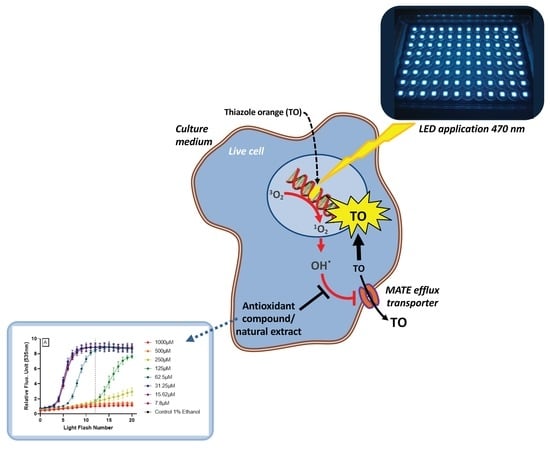
AOP1, a New Live Cell Assay for the Direct and Quantitative Measure of Intracellular Antioxidant Effects
Abstract
Share and Cite
Gironde, C.; Rigal, M.; Dufour, C.; Furger, C. AOP1, a New Live Cell Assay for the Direct and Quantitative Measure of Intracellular Antioxidant Effects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060471
Gironde C, Rigal M, Dufour C, Furger C. AOP1, a New Live Cell Assay for the Direct and Quantitative Measure of Intracellular Antioxidant Effects. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(6):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060471
Chicago/Turabian StyleGironde, Camille, Mylène Rigal, Cécile Dufour, and Christophe Furger. 2020. "AOP1, a New Live Cell Assay for the Direct and Quantitative Measure of Intracellular Antioxidant Effects" Antioxidants 9, no. 6: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060471
APA StyleGironde, C., Rigal, M., Dufour, C., & Furger, C. (2020). AOP1, a New Live Cell Assay for the Direct and Quantitative Measure of Intracellular Antioxidant Effects. Antioxidants, 9(6), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060471