State of the Art of Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Activity, Sources, Bioavailability, and Therapeutic Effect in Human Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Antioxidant Bioassays for Anthocyanins
2.1. DPPH (Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl) Assay
2.2. ORAC Assay (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity)
2.3. TRAP Assay (Total Peroxyl Radical Trapping Antioxidant Parameter)
2.4. FCT (Ferric Thiocyanate) Assay
2.5. FRAP (Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power) Assay
2.6. CUPRAC (Cupric Ion Reducing Antioxidant Capacity) Assay
2.7. ABTS (2,2′-Azino-bis (3-ehtylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) Diamonium Salt) Assay
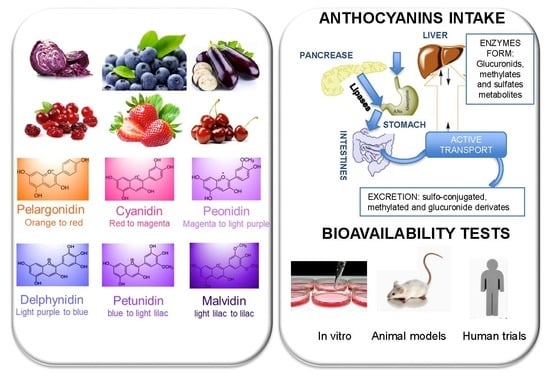
3. Classification and Natural Sources of Anthocyanins
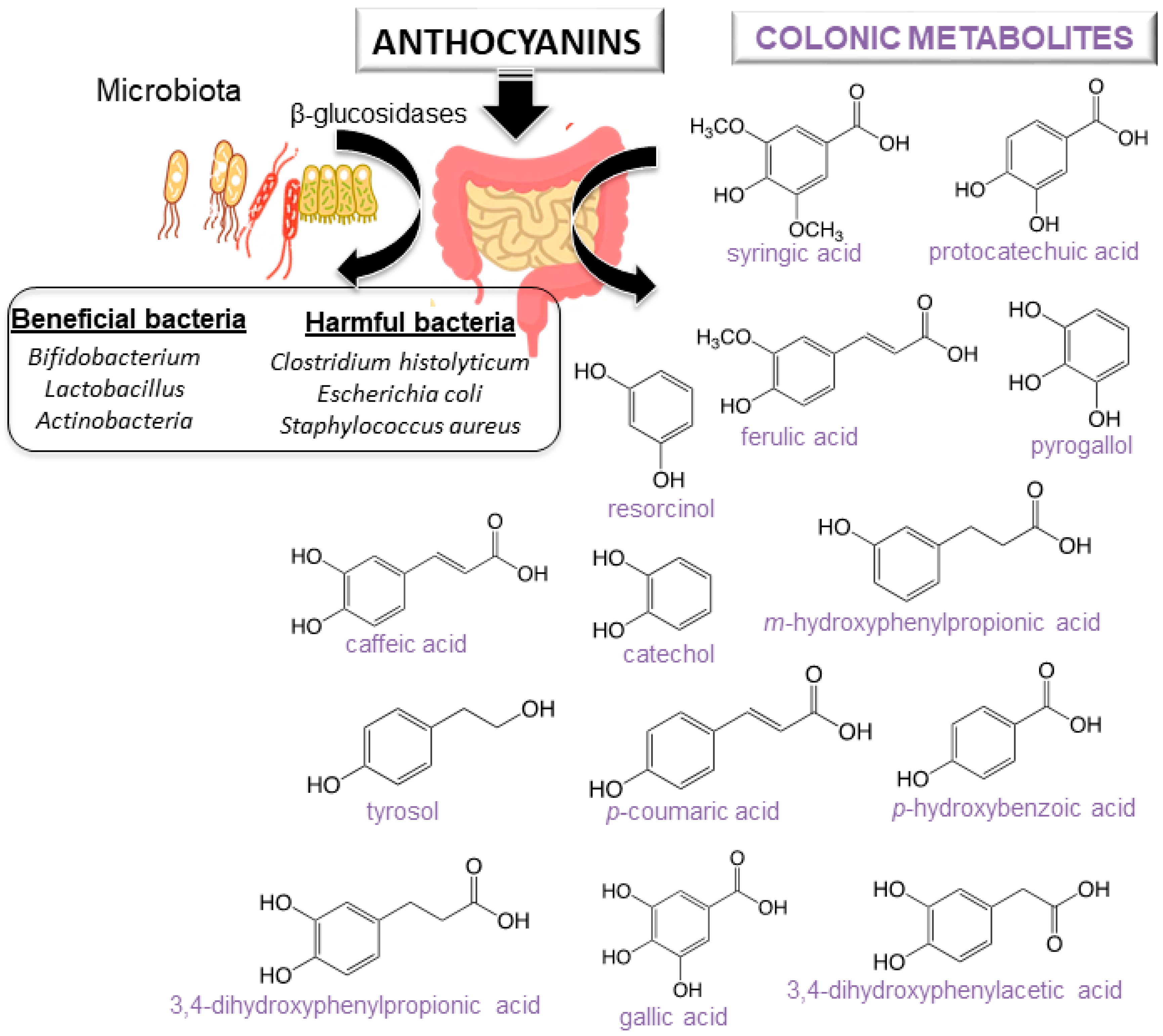
4. Bioavailability of Anthocyanins
5. Therapeutic Effects of Anthocyanins
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dangles, O.; Fenger, J.A. The Chemical Reactivity of Anthocyanins and Its Consequences in Food Science and Nutrition. Molecules 2018, 23, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, M.G. Anthocyanins: Antioxidant and/or anti-inflammatory activities. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, C.D.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Ludwig, I.A.; Clifford, M.N.; Crozier, A. Anthocyanins and flavanones are more bioavailable than previously perceived: A review of recent evidence. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lila, M.A.; Burton-Freeman, B.; Grace, M.; Kalt, W. Unraveling anthocyanin bioavailability for human health. Annu. Rev. Food Technol. 2016, 7, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J. Bioavailability of anthocyanins. Drug Metab. Rev. 2014, 46, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingua, M.S.; Fabani, M.P.; Wunderlin, D.A.; Baroni, M.V. From grape to wine: Changes in phenolic composition and its influence on antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2016, 208, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Kuskoski, E.M.; Navas, M.J.; Asuero, A.G. Antioxidant Capacity of Anthocyanin Pigments. In Flavonoids—From Biosynthesis to Human Health; Justino, J., Ed.; Science, Technology and Medicine Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; Chapter 11; pp. 205–255. [Google Scholar]
- Martín Bueno, J.; Sáez-Plaza, P.; Ramos-Escudero, F.; Jímenez, A.M.; Fett, R.; Asuero, A.G. Analysis and antioxidant capacity of anthocyanin pigments. Part II: Chemical structure, color, and intake of anthocyanins. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 42, 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, M.J.; Jiménez-Moreno, A.M.; Martín Bueno, J.; Sáez-Plaza, P.; Asuero, A.G. Analysis and antioxidant capacity of anthocyanin pigments. Part IV: Extraction of anthocyanins. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 42, 313–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamel, T.H.; Wright, A.J.; Tucker, A.J.; Pickard, M.; Rabalski, I.; Podgorski, M.; Di Ilio, N.; O’Brien, C.; Abdel-Aal, E.M. Absorption and metabolites of anthocyanins and phenolic acids after consumption of purple wheat crackers and bars by healthy adults. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 86, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante Braga, A.R.; Murador, D.C.; Mendes de Souza Mesquita, L.; Vera de Rosso, V. Bioavailability of anthocyanins: Gaps in knowledge, challenges and future research. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 68, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; Faria, A.; Calhau, C.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N. Bioavailability of anthocyanins and derivatives. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; Faria, A.; de Freitas, V.; Calhau, C.; Mateus, N. Multiple-approach studies to assess anthocyanin bioavailability. Phytochem. Rev. 2015, 14, 899–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eker, M.E.; Aaby, K.; Budic-Leto, I.; Rimac Brncˇic, S.; El, S.N.; Karakaya, S.; Simsek, S.; Manach, C.; Wiczkowski, W.; de Pascual-Teresa, S. A Review of Factors Affecting Anthocyanin Bioavailability: Possible Implications for the Inter-Individual Variability. Foods 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mülleder, U.; Murkovic, M.; Pfannhauser, W. Urinary excretion of cyanidin glycosides. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2002, 53, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bub, A.; Watzl, B.; Heeb, D.; Rechkemmer, G.; Briviba, K. Malvidin-3-glucoside bioavailability in humans after ingestion of red wine, dealcoholized red wine and red grape juice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2001, 40, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.T.; Netzel, M.E.; O’Hare, T.J. Optimization of extraction procedure and development of LC–DAD–MS methodology for anthocyanin analysis in anthocyanin-pigmented corn kernels. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda-Ovando, A.; Pacheco-Hernandez, M.L.; Paez-Hernandez, M.E.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Galan-Vidal, C.A. Chemical studies of anthocyanins: A review. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Aulis, F.; Hernandez-Vazquez, L.; Aguilar-Osorio, G.; Arrieta-Baez, D.; Navarro-Ocan, A. Extraction and Identification of Anthocyanins in Corn Cob and Corn Husk from Cacahuacintle Maize. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siti Azima, A.M.; Noriham, A.; Manshoor, N. Anthocyanin content in relation to the antioxidant activity and colour properties of Garcinia mangostana peel, Syzigium cumini and Clitoria ternatea extracts. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 2369–2375. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, N.; Kitts, D.D. Antioxidant Property of Coffee Components: Assessment of Methods that Define Mechanisms of Action. Molecules 2014, 19, 19180–19208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, E.A.; Shanab, S.M.M. Antioxidant compounds, assays of determination and mode of action. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupy, P.; Bautista-Ortin, A.-B.; Fulcrand, H.; Dangles, O. Antioxidant activity of wine pigments derived from anthocyanins: Hydrogen transfer reactions to the DPPH radical and inhibition of the heme-induced peroxidation of linoleic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5762–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, P. The use of the stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) for estimating antioxidant activity. Songklanakarin. J. Sci. Technol. 2004, 26, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Sudheeran, P.K.; Feygenberg, O.; Maurer, D.; Alkan, N. Improved Cold Tolerance of Mango Fruit with Enhanced Anthocyanin and Flavonoid Contents. Molecules 2018, 23, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Yang, K.M.; Chiang, P.Y. Roselle Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Properties and Stability to Heat and pH. Molecules 2018, 23, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, Z.; Kucuk, M.; Dogan, H. A new colorimetric DPPH scavenging activity method with no need for a spectrophotometer applied on synthetic and natural antioxidants and medicinal herbs. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlenfeldt, M.K.; Prior, R.L. Oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) and phenolic and anthocyanin concentrations in fruit and leaf tissues of highbush blueberry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido, G.G.; Beta, T. Anthocyanin Composition and Oxygen Radical Scavenging Capacity (ORAC) of Milled and Pearled Purple, Black, and Common Barley. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Zheng, W. Changes in strawberry phenolics, anthocyanins, and antioxidant capacity in response to high oxygen treatments. LWT 2007, 40, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denev, P.; Ciz, M.; Ambrozova, G.; Lojek, A.; Yanakieva, I.; Kratchanova, M. Solid-phase extraction of berries’ anthocyanins and evaluation of their antioxidative properties. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetto, M.; Vanzani, P.; Lunelli, M.; Scarpa, M.; Mattivi, F.; Rigo, A. Peroxyl radical trapping activity of anthocyanins and generation of free radical intermediates. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresch, R.R.; Kreinecker-Dresch, M.T.; Biegelmeyer, R.; Fretes-Argenta, D.; Fagundes da Rocha, R.; Ferreira-Teixeira, H.; Fonseca-Moreira, J.C.; Henriques, A.T. Potential use of secondary products of the agri-food industry for topical formulations and comparative analysis of antioxidant activity of grape leaf polyphenols. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpott, M.; Lim, C.C.; Ferguson, L.R. Dietary Protection Against Free Radicals: A Case for Multiple Testing to Establish Structure-activity Relationships for Antioxidant Potential of Anthocyanic Plant Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1081–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.S.; Chien, P.J. Antioxidant activity, anthocyanins, and phenolics of rabbiteye blueberry (Vaccinium ashei) fluid products as affected by fermentation. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgen, M.; Scheerens, J.C.; Neil Reese, R.; Miller, R.A. Total phenolic, anthocyanin contents and antioxidant capacity of selected elderberry (Sambucus canadensis L.) accessions. Pharm. Mag. 2010, 6, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.J.; Intosh, J.M.; Pearce, P.; Camden, B.; Jordan, B.R. Anthocyanin and antioxidant capacity in Roselle (Hibiscus Sabdariffa L.) extract. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelidis, G.E.; Vasilakakis, M.; Manganaris, G.A.; Diamantidis, G. Antioxidant capacity, phenol, anthocyanin and ascorbic acid contents in raspberries, blackberries, red currants, gooseberries and Cornelian cherries. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Deng, Z.; Zhu, H.; Hu, C.; Liu, R.; Young, J.C.; Tsao, R. Highly pigmented vegetables: Anthocyanin compositions and their role in antioxidant activities. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.K.; Shibamoto, T. Antioxidant Assays for Plant and Food Components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Ma, X. Composition and antioxidant activity of anthocyanins isolated from Yunnan edible rose (An ning). Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2013, 2, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frond, A.D.; Iuhas, C.I.; Stirbu, I.; Leopold, L.; Socaci, S.; Andreea, S.; Ayvaz, H.; Andreea, S.; Mihai, S.; Diaconeasa, Z.; et al. Phytochemical Characterization of Five Edible Purple-Reddish Vegetables: Anthocyanins, Flavonoids, and Phenolic Acid Derivatives. Molecules 2019, 24, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasko, P.; Barton, H.; Zagrodzki, P.; Gorinstein, S.; Fołta, M.; Zachwieja, Z. Anthocyanins, total polyphenols and antioxidant activity in amaranth andquinoa seeds and sprouts during their growth. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaño, D.; Fernández-Pachón, M.S.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.C. The Antioxidant Activity of Wines Determined by the ABTS (+) Method: Influence of Sample Dilution and Time. Talanta 2004, 64, 501–509. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.P.; Xu, J.G. Profiles of carotenoids, anthocyanins, phenolics, and antioxidant activity of selected color waxy corn grains during maturation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, C.U.; Toklucu, A.K. Effect of UV-C light on anthocyanin content and other quality parameters of pomegranate juice. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunea, A.; Rugina, D.O.; Pintea, A.M.; Conta, Z.; Bunea, C.I.; Socaciu, C. Comparative Polyphenolic Content and Antioxidant Activities of Some Wild and Cultivated Blueberries from Romania. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobo. 2011, 39, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Khalil, M.I.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Gan, S.H. Advances in the analytical methods for determining the antioxidant properties of honey: A review. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 9, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenhardt, A.; Knapp, H.; Winterhalter, P. Separation and Purification of Anthocyanins by High-Speed Countercurrent Chromatography and Screening for Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinskiene, M.; Jasutiene, I.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Viskelis, P. HPLC Determination of the Composition and Stability of Blackcurrant Anthocyanins. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2005, 43, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.R.; Wub, Q.; Simon, J.E. Recent Advances in Anthocyanin Analysis and Characterization. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2008, 4, 75–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorati, R.; Valgimigli, L. Methods to Measure the Antioxidant Activity of Phytochemicals and Plant Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3324–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix, R.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Félix, C.; Novais, S.C.; Lemos, M.F.L. Evaluating the in Vitro Potential of Natural Extracts to Protect Lipids from Oxidative Damage. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matera, R.; Gabbanini, S.; Berretti, S.; Amorati, R.; De Nicola, G.R.; Iori, R.; Valgimigli, L. Acylated anthocyanins from sprouts of Raphanus sativus cv. Sango: Isolation, structure elucidation and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Ohshima, K.; Norinobu, S.; Choi, S.W.; Kawakishi, S.; Osawa, T. Antioxidative Activity of the Anthocyanin Pigments Cyanidin 3-o-β-D-Glucoside and Cyanidin. J. Agri. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2407–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Guidance for the scientific requirements for health claims related to antioxidants, oxidative damage and cardiovascular health (Revision 1). EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5136. [Google Scholar]
