Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG)-Inducible SMILE Inhibits STAT3-Mediated Hepcidin Gene Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plasmid DNAs and Recombinant Adenoviruses
2.3. Animal Experiments
2.4. Cell Culture, Transfection and Luciferase Assay
2.5. Culture of Mouse Primary Hepatocytes
2.6. Quantitative PCR
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Co-immunoprecipitation Analysis
2.9. Immunocytochemistry
2.10. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.11. Serum Iron and Hepcidin Measurement
2.12. RNA Interference
2.13. Cell Viability
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
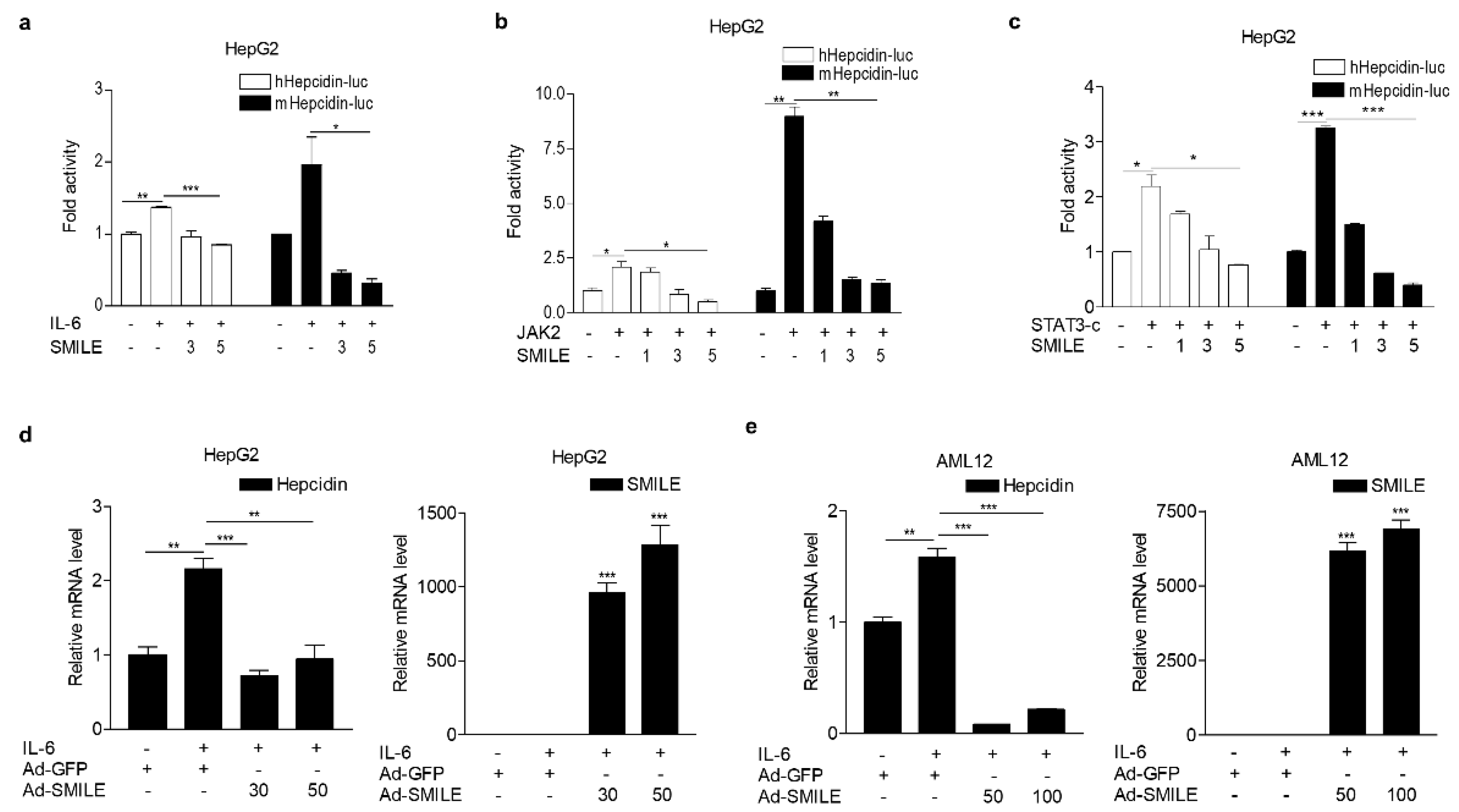
3.1. SMILE Inhibits IL-6-Mediated Hepcidin Production and Secretion
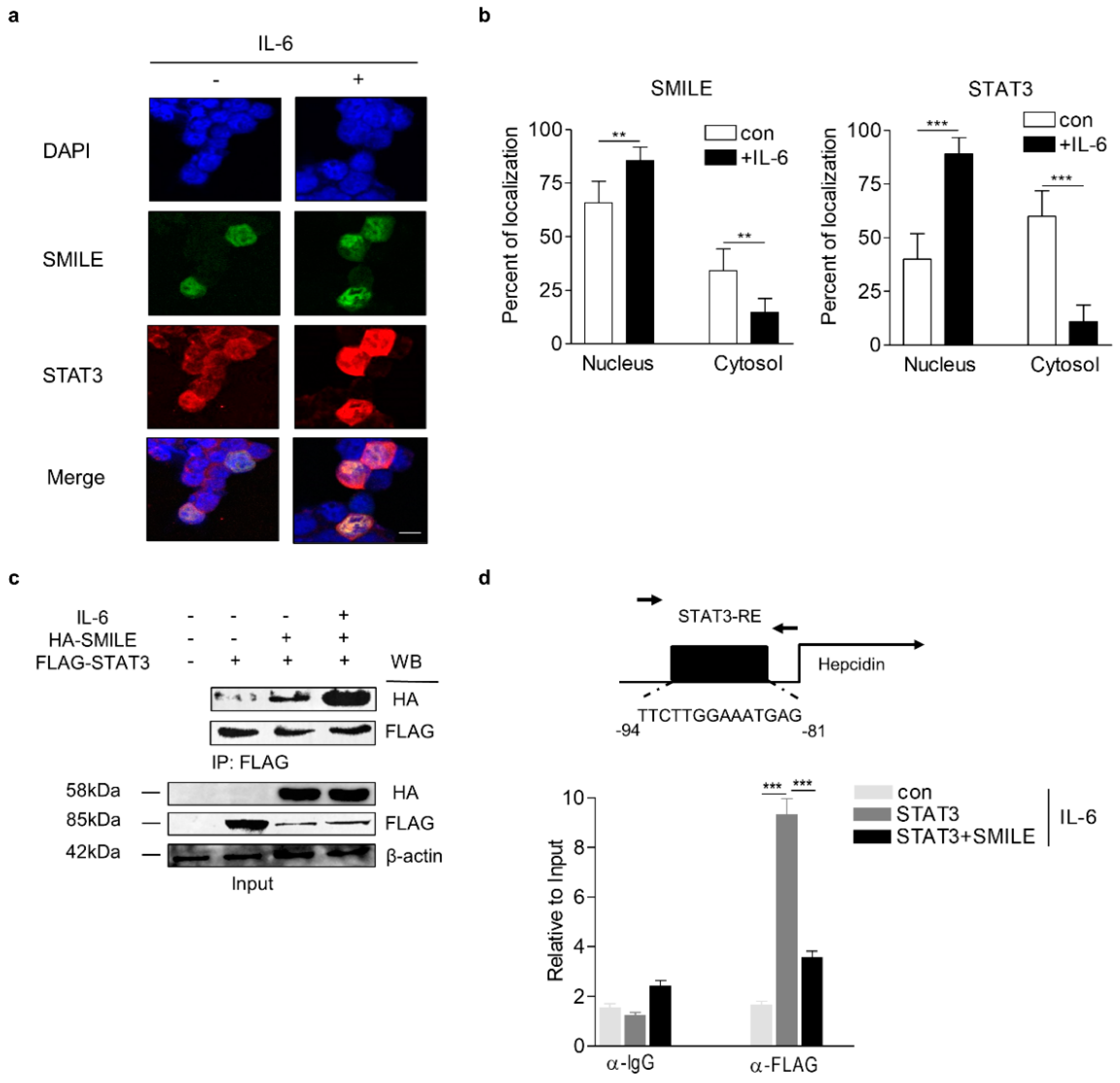
3.2. SMILE Represses Activity of The IL-6 Signaling Pathway via Inhibition of DNA-Binding of STAT3
3.3. EGCG Increases FoxO1 and SMILE Expression
3.4. FoxO1 Increases SMILE Expression
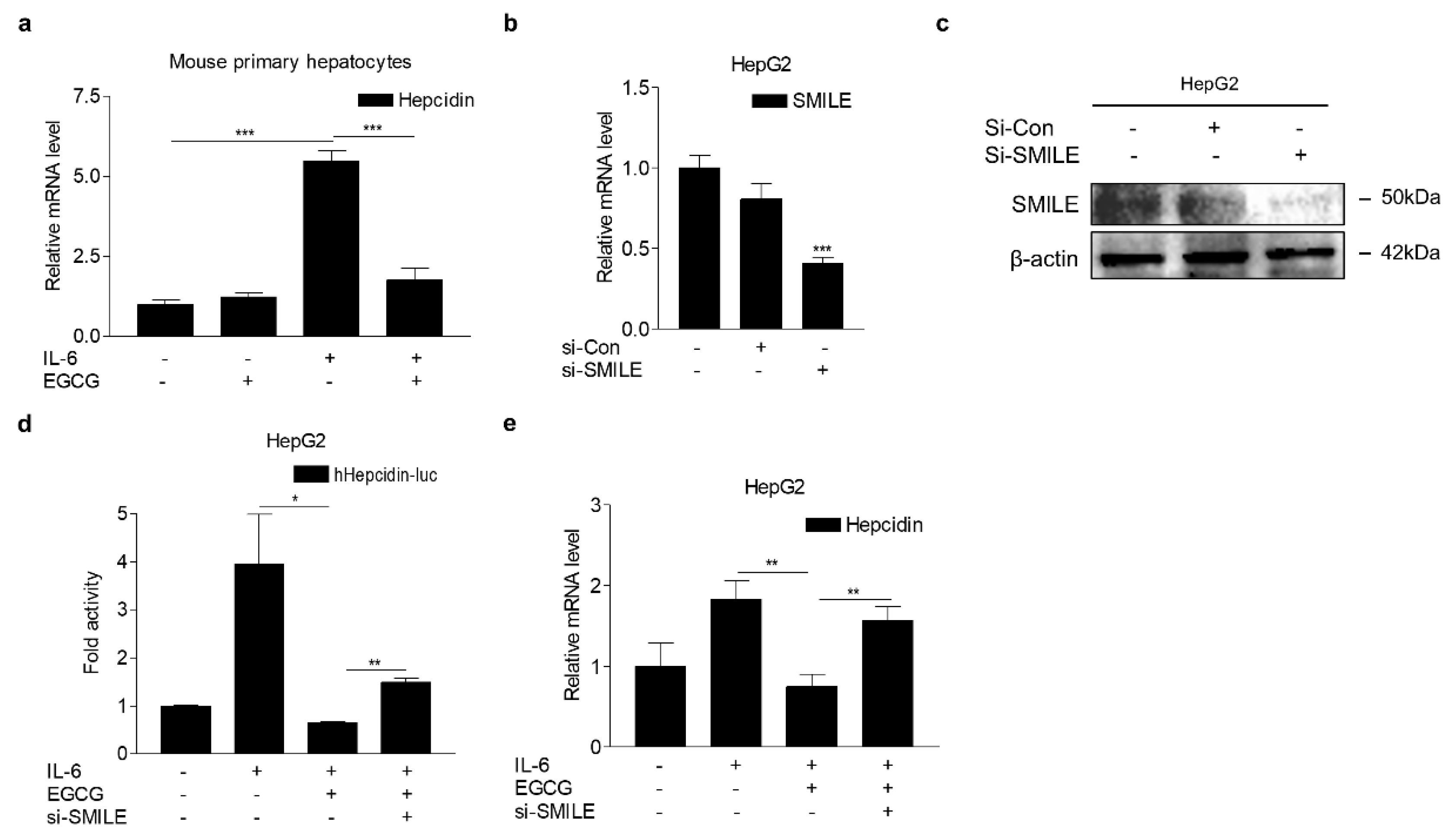
3.5. EGCG Attenuates IL-6-Induced Hepcidin Expression through SMILE
3.6. EGCG Inhibits LPS-Induced Hepcidin Expression and Hypoferremia in Mice
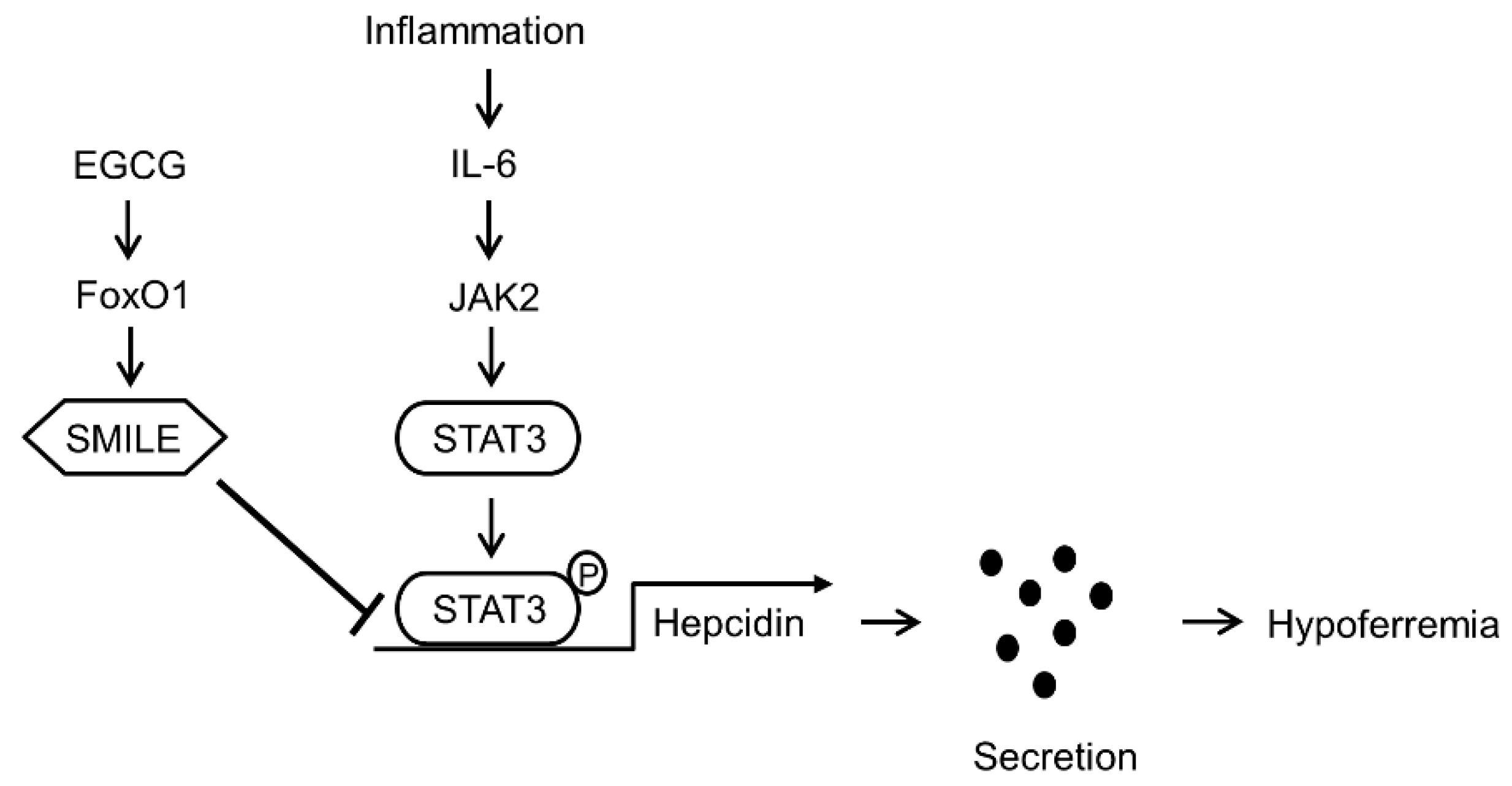
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Anemia of inflammation |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin-3-gallate |
| SMILE | Small heterodimer partner-interacting leucine zipper protein |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| STAT3-c | STAT3 constitutive active form |
| STAT3-RE | STAT3-responsive element |
| FoxO1 | Forkhead box protein O1 |
| FPN | Ferroportin |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| WT | Wild type mice |
| FoxO1-LKO | Liver-specific FoxO1 knockout mice |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| SHP | Small heterodimer partner |
| ERRγ | Estrogen-related receptor γ |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| Q-PCR | Quantitative PCR |
| BMP-6 | Bone morphogenetic protein-6 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| LKB1 | Liver kinase B1 |
| AMPK | AMP-dependent kinase |
References
