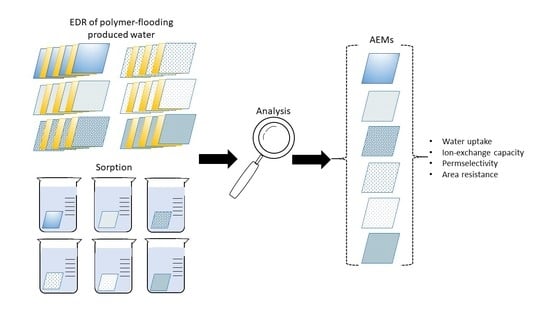
Experimental Evaluation of Anion Exchange Membranes for the Desalination of (Waste) Water Produced after Polymer-Flooding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of Solutions
2.1.2. Ion Exchange Membranes
2.1.3. Electrodialysis Setup
2.2. Methods for the EDR Runs
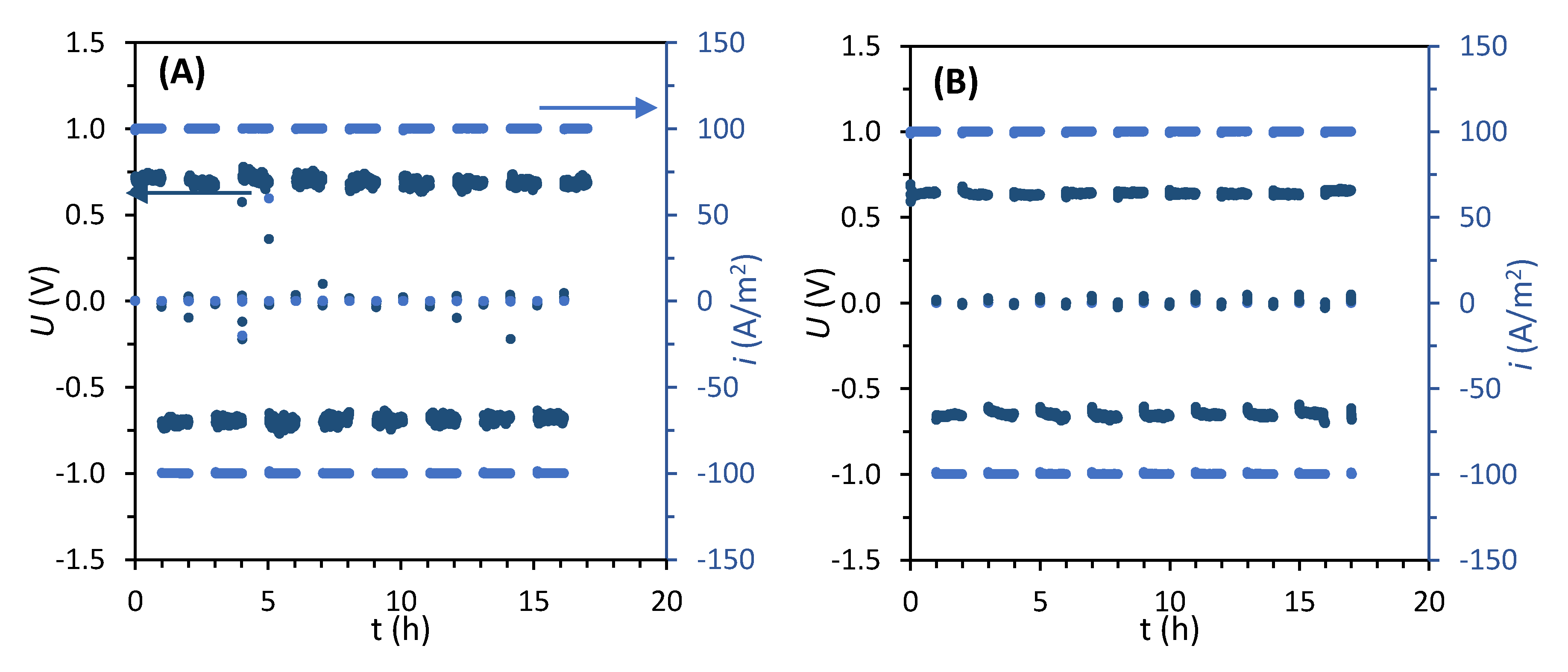
2.2.1. Electrodialysis Reversal Runs
2.2.2. Degree of Demineralization
2.3. Methods for Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. Water Uptake and Hydration Number
2.3.2. Ion-Exchange Capacity (IEC), Charge Density, and Charge per Area
2.3.3. Permselectivity
2.3.4. Electrical Resistance
2.3.5. Single AEM Characterization in Six-Compartment Cell
2.3.6. Sorption Tests
2.3.7. Solution Analysis
2.3.8. Electrodialysis Model
3. Results
3.1. Desalination Performance with Different AEMs
3.2. Evaluation of the Anion Exchange Membranes
3.2.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Virgin Membranes
3.2.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Virgin Membranes
3.2.3. Physico-Chemical Evaluation of Fouled Membranes
3.2.4. Electrochemical Characterization of Fouled Membranes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Huang, C. Electrodialysis-based separation technologies: A critical review. J. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2008, 54, 3147–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guolin, J.; Xiaoyu, W.; Chunjie, H. The effect of oilfield polymer-flooding wastewater on anion-exchange membrane performance. Desalination 2008, 220, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethmuller, G.; Abri, A.; Al Azri, N.; Stapel, G.; Nijman, S.; Subhi, W.; Mehdi, R. Opportunities and Challenges of Polymer Flooding in Heavy Oil Reservoir in South of Oman. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 31 March–2 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rellegadla, S.; Prajapat, G.; Agrawal, A. Polymers for enhanced oil recovery: Fundamentals and selection criteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 4387–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Fernandez, P.A.; Post, J.W.; Bruning, H.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. Electrodialysis-based desalination and reuse of sea and brackish polymer-flooding produced water. Desalination 2018, 447, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Xing, L.; Li, S.; Han, C. Reclaiming polymer-flooding produced water for beneficial use: Salt removal via electrodialysis. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 25, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H. Electromembrane Processes: Basic Aspects and Applications. In Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 391–429. ISBN 978-0-08-093250-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Intensification of demineralization process and decrease in scaling by application of pulsed electric field with short pulse/pause conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: Classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korngold, E.; de Korosy, F.; Rahav, R.; Taboch, M.F. Fouling of anionselective membranes in electrodialysis. Desalination 1970, 8, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Guo, H.; Ye, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R. Study on the fouling mechanism and cleaning method in the treatment of polymer flooding produced water with ion exchange membranes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29947–29957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xiao, L.; Yu, S.; Yang, H.; Hu, J.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. Analysis of anion exchange membrane fouling mechanism caused by anion polyacrylamide in electrodialysis. Desalination 2014, 346, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; You, F.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, D. Mechanisms of chemical cleaning of ion exchange membranes: A case study of plant-scale electrodialysis for oily wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guolin, J.; Lijie, X.; Yang, L.; Wenting, D.; Chunjie, H. Development of a four-grade and four-segment electrodialysis setup for desalination of polymer-flooding produced water. Desalination 2010, 264, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yu, S.; Hou, L. an Impacts of HPAM molecular weights on desalination performance of ion exchange membranes and fouling mechanism. Desalination 2017, 404, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Fernandez, P.A.; Miedema, S.J.; Bruning, H.