- Prior, R.L.; Go, L.; Wu, X.; Jacob, R.A.; Sotoudeh, G.; Kader, A.A.; Cook, R.A. Plasma antioxidant capacity changes following a meal as a measure of the ability of a food to alter in vivo antioxidant status. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comert, E.D.; Mogol, B.A.; Gokmen, V. Relationship between color and antioxidant capacity of fruits and vegetables. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakuradze, T.; Tausend, A.; Galan, J.; Groh, I.A.M.; Berry, D.; Tur, J.A.; Marko, D.; Richling, E. Antioxidative activity and health benefits of anthocyanin-rich fruit juice in healthy volunteers. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.E.; Lim, S.M.; Azlan, A. Evidence-based therapeutic effects of anthocyanins from foods. Pak. J. Nutr. 2019, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, G. The role of polyphenols in modern nutrition. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyasut, C.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Pengkumsri, N.; Sirilun, S.; Peerajan, S.; Chaiyasut, K.; Kesika, P. Anthocyanin profile and its antioxidant activity of widely used fruits, vegetables, and flowers in Thailand Asian. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, K.; Sakakibara, H.; Iwata, R.; Ishii, T.; Sato, T.; Goda, T.; Shimoi, K.; Kumazawa, S. Anthocyanin Composition and Antioxidant Activity of the Crowberry (Empetrum nigrum) and Other Berries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4457–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zykin, P.A.; Andreeva, E.A.; Lykholay, A.N.; Tsvetkova, N.V.; Voylokov, A.V. Anthocyanin Composition and Content in Rye Plants with Different Grain Color. Molecules 2018, 23, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Morais, J.S.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Dantas, A.M.; Silva, B.S.; Lima, M.S.; Borges, G.C.; Magnani, M. Antioxidant activity and bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds in white, red, blue, purple, yellow and orange edible flowers through a simulated intestinal barrier. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.E.; Azlan, A.; Tang, S.T.; Lim, S.M. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: Colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1361779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Yamagami, A. Antioxidative activity of monoacylated anthocyanins isolated from Muscat Bailey A grape. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, F.C.; Stintzing, A.S.; Carle, R.; Frei, B.; Wrolstad, R.E. Color and antioxidant properties of cyanidin-based anthocyanin pigments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6172–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T.; Shiga, K.; Ohshima, K.; Kawakishi, S.; Osawa, T. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation and the active oxygen radical scavenging effect of anthocyanin pigments isolated from Phaseolus vulgaris L. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 52, 1033–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.; Kelly, M.F. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by anthocyanins, anthocyanidins and their phenolic degradation products. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidot, T.; Harel, S.; Akiri, B.; Granit, R.; Kanner, J. pH-dependent forms of red wine anthocyanins as antioxidants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muselík, J.; García-Alonso, M.; Martín-López, M.P.; Žemlička, M.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C. Measurement of antioxidant activity of wine catechins, procyanidins, anthocyanins and pyranoanthocyanins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.K.; Joo, K.S.; Rho, S.J.; Kim, Y.R. pH-dependent antioxidant stability of black rice anthocyanin complexed with cycloamylose. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Dong, X.; Zhou, W. Combined effect of pH and high temperature on the stability and antioxidant capacity of two anthocyanins in aqueous solution. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Raychaudhuri, U. Determination of pH-dependent antioxidant activity of palm (Borassus flabellifer) polyphenol compounds by photoluminol and DPPH methods: A comparison of redox reaction sensitivity. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Março, P.H.; Poppi, R.J.; Scarminio, I.S.; Tauler, R. Investigation of the pH effect and UV radiation on kinetic degradation of anthocyanin mixtures extracted from Hibiscus acetosella. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1020–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Manach, C.; Williamson, G.; Morand, C.; Scalbert, A.; Remesy, C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felgines, C.; Talavéra, S.; Texier, O.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Lamaison, J.-L.; Remesy, C. Blackberry anthocyanins are mainly recovered from urine as methylated and glucuronidated conjugates in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7721–7727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamonti, S.; Vanzo, A.; Vrhovsek, U.; Terdoslavich, M.; Cocolo, A.; Decorti, G.; Mattivi, F. Hepatic uptake of grape anthocyanins and the role of bilitranslocase. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Ramírez, B.A.; Catalanń, U.; Fernanńdez-Castillejo, S.; Rubió, L.; Maciá, A.; Sola, R. Anthocyanin tissue bioavailability in animals: Possible implications for human health. A systematic review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11531–11543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucioli, S. Anthocyanins: Mechanism of action and therapeutic efficacy. In Medicinal Plants as Antioxidant Agents: Understanding Their Mechanism of Action and Therapeutic Efficacy; Capasso, A., Ed.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2012; pp. 27–57. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.A.D.; George, T.G.M.; Lovegrove, J.A.A. Randomised trial to investigate the effects of acute consumption of a blackcurrant juice drink on markers of vascular reactivity and bioavailability of anthocyanins in human subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cao, G.; Prior, R.L. Absorption and metabolism of anthocyanins in elderly women after consumption of elderberry or blueberry. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, G.; Clifford, M.N. Colonic metabolites of berry polyphenols: The missing link to biological activity? Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104 (Suppl. S3), S48–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, M.; Müller-Ehl, L.; Passon, M.; Schieber, A. Development and validation of methods for the determination of anthocyanins in physiological fluids via UHPLC-MSn. Molecules 2020, 25, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, I.A.; Mena, P.; Calani, L.; Borges, G.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Bresciani, L.; Del Rio, D.; Lean, M.E.J.; Crozier, A. New insights into the bioavailability of red raspberry anthocyanins and ellagitannins. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrars, R.M.; Cassidy, A.; Curtis, P.; Kay, C.D. Phenolic metabolites of anthocyanins following a dietary intervention study in post-menopausal women. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrars, R.M.; Czank, C.; Saha, S.; Needs, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Raheem, K.S.; Botting, N.P.; Kroon, P.A.; Kay, C.D. Methods for isolating, identifying, and quantifying anthocyanin metabolites in clinical samples. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10052–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, T.; Mursu, J.; Heinonen, M.; Nurmi, A.; Hiltunen, R.; Voutilainen, S. Metabolism of berry anthocyanins to phenolic acids in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2274–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czank, C.; Cassidy, A.; Zhang, Q.; Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T.; Kroon, P.A.; Botting, N.P.; Kay, C.D. Human metabolism and elimination of the anthocyanin, cyanidin-3-glucoside: A 13C-tracer study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, J.A. Anthocyanin Bioavailability: Past Progress and Current Challenges. In Emerging Trends in Dietary Components for Preventing and Combating Disease; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Chapter 32; pp. 559–568. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.; Moon, J.K.; Hur, S.J.; Lee, J. Structural changes in mulberry (Morus Microphylla. Buckl) and chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) anthocyanins during simulated in vitro human digestion. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowd, V.; Karim, N.; Xie, L.; Shishir, M.R.I.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W. In vitro study of bioaccessibility, antioxidant, and α-glucosidase inhibitory effect of pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside after interacting with beta-lactoglobulin and chitosan/pectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowd, V.; Bao, T.; Chen, W. Antioxidant potential and phenolic profile of blackberry anthocyanin extract followed by human gut microbiota fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xiec, M.; Yanga, F.; Liu, J. Antioxidant activity of high purity blueberry anthocyanins and the effects on human intestinal microbiota. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 628101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, H.; He, S.; Lou, Q.; Yu, M.; Tang, M.; Tu, L. Metabolism and prebiotics activity of anthocyanins from black rice (Oryza sativa L.) in vitro. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 0195754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, M.; Oruna-Concha, M.J.; Kolida, S.; Walton, G.E.; Kallithraka, S.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Gibson, G.R.; de Pascual-Teresa, S. Metabolism of anthocyanins by human gut microflora and their influence on gut bacterial growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3882–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boto-Ordóñez, M.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Tulipani, S.; Tinahones, F.J.; Andres-Lacueva, C. High levels of Bifidobacteria are associated with increased levels of anthocyanin microbial metabolites: A randomized clinical trial. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Lage, N.N.; Mertens-Talcott, S.; Talcott, S.; Chew, B.; Dowd, S.E.; Kawas, J.R.; Noratto, G.D. Effect of dark sweet cherry powder consumption on the gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and biomarkers of gut health in obese db/db mice. Peer J. 2018, 2018, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, A.; Li, R.W.; Klimis-Zacas, D.; Kristo, A.S.; Tadepalli, S.; Krauss, E.; Young, R.; Wu, V.C.H. Lowbush wild blueberries have the potential to modify gut microbiota and xenobiotic metabolism in the rat colon. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 67497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, G.; Ruiz del Castillo, M.L.; Costabile, A.; Klee, A.; Bigetti Guergoletto, K.; Gibson, G.R. In vitro fermentation of anthocyanins encapsulated with cyclodextrins: Release, metabolism and influence on gut microbiota growth. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 16, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guergoletto, K.B.; Costabile, A.; Flores, G.; Garcia, S.; Gibson, G.R. In vitro fermentation of juçara pulp (Euterpe edulis) by human colonic microbiota. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Han, Y.; Tao, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, G.; Show, P.L.; Lee, S.Y. In vitro gastrointestinal digestion and fecal fermentation reveal the effect of different encapsulation materials on the release, degradation and modulation of gut microbiota of blueberry anthocyanin extract. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, N.; Khoshnoudi-Nia, S.; Jafari, S.M. Nano/microencapsulation of anthocyanins; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, B.; Gul, K.; Wani, A.A.; Singh, P. Health benefits of anthocyanins and their encapsulation for potential use in food systems: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2223–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, S.A.; Jafari, S.M.; Ghorbani, M.; Assadpoor, E. Spray-drying microencapsulation of anthocyanins by natural biopolymers: A review. Dry Technol. 2014, 32, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, P.; Fredes, C. The encapsulation of anthocyanins from berry-type fruits. Trends in foods. Molecules 2015, 20, 5875–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, R.N.; Santos, D.T.; Meireles, M.A.A. Non-thermal stabilization mechanisms of anthocyanins in model and food systems—An overview. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Bhandari, B. Encapsulation of polyphenols—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Rocha, M.; Santos, L.; Brás, J.; Oliveira, J.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Blackberry anthocyanins: β-Cyclodextrin fortification for thermal and gastro- intestinal stabilization. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, W.B. Microencapsulation of anthocyanins through two-step emulsification and release characteristics during in vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascual-Teresa, S.; Sanchez-Ballesta, M.T. Anthocyanins: From plant to health. Phytochem. Rev. 2008, 7, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N. Anthocyanins—Nature, occurrence and dietary sources. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, C.Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Park, K.H. Ginkgo biloba extract and bilberry anthocyanins improve visual function in patients with normal tension glaucoma. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Kaleem, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Shafiq, H. Therapeutic potential of flavonoids and their mechanism of action against microbial and viral infections—A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, S.; Takahashi, N.; Sasaki, M.; Takahashi, N.; Ozawa, Y. Vision preservation during retinal inflammation by anthocyanin- rich bilberry extract: Cellular and molecular mechanism. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Hong, Y.J.; Choe, C.M.; You, T.W.; Seong, G.J. Purified high-dose anthocyanoside oligomer administration improves nocturnal vision and clinical symptoms in myopia subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 93, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiraphatthanavong, P.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Wipawee, T.M.; Wannanon, P.; Terdthai, T.U.; Suriharn, B.; Lertrat, K. Preventive effect of Zea mays L. (purple waxy corn) on experimental diabetic cataract. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 507435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.W.; Chang, D.J.; Joo, C.K. Antiapoptotic effects of anthocyanin from the seed coat of black soybean against oxidative damage of human lens epithelial cell induced by H2O2. Curr. Eye Res. 2014, 39, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.S.; Jeong, E.; Jung, S.W.; Ha, T.J.; Kang, S.; Sim, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Chun, M.H.; Kim, I.B. Anthocyanins from the seed coat of black soybean reduce retinal degeneration induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 97, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohguro, H.; Ohguro, I.; Katai, M.; Tanaka, S. Two-year randomized, placebo-controlled study of black currant anthocyanins on visual field in glaucoma. Ophthalmologica 2012, 228, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Reheman, A.; Jin, W.; Li, C.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Y.; Freedman, J.J.; Ling, W.; Ni, H. Anthocyanins inhibit platelet activation and attenuate thrombus growth in both human and murine thrombosis models. Blood 2010, 116, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Xia, M.; Ma, J.; Hao, Y.; Liu, J.; Mou, H.; Cao, L.; Ling, W. Anthocyanin supplementation improves serum LDL-and HDL-cholesterol concentrations associated with the inhibition of cholesteryl ester transfer protein in dyslipidemic subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, A.; Bertoia, M.; Chiuve, S.; Flint, A.; Forman, J.; Rimm, E.B. Habitual intake of anthocyanins and flavanones and risk of cardiovascular disease in men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.R.; Gochenaur, K. Direct vasoactive and vasoprotective properties of anthocyanin-rich extracts. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toufektsian, M.C.; De Lorgeril, M.; Nagy, N.; Salen, P.; Donati, M.B.; Giordano, L.; Mock, H.-P.; Peterek, S.; Matros, A.; Petroni., K.; et al. Chronic dietary intake of plant-derived anthocyanins protects the rat heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Tulipani, S.; Casoli, T.; di Stefano, G. One month strawberry-rich anthocyanin supplementation ameliorates cardiovascular risk, oxidative stress markers and platelet activation in humans. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ahn, I.S.; Kim, S.O.; Kong, C.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Do, M.S.; Park, K.Y. Anti-obesity and hypolipidemic effects of black soybean anthocyanins. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Yu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Song, H.; Gao, Z.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X. Honeysuckle anthocyanin supplementation prevents diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, A.; Jankowska, B.; Niedworok, J. The effects of anthocyanin dye from grapes on experimental diabetes. Folia Med. Cracov. 2000, 41, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaprakasam, B.; Vareed, S.K.; Olson, L.K.; Nair, M.G. Insulin secretion by bioactive anthocyanins and anthocyanidins present in fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T.; Ueno, Y.; Aoki, H.; Koda, T.; Horio, F.; Takahashi, N.; Kawada, T.; Osawa, T. Anthocyanin enhances adipocytokine secretion and adipocyte-specific gene expression in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T.; Horio, F.; Uchida, K.; Aoki, H.; Osawa, T. Dietary cyanidin 3- O-β-D-glucoside-rich purple corn color prevents obesity and ameliorates hyperglycemia in mice. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, M.; Inoue, S.; Horio, F.; Tsuda, T. Dietary anthocyanin-rich bilberry extract ameliorates hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetic mice. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.; Xia, M. Purified anthocyanin supplementation reduces dyslipidemia, enhances antioxidant capacity, and prevents insulin resistance in diabetic patients. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.K.; Lim, S.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yeo, K.M.; Kang, Y.-H. Anthocyanin-rich purple corn extract inhibit diabetes-associated glomerular angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 79823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Johnson, M.H.; Lila, M.A.; Yousef, G.; de Mejia, E.G. Berry and citrus phenolic compounds inhibit dipeptidyl peptidase IV: Implications in diabetes management. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 479505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.S.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Chung, S.; Shin, S.J.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, H.W.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, C.W.; et al. Anthocyanin-rich Seoritae extract ameliorates renal lipotoxicity via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetic mice. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Xia, M. Anthocyanin increases adiponectin secretion and protects against diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E975–E988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojer, E.; Mattivi, F.; Johnson, D.; Stockley, C.S. The case for anthocyanin consumption to promote human health: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 483–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genskowsky, E.; Puente, L.A.; Perez-Alvarez, J.A.; Fernández-López, J.; Muñoz, L.A.; Viuda-Martos, M. Determination of polyphenolic profile, antioxidant activity and antibacterial properties of maqui [Aristotelia chilensis (Molina) Stuntz] a Chilean blackberry. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2016, 96, 4235–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Caillet, S.; Doyon, G.; Ng, K. Antimicrobial effect of cranberry juice and extracts. Food Cont. 2011, 22, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puupponen-Pimiä, R.; Nohynek, L.; Meier, C.; Kähkönen, M.; Heinonen, M.; Hopia, A.; Oksman-Caldentey, K.M. Antimicrobial properties of phenolic compounds from berries. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Hecht, S.S.; Carmella, S.G.; Yu, N.; Larue, B.; Henry, C.; McIntyre, C.; Rocha, C.; Lechner, J.F.; Stoner, G.D. Anthocyanins in black raspberries prevent esophageal tumors in rats. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, A.; Pestana, D.; Teixeira, D.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N.; Calhau, C. Blueberry anthocyanins and pyruvic acid adducts: Anticancer properties in breast cancer cell lines. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.; Bin, Y.; Xiaoping, Y.; Long, Y.; Chunye, C.; Mantian, M.; Wenhua, L. Anticancer activities of an anthocyanin-rich extract from black rice against breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, J.; Luo, L.P.; Han, B.; Li, F.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Chen, W.; Yu, X.P. Black rice anthocyanins suppress metastasis of breast cancer cells by targeting RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 414250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, M.; Zhao, C.; Schoene, N.; Guisti, M.M.; Moyer, M.P.; Magnuson, B.A. Anthocyanin-rich extract from Aronia meloncarpa E. induces a cell cycle block in colon cancer but not normal colonic cells. Nutr. Cancer 2003, 46, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, G.; Malik, M.; Zhao, C.; He, J.; Kwon, Y.; Giusti, M.M.; Magnuson, B.A. Anthocyanin-rich extracts inhibit multiple biomarkers of colon cancer in rats. Nutr. Cancer 2006, 54, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Xu, J.; Kim, J.; Chen, T.Y.; Su, X.; Standard, J.; Carey, E.; Griffin, J.; Herndon, B.; Katz, B.; et al. Role of anthocyanin-enriched purple-fleshed sweet potato p40 in colorectal cancer prevention. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1908–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Ha, U.S.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, B.I.; Han, D.S.; Yuk, S.M.; Kim, S.W. Anthocyanin extracted from black soybean reduces prostate weight and promotes apoptosis in the prostatic hyperplasia-induced rat model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12686–12691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.J.; Yun, J.W.; Lu, J.N.; Lee, S.J.; Tsoy, I.; Kim, H.J.; Ryu, C.H.; et al. Anti-invasive activity of anthocyanins isolated from Vitis coignetiae in human hepatocarcinoma cells. J. Med. Food. 2009, 12, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempo, P.; de Masi, L.; Carafa, V.; Rigano, D.; Scisciola, L.; Iside, C.; Grassi, R.; Molinari, A.M.; Aversano, R.; Nebbioso, A.; et al. Anticancer activities of anthocyanin extract from genotyped Solanum tuberosum L. “Vitelotte”. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathearn, K.E.; Yousef, G.G.; Grace, M.H.; Roy, S.L.; Tambe, M.A.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Wu, Q.-L.; Simon, J.E.; Lila, M.A.; Rochet, J.-C. Neuroprotective effects of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin-rich extracts in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2014, 1555, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, P.-H.; Chan, Y.-C.; Liao, J.-W.; Wang, M.-F.; Yen, G.-C. Antioxidant and cognitive promotion effects of anthocyanin-rich mulberry (Morus atropurpurea L.) on senescence-accelerated mice and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierres, J.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Agostinho, P.; Marisco, P.C. Neuroprotective effect of anthocyanins on acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuation of scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 33, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.U.; Shah, S.A.; Ali, T.; Chung, J.I.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins reversed D-galactose-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation mediated cognitive impairment in adult rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, F.U.; Shah, S.A.; Badshah, H.; Khan, M.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanins encapsulated by PLGA@PEG nanoparticles potentially improved its free radical scavenging capabilities via p38/JNK pathway against Abeta1-42-induced oxidative stress. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Rehman, S.U.; Amin, F.U.; Kim, M.O. Enhanced neuroprotection of anthocyanin-loaded PEG-gold nanoparticles against Abeta1-42-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via the NF-KB /JNK/GSK3beta signaling pathway. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 2533–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.; Kim, M.J.; Rehman, S.U.; Ahmad, A.; Kim, M.O. Anthocyanin-Loaded PEG-Gold nanoparticles enhanced the neuroprotection of anthocyanins in an Abeta1-42 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6490–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomi, Y.; Iwasaki-Kurashige, K.; Matsumoto, H. Therapeutic effects of anthocyanins for vision and eye health. Molecules 2019, 24, 3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Konishi, T. Anthocyanins and anthocyanin-rich extracts: Role in diabetes and eye function. Asian Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 200–208. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda, T. Anthocyanins as functional food factors: Chemistry, nutrition and health promotion. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 18, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeriglio, A.; Monteleone, D.; Trombetta, D. Health effects of Vaccinium myrtillus L.: Evaluation of efficacy and technological strategies for preservation of active ingredients. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.K.; Lee, H.J.; Shih, Y.W.; Chyau, C.C.; Wang, C.J. Mulberry anthocyanins extracts inhibit LDL oxidation and macrophage-derived foam cell formation induced by oxidative LDL. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 4113–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechner, A.R.; Kroner, C. Anthocyanins and colonic metabolites of dietary polyphenols inhibit platelet function. Thromb. Res. 2005, 116, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luís, Â.; Domingues, F.; Pereira, L. Association between berries intake and cardiovascular diseases risk factors: A systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Conesa, M.T.; Chambers, K.; Combet, E.; Pinto, P.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Andresń-Lacueva, C.; dePascual-Teresa, S.; Mena, P.; Konic Ristic, A.; Hollands, W.J.; et al. Meta-Analysis of the effects of foods and derived products containing ellagitannins and anthocyanins on cardiometabolic biomarkers: Analysis of factors influencing variability of the individual responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksonzékova, P.; Mariychuk, R.; Eliasova, A.; Mudronova, D.; Csank, T.; Kiraly, J.; Marcincakova, D.; Pistl, J.; Tkacikova, L. In vitro studies of biological activities of anthocyanin-rich berry extracts on porcine intestinal epithelial cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, K.; Mills, S. Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy: Modern Herbal Medicine; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburg, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Su, H.; Sun, C.; Zheng, X.; Chen, W. Recent advances in understanding the anti-obesity activity of anthocyanins and their biosynthesis in microorganisms. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Arumuggam, N. Health benefits of anthocyanins. Food Chem. Func. Anal. 2019, 2019, 123–158. [Google Scholar]
- Heyman, L.; Axling, U.; Blanco, N.; Sterner, O.; Holm, C.; Berger, K. Evaluation of beneficial metabolic effects of berries in high-fat fed C57BL/6J mice. J. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 2014, 403041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachin, T.; Reza, H. Anti diabetic effect of cherries in alloxan induced diabetic rats. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2012, 6, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orqueda, M.E.; Torres, S.; Zampini, I.C.; Cattaneo, F.; Fernandez Di Pardo, A.; Valle, E.M.; Jimenez-Aspee, F.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Isla, M.I. Integral use of Argentinean Solanum betaceum red fruits as functional food ingredient to prevent metabolic syndrome: Effect of in vitro simulated gastroduodenal digestión. Heliyon 2020, 6, 03387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedick, N.M.; Pan, A.; Cassidy, A.; Rimm, E.B.; Sampson, L.; Rosner, B.; Willett, W.; Hu, F.B.; Sun, Q.; van Dam, R.M. Dietary flavonoid intakes and risk of type 2 diabetes in US men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisowska, A.; Wojnicz, D.; Hendrich, A.B. Anthocyanins as antimicrobial agents of natural plant origin. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helander, I.M.; Alakomi, H.L.; Latva-Kala, K.