β-Naphthoflavone Activation of the Ah Receptor Alleviates Irradiation-Induced Intestinal Injury in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Irradiation
2.2. Evaluation of BNF by Cytotoxicity and Radioprotection on Cell Lines
2.3. Animals and Irradiation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
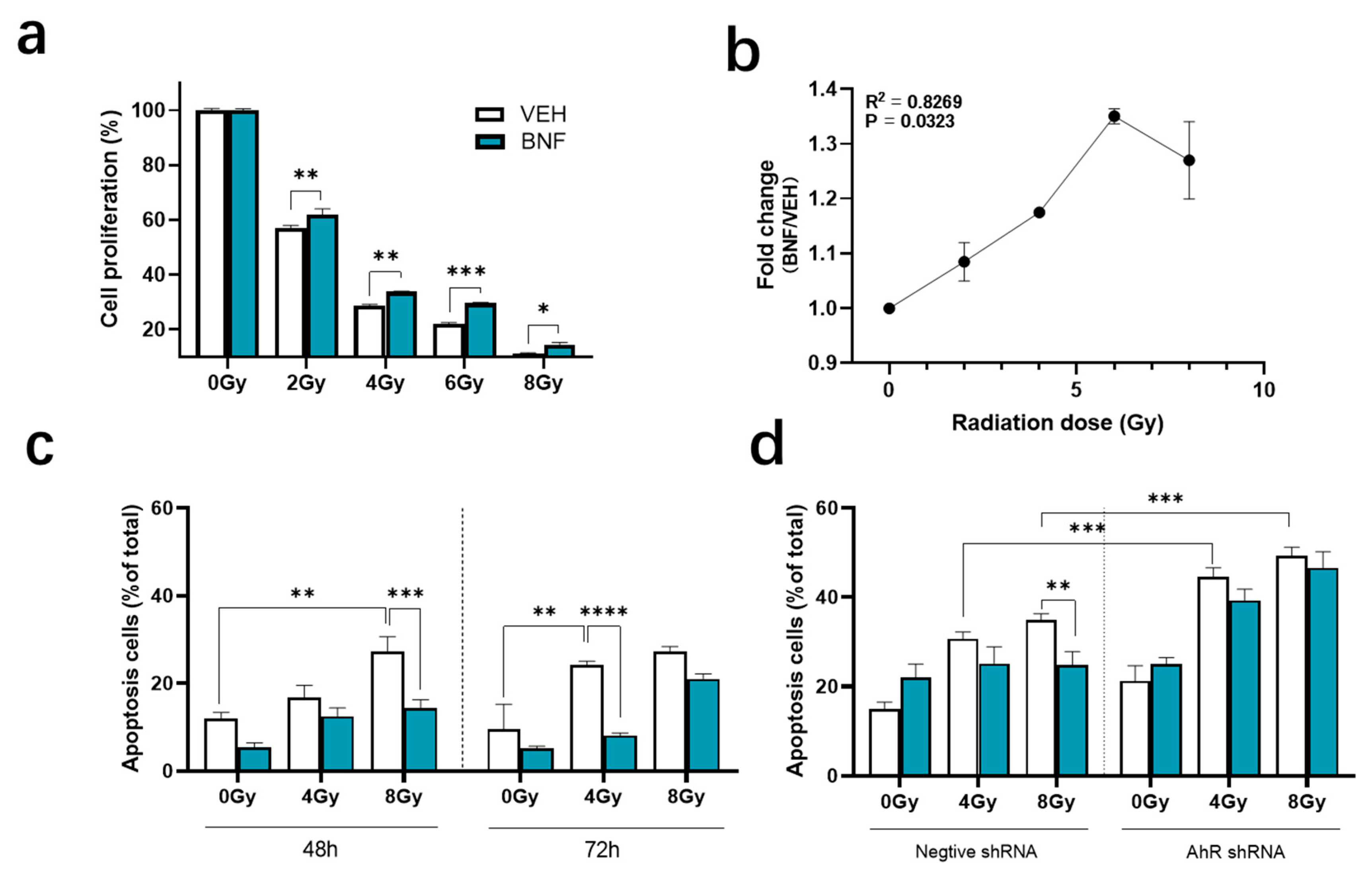
3.1. BNF Improves Cell Viability after Ionizing Radiation
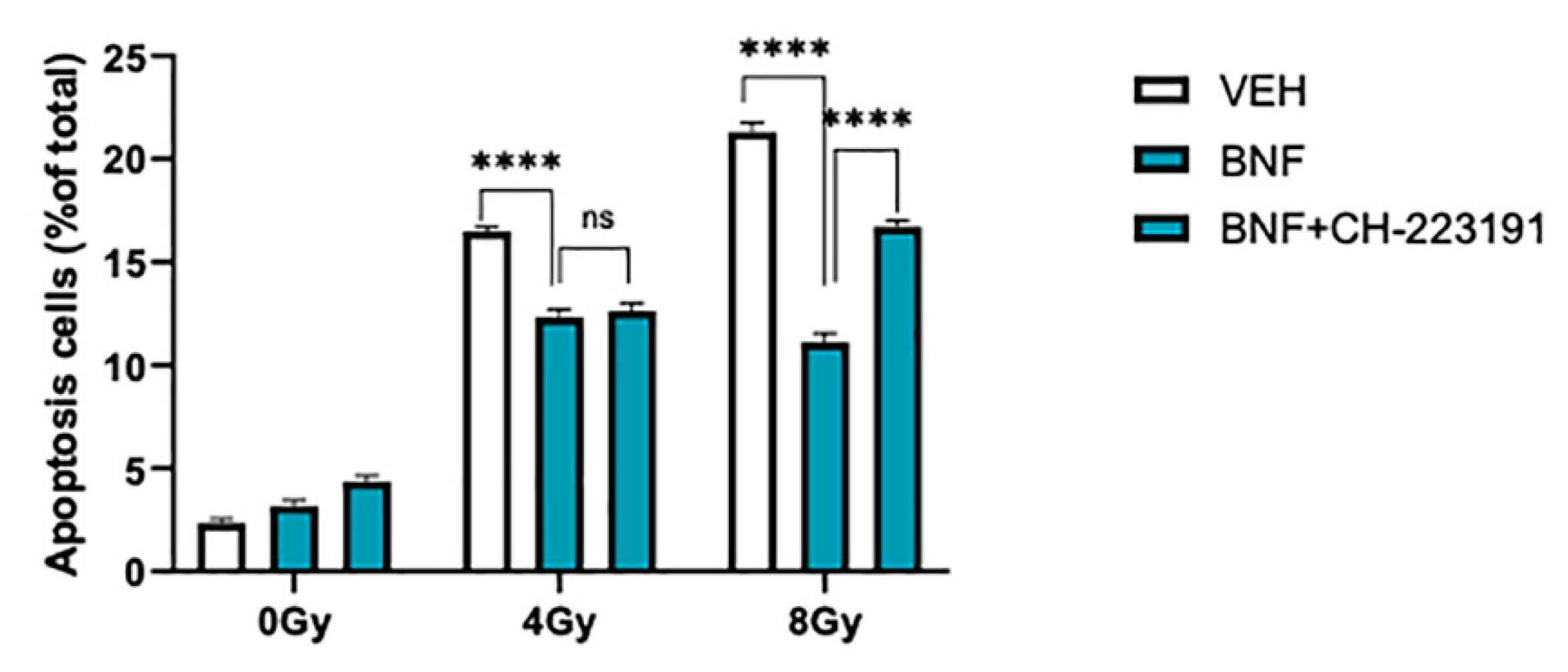
3.2. BNF Attenuates Cell Apoptosis after Radiation Exposure
3.3. BNF Induces Cell Cycle Arrest through AhR Activation
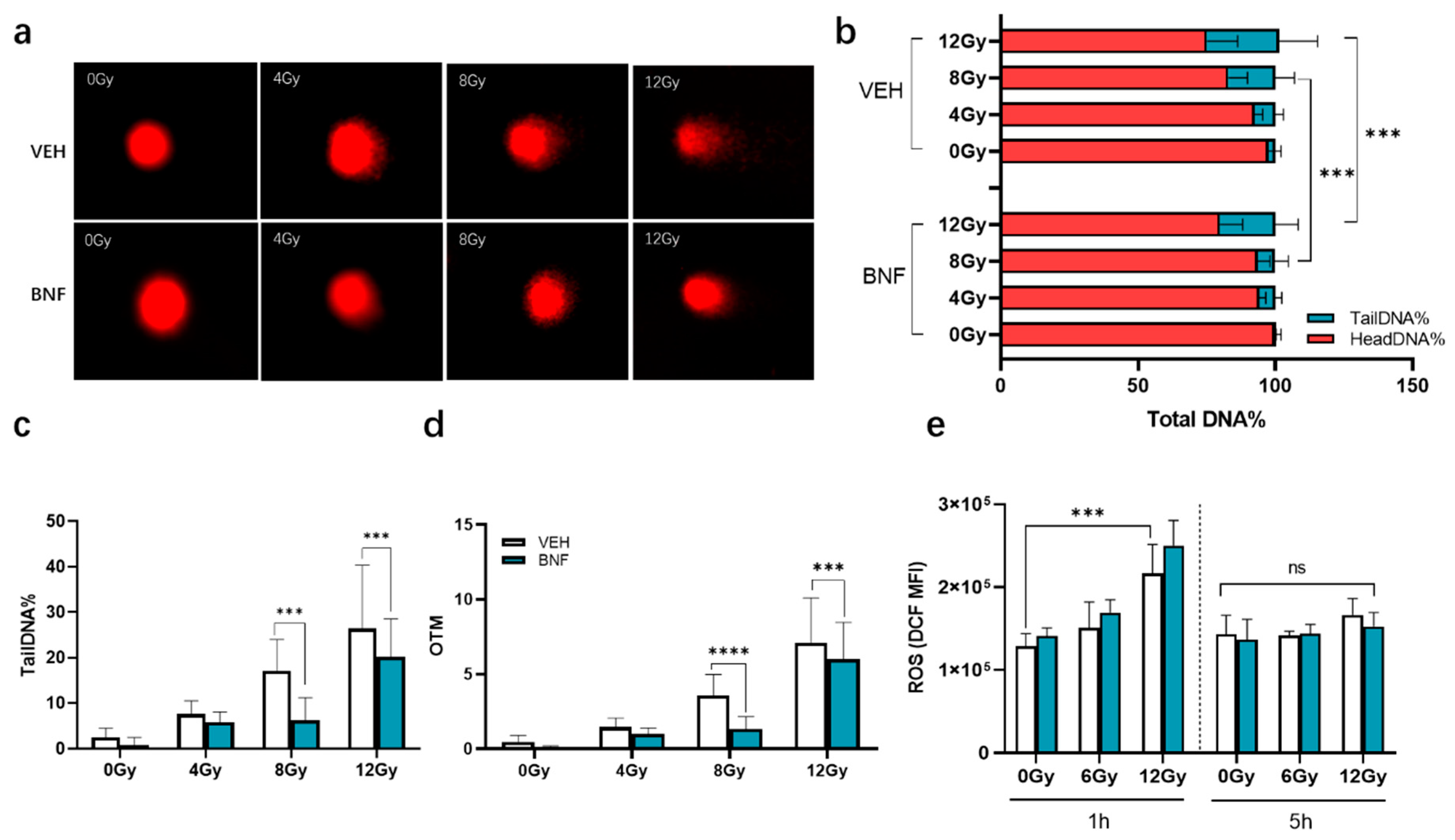
3.4. BNF Protected DNA from Radiation-Induced Strands Break
3.5. BNF does not Directly Contribute to ROS Scavenging
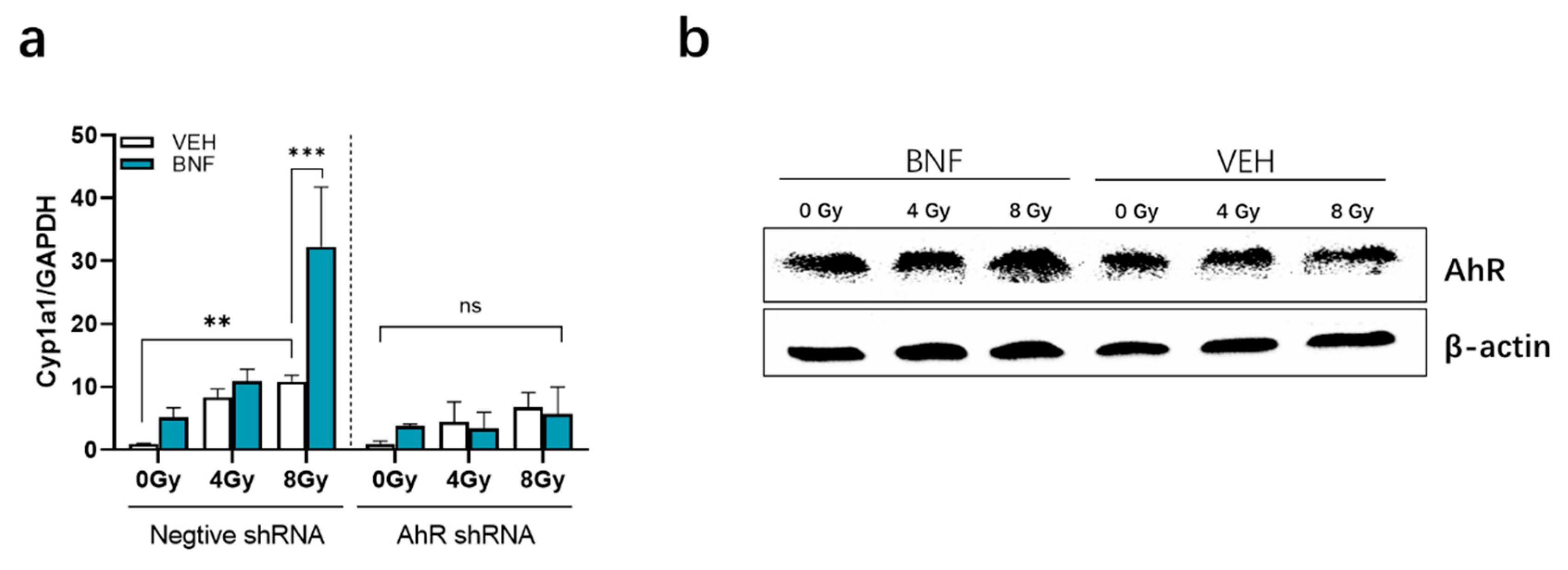
3.6. BNF Activates AhR Activity in IEC-6 Cells after Irradiation
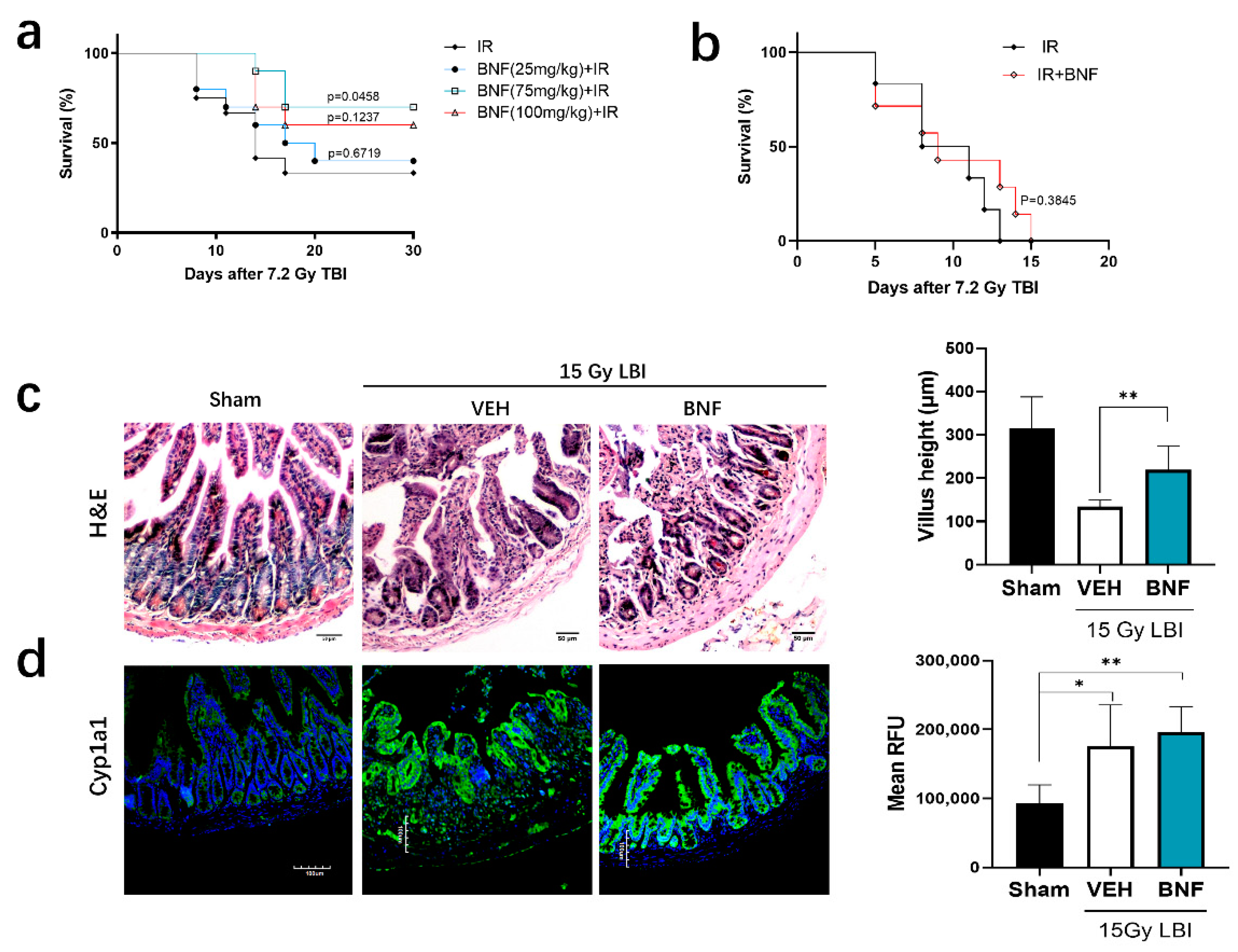
3.7. BNF Improves Survival Time after TBI and Ameliorates Damage of Intestinal Morphology in Mice Exposed to LBI
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaves-Perez, A.; Yilmaz, M.; Perna, C.; de la Rosa, S.; Djouder, N. URI is required to maintain intestinal architecture during ionizing radiation. Science 2019, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockinger, B.; Di Meglio, P.; Gialitakis, M.; Duarte, J.H. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: Multitasking in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 403–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothhammer, V.; Quintana, F.J. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: An environmental sensor integrating immune responses in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, I.A.; Nichols, R.G.; Zhang, L.