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Post, J.W. Influence of solution composition on fouling of anion exchange membranes desalinating polymer-flooding produced water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wever, D.A.Z.; Picchioni, F.; Broekhuis, A.A. Polymers for enhanced oil recovery: A paradigm for structure-property relationship in aqueous solution. Prog. Polym. Sci. (Oxf.) 2011, 36, 1558–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; de Hart, N.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. CO2 saturated water as two-phase flow for fouling control in reverse electrodialysis. Water Res. 2017, 125, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyati, S.; Takagi, R.; Fujii, A.; Ohmukai, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Improvement of the antifouling potential of an anion exchange membrane by surface modification with a polyelectrolyte for an electrodialysis process. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Lee, L.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Chowdhury, P.; Siah, K.B.; Ng, H.Y. Electrodialysis reversal for industrial reverse osmosis brine treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dong, X.; Ban, H.; Wang, T.; Pan, W.; Yu, H.; Guo, C.; Suo, C. Technology for confecting polymer solution with desalinated produced water. SPE Prod. Oper. 2009, 24, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.H.; Yu, S.L.; Wang, B.F.; Zheng, H.F.; Ban, H.; Miao, B.L. Ultrafiltration experiment of electrodialysis pretreatment for produced water desalination. Zhongguo Shiyou Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2006, 30, 134–137. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Qiu, L.; Yu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Ye, Y.; Gu, Z.; Ren, L.; Liu, G. Effects of Alkaline Cleaning on the Conversion and Transformation of Functional Groups on Ion-Exchange Membranes in Polymer-Flooding Wastewater Treatment: Desalination Performance, Fouling Behavior, and Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14430–14440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Fernandez, P.A.; Post, J.W.; Ramdlan, M.S.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. Improving the performance of polymer-flooding produced water electrodialysis through the application of pulsed electric field. Desalination 2020, 484, 114424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnaarts, T.; Moreno, J.; Saakes, M.; de Vos, W.M.; Nijmeijer, K. Role of anion exchange membrane fouling in reverse electrodialysis using natural feed waters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Wang, L.; He, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, S. SEM-EDX studies of SiO2/PVDF membranes fouling in electrodialysis of polymer-flooding produced wastewater: Diatomite, APAM and crude oil. Desalination 2014, 347, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hashmi, A.R.; Divers, T.; Al-Maamari, R.S.; Favero, C.; Thomas, A. Improving polymer flooding efficiency in Oman oil fields. Paper SPE-179834-MS. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 21–23 March 2016; SPE: Muscat, Oman, 2016; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, M.; Kancir, E.; Øye, G. Influence of the Crude Oil and Water Compositions on the Quality of Synthetic Produced Water. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 3708–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długołecki, P.; Ogonowski, P.; Metz, S.J.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. On the resistances of membrane, diffusion boundary layer and double layer in ion exchange membrane transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długołecki, P.; Nymeijer, K.; Metz, S.; Wessling, M. Current status of ion exchange membranes for power generation from salinity gradients. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 319, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, V.; Shkorkina, I.; Mareev, S.; Pismenskaya, N.; Kononenko, N.