Milk Protein-Derived Antioxidant Tetrapeptides as Potential Hypopigmenting Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
2.3. Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition Test
2.4. Lipid Peroxidation Ferric Thiocyanate Assay
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cytotoxicity Test
2.7. Melanogenesis Inhibition Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Peptides
3.2. Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition Activity
3.3. Antioxidant Activity
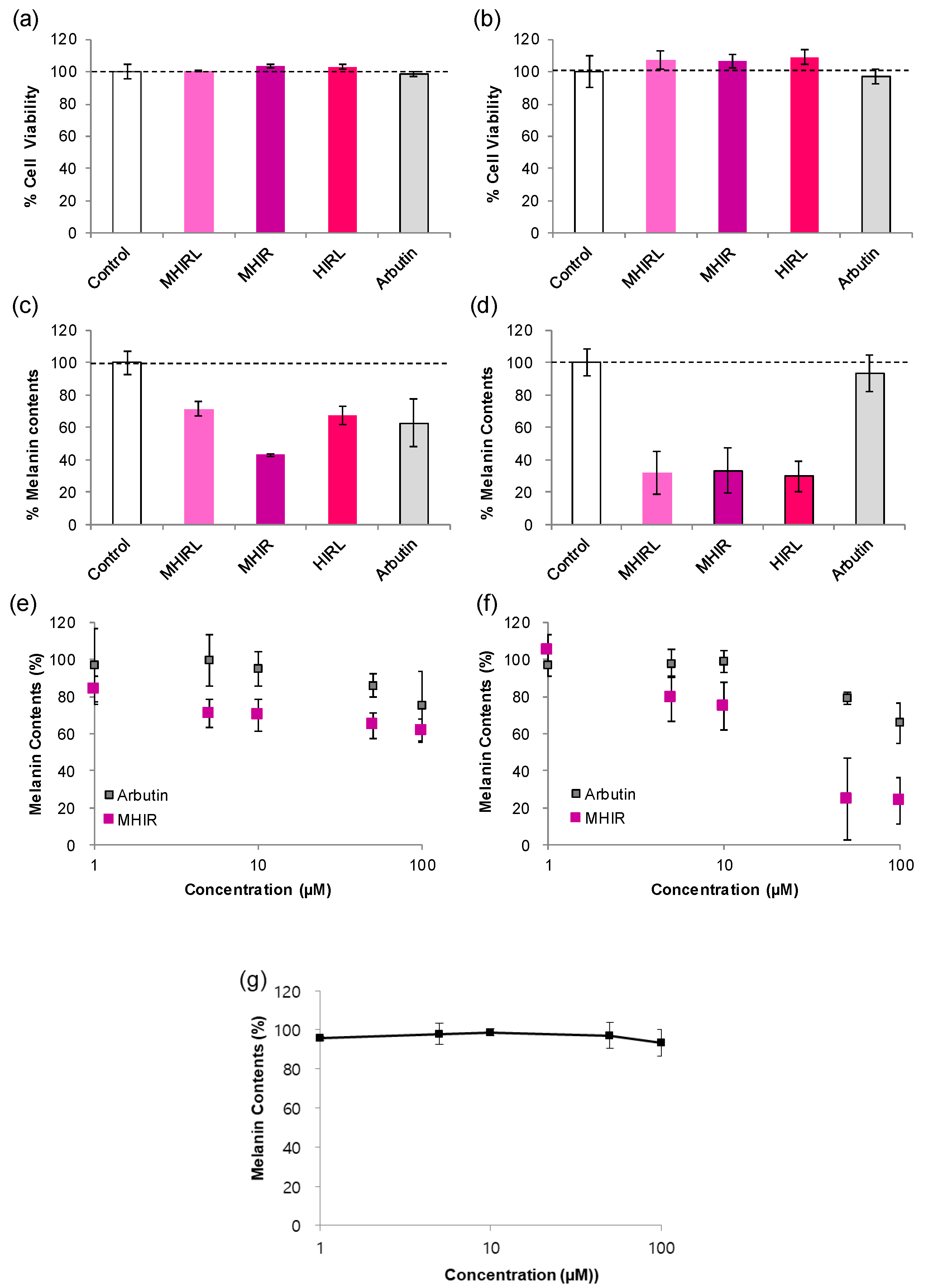
3.4. Melanogenesis Inhibition in Melanocytes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mcginnes, J.; Proctor, P. Importance of Fact That Melanin Is Black. J. Theor. Biol. 1973, 39, 677–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, H.Z. The Function of Melanin or 6 Blind People Examine an Elephant. Bioessays 1992, 14, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, P.H.; Mcginness, J.E. The Function of Melanin. Arch. Dermatol. 1986, 122, 507–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, T.; Gerwat, W.; Batzer, J.; Eggers, K.; Scherner, C.; Wenck, H.; Stab, F.; Hearing, V.J.; Rohm, K.H.; Kolbe, L. Inhibition of Human Tyrosinase Requires Molecular Motifs Distinctively Different from Mushroom Tyrosinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zolghadri, S.; Bahrami, A.; Hassan Khan, M.T.; Munoz-Munoz, J.; Garcia-Molina, F.; Garcia-Canovas, F.; Saboury, A.A. A comprehensive review on tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 279–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Malek, Z.A.; Ruwe, A.; Kavanagh-Starner, R.; Kadekaro, A.L.; Swope, V.; Haskell-Luevano, C.; Koikov, L.; Knittel, J.J. alpha-MSH tripeptide analogs activate the melanocortin 1 receptor and reduce UV-induced DNA damage in human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009, 22, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzoska, T.; Luger, T.A.; Maaser, C.; Abels, C.; Bohm, M. alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and related tripeptides: Biochemistry, antiinflammatory and protective effects in vitro and in vivo, and future perspectives for the treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 581–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawyer, T.K.; Staples, D.J.; Castrucci, A.M.; Hadley, M.E.; Al-Obeidi, F.A.; Cody, W.L.; Hruby, V.J. Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone message and inhibitory sequences: Comparative structure-activity studies on melanocytes. Peptides 1990, 11, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, M.; Kawai, K.; Kawai, K. Contact Allergy to Kojic Acid in Skin Care Products. Contact Dermat. 1995, 32, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Qiang, M.; Dong, T.; Li, H. Role of Vitamin C in Skin Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babu, B.R.; Diwakar, G.; Ramaiah, A.; Fatma, T. Effect of an abundant human skin melanosomal 66 kDa protein (MP 66) on murine tyrosinase: Its physiological implications on melanogenesis. J. Biosci. 1998, 23, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benathan, M.; Labidi, F. Insulin inhibits tyrosinase activity and 5-S-cysteinyldopa formation in human melanoma cells. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1997, 77, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, E.; Husain, I.; Ramaiah, A.; Madan, N.C. Purification of human skin tyrosinase and its protein inhibitor: Properties of the enzyme and the mechanism of inhibition by protein. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1982, 217, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetghebeur, M.; Kermasha, S. Inhibition of polyphenol oxidase by copper-metallothionein from Aspergillus niger. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakot, P.; Chaitanawisuti, N.; Sangtanoo, P.; Saisavoey, T.; Karnchanatat, A. Inhibitory Activities of Protein Hydrolysates from Spotted Babylon Snails on Tyrosinase and Melanogenesis. