke, J.W.; et al. Ablation of the inflammatory enzyme myeloperoxidase mitigates features of Parkinson’s disease in mice. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6594–65600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieu, K.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Przedborski, S. Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in Parkinson’s disease. IUBMB Life 2003, 55, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, M.; Palencia, C.A.; Pahan, K. Fibrillar amyloid-beta peptides activate microglia via TLR2: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7254–7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, K.; Yoo, H.-R.; Park, G. Inhibitory Effects of Myricetin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limón, I.D.; Diaz, A.; Mendieta, L.; Chamorro, G.; Espinosa, B.; Zenteno, E.; Guevara, J. Amyloid-β25–35 impairs memory and increases NO in the temporal cortex of rats. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 63, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.H.; Chung, Y.C.; Piao, Y.; Jin, M.Y.; Son, H.J.; Yoon, N.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Pak, Y.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Hong, J.K.; et al. Ethyl Pyruvate Rescues Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons by Regulating Glial Activation in a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marik, C.; Felts, P.A.; Bauer, J.; Lassmann, H.; Smith, K.J. Lesion genesis in a subset of patients with multiple sclerosis: A role for innate immunity? Brain 2007, 130, 2800–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnhold, J.; Flemmig, J. Human myeloperoxidase in innate and acquired immunity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 500, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, M.B.; Kettle, A.J.; Winterbourn, C.C. Inside the neutrophil phagosome: Oxidants, myeloperoxidase, and bacterial killing. Blood 1998, 92, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.C.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, S.R.; Ko, H.W.; Bok, E.; Shin, W.-H.; Won, S.-Y.; Jin, B.K. Capsaicin prevents degeneration of dopamine neurons by inhibiting glial activation and oxidative stress in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Ding, Y.; Tian, R.; Peng, Y. Inhibition of myeloperoxidase-mediated oxidative damage by nitrite in SH-SY5Y cells: Relevance to neuroprotection in neurodegenerative diseases. Eur. J. Pharm. 2016, 780, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, T.; Esposito, E.; Mazzon, E.; Di Paola, R.; Meli, R.; Caminiti, R.; Bramanti, P.; Fink, M.P.; Cuzzocrea, S. Beneficial effects of ethyl pyruvate in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Shock 2009, 32, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Zu, H.-B. Microglial polarization: Novel therapeutic mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 28, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Primary Antibody | Dilution | Company | Catalog No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| OX-42 | 1:400 | Bio-rad | MCA275G |
| OX-6 | 1:400 | BD Biosciences | 554926 |
| FITC-TL | 1:1000 | Vector Laboratories | FL-1171 |
| NeuN | 1:1000 | Merck | MAB377 |
| GFAP | 1:500 | Sigma-Aldrich | G3893 |
| IL-4 | 1:400 | Abbiotec | 251223 |
| MPO | 1:500 | DakoCytomation | A0398 |
| iNOS | 1:200 | BD Biosciences | 610333 |
| 8-OHdG | 1:300 | Jaica | MOG-100P |
| Nitrotyrosine | 1:50 | Abcam | ab7048 |
| Secondary Antibody | Dilution | Company | Catalog No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biotin-conjugated anti-mouse IgG | 1:400 | KPL | 16-18-15 |
| FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG | 1:500 | Sigma-Aldrich | AP124F |
| Fluorescein-conjugated anti-mouse IgG | 1:300 | Vector Laboratories | FI-2000 |
| Cy3-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG | 1:1000 | Sigma-Aldrich | AP132C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, Y.C.; Jeong, J.Y.; Jin, B.K. Interleukin-4-Mediated Oxidative Stress Is Harmful to Hippocampal Neurons of Prothrombin Kringle-2-Lesioned Rat In Vivo. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111068
Chung YC, Jeong JY, Jin BK. Interleukin-4-Mediated Oxidative Stress Is Harmful to Hippocampal Neurons of Prothrombin Kringle-2-Lesioned Rat In Vivo. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(11):1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111068
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Young Cheul, Jae Yeong Jeong, and Byung Kwan Jin. 2020. "Interleukin-4-Mediated Oxidative Stress Is Harmful to Hippocampal Neurons of Prothrombin Kringle-2-Lesioned Rat In Vivo" Antioxidants 9, no. 11: 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111068
APA StyleChung, Y. C., Jeong, J. Y., & Jin, B. K. (2020). Interleukin-4-Mediated Oxidative Stress Is Harmful to Hippocampal Neurons of Prothrombin Kringle-2-Lesioned Rat In Vivo. Antioxidants, 9(11), 1068. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111068