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Expression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor contributes to the establishment of intestinal microbial community structure in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, I.A.; Perdew, G.H. Ligand activation of the Ah receptor contributes to gastrointestinal homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Bodduluri, S.R.; Baby, B.V.; Hegde, B.; Kotla, N.G.; Hiwale, A.A.; Saiyed, T.; Patel, P.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; et al. Enhancement of the gut barrier integrity by a microbial metabolite through the Nrf2 pathway. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmann, K.H.; Rothmund, M.C.; Paasch, A.; Mayer, C.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Frauenstein, K.; Fritsche, E.; Haarmann-Stemmann, T.; Braeuning, A.; et al. The nuclear aryl hydocarbon receptor is involved in regulation of DNA repair and cell survival following treatment with ionizing radiation. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 240, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Takechi, S. beta-Naphthoflavone, an exogenous ligand of aryl hydrocarbon receptor, disrupts zinc homeostasis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 44, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nannelli, A.; Rossignolo, F.; Tolando, R.; Rossato, P.; Longo, V.; Gervasi, P.G. Effect of beta-naphthoflavone on AhR-regulated genes (CYP1A1, 1A2, 1B1, 2S1, Nrf2, and GST) and antioxidant enzymes in various brain regions of pig. Toxicology 2009, 265, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.Y.; Liou, J.W.; Cheng, T.L.; Peng, S.