Protein Formulations Containing Polysorbates: Are Metal Chelators Needed at All?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Solvents and Reagents
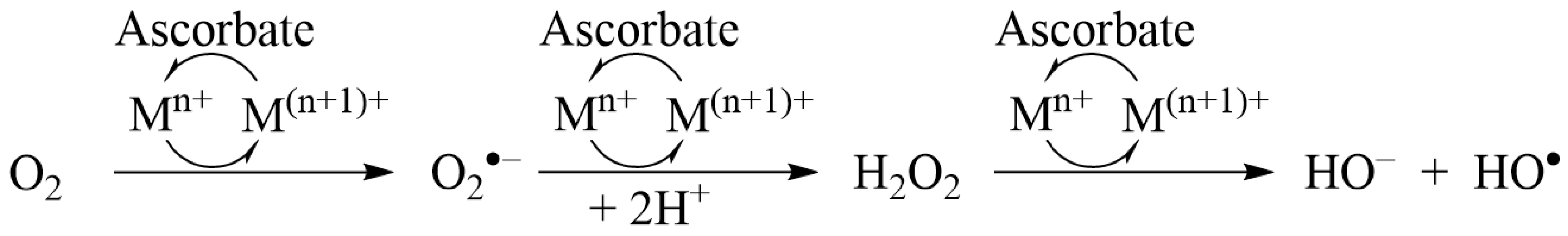
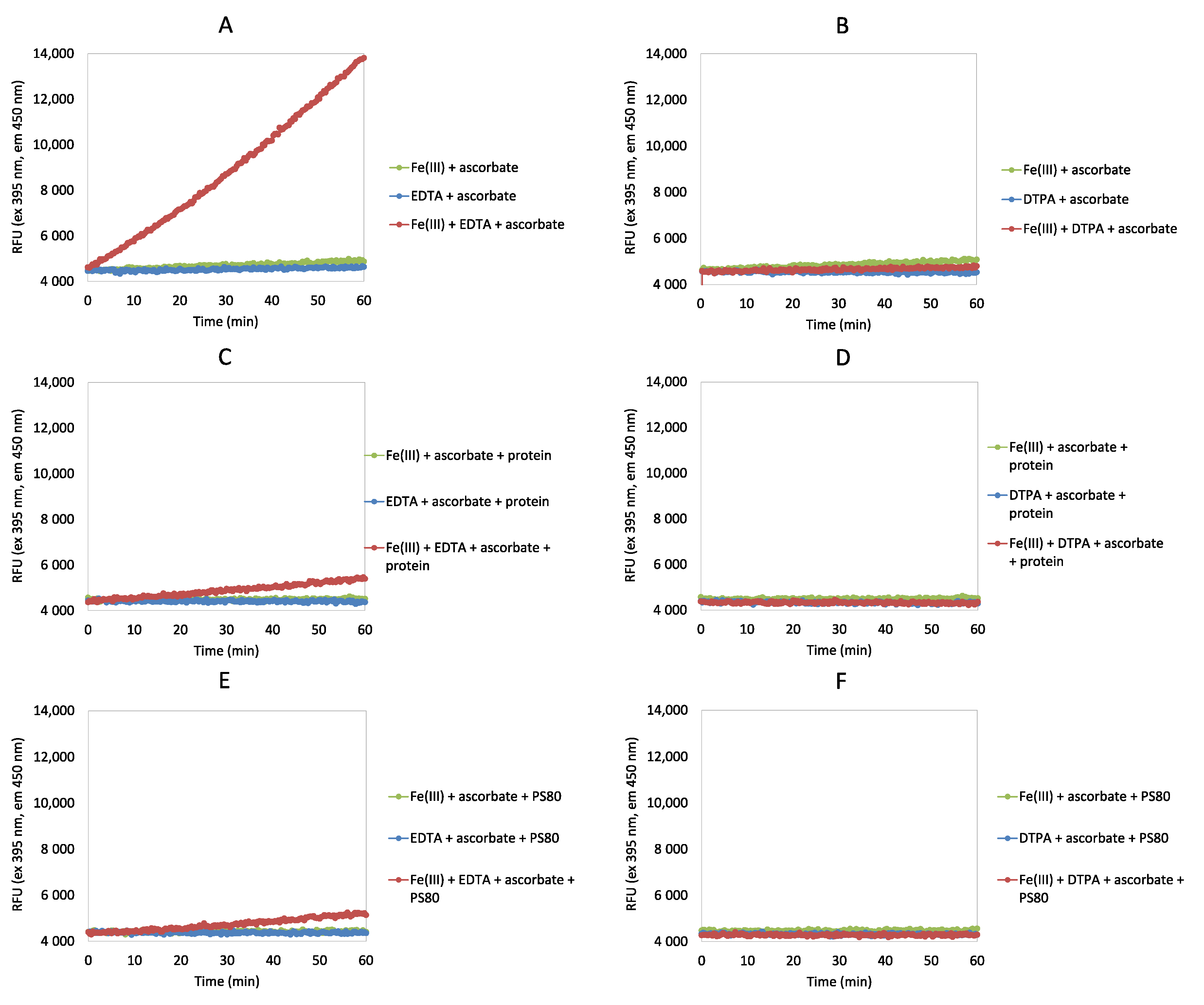
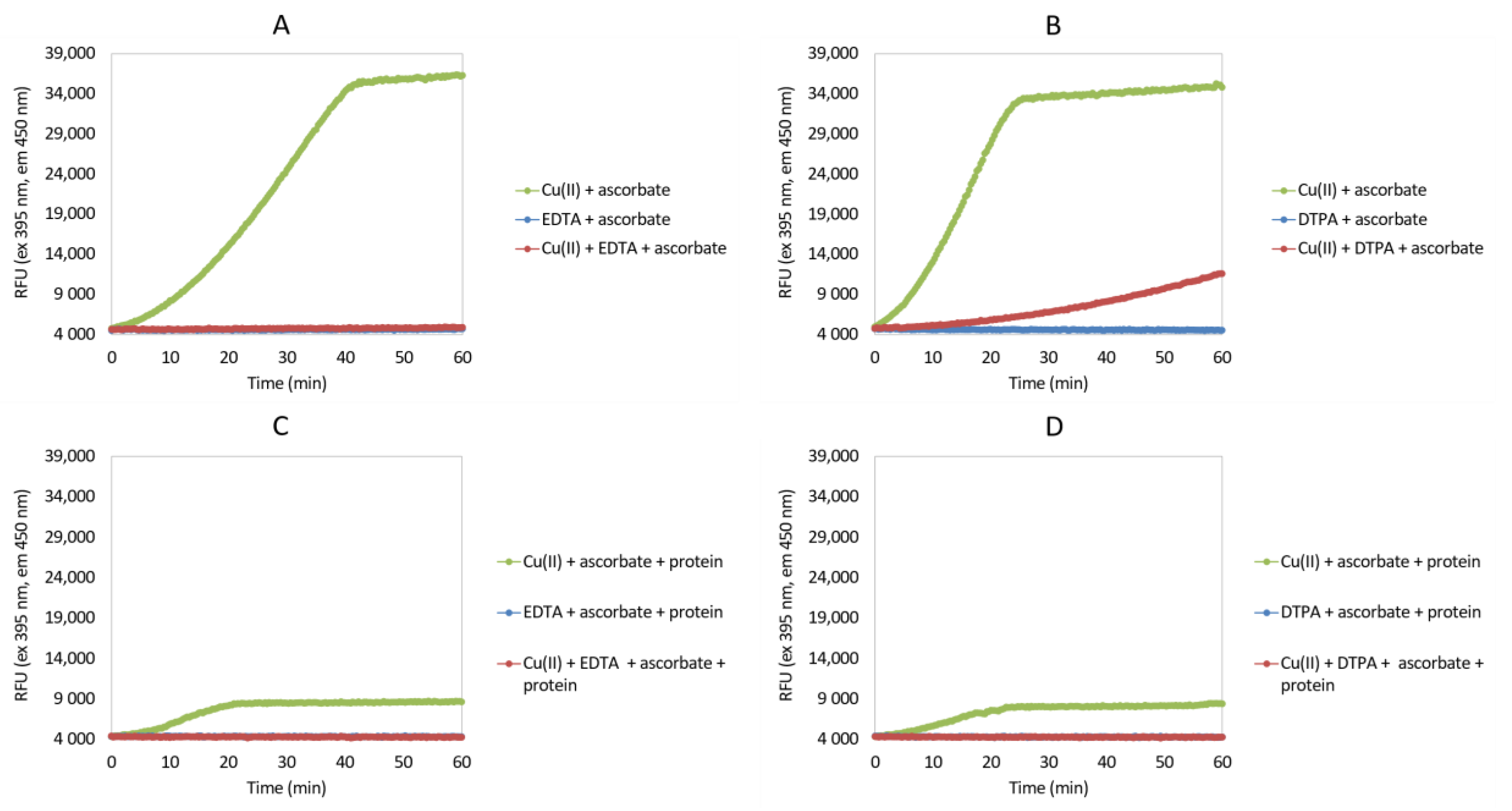
2.2. Ascorbate Redox System Assay
2.3. Peptide Mapping
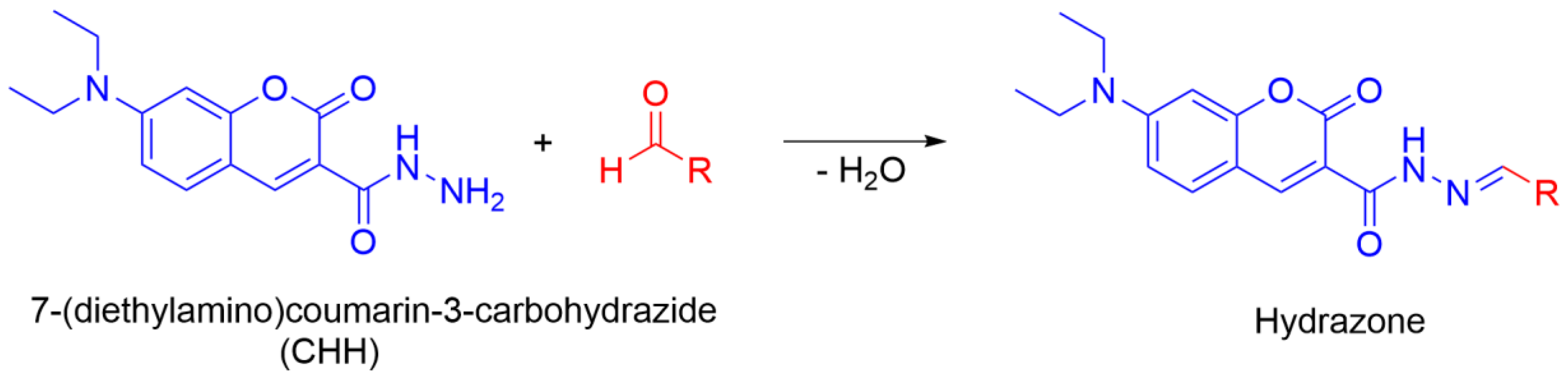
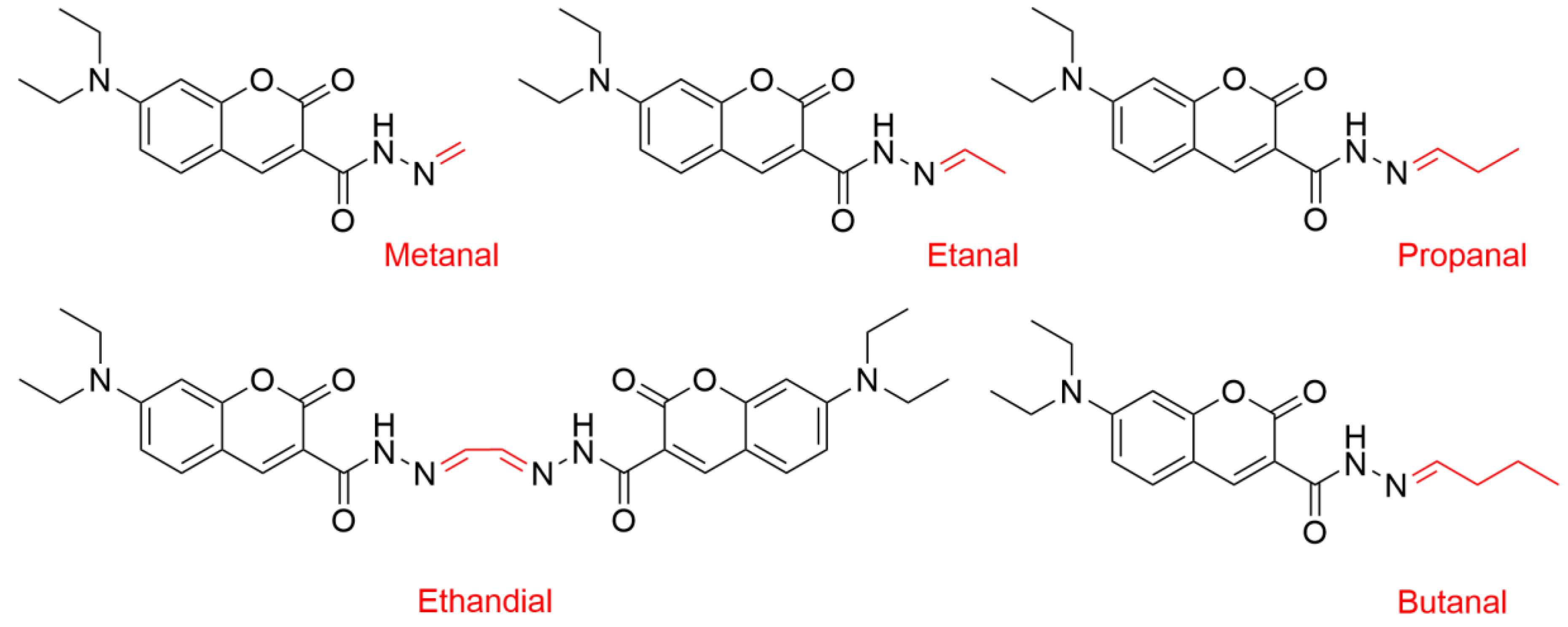
2.4. Oxidation of Polysorbates
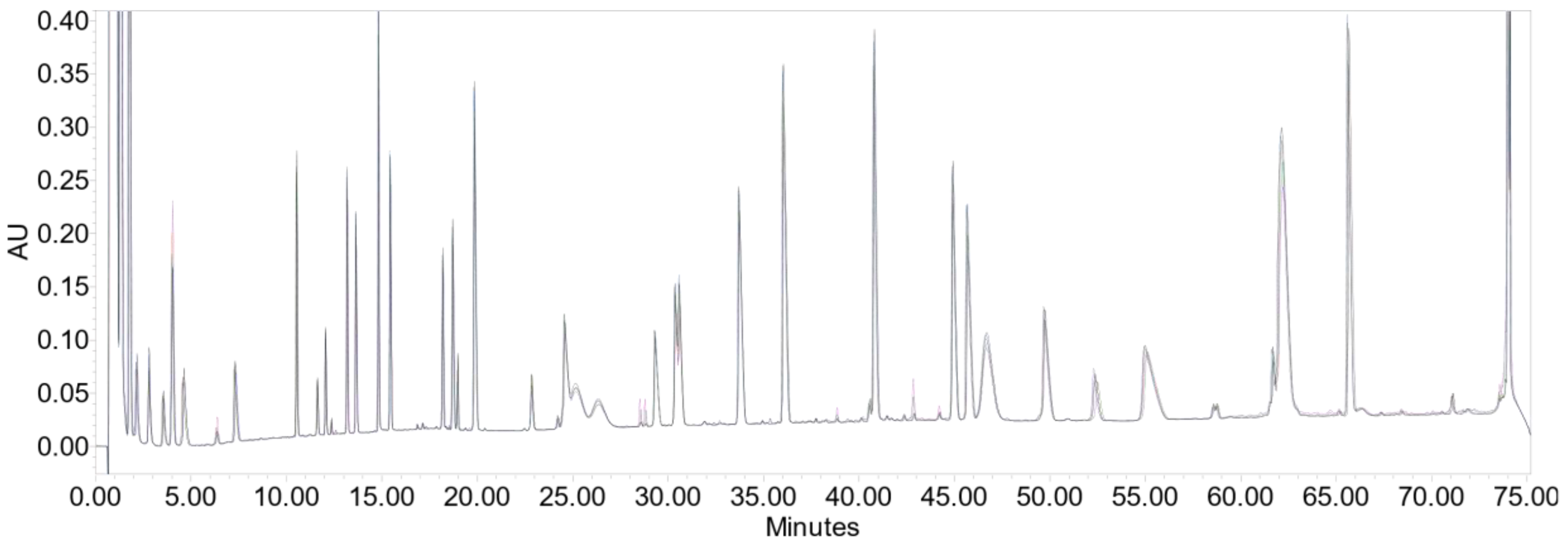
2.5. Polysorbate Composition Profile
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ascorbate Redox System Assay
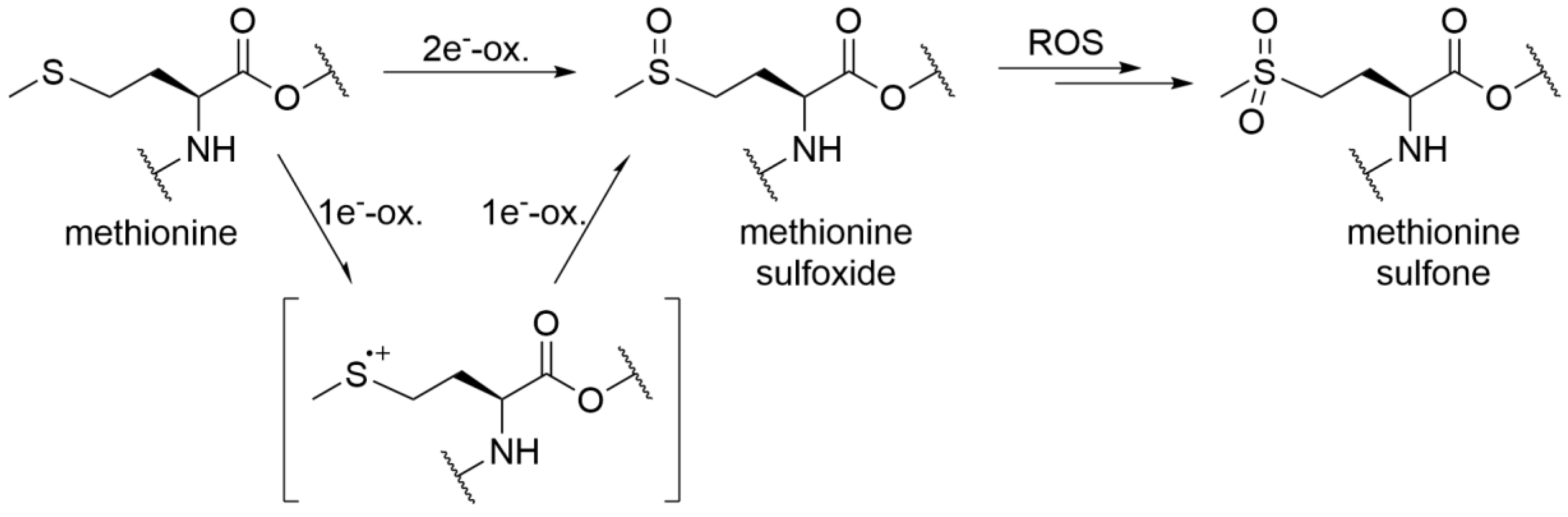
3.2. Peptide Mapping
3.3. Polysorbates Degradation: Oxidation of Polysorbates and Their Composition Profiles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torosantucci, R.; Schöneich, C.; Jiskoot, W. Oxidation of therapeutic proteins and peptides: Structural and biological consequences. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Schöneich, C.; Borchardt, R.T. Chemical instability of protein pharmaceuticals: Mechanisms of oxidation and strategies for stabilization. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 48, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovorka, S.W.; Schöneich, C. Oxidative degradation of pharmaceuticals: Theory, mechanisms and inhibition. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.; Wang, W.; John Wang, Y. Peroxide formation in polysorbate 80 and protein stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2252–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.R.; Zhang, J.; O’Dell, C.