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; Pol, I.; Smid, E.J.; Gorris, L.G.M.; von Wright, A. Characterization of the action of selected essential oil components on Gram-negative bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3590–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Saad, B. Anthocyanins and Human Health: Biomolecular and Therapeutical Aspects; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, T.C.; Giusti, M.M. Anthocyanins in Health and Disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, C.G. (Ed.) Plant Phenolics and Human Health: Biochemistry, Nutrition and Pharmacology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Giusti, M.M. Anthocyanins: Natural colorants with health-promoting properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvano, F.; Salamone, F.; Nicolosi, A.; Vitaglione, P. Anthocyanins-based drugs for colon cancer treatment: The nutriotionist’s point of view. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 64, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.R.; Min, K.; Ebeler, S.E. Anthocyanins interactions with DNA: Intercalation, topoisomerase I inhibition and oxidative reactions. J. Food Biochem. 2008, 32, 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; Faria, A.; Azevedo, J.; Soares, S.; Calhau, C.; De Freitas, V.; Mateus, N. Influence of anthocyanins, derivative pigments and other catechol and pyrogallol-type phenolics on breast cancer cell proliferation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3785–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hai Liu, R. Cranberry phytochemical extracts induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2006, 241, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshyar, R.; Mahboob, Z.; Zarban, A. The antioxidant and chemical properties of Berberis vulgaris and its cytotoxic effect on human breast carcinoma cells. Cytotechnology 2015, 68, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, N.K.; Jang, W.J.; Jeong, C.H.; Jeong, G.S. Delphinidin suppresses PMA-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking the NF-kappaB activation through MAPK signaling pathways in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. J. Med. Food. 2014, 17, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forester, S.C.; Choy, Y.Y.; Waterhouse, A.L.; Oteiza, P.I. The anthocyanin metabolites gallic acid, 3-O-methylgallic acid, and 2,4,6- trihydroxybenzaldehyde decrease human colon cancer cell viability by regulating pro-oncogenic signals. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.N.; Kuo, W.H.; Chiang, C.L.; Chiou, H.L.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Chu, S.C. Black rice anthocyanins inhibit cancer cells invasion via repressions of MMPs and u-PA expression. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 163, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, P.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, F. Health benefits of anthocyanins and molecular mechanisms: Update from recent decade. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1729–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, P.; Bomser, J.A.; Schwartz, S.J.; He, J.; Magnuson, B.A.; Giusti, M.M. Structure–function relationships of anthocyanins from various anthocyanin-rich extracts on the inhibition of colon cancer cell growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 9391–9398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Giusti, M.M.; Malik, M.; Moyer, M.P.; Magnuson, B.A. Effects of commercial anthocyanin-rich extracts on colonic cancer and nontumorigenic colonic cell growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6122–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.N.; Bickford, P.C. Anthocyanins and their metabolites as therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative disease. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkenberg, I.; Blokland, A. The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: A review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 1307–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bioassay | Reagents Involved in the Reaction | Detection | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH (Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) assay | Free radical (DPPH•+) | Decrease of Abs. at 515 nm | Spectrophotometric or colorimetric |
| ORAC Assay (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) | 2,2′-azobis(2-amidino-propane) dihydrochloride (AAPH) to produce free radical β-phycoerythrin or Fluorescein or Pyrogallol red | Decrease of fluorescence | Fluorescence spectroscopy |
| TRAP assay (total peroxyl radical trapping antioxidant parameter) | 2,2′-azobis(2-amidopropane) hydrochloride (ABAP) to produce free radical Luminol | Decrease of luminescence | Chemiluminescence |
| FCT (ferric thiocyanate) assay | Ferrous chloride, formation of red ferric thiocyanate | Increase of Abs. at 500 nm | Spectrophotometric |
| FRAP (Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power) assay | FeCl3·6H2O, formation of blue ferrous complexes | Increase of Abs. at 593 nm | Colorimetric |
| CUPRAC, Cupric Ion Reducing Antioxidant Capacity | Cupric neocuproine, formation of Cu(I)-neocuproine | Increase of Abs. at 550 nm | Spectrophotometric |
| ABTS [2,2′-azino-bis (3-ehtylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diamonium salt] assay | Free radical (ABTS•+) | Decrease of Abs. at 415 nm | Colorimetric |
| Methods of inhibited autoxidation | Lipid molecules, azoinitiator | O2 consumption/hydroperoxide formation | Oxygen electrode, pressure gauge, detection of conjugated dienes |
| Code | Anthocyanin | Code | Anthocyanin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Delphinidin | 30 | Petunidin 3-arabinoside |
| 2 | Delphinidin 3-arabinoside | 31 | Petunidin 3-galactoside |
| 3 | Delphinidin 3-galactoside | 32 | Petunidin 3-glucoside |
| 4 | Delphinidin 3-glucoside | 33 | Petunidin 3-halactoside |
| 5 | Delphinidin 3,5-diglucoside | 34 | Petunidin 3-rutinoside |
| 6 | Delphinidin 3-rutinoside | 35 | Peonidin |
| 7 | Delphinidin 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl-glucoside) | 36 | Peonidin 3-galactoside |
| 8 | Cyanidin | 37 | Peonidin 3-glucoside |
| 9 | Cyanidin 3-arabidoside | 38 | Peonidin 3-rutinoside |
| 10 | Cyanidin 3-galactoside | 39 | Peonidin 3-(6′-malonylglucoside) |
| 11 | Cyanidin 3-glucoside | 40 | Peonidin 3-(3″,6″-dimalonylglucoside) |
| 12 | Cyanidin 3,5-diglucoside | 41 | Peonidin 3-glucoside/malvidin 3-galactoside |
| 13 | Cyanidin 3-rutinoside | 42 | Peonidin 3-arabinoside/malvidin 3-glucoside |
| 14 | Cyanidin 3-(6′-malonylglucoside) | 43 | Peonidin 3-O-sophoroside-5-O-glucoside |
| 15 | Cyanidin 3-(3″,6″-dimalonylglucoside) | 44 | Peonidin 3-p-hydroxybenzoylsophoroside-5-glucoside |
| 16 | Cyanidin 3-xyloside | 45 | Peonidin 3-caffeoylsophoroside-5-glucoside |
| 17 | Cyanidin 3-xylosylrutinoside | 46 | Peonidin 3-dicaffeoylsophoroside-5-glucoside |
| 18 | Cyanidin 3-dioxaloylglucoside | 47 | Peonidin 3-caffeoyl-p-hydroxybenzoylsophoroside-5-glucoside |
| 19 | Cyanidin 3-halavtoside | 48 | Peonidin 3-caffeoy-feruloylsophoroside-5-glucoside |
| 20 | Cyanidin 3-O-sophoroside | 49 | Malvidin |
| 21 | Cyanidin 3-sophoroside-5-rhamnoside | 50 | Malvidin 3-arabinoside |
| 22 | Cyanidin 3-sambubioside | 51 | Malvidin 3-galactoside |
| 23 | Cyanidin 3-sambubioside-5-rhamnoside | 52 | Malvidin 3-glucoside |
| 24 | Cyanidin-3-p-hydroxybenzoylsophoroside-5-glucoside | 53 | Malvidin 3,5-diglucoside |
| 25 | Cyanidin-3-caffeoylsophoroside-5-glucoside | 54 | Pelargonidin |
| 26 | Cyanidin-3-caffeoyl-p-hydroxybenzoylsophoroside-5-glucoside | 55 | Pelargonidin 3-glucoside |
