Diet and Mental Health: Review of the Recent Updates on Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
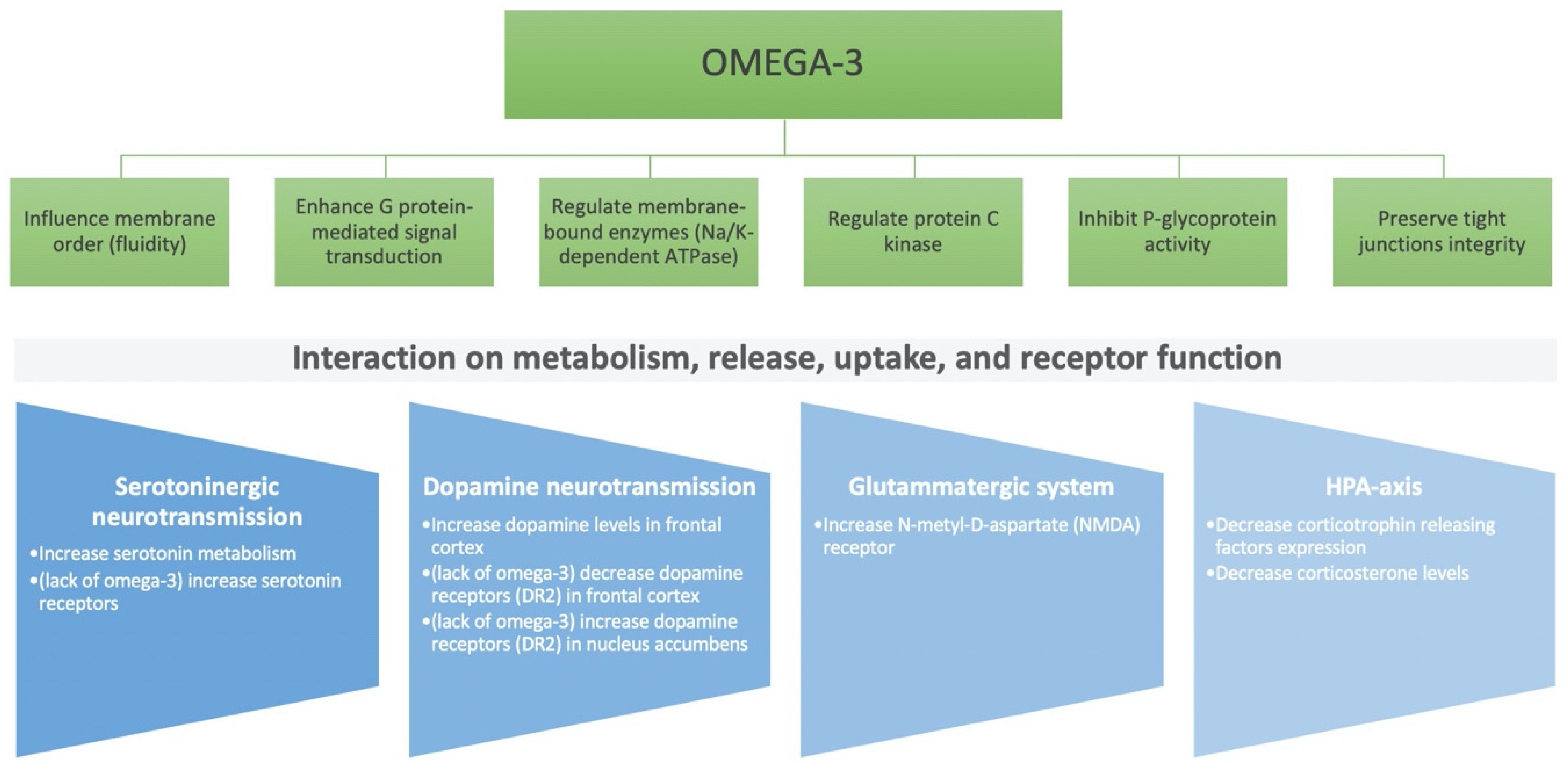
2. Role of Nutritional Components on the Brain: Micro- and Macro-Nutrients
3. Feeding Time, Circadian Rhythm, and Hormonal Homeostasis
4. Gut–Brain Axis
5. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whiteford, H.A.; Degenhardt, L.; Rehm, J.; Baxter, A.J.; Ferrari, A.J.; Erskine, H.E.; Charlson, F.J.; Norman, R.E.; Flaxman, A.D.; Johns, N.; et al. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013, 382, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.J. Depression is the leading cause of disability around the world. JAMA 2017, 317, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.M.; Currie, K.C. Depression, anxiety and their relationship with chronic diseases: A review of the epidemiology, risk and treatment evidence. Med. J. Aust. 2009, 190, S54–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.; Gonzalez, K.; Lee-Ang, L.; Young, M.C.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. Diet and sleep physiology: Public health and clinical implications. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, A.C.; Jacka, F.N. Nutritional psychiatry research: An emerging discipline and its intersection with global urbanization, environmental challenges and the evolutionary mismatch. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2014, 33, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, F.; Lartey, A.; Oenema, S.; Aguayo, V.; Stordalen, G.A.; Richardson, R.; Arvelo, M.; Afshin, A. Transforming the food system to fight non-communicable diseases. BMJ 2019, 364, l296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD Diet Collaborators. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M.; Munoz-Garcia, M.; Godos, J.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A. Dietary patterns and cognitive decline: Key features for prevention. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2428–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pot, G.K. Sleep and dietary habits in the urban environment: The role of chrono-nutrition. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassale, C.; Batty, G.D.; Baghdadli, A.; Jacka, F.; Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Kivimaki, M.; Akbaraly, T. Healthy dietary indices and risk of depressive outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 965–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, K.P. Mind-Body interface: The role of n-3 fatty acids in psychoneuroimmunology, somatic presentation, and medical illness comorbidity of depression. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. 1), 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Grosso, G.; Galvano, F.; Marventano, S.; Malaguarnera, M.; Bucolo, C.; Drago, F.; Caraci, F. Omega-3 fatty acids and depression: Scientific evidence and biological mechanisms. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 313570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartorius, T.; Ketterer, C.; Kullmann, S.; Balzer, M.; Rotermund, C.; Binder, S.; Hallschmid, M.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Somoza, V.; et al. Monounsaturated fatty acids prevent the aversive effects of obesity on locomotion, brain activity, and sleep behavior. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, J.M.; Madero, E.N.; Bott, N.T. Dietary protein and amino acid intake: Links to the maintenance of cognitive health. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Analysis, nutrition, and health benefits of tryptophan. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannai, M.; Kawai, N. New therapeutic strategy for amino acid medicine: Glycine improves the quality of sleep. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 118, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, K.; Nagasawa, M.; Tomonaga, S.; Aoki, M.; Akiduki, S.; Morishita, K.; Denbow, D.M.; Furuse, M. Orally administered L-ornithine reduces restraint stress-induced activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 506, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtman, J.; Wurtman, R. The trajectory from mood to obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R.; Carroll, J.E. Sleep disturbance, sleep duration, and inflammation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies and experimental sleep deprivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceppa, F.; Mancini, A.; Tuohy, K. Current evidence linking diet to gut microbiota and brain development and function. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvucci, E. The human-microbiome superorganism and its modulation to restore health. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H. Homocysteine, B vitamins, and cognitive impairment. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffer, A.; Prousky, J. Successful treatment of schizophrenia requires optimal daily doses of vitamin B3. Altern. Med. Rev. 2008, 13, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bourre, J.M. Effects of nutrients (in food) on the structure and function of the nervous system: Update on dietary requirements for brain. Part 1: Micronutrients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2006, 10, 377–385. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, J.; Du, J.; Pu, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, S.; Yang, T. Strategies of functional foods promote sleep in human being. Curr. Signal Transduct. Ther. 2014, 9, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Tangney, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.T. MIND diet slows cognitive decline with aging. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Tangney, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.T. MIND diet associated with reduced incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; Medina-Remon, A.; Quintana, M.; Corella, D.; Pinto, X.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Estruch, R.; Ros, E. Polyphenol-Rich foods in the Mediterranean diet are associated with better cognitive function in elderly subjects at high cardiovascular risk. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 29, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.; Halliwell, B. Do polyphenols enter the brain and does it matter? Some theoretical and practical considerations. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafaru, M.S.; Abd Karim, N.A.; Enas, M.E.; Rollin, P.; Mazzon, E.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Protective effect of glucosinolates hydrolytic products in neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs). Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, K.; Gleason, C.E.; Mares, J.A. Dietary carotenoids and cognitive function among US adults, NHANES 2011–2014. Nutr. Neurosci. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.D.; Mattson, M.P. Fasting: Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, R.N.; Buhr, E.D. Ocular photoreception for circadian rhythm entrainment in mammals. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 2016, 2, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, Y.; Acar Tek, N. Effect of circadian rhythm on metabolic processes and the regulation of energy balance. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.D.; Panda, S. Fasting, circadian rhythms, and time-restricted feeding in healthy lifespan. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelissen, G. Metabolic syndrome, adiponectin, sleep, and the circadian system. EBioMedicine 2018, 33, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, N.S.; Banks, S.; Arroyo, S.; Dinges, D.F. Effects of sleep restriction on adiponectin levels in healthy men and women. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 101, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, E.; Nothling, J.; Lombard, C.; Jewkes, R.; Peer, N.; Abrahams, N.; Seedat, S. Peripheral adiponectin levels in anxiety, mood, trauma-and stressor-related disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 260, 372–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, B.C.; Monteiro, S.; Candida, M.; Adler, N.; Paes, F.; Rocha, N.; Nardi, A.E.; Murillo-Rodriguez, E.; Machado, S. Relationship between brain-derived neurotrofic factor (Bdnf) and sleep on depression: A critical review. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2017, 13, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P. Energy intake and exercise as determinants of brain health and vulnerability to injury and disease. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 706–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, K.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Eckert, A. BDNF in sleep, insomnia, and sleep deprivation. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castren, E.; Rantamaki, T. The role of BDNF and its receptors in depression and antidepressant drug action: Reactivation of developmental plasticity. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B. The role of microbiome in insomnia, circadian disturbance and depression. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arola-Arnal, A.; Cruz-Carrion, A.; Torres-Fuentes, C.; Avila-Roman, J.; Aragones, G.; Mulero, M.; Bravo, F.I.; Muguerza, B.; Arola, L.; Suarez, M. Chrononutrition and polyphenols: Roles and diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine-Casado, R.; Domenech-Coca, C.; Del Bas, J.M.; Blade, C.; Caimari, A.; Arola, L. Cherry consumption out of season alters lipid and glucose homeostasis in normoweight and cafeteria-fed obese Fischer 344 rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 63, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibars, M.; Aragones, G.; Ardid-Ruiz, A.; Gibert-Ramos, A.; Arola-Arnal, A.; Suarez, M.; Blade, C. Seasonal consumption of polyphenol-rich fruits affects the hypothalamic leptin signaling system in a photoperiod-dependent mode. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenit, M.C.; Sanz, Y.; Codoner-Franch, P. Influence of gut microbiota on neuropsychiatric disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5486–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, R.D., Jr.; Pontefract, B.A.; Mishcon, H.R.; Black, C.A.; Sutton, S.C.; Theberge, C.R. Gut microbiome: Profound implications for diet and disease. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, F.; Rizzetto, L.; Tuohy, K.M. Gut microbiota and health: Connecting actors across the metabolic system. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, S.L.; Dash, S.R.; Jacka, F.N. The importance of diet and gut health to the treatment and prevention of mental disorders. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2016, 131, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makki, K.; Deehan, E.C.; Walter, J.; Backhed, F. The impact of dietary fiber on gut microbiota in host health and disease. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, D.; Hardy, T.; Stewart, C.; Errington, L.; Day, C.P.; Trenell, M.I.; Avery, L. Systematic review assessing the effectiveness of dietary intervention on gut microbiota in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1700–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Onge, M.P.; Zuraikat, F.M. Reciprocal roles of sleep and diet in cardiovascular health: A review of recent evidence and a potential mechanism. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2019, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S.; Clarke, G.; Berk, M.; Jacka, F.N. The gut microbiome and diet in psychiatry: Focus on depression. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2015, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiy, V.; Martin, C.R.; Mayer, E.A. The gut-brain axis and the microbiome: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuohy, K.M.; Venuti, P.; Cuva, S.; Furlanello, C.; Gasperotti, M.; Mancini, A.; Ceppa, F.; Cavalieri, D.; de Filippo, C.; Vrhovsek, U.; et al. Diet and the Gut Microbiota—How the Gut: Brain Axis Impacts on Autism; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gershon, M.D. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2013, 20, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, G.