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Goldstein, J.; Liu, J.; Srivastava, A. Effect of polysorbate 80 quality on photostability of a monoclonal antibody. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.; Sorensen, K.; Wolff, S.P. Peroxide accumulation in detergents. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1994, 29, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B. Metal protein interactions. Prog. Food Nutr. Sci. 1987, 11, 363–400. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, D.J.; Frieden, E. Binding of transition metal ions by ceruloplasmin (ferroxidase). Biochemistry 1971, 10, 3880–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.M.; Wesson, L.; Eisenman, G.; Eisenberg, D. Where metal ions bind in proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernigan, R.; Raghunathan, G.; Bahar, I. Characterization of interactions and metal ion binding sites in proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1994, 4, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R. Metal ion-catalyzed oxidation of proteins: Biochemical mechanism and biological consequences. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1990, 9, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.R. Oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins by radiolysis and by metal-catalyzed reactions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1993, 62, 797–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, G.; Chevion, M. Site-specific modification of albumin by free radicals. Reaction with copper (II) and ascorbate. Biochem. J. 1986, 236, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, B.; Sturm, E.; Teagarden, D.L.; Schöneich, C.; Kolhe, P.; Lewis, L.M.; Muralidhara, B.K.; Singh, S.K. Comparative evaluation of disodium edetate and diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid as iron chelators to prevent metal-catalyzed destabilization of a therapeutic monoclonal antibody. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4239–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.A.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Y.J. Methionine, tryptophan, and histidine oxidation in a model protein, PTH: Mechanisms and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4485–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachur, A.V.; Tuttle, S.W.; Biaglow, J.E. Autoxidation of ferrous ion complexes: A method for the generation of hydroxyl radicals. Radiat. Res. 1998, 150, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biaglow, J.E.; Kachur, A.V. The generation of hydroxyl radicals in the reaction of molecular oxygen with polyphosphate complexes of ferrous ion. Radiat. Res. 1997, 148, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocha, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ohtaki, H.; Fukuda, T.; Aoyagi, T. Hydrogen peroxide-mediated degradation of protein: Different oxidation modes of copper-and iron-dependent hydroxyl radicals on the degradation of albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1997, 1337, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, J.R. Oxidation of human insulin-like growth factor I in formulation studies. 