- Weiss, G.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of Chronic Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poggiali, E.; De Amicis, M.M.; Motta, I. Anemia of chronic disease: A unique defect of iron recycling for many different chronic diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannikourides, A.; Latunde-Dada, G.O. A Short Review of Iron Metabolism and Pathophysiology of Iron Disorders. Medicines 2019, 6, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinbicker, A.U.; Muckenthaler, M.U. Out of Balance—Systemic Iron Homeostasis in Iron-Related Disorders. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3034–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangat, N.; Wolanskyj, A.P. Anemia of Chronic Disease. Semin. Hematol. 2013, 50, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Vaja, V.; Babitt, J.L.; Lin, H.Y. Targeting the hepcidin-ferroportin axis to develop new treatment strategies for anemia of chronic disease and anemia of inflammation. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyssonnaux, C.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Rankin, E.B.; Vaulont, S.; Haase, V.H.; Nizet, V.; Johnson, R.S. Regulation of iron homeostasis by the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs). J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastrogiannaki, M.; Matak, P.; Mathieu, J.R.; Delga, S.; Mayeux, P.; Vaulont, S.; Peyssonnaux, C. Hepatic hypoxia-inducible factor-2 down-regulates hepcidin expression in mice through an erythropoietin-mediated increase in erythropoiesis. Haematologica 2011, 97, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Babitt, J.L. Hepcidin regulation in the anemia of inflammation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Quon, M.; Kim, J. New insights into the mechanisms of polyphenols beyond antioxidant properties; lessons from the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin 3-gallate. Redox Boil. 2014, 2, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.A.; Mandal, A.K.A.; Khan, Z.A. Potential neuroprotective properties of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, T.; Lee, J.; Lou, Z.; Lee, B.