Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Blood Glutathione Redox State in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy, Eligibility Criteria and Study Selection
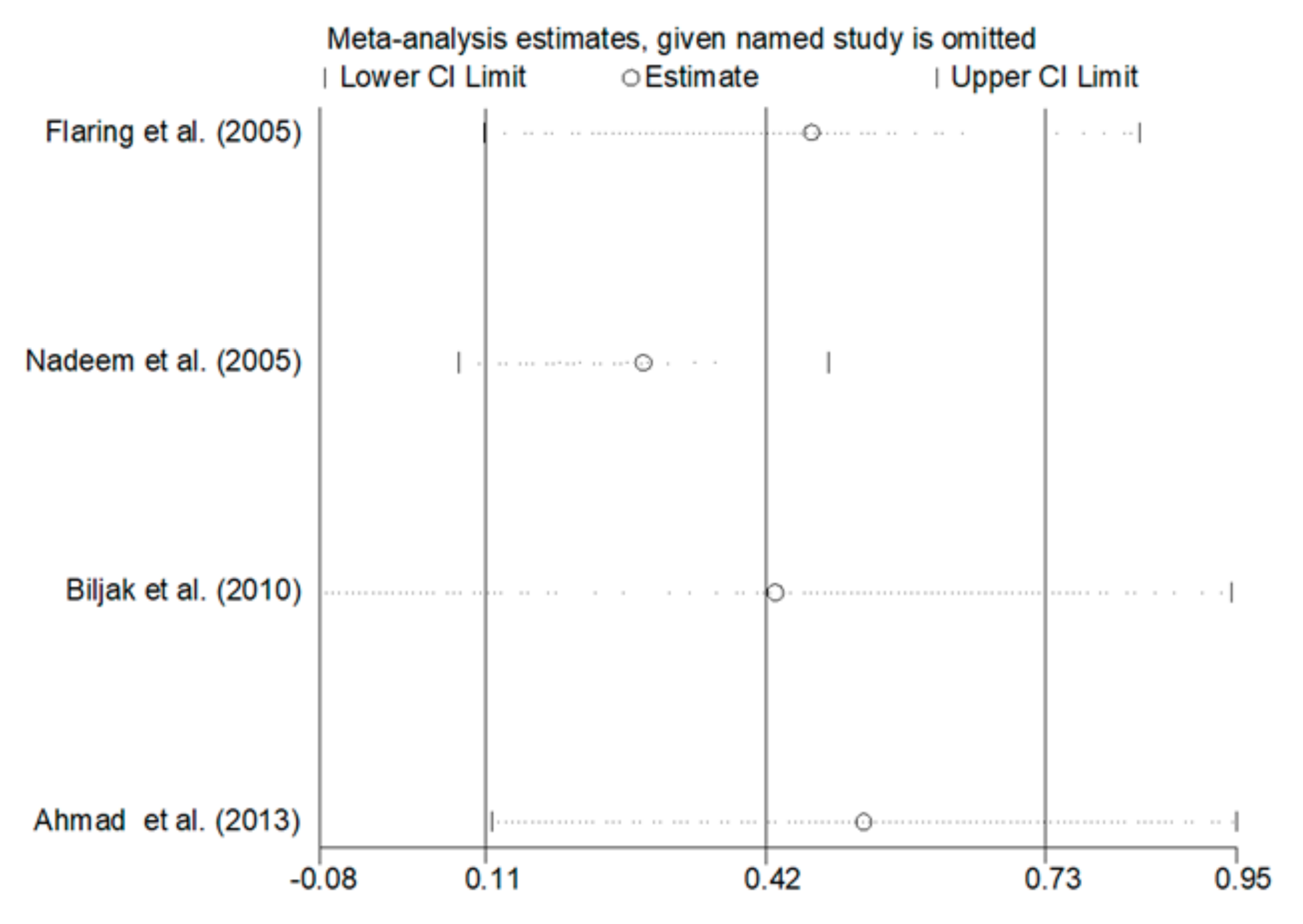
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
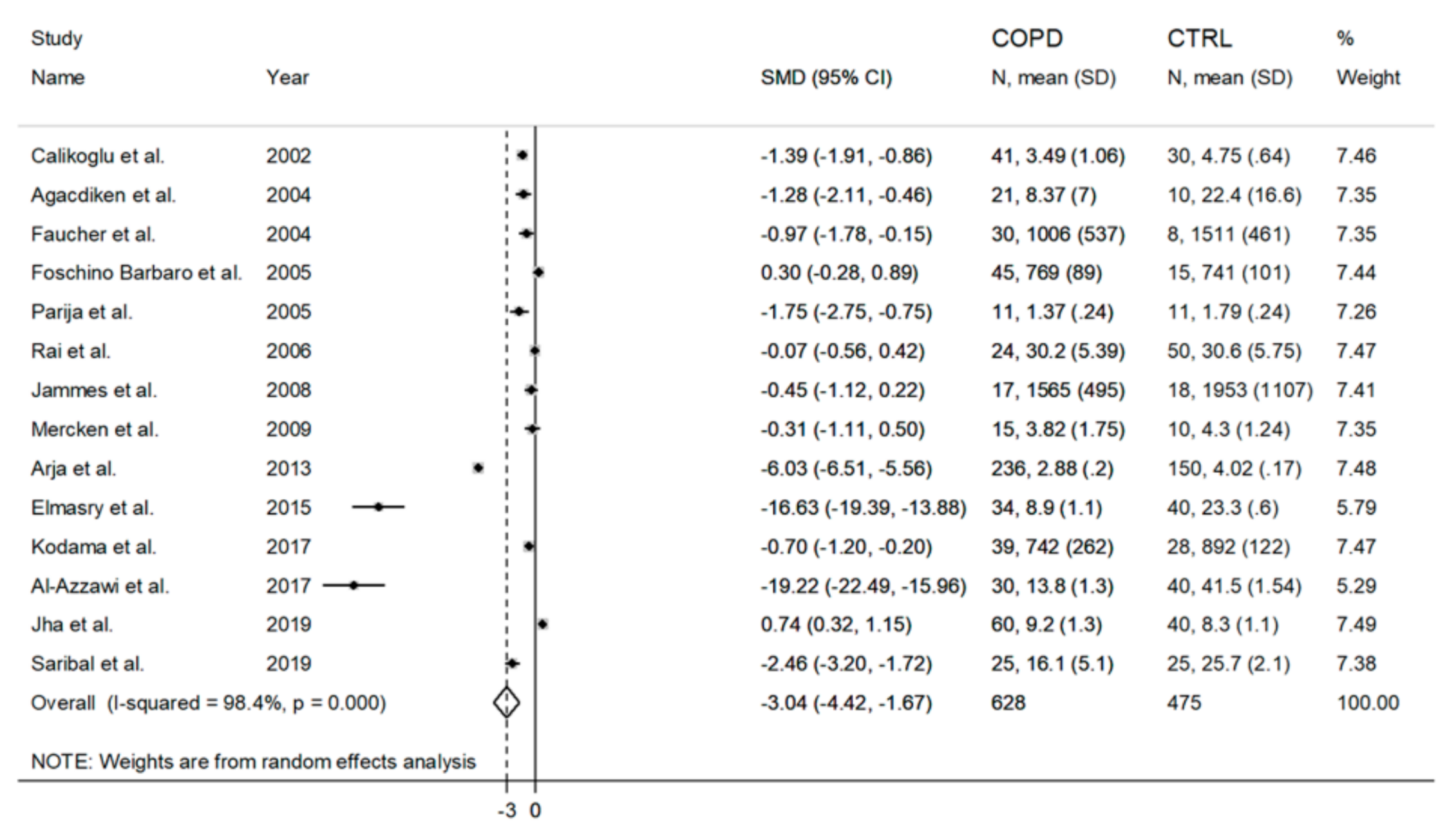
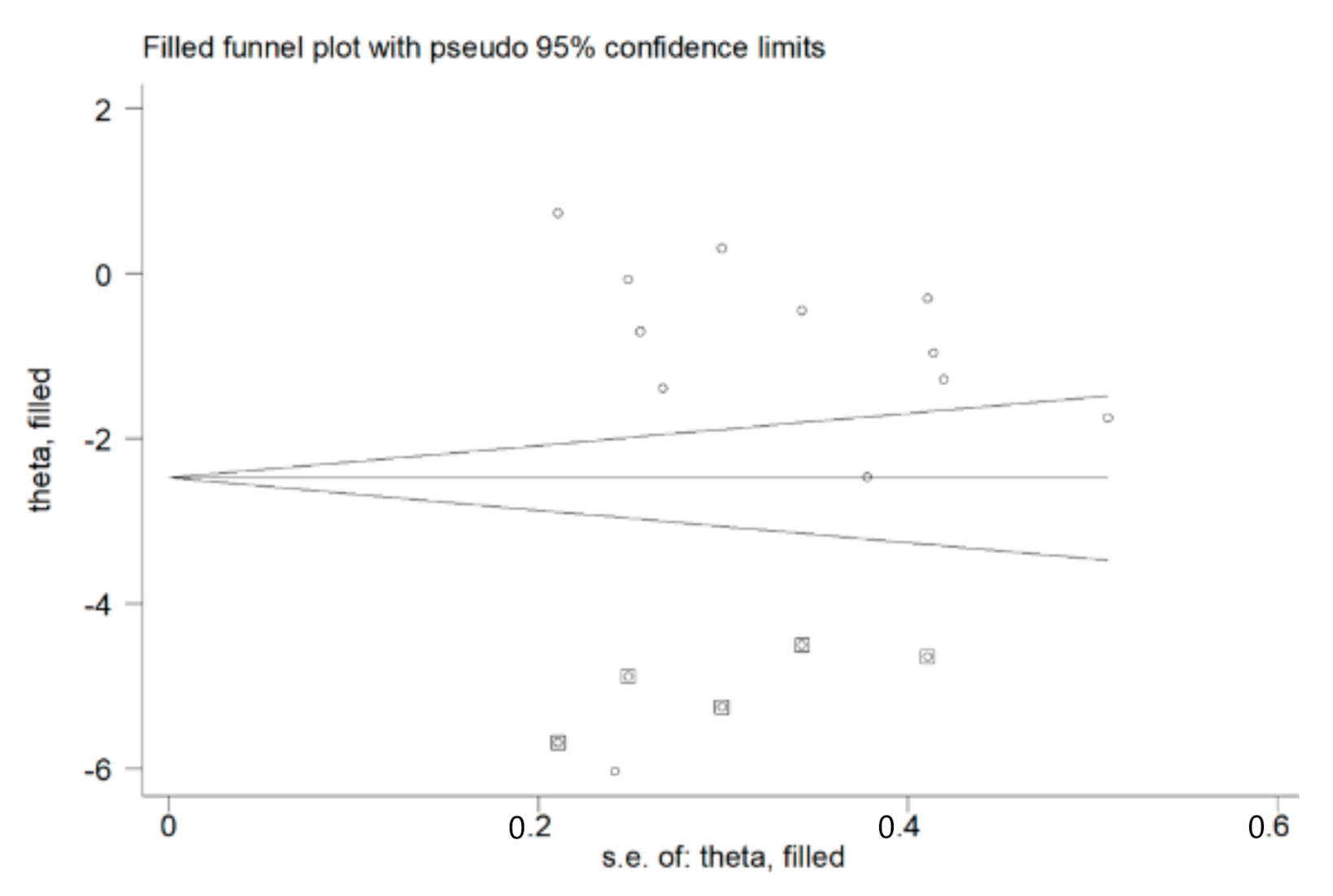
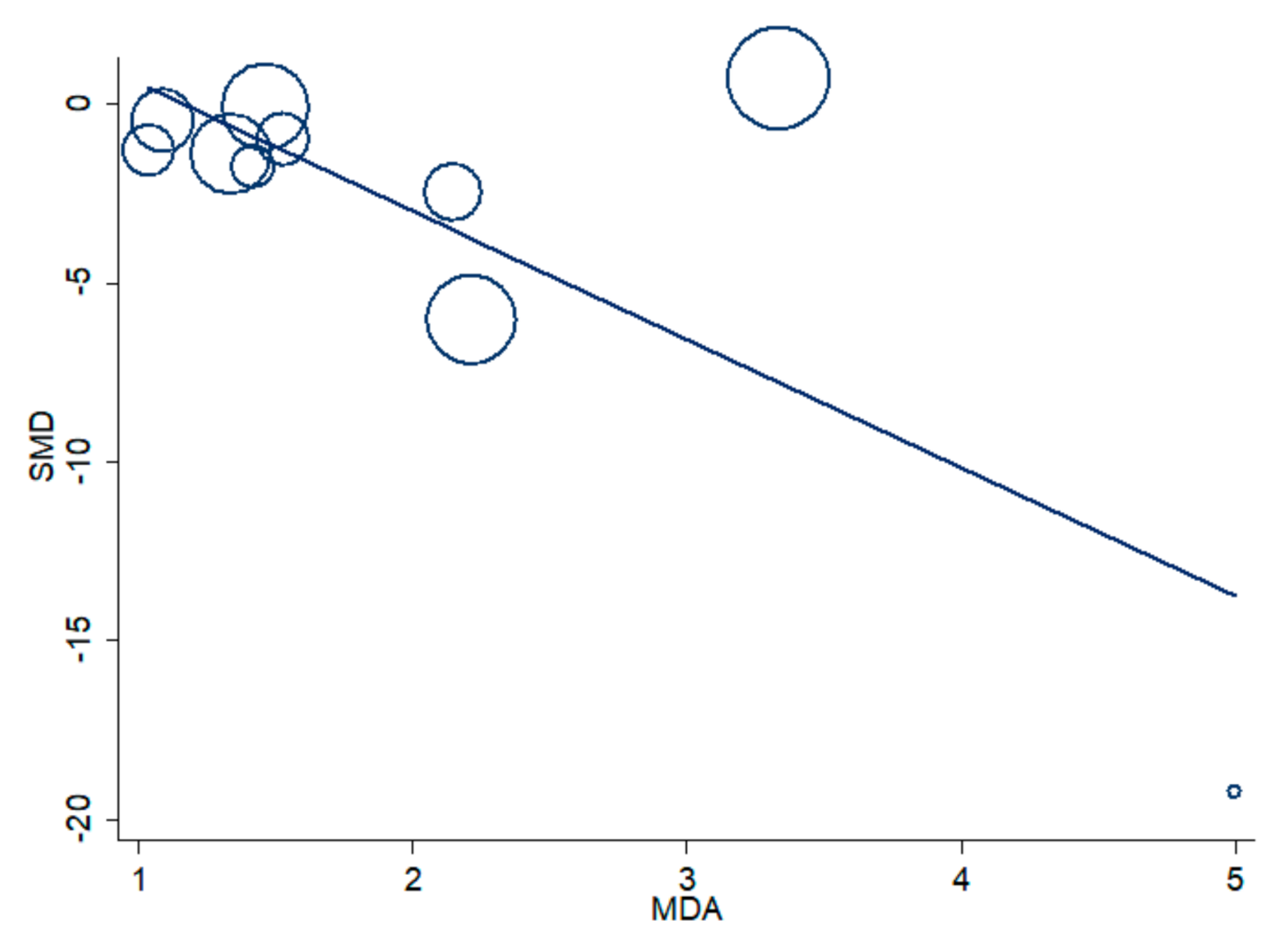