| 27 | Cyanidin 3-(p-coumaroyl)-diglucoside-5-glucoside | 56 | Pelargonidin 3-rutinoside |
| 28 | Cyanidin 3-(p-coumaroyl)-diglucoside-5-glucoside | 57 | Pelargonidin 3,5-diglucoside |
| 29 | Petunidin |
| Eye Health | Administration | References |
|---|---|---|
| Improvement of vision in patients with open-angle glaucoma | Oral capsule | [114] |
| Protective effect during retinal inflammation | IV in rats | [115] |
| Regeneration of rhodopsin and smooth muscle relaxation | IV in mouse model | [116] |
| Improvement of dark adaptation | Oral capsule | [117] |
| Prevention of cataractogenesis of diabetic cataract | Incubation of Enucleated rat lenses | [118] |
| Antiapoptotic effects against oxidative damage of lens epithelial cell | Cell studies | [119] |
| Prevention of retinal degeneration induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea | Oral solution | [120] |
| Increase of ocular blood flows | Oral capsule | [121] |
| Cardiovascular diseases | ||
| Inhibition of platelet aggregation (in vitro antithrombotic properties) | Cell studies | [122] |
| Increase of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and decrease of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels | Oral capsule | [123] |
| Lower risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction | Oral intake | [124] |
| Vasorelaxation properties in isolated coronary artery rings in pigs | Cell studies | [125] |
| Decrease of susceptibility to ischemia-reperfusion injury and infarct size | Rodent food | [126] |
| Improvement of lipid profile and platelet function | Oral capsule | [127] |
| Antiobesity effects | ||
| Improvement of weight gain and lipid profile on obese rats | Fat diet-induced mouse model | [128] |
| Suppression of body weight gain and improve blood lipid profile in rats | Fat diet-induced mouse model | [129] |
| Reduction of sugar concentration in urine and plasma in rats | Intraperitoneal and intragastric administration | [130] |
| Ameliorated obesity in high-fat-fed mice | Cell studies | [131] |
| Upregulation of adipocytokine secretion and gene expression in rat adipocytes | Cell studies | [132] |
| Suppression of fat tissue gain, weight gain and other metabolic disorders | Fat diet-induced mouse model | [133] |
| Antidiabetic effects | ||
| Amelioration of hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity in diabetic mice | Fat diet-induced mouse model | [134] |
| Improvement of dyslipidemia, enhancement of antioxidant capacity, and prevention of insulin resistance in human with type 2 diabetes | Oral capsule | [135] |
| Alleviation of glomerular angiogenesis of diabetic kidneys in mice | Cell studies | [136] |
| Inhibition of DPP IV activity (a protease that regulates blood glucose levels via degradation of incretins) | Computational studies | [137] |
| Amelioration of renal apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy mice | Oral solution | [138] |
| Activation of adipose tissue-derived adiponectin to defend against diabetes-related endothelial dysfunction in mice | Diet-induced mouse model | [139] |
| Antimicrobial effects | ||
| Induction of cell damage by destroying the cell wall, membrane, and intercellular matrix | Cell studies | [140] |
| Highest sensitivity to Aeromonas hydrophila and Listeria innocua | Microbial strains | [141] |
| Antibacterial effects towards Enterococcus faecium resistant to vancomycin, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli | Microbial strains | [142] |
| Inhibition of Gram-negative bacteria | Microbial strains | [143] |
| Anticancer effects | ||
| Suppression of cell proliferation, inflammation, and angiogenesis and induction of apoptosis in esophageal tissue of rats | Diet-induced rat model | [144] |
| Anti-invasive potential in breast cancer cell lines | Cell studies | [145] |
| Anticancer effect on BALB/c nude mice bearing MDA-MB-453 cell xenografts and breast cancer cell lines | Cell studies | [146] |
| Inhibition of cell migration and invasion, suppression of activation of rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma, mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and downregulation of secretion of matrix metalloproteinase 2 | Cell studies | [147] |
| Inhibition of growth of human HT-29 colon cancer cells, increase of expression of tumor suppression genes and decrease of cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression | Cell studies | [148] |
| Reduction of colonic aberrant crypt foci, colonic cellular proliferation and COX-2 mRNA expression in rats | Diet-induced rat model | [149] |
| Suppression of formation of aberrant crypt foci in colons of CF-1 mice | Cell studies and diet-induced rat model | [150] |
| Promotion of apoptosis in benign prostatic hyperplasia rats | Oral doses in rat model | [151] |
| Anti-invasive effect on human hepatoma Hep3B cells and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2 and MMP-9 gene expression | Cell studies | [152] |
| Inhibition of Akt-mTOR signaling thereby inducing maturation of acute myeloid leukemia cells, besides inducing apoptotic players such as TRAIL in cancer systems | Cell studies | [153] |
| Neurodegenerative diseases | ||
| Neuroprotective activity by suppression of dopaminergic cell death in Parkinson’s disease | Cell studies | [154] |
| Improvement of learning and memory ability in mice. Higher antioxidant enzyme activity and less lipid oxidation in both brain and liver | Diet-induced mouse model | [155] |
| Regulation of cholinergic neurotransmission to restore Na+, K+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase activities and to prevent memory deficits in rats | Oral and injected rat models | [156] |
| Neuroprotective effect: Memory and synaptic dysfunction | Oral rat models | [157] |
| Improvement of its free radical scavenging capabilities via p38/JNK pathway against Abeta1-42-induced oxidative stress | Cell studies | [158] |
| Enhancement of neuroprotection against Abeta1-42-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration | Oral mouse model and cell studies | [159] |
| Enhancement of the neuroprotection in an Abeta1-42 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease | Oral mouse model and cell studies | [160] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tena, N.; Martín, J.; Asuero, A.G. State of the Art of Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Activity, Sources, Bioavailability, and Therapeutic Effect in Human Health. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050451
Tena N, Martín J, Asuero AG. State of the Art of Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Activity, Sources, Bioavailability, and Therapeutic Effect in Human Health. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(5):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050451
Chicago/Turabian StyleTena, Noelia, Julia Martín, and Agustín G. Asuero. 2020. "State of the Art of Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Activity, Sources, Bioavailability, and Therapeutic Effect in Human Health" Antioxidants 9, no. 5: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050451
APA StyleTena, N., Martín, J., & Asuero, A. G. (2020). State of the Art of Anthocyanins: Antioxidant Activity, Sources, Bioavailability, and Therapeutic Effect in Human Health. Antioxidants, 9(5), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050451