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Transport characteristics of Fujifilm ion-exchange membranes as compared to homogeneous membranes АМХ and СМХ and to heterogeneous membranes MK-40 and MA-41. Membranes 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casademont, C.; Sistat, P.; Ruiz, B.; Pourcelly, G.; Bazinet, L. Electrodialysis of model salt solution containing whey proteins: Enhancement by pulsed electric field and modified cell configuration. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagesteijn, K.F.L.; Jiang, S.; Ladewig, B.P. A review of the synthesis and characterization of anion exchange membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 11131–11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Cassady, H.J.; Paul, D.R.; Logan, B.E.; Hickner, M.A. Specific ion effects on membrane potential and the permselectivity of ion exchange membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 21673–21681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaysom, C.; Marschall, R.; Wang, L.; Ladewig, B.P.; Lu, G.Q.M. Synthesis of composite ion-exchange membranes and their electrochemical properties for desalination applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4669–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wright, A.; Weissbach, T.; Holdcroft, S. Water permeation through anion exchange membranes. J. Power Sources 2018, 375, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, F.; Hnát, J.; Paidar, M.; Schauer, J.; Bouzek, K. Determination of the ion-exchange capacity of anion-selective membranes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5054–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, M.; Hickner, M.A.; Logan, B.E. Ionic Resistance and Permselectivity Tradeoffs in Anion Exchange Membranes. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10294–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, A.H.; Vermaas, D.A.; Veerman, J.; Saakes, M.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Post, J.W.; Nijmeijer, K. Membrane resistance: The effect of salinity gradients over a cation exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, J.W.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Buisman, C.J.N. Energy recovery from controlled mixing salt and fresh water with a reverse electrodialysis system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5785–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Fernandez, P.A.; Post, J.W.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Bruning, H. Removal of divalent ions from viscous polymer-flooding produced water and seawater via electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 589, 117251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Tanaka, N.; Nagase, M.; Yutani, K.; Kameyama, T.; Takamura, K.; Kakihana, Y. Electrodialytic properties of aromatic and aliphatic type hydrocarbon-based anion-exchange membranes with various anion-exchange groups. Polymer 2014, 55, 3951–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfferich, F. Ion Exchange; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Ghalloussi, R.; Garcia-Vasquez, W.; Chaabane, L.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Deabate, S.V.; Nevakshenova, E.; Nikonenko, V.; Grande, D. Ageing of ion-exchange membranes in electrodialysis: A structural and physicochemical investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabolotsky, V.I.; Nikonenko, V.V. Effect of structural membrane inhomogeneity on transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 79, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Nagase, M.; Higa, M. Organic fouling behavior of commercially available hydrocarbon-based anion-exchange membranes by various organic-fouling substances. Desalination 2012, 296, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus, E.J.M.; Heertjes, P.M. The poisoning of anion-selective membranes by humic substances. Desalination 1973, 12, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Ion | Concentration (mM) |
|---|---|
| Na+ | 73.92 |
| K+ | 0.72 |
| Ca2+ | 0.65 |
| Mg2+ | 0.46 |
| Cl− | 56.24 |
| HCO3− | 15.59 |
| SO42− | 2.51 |