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Anxiety, depression, and the microbiome: A role for gut peptides. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The brain-gut-microbiome axis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zietek, T.; Rath, E. Inflammation meets metabolic disease: Gut feeling mediated by GLP-1. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballaz, S. The unappreciated roles of the cholecystokinin receptor CCK(1) in brain functioning. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 28, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, L.S.; Voon, V.; Leggio, L. Stress, motivation, and the gut-brain axis: A focus on the ghrelin system and alcohol use disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.H.; Lowry, C.A. Corticotropin-Releasing factor-related peptides, serotonergic systems, and emotional behavior. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; Bailey, M.T. Impact of stressor exposure on the interplay between commensal microbiota and host inflammation. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatoo, M.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Coote, J.; Du, J.; Chen, X. Involvement of corticotropin-releasing factor and receptors in immune cells in irritable bowel syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (poly)phenolics in human health: Structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, P.; Bresciani, L.; Brindani, N.; Ludwig, I.A.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Angelino, D.; Llorach, R.; Calani, L.; Brighenti, F.; Clifford, M.N.; et al. Phenyl-γ-valerolactones and phenylvaleric acids, the main colonic metabolites of flavan-3-ols: Synthesis, analysis, bioavailability, and bioactivity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 714–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelino, D.; Carregosa, D.; Domenech-Coca, C.; Savi, M.; Figueira, I.; Brindani, N.; Jang, S.; Lakshman, S.; Molokin, A.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; et al. 5-(Hydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone-sulfate, a key microbial metabolite of Flavan-3-ols, is able to reach the brain: Evidence from different in silico, In Vitro and In Vivo experimental models. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, R.; Minato, I.; La Vitola, P.; Artioli, L.; Curti, C.; Franceschi, V.; Brindani, N.; Amidani, D.; Colombo, L.; Salmona, M.; et al. Flavonoid-Derived human phenyl-gamma-valerolactone metabolites selectively detoxify amyloid-β oligomers and prevent memory impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carregosa, D.; Carecho, R.; Figueira, I.; Santos, C.N. Low-Molecular weight metabolites from polyphenols as effectors for attenuating neuroinflammation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1790–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, P.; Sagaspe, P.; Taillard, J.; Mandon, C.; Constans, J.; Pourtau, L.; Pouchieu, C.; Angelino, D.; Mena, P.; Martini, D.; et al. Acute intake of a grape and blueberry polyphenol-rich extract ameliorates cognitive performance in healthy young adults during a sustained cognitive effort. Antioxidants 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, E.; Sandhu, K.V.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. May the force be with you: The light and dark sides of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatry. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 1019–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarczyk, M.M.; Miller, M.J.; Freund, G.G. The health benefits of dietary fiber: Beyond the usual suspects of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and colon cancer. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.I.; Ghia, J.E. Gut hormones: Emerging role in immune activation and inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 161, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C. Microglia and neurodegeneration: The role of systemic inflammation. Glia 2013, 61, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, R.