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Identification of epithelial–specific ETS–1 (ESE–1) as a tumor suppressor and molecular target of green tea compound, EGCG. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, C.; Guan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ling, F.; Niu, Y.; Li, Y. Epigallocatechin gallate improves insulin resistance in HepG2 cells through alleviating inflammation and lipotoxicity. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2018, 142, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R. Zhangfei: A second cellular protein interacts with herpes simplex virus accessory factor HCF in a manner similar to Luman and VP16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misra, J.; Chanda, D.; Kim, N.-K.; Li, T.; Koo, S.-H.; Back, S.-H.; Chiang, J.Y.; Choi, H.-S. Curcumin Differentially Regulates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress through Transcriptional Corepressor SMILE (Small Heterodimer Partner-interacting Leucine Zipper Protein)-mediated Inhibition of CREBH (cAMP Responsive Element-binding Protein H). J. Boil. Chem. 2011, 286, 41972–41984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-M.; Seo, W.-Y.; Han, H.-S.; Oh, K.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, N.-K.; Choi, S.; Choi, B.H.; Harris, R.A.; Lee, C.-H.; et al. Insulin-Inducible SMILE Inhibits Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 2015, 65, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-M.; Gang, G.-T.; Kim, N.-K.; Kim, Y.D.; Koo, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Choi, H.-S. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Inhibits Liver X Receptor α-mediated Hepatic Lipogenesis via Induction of the Nuclear Corepressor SMILE*. J. Boil. Chem. 2013, 289, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.-B.; Lee, O.-H.; Nedumaran, B.; Seong, H.-A.; Lee, K.-M.; Ha, H.; Lee, I.-K.; Yun, Y.; Choi, H.-S. SMILE, a new orphan nuclear receptor SHP-interacting protein, regulates SHP-repressed estrogen receptor transactivation. Biochem. J. 2008, 416, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-B.; Nedumaran, B.; Choi, H.