| AEM Type. | Thickness (µm) | Area Resistance * (Ω·cm2) | Chemistry | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neosepta AMX | 135 | 2.4 | Styrene-divinyl benzene | High crosslinking, high mechanical strength | Desalination of food, concentration of inorganic salt, hardness removal |
| FujiFilm-1 | 110 | 0.9 | 3D-structure of inert polyolefin fibers filled with aliphatic polyamide [32] | Low power consumption and medium water permeating | Water softening by capacitive deionization |
| FujiFilm-10 | 130 | 1.6 | 3D-structure of inert polyolefin fibers filled with ion-exchange material [32] | Low power consumption and medium water permeating | Purifying process/wastewater/brackish water/food streams by ED |
| FujiFilm-12 | 130 | 1.7 | Same chemistry as FujiFilm-10, but different support | - | - |
| Suez AR204E | 550 | 5.5 | Copolymers of vinyl monomers | Homogeneous ion-exchange film. Long-term stability and high resistance to fouling by organic materials | Water treatment |
| Suez AR908E | 650 | 6.0 | Copolymers of vinyl monomers | Homogeneous ion-exchange film. Long-term stability and high resistance to fouling by organic materials | Wastewater treatment |
| Stage | Feed Solution (10 L Volume) | Current Density (A/m2) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Fluid Velocity (cm/s) | Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.5 M NaCl | 100 | 150 | 1.6 | Overnight |
| II | BW | 100 | 150 | 1.6 | 6 |
| III | BW + 50 mg/L HPAM | 100 | 180 | 1.9 | 24 |
| IV | BW + 100 mg/L HPAM | 100 | 210 | 2.2 | 24 |
| V | BW + 200 mg/L HPAM | 75 | 240 | 2.5 | 24 |
| VI | BW + 200 mg/L HPAM + 20 mg/L oil | 75 | 240 | 2.5 | 48 |
| VII | BW + 200 mg/L HPAM + 40 mg/L oil | 75 | 240 | 2.5 | 60 |
| VIII | BW + 200 mg/L HPAM + 40 mg/L oil | 100 | 240 | 2.5 | 14 |
| Stack | |Ū| (V) Stage A (0.5 M NaCl) |
|---|---|
| Neosepta AMX | 0.68 |
| Suez AR204E | 0.81 |
| FujiFilm-10 | 0.63 |
| Suez AR908E | 0.74 |
| FujiFilm-1 | 0.54 |
| FujiFilm-12 | 0.93 |
| AEM Type | Wet Thickness (µm) | IEC (meq/g Dry AEM) | Water Uptake (g H2O/g dry AEM) | Hydration Number λ (mmol H2O/meq) | Perm-Selectivity (−) | Area Resistance in 0.5 M NaCl (Ω.cm2) | Area Resistance in BW (Ω.cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neosepta AMX | 137 ± 2 141 [26], 138 [30] | 1.3 ± 0.03 1.4 [26], 1.3 [30] | 0.25 ± 0.02 0.23 [26], 0.16 [30] | 10.6 ± 0.9 | 0.94 0.94 [26], 0.91 [30] | 2.39 ± 0.05 2.77 [26], 2.35 [30] | 9.92 ± 0.14 |
| FujiFilm-1 | 127 ± 2 139 [25] | 1.49 ± 0.24 1.8 [26] | 0.40 ± 0.03 0.56 [26] | 17.1 ± 1.4 | 0.86 0.90 [26] | 1.24 ± 0.01 1.05 [26] | 8.77 ± 0.11 |
| FujiFilm-10 | 151 ± 3 | 2.16 ± 0.12 | 0.63 ± 0.03 | 16.3 ± 0.8 | 0.91 | 1.56 ± 0.02 | 5.54 ± 0.12 |
| FujiFilm-12 | 148 ± 13 | 1.49 ± 0.18 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 7.9 ± 0.23 | 0.90 | 5.13 ± 0.03 | 14.19 ± 0.26 |
| Suez AR204E | 616 ± 11 | 1.35 ± 0.18 2.34 a | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 14.8 ± 0.3 0.42 b | 0.90 | 4.73 ± 0.01 | 11.09 ± 0.18 |
| Suez AR908E | 655 ± 14 | 1.84 ± 0.19 1.97 a | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 16.7 ± 0.9 0.43 b | 0.92 | 4.96 ± 0.03 | 10.08 ± 0.19 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sosa-Fernández, P.A.; Post, J.W.; Nabaala, H.L.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H. Experimental Evaluation of Anion Exchange Membranes for the Desalination of (Waste) Water Produced after Polymer-Flooding. Membranes 2020, 10, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110352
Sosa-Fernández PA, Post JW, Nabaala HL, Bruning H, Rijnaarts H. Experimental Evaluation of Anion Exchange Membranes for the Desalination of (Waste) Water Produced after Polymer-Flooding. Membranes. 2020; 10(11):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110352
Chicago/Turabian StyleSosa-Fernández, Paulina A., Jan W. Post, Harrison L. Nabaala, Harry Bruning, and Huub Rijnaarts. 2020. "Experimental Evaluation of Anion Exchange Membranes for the Desalination of (Waste) Water Produced after Polymer-Flooding" Membranes 10, no. 11: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110352
APA StyleSosa-Fernández, P. A., Post, J. W., Nabaala, H. L., Bruning, H., & Rijnaarts, H. (2020). Experimental Evaluation of Anion Exchange Membranes for the Desalination of (Waste) Water Produced after Polymer-Flooding. Membranes, 10(11), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110352