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Chu, Y.Y.; Luo, W.C.; Huang, Z.K.; Jiang, S.J. beta-Naphthoflavone protects from peritonitis by reducing TNF-alpha-induced endothelial cell activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 102, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Bi, F.; Li, Y.; Yin, H.; Deng, N.; Pan, H.; Li, D.; Xiao, B. alpha- and beta-Naphthoflavone synergistically attenuate H2O2-induced neuron SH-SY5Y cell damage. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, C.B.; Guthrie, E.H.; Huang, M.T.; Taxman, D.J. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA): Design, delivery, and assessment of gene knockdown. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 629, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.P. The comet assay: Reflections on its development, evolution and applications. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2016, 767, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Jones, N.J. Assessment of DNA interstrand crosslinks using the modified alkaline comet assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 817, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konca, K.; Lankoff, A.; Banasik, A.; Lisowska, H.; Kuszewski, T.; Gozdz, S.; Koza, Z.; Wojcik, A. A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat. Res. 2003, 534, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiering, C.; Wincent, E.; Metidji, A.; Iseppon, A.; Li, Y.; Potocnik, A.J.; Omenetti, S.; Henderson, C.J.; Wolf, C.R.; Nebert, D.W.; et al. Feedback control of AHR signalling regulates intestinal immunity. Nature 2017, 542, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shadad, A.K.; Sullivan, F.J.; Martin, J.D.; Egan, L.J. Gastrointestinal radiation injury: Symptoms, risk factors and mechanisms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, C.; Verslegers, M.; Baatout, S.; Leys, N.; Lebeer, S.; Mastroleo, F. Food supplements to mitigate detrimental effects of pelvic radiotherapy. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiss, E.A.; Vonarbourg, C.; Kopfmann, S.; Hobeika, E.; Finke, D.; Esser, C.; Diefenbach, A. Natural aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands control organogenesis of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Science 2011, 334, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Heller, J.J.; Guo, X.; Chen, Z.M.; Fish, K.; Fu, Y.X.; Zhou, L. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates gut immunity through modulation of innate lymphoid cells. Immunity 2012, 36, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindemans, C.A.; Calafiore, M.; Mertelsmann, A.M.; O’Connor, M.H.; Dudakov, J.A.; Jenq, R.R.; Velardi, E.; Young, L.F.; Smith, O.M.; Lawrence, G.; et al. Interleukin-22 promotes intestinal-stem-cell-mediated epithelial regeneration. Nature 2015, 528, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metidji, A.; Omenetti, S.; Crotta, S.; Li, Y.; Nye, E.; Ross, E.; Li, V.; Maradana, M.R.; Schiering, C.; Stockinger, B. The environmental sensor ahr protects from inflammatory damage by maintaining intestinal stem cell homeostasis and barrier integrity. Immunity 2018, 49, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ljungdahl, A.; Kristensson, K.; Lundberg, J.M.; Lycke, E.; Svennerholm, B.; Ziegler, R. Herpes simplex virus infection in capsaicin-treated mice. J. Neurol. Sci. 1986, 72, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, A.J.; Kim, S.J.; Cheong, S.W.; Jeong, S.Y. AhR activation by 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin inhibit the development of mouse intestinal epithelial cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 43, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, T.D.; Murray, I.A.; Nichols, R.G.; Cassel, K.; Podolsky, M.; Kuzu, G.; Tian, Y.; Smith, P.; Kennett, M.J.; Patterson, A.D.; et al. Dietary broccoli impacts microbial community structure and attenuates chemically induced colitis in mice in an ah receptor dependent manner. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.C.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, J.M.; Merino, J.M.; Mulero-Navarro, S.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.M. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the crossroad of signalling networks with therapeutic value. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 185, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubli, S.P.; Bassi, C.; Roux, C.; Wakeham, A.; Gobl, C.; Zhou, W.; Jafari, S.M.; Snow, B.; Jones, L.; Palomero, L.; et al. AhR controls redox homeostasis and shapes the tumor microenvironment in BRCA1-associated breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3604–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furue, M.; Tsuji, G.; Mitoma, C.; Nakahara, T.; Chiba, T.; Morino-Koga, S.; Uchi, H. Gene regulation of filaggrin and other skin barrier proteins via aryl hydrocarbon receptor. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 80, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.O. Air particulate matter induced oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis: The role of Nrf2 and AhR-mediated pathways. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 270, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Sheng, B.; Han, B.; Pu, A.; Yang, K.; Li, P.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, W.; Yang, H. The AhR is involved in the regulation of LoVo cell proliferation through cell cycle-associated proteins. Cell. Biol. Int. 2016, 40, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neave, A.S.; Sarup, S.M.; Seidelin, M.; Duus, F.; Vang, O. Characterization of the N-methoxyindole-3-carbinol (NI3C)-induced cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer cell lines. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 83, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Xu, C.X.; Bu, Y.; Bottum, K.M.; Tischkau, S.A. Beta-naphthoflavone (DB06732) mediates estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell cycle arrest through AhR-dependent regulation of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duronio, R.J.; Xiong, Y. Signaling pathways that control cell proliferation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, E.F.; Jang, H.S.; Pearce, M.; Kerkvliet, N.I.; Kolluri, S.K. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is required for induction of p21cip1/waf1 expression and growth inhibition by SU5416 in hepatoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25211–25225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Milner, J.A. Targets for indole-3-carbinol in cancer prevention. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marlowe, J.L.; Puga, A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor, cell cycle regulation, toxicity, and tumorigenesis. J. Cell Biochem. 2005, 96, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M. Targeting DNA Double-strand break repair pathways to improve radiotherapy response. Genes 2019, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faust, D.; Nikolova, T.; Watjen, W.; Kaina, B.; Dietrich, C. The Brassica-derived phytochemical indolo[3,2-b]carbazole protects against oxidative DNA damage by aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, K.