3. Factorial experiments of the effects of ferric ions, EDTA, and visible light on methionine oxidation and covalent aggregation in aqueous solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilloreau, L.; Combalbert, S.; Sournia-Saquet, A.; Mazarguil, H.; Faller, P. Redox Chemistry of Copper--Amyloid-β: The generation of hydroxyl radical in the presence of ascorbate is linked to redox-potentials and aggregation state. ChemBioChem 2007, 8, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, K.M.; Richardson, T.E.; Rutter, L.; Gonzalez, P.; Simpkins, J.W.; Green, K.N. An N-heterocyclic amine chelate capable of antioxidant capacity and amyloid disaggregation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, F.; Yan, J.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Miao, H.; Sun, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, X. New multi-target-directed small molecules against Alzheimer’s disease: A combination of resveratrol and clioquinol. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 5936–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J. Protein oxidation and peroxidation. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 805–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermeling, S.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; Schellekens, H.; Jiskoot, W. Structure-immunogenicity relationships of therapeutic proteins. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donbrow, M.; Azaz, E.; Pillersdorf, A. Autoxidation of polysorbates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1978, 67, 1676–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, B.A. Polysorbates 20 and 80 used in the formulation of protein biotherapeutics: Structure and degradation pathways. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2924–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.S.K.; Pappenberger, A.; Dauphin, I.B.; Ross, A.; Buergi, B.; Staempfli, A.; Mahler, H.-C. Degradation of polysorbates 20 and 80: Studies on thermal autoxidation and hydrolysis. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.S.K.; Kiese, S.; Fischer, S.; Pappenberger, A.; Grauschopf, U.; Mahler, H.C. The degradation of polysorbates 20 and 80 and its potential impact on the stability of biotherapeutics. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1194–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahotre, S.; Tomlinson, A.; Lin, B.; Yadav, S. Novel markers to track oxidative polysorbate degradation in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 157, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepp, V.M.; Whatley, J.L.; Muchnik, A.; Calderwood, T.S. Identification of antioxidants for prevention of peroxide-mediated oxidation of recombinant human ciliary neurotrophic factor and recombinant human nerve growth factor. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 1996, 50, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Porter, N.A. New insights regarding the autoxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borisov, O.V.; Ji, J.A.; John Wang, Y. Oxidative degradation of polysorbate surfactants studied by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, N.A.; Caldwell, S.E.; Mills, K.A. Mechanisms of free radical oxidation of unsaturated lipids. Lipids 1995, 30, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vittala, P.; Saxena, A.; Bob, M.; Kashibhatta, R.; Ashawat, P.; Ashawat, M. A sensitive LC-ESI-MS/MS method to quantify tibolone as oxime-derivative in human plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 10, 400–419. [Google Scholar]