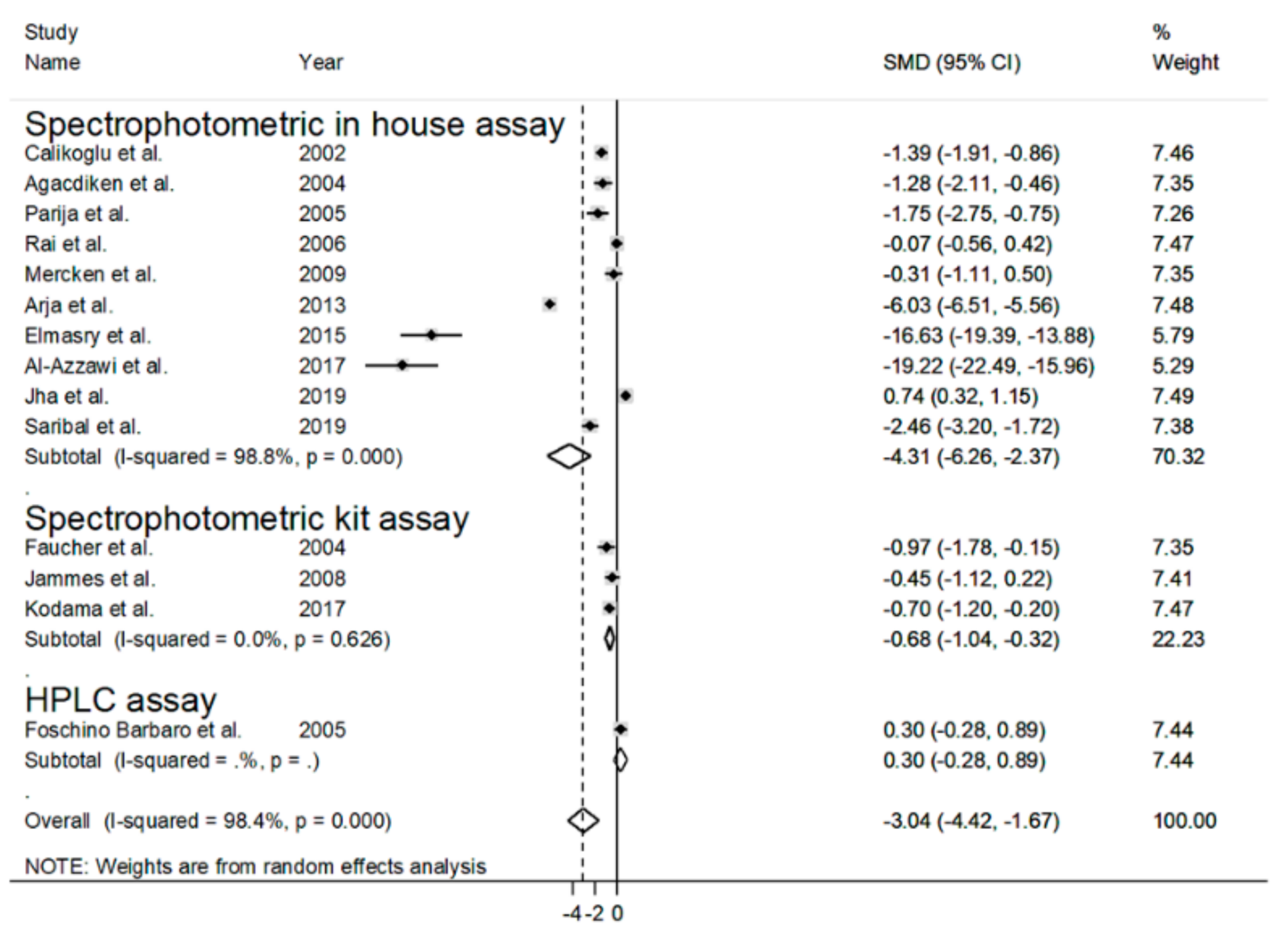
3.2. Blood Reduced GSH (rGSH) and COPD
3.3. Blood Total GSH (tGSH) and COPD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagdonas, E.; Raudoniute, J.; Bruzauskaite, I.; Aldonyte, R. Novel aspects of pathogenesis and regeneration mechanisms in COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2015, 10, 995–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Duangrithi, D.; Saiprom, K.; SaeTew, J.; Sa-u, Y. Impact of exacerbation on the errors of inhaler techniques in COPD patients. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Quaderi, S.A.; Hurst, J.R. The unmet global burden of COPD. Glob. Health Epidemiol. Genom. 2018, 3, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, I. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of COPD. Treat. Respir. Med. 2005, 4, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Adcock, I.M. Oxidative stress and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, L.J.L.; Kapetanakis, V.; Rudnicka, A.R.; Cook, D.G.; Bush, T.; Stedman, J.R.; Whincup, P.H.; Strachan, D.P.; Anderson, H.R. Chronic exposure to outdoor air pollution and lung function in adults. Thorax 2009, 64, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvi, S.S.; Barnes, P.G. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in non-smokers. Lancet 2009, 374, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. How Tobacco Smoke Causes Disease: The Biology and Behavioral Basis for Smoking-Attributable Disease: A Report of the Surgeon General. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA; Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010.