-S. Molecular characterization of SMILE as a novel corepressor of nuclear receptors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 4100–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.-B.; Park, J.-H.; Kim, N.-K.; Hwang, J.H.; Oh, S.; Park, S.B.; Shong, M.; Lee, I.-K.; Choi, H.-S. Transcriptional Corepressor SMILE Recruits SIRT1 to Inhibit Nuclear Receptor Estrogen Receptor-related Receptor γ Transactivation. J. Boil. Chem. 2009, 284, 28762–28774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mleczko-Sanecka, K.; Casanovas, G.; Ragab, A.; Breitkopf, K.; Müller, A.; Boutros, M.; Dooley, S.; Hentze, M.W.; Muckenthaler, M.U. SMAD7 controls iron metabolism as a potent inhibitor of hepcidin expression. Blood 2010, 115, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.-K.; Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, J.-M.; Kim, H.R.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, Y.D.; Koh, M.; Shin, M.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, H.; et al. Inverse agonist of estrogen-related receptor γ controls Salmonella typhimurium infection by modulating host iron homeostasis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.D.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, Y.M.; Kim, D.; Ahn, S.W.; Lee, J.M.; Chanda, D.; Shong, M.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, H.-S. Metformin ameliorates IL-6-induced hepatic insulin resistance via induction of orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner (SHP) in mouse models. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1482–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, K.T.; Park, Y.-Y.; Seong, H.-A.; Park, K.C.; Lee, I.-K.; Ha, H.; Shong, M.; Park, S.C.; et al. Orphan Nuclear Receptor Small Heterodimer Partner Represses Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 3/Foxa Transactivation via Inhibition of Its DNA Binding. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 2880–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, N.-K.; Na, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Choi, H.-S. Hepatocyte toll-like receptor 4 mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced hepcidin expression. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.-K.; Kim, Y.-H.; Hynx, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.-J.; Ryu, D.; Kim, K.S.; Yoo, E.-K.; Kim, J.-S.; Koo, S.-H.; et al. PKB/Akt phosphorylation of ERRγ contributes to insulin-mediated inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2576–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrighting, D.M.; Andrews, N. Interleukin-6 induces hepcidin expression through STAT3. Blood 2006, 108, 3204–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S. Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses hepatic cholesterol synthesis by targeting SREBP-2 through SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 448, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemna, E.H.; Pickkers, P.; Nemeth, E.; Van Der Hoeven, H.; Swinkels, D. Time-course analysis of hepcidin, serum iron, and plasma cytokine levels in humans injected with LPS. Blood 2005, 106, 1864–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T.; Nemeth, E. Iron homeostasis in host defence and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.-K.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, K.-S.; Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Yuk, J.-M.; Oh, B.-C.; Choy, H.E.; Dooley, S.; et al. Orphan nuclear receptor SHP regulates iron metabolism through inhibition of BMP6-mediated hepcidin expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, F.; Cui, A.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Bai, J.; et al. CREBZF as a Key Regulator of STAT3 Pathway in the Control of Liver Regeneration in Mice. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1421–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Pamu, S.; Cui, Q.; Chan, T.-H.; Dou, Q.P. Novel epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) analogs activate AMP-activated protein kinase pathway and target cancer stem cells. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3031–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murase, T.; Misawa, K.; Haramizu, S.; Hase, T. Catechin-induced activation of the LKB1/AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sakamoto, K. (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate suppresses adipocyte differentiation through the MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Cell Boil. Int. 2011, 36, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.Z.; Pan, Q.; Yang, W.; Yan, H.; Liu, H.; Ai, W.; Liao, W.; Guo, S.; et al. Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits Hepatic Glucose Production in Primary Hepatocytes via Downregulating PKA Signaling Pathways and Transcriptional Factor FoxO1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3651–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, L.-O.; Sánchez-Ramos, C.; Prieto, I.; Urbanek, P.; Steinbrenner, H.; Monsalve, M. Redox regulation of FoxO transcription factors. Redox Boil. 2015, 6, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, K.-S.; Lim, D.; Yang, D.J.; Park, J.-I.; Kim, K.W.; Jeong, J.-H.; Choi, H.-S.; Kim, D.-K. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG)-Inducible SMILE Inhibits STAT3-Mediated Hepcidin Gene Expression. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060514
Kim Y-J, Kim K-S, Lim D, Yang DJ, Park J-I, Kim KW, Jeong J-H, Choi H-S, Kim D-K. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG)-Inducible SMILE Inhibits STAT3-Mediated Hepcidin Gene Expression. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(6):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060514
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yu-Ji, Ki-Sun Kim, Daejin Lim, Dong Ju Yang, Jae-Il Park, Ki Woo Kim, Jae-Ho Jeong, Hueng-Sik Choi, and Don-Kyu Kim. 2020. "Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG)-Inducible SMILE Inhibits STAT3-Mediated Hepcidin Gene Expression" Antioxidants 9, no. 6: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060514
APA StyleKim, Y.-J., Kim, K.-S., Lim, D., Yang, D. J., Park, J.-I., Kim, K. W., Jeong, J.-H., Choi, H.-S., & Kim, D.-K. (2020). Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG)-Inducible SMILE Inhibits STAT3-Mediated Hepcidin Gene Expression. Antioxidants, 9(6), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060514