- Milic, I.; Hoffmann, R.; Fedorova, M. Simultaneous detection of low and high molecular weight carbonylated compounds derived from lipid peroxidation by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manevich, Y.; Held, K.D.; Biaglow, J.E. Coumarin-3-carboxylic acid as a detector for hydroxyl radicals generated chemically and by gamma radiation. Radiat. Res. 1997, 148, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.N.; Lincoln, K.M.; Gonzalez, P. Antioxidant Small Molecules Aimed at Targeting Metal-Based Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disorders. U.S. Patent 8969548B2, 3 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Knez, D.; Sosič, I.; Pišlar, A.; Mitrović, A.; Jukič, M.; Kos, J.; Gobec, S. Biological evaluation of 8-hydroxyquinolines as multi-target directed ligands for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravljak, J.; Jakopin, Ž. Iron-binding and anti-Fenton properties of novel amino-acid-derived cyclic imide dioximes. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, S.W.; Cooney, C.L. Development of a peptide mapping procedure to identify and quantify methionine oxidation in recombinant human α1-antitrypsin. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 942, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Ganzler, K.; Fekete, J. Fast and sensitive determination of polysorbate 80 in solutions containing proteins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöneich, C. Methionine oxidation by reactive oxygen species: Reaction mechanisms and relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1703, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.