- Van der Toorn, M.; Rezayat, D.; Kauffman, J.F.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Gans, R.O.B.; Koëter, G.H.; Choi, A.M.K.; Van Oosterhout, A.J.M.; Slebos, D.J. Lipidsoluble components in cigarette smoke induce mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species in lung epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L109–L114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tkaczyk, J.; Vízek, M. Oxidative stress in the lung tissue—Sources of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defence. Prague Med. Rep. 2007, 108, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Dröge, W. Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Fois, A.G.; Sotgia, S.; Zinellu, E.; Bifulco, F.; Pintus, G.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; Pirina, P. Plasma protein thiols: An early marker of oxidative stress in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 28, 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, A. Glutathione deficiency produced by inhibition of its synthesis, and its reversal; applications in research and therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991, 51, 155–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffner, J.A.; Repine, J.E. State of the art: Pulmonary strategies of antioxidant defense. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 140, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.P. Redox potential of GSH/GSSG couple: Assay and biological significance. Methods Enzymol. 2002, 348, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beeh, K.M.; Beier, J.; Koppenhoefer, N.; Buhl, R. Increased glutathione disulfide and nitrosothiols in sputum supernatant of patients with stable COPD. Chest 2004, 126, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Thomas, P.S. Oxidative Stress in COPD and Its Measurement through Exhaled Breath Condensate. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2009, 2, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drost, E.M.; Skwarski, K.M.; Sauleda, J.; Soler, N.; Roca, J.; Agusti, A.; MacNee, W. Oxidative stress and airway inflammation in severe exacerbations of COPD. Thorax 2005, 60, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Vliet, A.; O’Neill, C.A.; Cross, C.E.; Koostra, J.M.; Volz, W.G.; Halliwell, B.; Louie, S. Determination of low-molecular-mass antioxidant concentrations in human respiratory tract lining fluids. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, L289–L296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, N.S.; Min, E.; Gauthier, S.; Martin, R.J.; Day, B.J. Lung glutathione adaptive responses to cigarette smoke exposure. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cross, C.E.; Van der Vliet, A.; O’Neill, C.A.; Louie, S.; Halliwell, B. Oxidants, antioxidants, and respiratory tract lining fluids. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Freels, J.L.; Robbins, R.A.; Campbell, S.C. Exhaled Breath Condensate the Past, Present, and Future. Clin. Pulm. Med. 2003, 10, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2013. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowden, J.; Tierney, J.F.; Copas, A.J.; Burdett, S. Quantifying, displaying and accounting for heterogeneity in the meta-analysis of RCTs using standard and generalised Q statistics. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, A. Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Tech. Bull. 1999, 47, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: Guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fläring, U.B.; Rooyackers, O.E.; Hebert, C.; Bratel, T.; Hammarqvist, F.; Wernerman, J. Temporal changes in whole-blood and plasma glutathione in ICU patients with multiple organ failure. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 31, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljak, V.R.; Rumora, L.; Cepelak, I.; Pancirov, D.; Popović-Grle, S.; Sorić, J.; Grubisić, T.Z. Glutathione cycle in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2010, 28, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calikoğlu, M.; Unlü, A.; Tamer, L.; Ercan, B.; Buğdayci, R.; Atik, U. The levels of serum vitamin C, malonyldialdehyde and erythrocyte reduced glutathione in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and in healthy smokers. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agacdiken, A.; Basyigit, I.; Ozden, M.; Yildiz, F.; Ural, D.; Maral, H.; Boyaci, H.; Ilgazli, A.; Komsuoglu, B. The effects of antioxidants on exercise-induced lipid peroxidation in patients with COPD. Respirology 2004, 9, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucher, M.; Steinberg, J.G.; Barbier, D.; Hug, F.; Jammes, Y. Influence of chronic hypoxemia on peripheral muscle function and oxidative stress in humans. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2004, 24, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foschino Barbaro, M.P.; Serviddio, G.; Resta, O.; Rollo, T.; Tamborra, R.; Carpagnano, E.G.; Vendemiale, G.; Altomare, E. Oxygen therapy at low flow causes oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Prevention by N-acetyl cysteine. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, A.; Raj, H.G.; Chhabra, S.K. Increased oxidative stress and altered levels of antioxidants in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Inflammation 2005, 29, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parija, M.; Bobby, Z.; Kumar, V.; Saradha, B. Oxidative stress and protein glycation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 49, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, R.R.; Phadke, M.S. Plasma oxidant-antioxidant status in different respiratory disorders. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 21, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jammes, Y.; Steinberg, J.G.; Ba, A.; Delliaux, S.; Brégeon, F. Enhanced exercise-induced plasma cytokine response and oxidative stress in COPD patients depend on blood oxygenation. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2008, 28, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercken, E.M.; Gosker, H.R.; Rutten, E.P.; Wouters, E.F.; Bast, A.; Hageman, G.J.; Schols, A.M. Systemic and pulmonary oxidative stress after single-leg exercise in COPD. Chest 2009, 136, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Shameem, M.; Husain, Q. Altered oxidant-antioxidant levels in the disease prognosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2013, 17, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arja, C.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Raya, P.; Adimoolam, C.; Balisetty, B.; Kanala, K.R. Oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activity in South Indian male smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respirology 2013, 18, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elmasry, S.A.; Al-Azzawi, M.A.; Ghoneim, A.H.; Nasr, M.Y.; AboZaid, M.M.N. Role of oxidant–antioxidant imbalance in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Egypt. J. Chest Dis Tuberc. 2015, 64, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kodama, Y.; Kishimoto, Y.; Muramatsu, Y.; Tatebe, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirota, N.; Itoigawa, Y.; Atsuta, R.; Koike, K.; Sato, T.; et al. Antioxidant nutrients in plasma of Japanese patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma-COPD overlap syndrome and bronchial asthma. Clin. Respir. J. 2017, 11, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Azzawi, M.A.; Ghoneim, A.H.; Elmadbouh, I. Evaluation of Vitamin D, Vitamin D Binding Protein Gene Polymorphism with Oxidant—Antioxidant Profiles in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Med. Biochem. 2017, 28, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, S.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Chowdhuri, S.; Mitra, A.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, K. Oxidants and Antioxidants in COPD Associated with Tobacco Smoke and Biomass Exposure. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2019, 8, 3449–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saribal, D.; Hocaoglu-Emre, F.S.; Aydemir, B.; Akyolcu, M. Determination of Relationship between Lipid Peroxidation, Antioxidant Defence, Trace Elements and Hemorheology in COPD. Trace Elem. Electroly. 2019, 36, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van ‘t Erve, T.J.; Wagner, B.A.; Ryckman, K.K.; Raife, T.J.; Buettne, G.R. The Concentration of Glutathione in Human Erythrocytes is a Heritable Trait. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carru, C.; Zinellu, A.; Pes, G.M.; Marongiu, G.; Tadolini, B.; Deiana, L. Ultrarapid capillary electrophoresis method for the determination of reduced and oxidized glutathione in red blood cells. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carru, C.; Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Marongiu, G.; Farina, M.G.; Usai, M.F.; Pes, G.M.; Tadolini, B.; Deiana, L. Optimization of the principal parameters for the ultrarapid electrophoretic separation of reduced and oxidized glutathione by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1017, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Sotgia, S.; Usai, M.F.; Zinellu, E.; Deiana, L.; Carru, C. GSH depletion after erythrocytes acidic treatment is related to intracellular hemoglobin levels. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2006, 366, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutler, E.; Duron, O.; Kelly, B.M. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1963, 61, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.P.; Carlson, J.L.; Samiec, P.S.; Sternberg, P.; Mody, V.C.; Reed, R.L.; Brown, L.A. Glutathione measurement in human plasma. Evaluation of sample collection, storage and derivatization conditions for analysis of dansyl derivatives by HPLC. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1998, 275, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinellu, A.; Zinellu, E.; Sotgiu, E.; Fois, A.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Scano, V.; Piras, B.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Carru, C.; et al. Systemic transsulfuration pathway thiol concentrations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 7, e13267. [Google Scholar]