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Takahara, M.; Tsuji, G.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. Cynaropicrin attenuates UVB-induced oxidative stress via the AhR-Nrf2-Nqo1 pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 234, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, A.; Wincent, E.; Vikstrom Bergander, L.; Alsberg, T.; Bergman, J.; Rannug, A.; Rannug, U. Evidence for new light-independent pathways for generation of the endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist FICZ. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.A.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer: Friend and foe. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Li, D.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Perdew, G.H. β-Naphthoflavone Activation of the Ah Receptor Alleviates Irradiation-Induced Intestinal Injury in Mice. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121264
Zhou X, Li D, Xu W, Zhang H, Wang H, Perdew GH. β-Naphthoflavone Activation of the Ah Receptor Alleviates Irradiation-Induced Intestinal Injury in Mice. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(12):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121264
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaoliang, Deguan Li, Wenqing Xu, Heng Zhang, Hao Wang, and Gary H. Perdew. 2020. "β-Naphthoflavone Activation of the Ah Receptor Alleviates Irradiation-Induced Intestinal Injury in Mice" Antioxidants 9, no. 12: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121264
APA StyleZhou, X., Li, D., Xu, W., Zhang, H., Wang, H., & Perdew, G. H. (2020). β-Naphthoflavone Activation of the Ah Receptor Alleviates Irradiation-Induced Intestinal Injury in Mice. Antioxidants, 9(12), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9121264