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H.; Somoto, A.; Kuranari, J.; Kimura, A.; Chiba, S. A Novel Cyclotetrapeptide Produced by Lactobacillus-Helveticus as a Tyrosinase Inhibitor. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 3439–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.W.; Ko, S.C.; Heo, S.Y.; Nguyen, V.T.; Kim, G.; Jang, C.H.; Park, W.S.; Choi, I.W.; Qian, Z.J.; Jung, W.K. A novel peptide purified from the fermented microalga Pavlova lutheri attenuates oxidative stress and melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells. Process. Biochem. 2015, 50, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Seok, J.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Boo, Y.C. Identification of small peptides and glycinamide that inhibit melanin synthesis using a positional scanning synthetic peptide combinatorial library. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurink, M.; van Berkel, W.J.; Wichers, H.J.; Boeriu, C.G. Novel peptides with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Peptides 2007, 28, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Ubeid, A.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Hantash, B.M. Short-sequence oligopeptides with inhibitory activity against mushroom and human tyrosinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2242–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, H.; Kayashita, T.; Kobata, H.; Gonda, A.; Takeya, K.; Itokawa, H. Pseudostellarins D-F, New Tyrosinase Inhibitory Cyclic-Peptides from Pseudostellaria-Heterophylla. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 9975–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.L.; Liu, L.; Yang, H.Q.; Guo, H.Z.; Liu, X.; Tan, Y.H.; Wang, W.; Quan, J.; Zhu, L.M. A Novel Heptapeptide with Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity Identified from a Phage Display Library. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, S.; Pekyardimci, S.; Cokmus, C. Partial characterization of a peptide from honey that inhibits mushroom polyphenol oxidase. J. Food Biochem. 2001, 25, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oszmianski, J.; Lee, C.Y. Inhibition of Polyphenol Oxidase Activity and Browning by Honey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Shinoda, I.; Samejima, Y.; Miyauchi, H.; Fukuwatari, Y.; Hayasawa, H. Kappa-casein suppresses melanogenesis in cultured pigment cells. Pigment Cell Res. 1996, 9, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Shinoda, I.; Mikogami, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Miyauchi, H.; Fukuwatari, Y.; Hayasawa, H. Beta-lactoglobulin suppresses melanogenesis in cultured human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 1997, 10, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Liu, J.R.; Sheu, J.F.; Lin, C.W.; Chuang, C.L. Study on skin care properties of milk kefir whey. Asian Australas. J. Anim. 2006, 19, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Paskewitz, S.M. Hen egg white lysozyme as an inhibitor of mushroom tyrosinase. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochiai, A.; Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, T.; Taniguchi, M. Rice Bran Protein as a Potent Source of Antimelanogenic Peptides with Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2545–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, V. Effect of Proteins, Protein Hydrolyzates and Amino-Acids on Ortho-Dihydroxyphenolase Activity of Polyphenol Oxidase of Mushroom, Avocado, and Banana. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsuna, K.; Ukeda, H.; Ochi, H. Isolation and characterization of free radical scavenging activities peptides derived from casein. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000, 11, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Ledesma, B.; Davalos, A.; Bartolome, B.; Amigo, L. Preparation of antioxidant enzymatic hydrolysates from (alpha-lactalbumin and beta-lactoglobulin. Identification of active peptides by HPLC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addar, L.; Bensouici, C.; Zennia, S.S.A.; Haroun, S.B.; Mati, A. Antioxidant, tyrosinase and urease inhibitory activities of camel alpha S-casein and its hydrolysate fractions. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 173, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.K.; Lee, E.; Hwang, I.J.; Yim, D.; Han, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.H. beta-Lactoglobulin Peptide Fragments Conjugated with Caffeic Acid Displaying Dual Activities for Tyrosinase Inhibition and Antioxidant Effect. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.S. Chemical Modulation of Bioactive Compounds via Oligopeptide or Amino Acid Conjugation. Biopolymers 2013, 100, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Tseng, T.S.; Hsiao, N.W.; Lin, Y.L.; Wen, Z.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Lin, H.H.; Tsai, K.C. Discovery of Highly Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitor, T1, with Significant Anti-Melanogenesis Ability by zebrafish in vivo Assay and Computational Molecular Modeling. Sci. Rep. UK 2015, 5, 7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochiai, A.; Tanaka, S.; Imai, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kanaoka, T.; Tanaka, T.; Taniguchi, M. New tyrosinase inhibitory decapeptide: Molecular insights into the role of tyrosine residues. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, R.; Valentao, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Felix, C.; Novais, S.C.; Lemos, M.F.L. Evaluating the In Vitro Potential of Natural Extracts to Protect Lipids from Oxidative Damage. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dooley, T.P.; Gadwood, R.C.; Kilgore, K.; Thomasco, L.M. Development of an in vitro primary screen for skin depigmentation and antimelanoma agents. Skin Pharmacol. 1994, 7, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.; Wilson, R.E.; Dooley, T.P.; Goss, M.W.; Hart, I.R. Protein-Kinase-C down-Regulation, and Not Transient Activation, Correlates with Melanocyte Growth. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 3281–3288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Borron, J.C.; Sanchez-Laorden, B.L.; Jimenez-Cervantes, C. Melanocortin-1 receptor structure and functional regulation. Pigment Cell Res. 2005, 18, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, A.M.; Blumenthal, D.K.; Krebs, E.G. Protein Serine Threonine Kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 567–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neeley, E.; Fritch, G.; Fuller, A.; Wolfe, J.; Wright, J.; Flurkey, W. Variations in IC50 Values with Purity of Mushroom Tyrosinase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3811–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Source | Original Peptide Sequence | Tetrapeptide Fragments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| κ-casein | YFYPEL | YFYP | FYPE | YPEL |
| β-lactoglobulin | YVEEL | YVEE | VEEL | YVEL |
| MHIRL | MHIR | HIRL | ||
| WYSLAMAA | WYSL | YSLA | SLAM | |
| LAMA | AMAA | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, S.; Choi, H.-R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Park, K.-C.; Kwak, S.-Y. Milk Protein-Derived Antioxidant Tetrapeptides as Potential Hypopigmenting Agents. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111106
Kong S, Choi H-R, Kim Y-J, Lee Y-S, Park K-C, Kwak S-Y. Milk Protein-Derived Antioxidant Tetrapeptides as Potential Hypopigmenting Agents. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(11):1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111106
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Saerom, Hye-Ryung Choi, Yoon-Jeong Kim, Yoon-Sik Lee, Kyoung-Chan Park, and Seon-Yeong Kwak. 2020. "Milk Protein-Derived Antioxidant Tetrapeptides as Potential Hypopigmenting Agents" Antioxidants 9, no. 11: 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111106
APA StyleKong, S., Choi, H.-R., Kim, Y.-J., Lee, Y.-S., Park, K.-C., & Kwak, S.-Y. (2020). Milk Protein-Derived Antioxidant Tetrapeptides as Potential Hypopigmenting Agents. Antioxidants, 9(11), 1106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111106