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Zhou, J.R. Microbiome, inflammation, epigenetic alterations, and mental diseases. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2017, 174, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-Derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-TrkB signaling in inflammation-related depression and potential therapeutic targets. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.A.; Vissel, B. Inflammation-Sleep interface in brain disease: TNF, insulin, orexin. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Giuliani, F. The role of inflammation in depression and fatigue. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S.; Chugh, G.; Asghar, M. Inflammation in anxiety. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2012, 88, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraci, F.; Spampinato, S.F.; Morgese, M.G.; Tascedda, F.; Salluzzo, M.G.; Giambirtone, M.C.; Caruso, G.; Munafo, A.; Torrisi, S.A.; Leggio, G.M.; et al. Neurobiological links between depression and AD: The role of TGF-β1 signaling as a new pharmacological target. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauche, D.; Marie, J.C. Transforming growth factor β: A master regulator of the gut microbiota and immune cell interactions. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Beguet-Crespel, F.; Marinelli, L.; Jamet, A.; Ledue, F.; Blottiere, H.M.; Lapaque, N. Butyrate produced by gut commensal bacteria activates TGF-beta1 expression through the transcription factor SP1 in human intestinal epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayefi, M.; Shafiee, M.; Kazemi-Bajestani, S.M.R.; Esmaeili, H.; Darroudi, S.; Khakpouri, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Ghaneifar, Z.; Azarpajouh, M.R.; Moohebati, M.; et al. Depression and anxiety both associate with serum level of hs-CRP: A gender-stratified analysis in a population-based study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 81, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minihane, A.M.; Vinoy, S.; Russell, W.R.; Baka, A.; Roche, H.M.; Tuohy, K.M.; Teeling, J.L.; Blaak, E.E.; Fenech, M.; Vauzour, D.; et al. Low-Grade inflammation, diet composition and health: Current research evidence and its translation. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisson-Silva, F.; Kawanishi, K.; Varki, A. Human risk of diseases associated with red meat intake: Analysis of current theories and proposed role for metabolic incorporation of a non-human sialic acid. Mol. Asp. Med. 2016, 51, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Meneguelli, T.; Viana Hinkelmann, J.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M.; Zulet, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Bressan, J. Food consumption by degree of processing and cardiometabolic risk: A systematic review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godos, J.; Currenti, W.; Angelino, D.; Mena, P.; Castellano, S.; Caraci, F.; Galvano, F.; Del Rio, D.; Ferri, R.; Grosso, G. Diet and Mental Health: Review of the Recent Updates on Molecular Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040346
Godos J, Currenti W, Angelino D, Mena P, Castellano S, Caraci F, Galvano F, Del Rio D, Ferri R, Grosso G. Diet and Mental Health: Review of the Recent Updates on Molecular Mechanisms. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(4):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040346
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodos, Justyna, Walter Currenti, Donato Angelino, Pedro Mena, Sabrina Castellano, Filippo Caraci, Fabio Galvano, Daniele Del Rio, Raffaele Ferri, and Giuseppe Grosso. 2020. "Diet and Mental Health: Review of the Recent Updates on Molecular Mechanisms" Antioxidants 9, no. 4: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040346
APA StyleGodos, J., Currenti, W., Angelino, D., Mena, P., Castellano, S., Caraci, F., Galvano, F., Del Rio, D., Ferri, R., & Grosso, G. (2020). Diet and Mental Health: Review of the Recent Updates on Molecular Mechanisms. Antioxidants, 9(4), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040346