-R.; Narhi, L.O.; Spahr, C.; Langley, K.E.; Lu, H.S. In vitro methionine oxidation of escherichia coli-derived human stem cell factor: Effects on the molecular structure, biological activity, and dimerization. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulinacci, F.; Poirier, E.; Capelle, M.A.H.; Gurny, R.; Arvinte, T. Influence of methionine oxidation on the aggregation of recombinant human growth hormone. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocijan, A.; Milošev, I.; Pihlar, B. The influence of complexing agent and proteins on the corrosion of stainless steels and their metal components. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Schöneich, C.; Singh, S.K. Biologics formulation factors affecting metal leachables from stainless steel. Aaps Pharmscitech 2011, 12, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yadav, S.; Demeule, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Mozziconacci, O.; Schӧneich, C. Degradation mechanisms of polysorbate 20 differentiated by 18O-labeling and mass spectrometry. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Dokuru, D.K.; Noestheden, M.; Park, S.S.; Kerwin, B.A.; Jona, J.; Ostovic, D.; Reid, D.L. A quantitative kinetic study of polysorbate autoxidation: The role of unsaturated fatty acid ester substituents. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, A.; Koch, W.; Jiskoot, W.; Wuchner, K.; Winter, G.; Friess, W.; Hawe, A. Trends on analytical characterization of polysorbates and their degradation products in biopharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1722–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, W.; Wuchner, K.; Corradini, E.; Berger, M.; Hawe, A. Factors influencing polysorbate sensitivity against enzymatic hydrolysis and oxidative degradation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
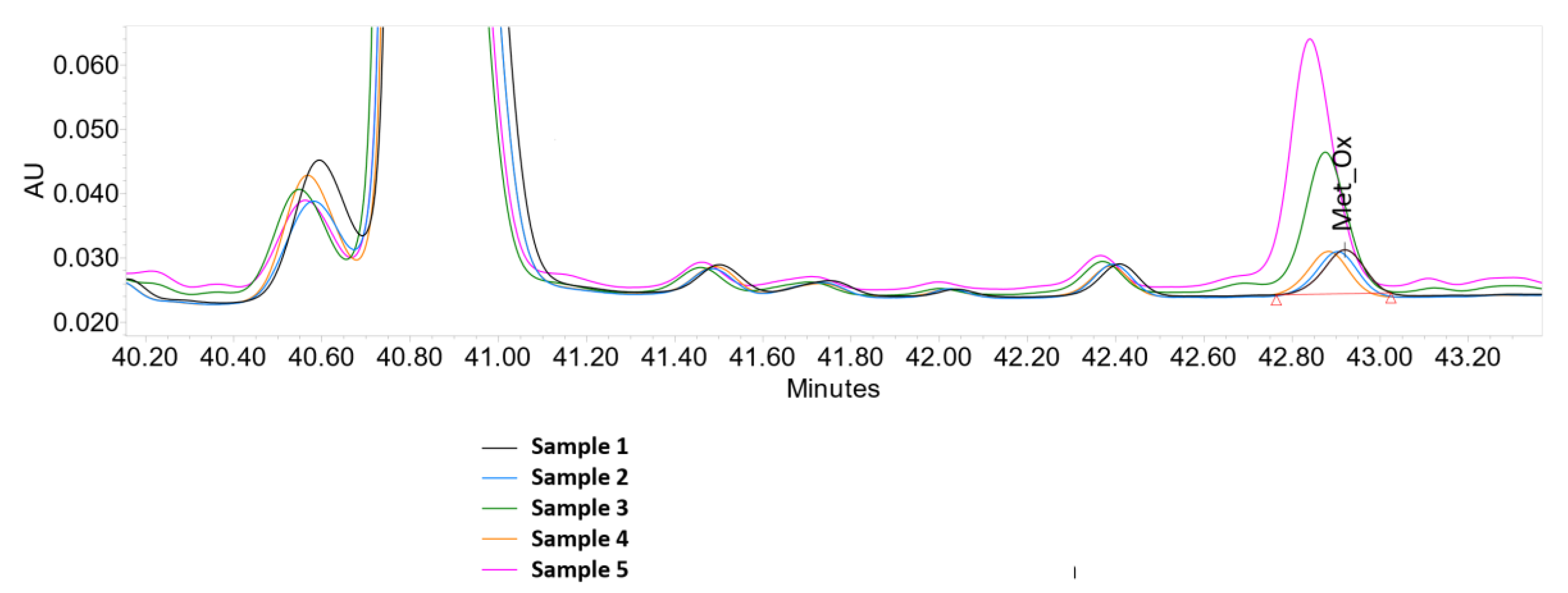
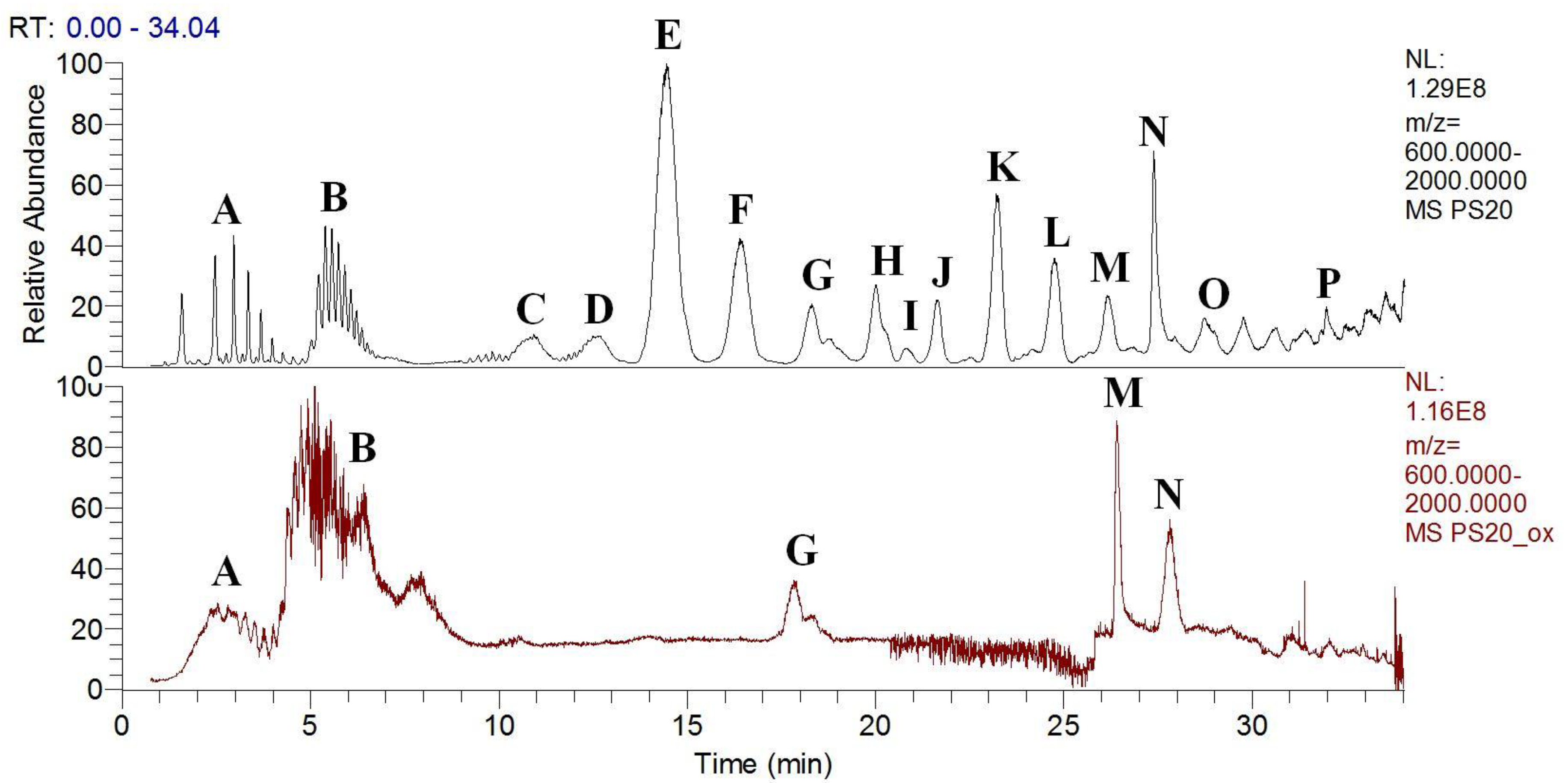
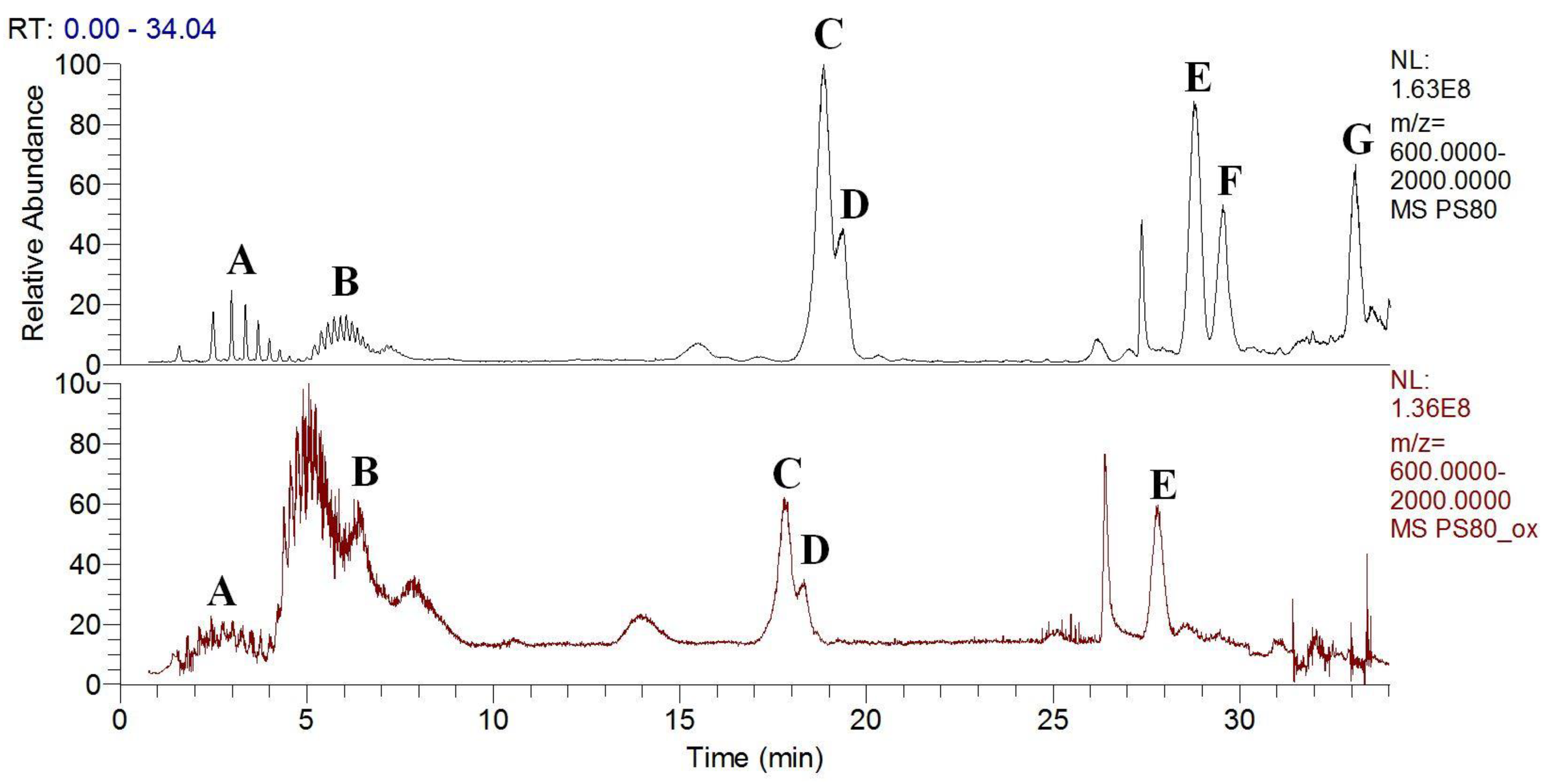
| Sample | Composition | Met_Ox |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | control sample (without additives) | 1.8 |
| 2 | Fe(III) | 1.7 |
| 3 | Fe(III) + ascorbate | 6.4 |
| 4 | Fe(III) + EDTA | 1.8 |
| 5 | Fe(III) + EDTA + ascorbate | 12.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brovč, E.V.; Pajk, S.; Šink, R.; Mravljak, J. Protein Formulations Containing Polysorbates: Are Metal Chelators Needed at All? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050441
Brovč EV, Pajk S, Šink R, Mravljak J. Protein Formulations Containing Polysorbates: Are Metal Chelators Needed at All? Antioxidants. 2020; 9(5):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050441
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrovč, Ema Valentina, Stane Pajk, Roman Šink, and Janez Mravljak. 2020. "Protein Formulations Containing Polysorbates: Are Metal Chelators Needed at All?" Antioxidants 9, no. 5: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050441
APA StyleBrovč, E. V., Pajk, S., Šink, R., & Mravljak, J. (2020). Protein Formulations Containing Polysorbates: Are Metal Chelators Needed at All? Antioxidants, 9(5), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050441