- Paliogiannis, P.; Fois, A.G.; Sotgia, S.; Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; Zinellu, A. Circulating malondialdehyde concentrations in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Control Group | COPD Group | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Author, Year, Country | Diagnosis | NOS (Stars) | Matrix | GSH Form | Measurement Units | n | Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | GSH Mean ± SD | n | Age (Years) | Gender (M/F) | GSH Mean ± SD |
| Calikoglu et al. 2002, Turkey | BTS | 8 | RBC | Red | μmol/gHb | 30 | 62.56 | 15/15 | 4.75 ± 0.64 | 41 | 58.21 | 20/21 | 3.49 ± 1.06 |
| Agacdiken et al. 2004, Turkey | NR | 8 | WB | Red | mg/dL | 10 | 49 | 10/0 | 22.4 ± 16.6 | 21 | 63 | 21/0 | 8.37 ± 7 |
| Faucher et al. 2004, France | NR | 6 | RBC | Red | nmol/mL | 8 | 59 | 7/1 | 1511 ± 461 | 30 | 66 | 29/1 | 1006 ± 537 |
| Foschino Barbaro et al. 2005, Italy | GOLD | 6 | RBC | Red | µmol/L | 15 | 61 | 15/0 | 741 ± 101 | 45 | 62 | 45/0 | 769 ± 89 |
| Flaring et al. 2005, Sweden | NR | 6 | WB | Tot | µmol/L | 10 | 42 | 3/7 | 1206 ± 264 * | 21 | 75 | NR | 1231 ± 184 * |
| Nadeem et al. 2005, India | GOLD | 8 | WB | Tot | mmol/L | 20 | NR | 20/0 | 0.420 ± 0.057 | 76 | NR | 76/0 | 0.754 ± 0.043 |
| Parija et al. 2005, India | NR | 8 | WB | Red | mg/gHb | 11 | 55 | 9/2 | 1.79 ± 0.24 | 11 | 57 | 10/1 | 1.37 ± 0.24 |
| Rai et al. 2006, India | NR | 6 | WB | Red | mg/dL | 50 | 22–55 | NR | 30.6 ± 5.75 | 24 | 35–65 | NR | 30.2 ± 5.39 |
| Jammes et al. 2008, Senegal | ATS/ERS | 6 | RBC | Red | nmol/mL | 18 | 48 | 13/5 | 1953 ± 1107 | 17 | 53 | 13/4 | 1565 ± 495 |
| Mercken et al. 2009, Netherlands | GOLD | 9 | RBC | Red | µmol/gHb | 10 | 56 | 4/6 | 4.30 ± 1.24 | 15 | 57 | 10/5 | 3.82 ± 1.75 |
| Biljak et al. 2010, Croatia | GOLD | 6 | RBC | Tot | µmol/L | 51 | 52 | 21/30 | 221 ± 114 * | 109 | 71 | 82/27 | 259 ± 77 * |
| Ahmad et al. 2013, India | GOLD | 6 | WB | Tot | mmol/L | 75 | 42 | 53/22 | 0.84 ± 0.34 | 140 | 45 | 111/29 | 0.93 ± 0.47 |
| Arja et al. 2013, India | GOLD | 6 | RBC | Red | nmol/mL | 150 | 61 | 150/0 | 4.02 ± 0.17 | 236 | 63 | 236/0 | 2.88 ± 0.20 |
| Elmasry et al. 2015, Egypt | GOLD | 6 | WB | Red | mg/dL | 40 | 54 | 31/9 | 23.3 ± 0.6 | 34 | 55 | 27/7 | 8.9 ± 1.1 |
| Kodama et al. 2017, Japan | GOLD | 6 | WB | Red | µmol/L | 28 | 69 | 19/9 | 892 ± 122 | 39 | 73 | 34/5 | 742 ± 262 |
| Al-Azzawi et al. 2017, India | ATS/ERS | 6 | WB | Red | µg/mL | 40 | 45 | 28/12 | 41.53 ± 1.54 | 30 | 65 | 21/9 | 13.8 ± 1.3 |
| Jha et al. 2019, India | GOLD | 6 | RBC | Red | µmol/gHb | 40 | 55 | 31/9 | 8.3 ± 1.1 | 60 | 59 | 36/24 | 9.2 ± 1.3 |
| Saribal et al. 2019, Turkey | NR | 7 | RBC | Red | mg/dL | 25 | NR | 25/0 | 25.7 ± 2.1 | 25 | NR | 25/0 | 16.1 ± 5.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sotgia, S.; Paliogiannis, P.; Sotgiu, E.; Mellino, S.; Zinellu, E.; Fois, A.G.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; Mangoni, A.A.; Zinellu, A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Blood Glutathione Redox State in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111146
Sotgia S, Paliogiannis P, Sotgiu E, Mellino S, Zinellu E, Fois AG, Pirina P, Carru C, Mangoni AA, Zinellu A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Blood Glutathione Redox State in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(11):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111146
Chicago/Turabian StyleSotgia, Salvatore, Panagiotis Paliogiannis, Elisabetta Sotgiu, Sabrina Mellino, Elisabetta Zinellu, Alessandro G. Fois, Pietro Pirina, Ciriaco Carru, Arduino A. Mangoni, and Angelo Zinellu. 2020. "Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Blood Glutathione Redox State in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease" Antioxidants 9, no. 11: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111146
APA StyleSotgia, S., Paliogiannis, P., Sotgiu, E., Mellino, S., Zinellu, E., Fois, A. G., Pirina, P., Carru, C., Mangoni, A. A., & Zinellu, A. (2020). Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Blood Glutathione Redox State in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Antioxidants, 9(11), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111146









