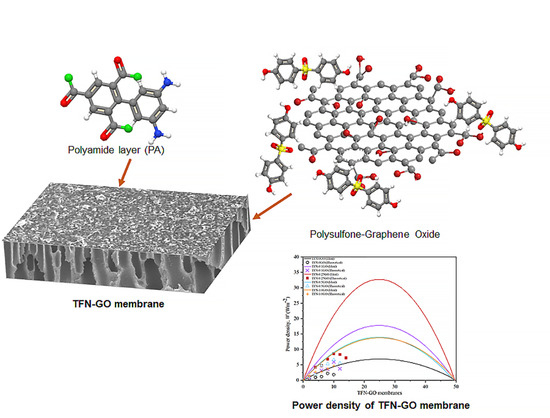
Graphene Oxide Incorporated Polysulfone Substrate for Flat Sheet Thin Film Nanocomposite Pressure Retarded Osmosis Membrane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
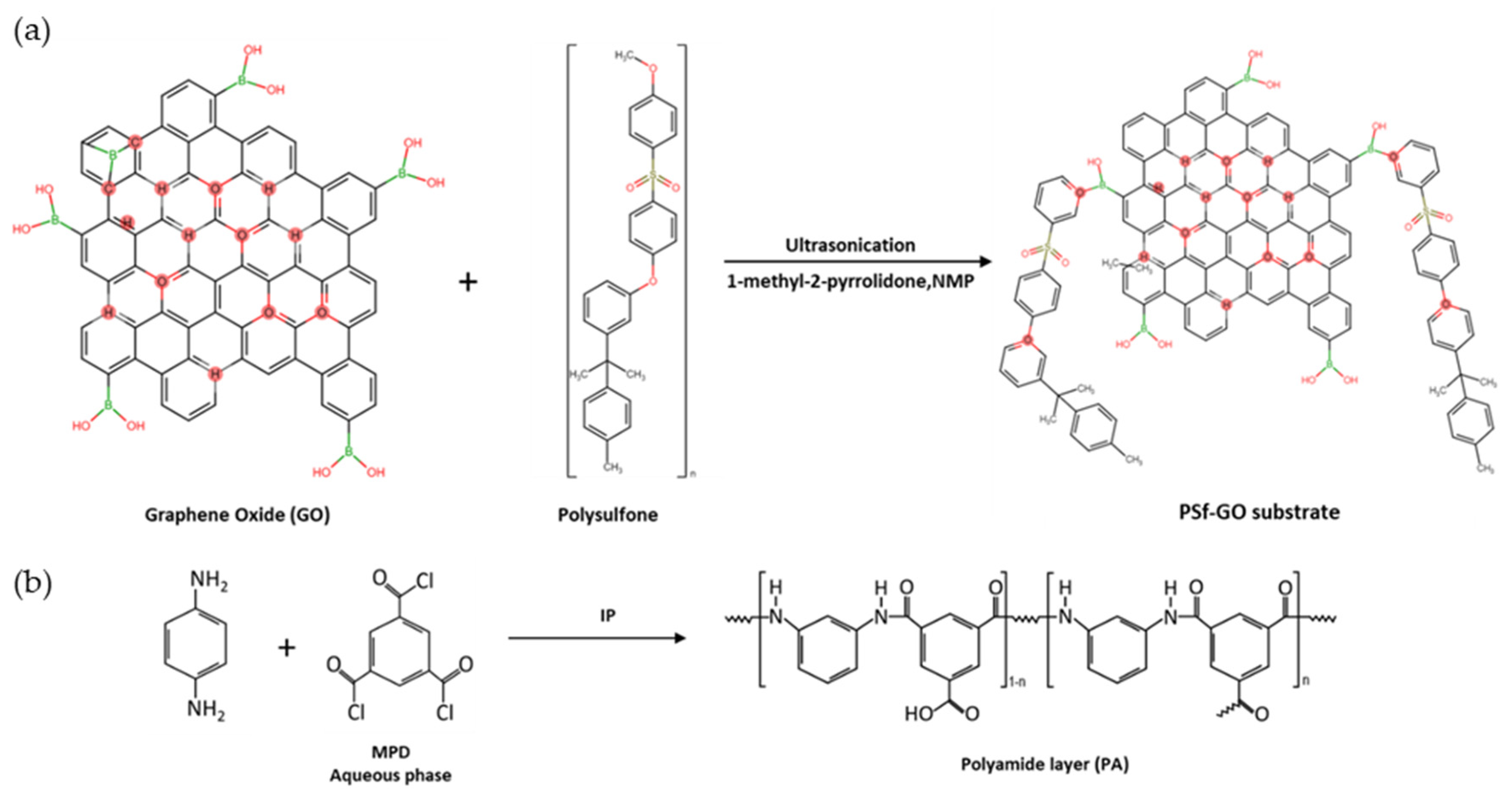
2.2. Preparation of GO
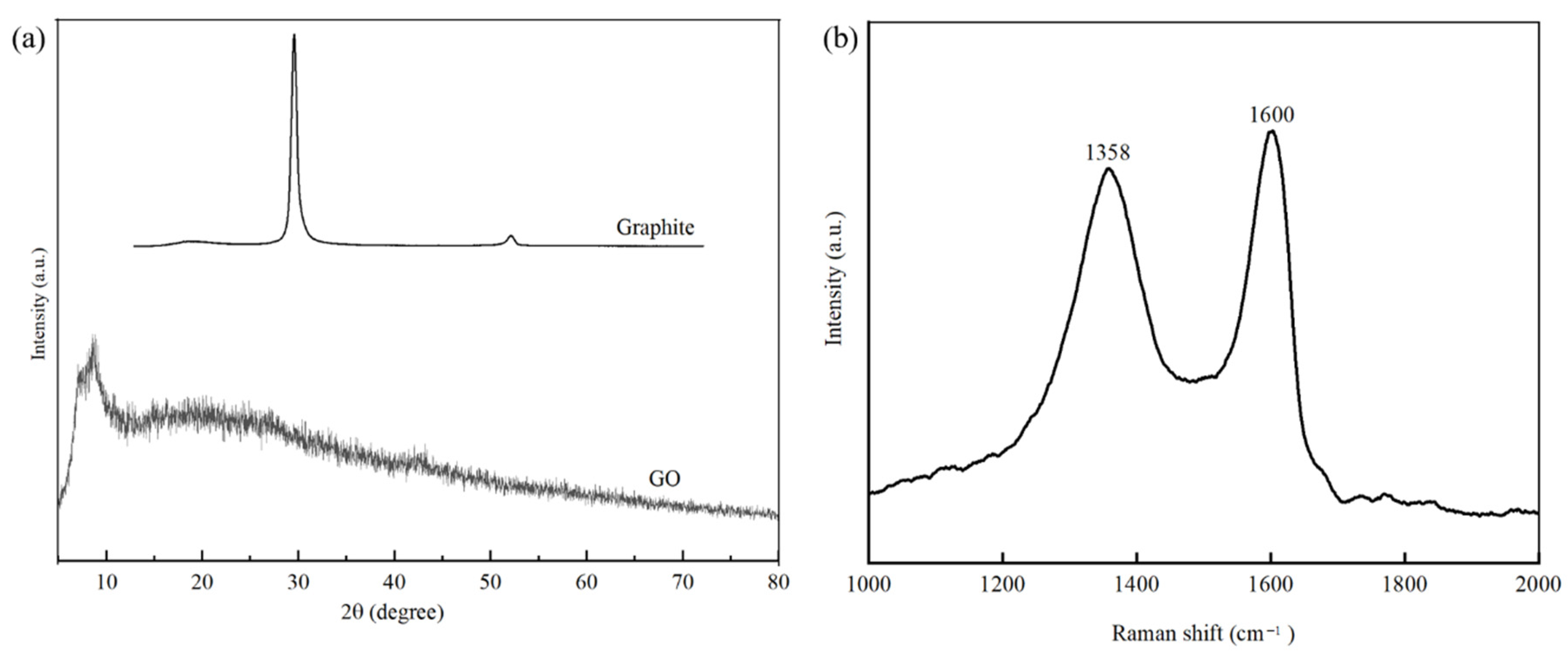
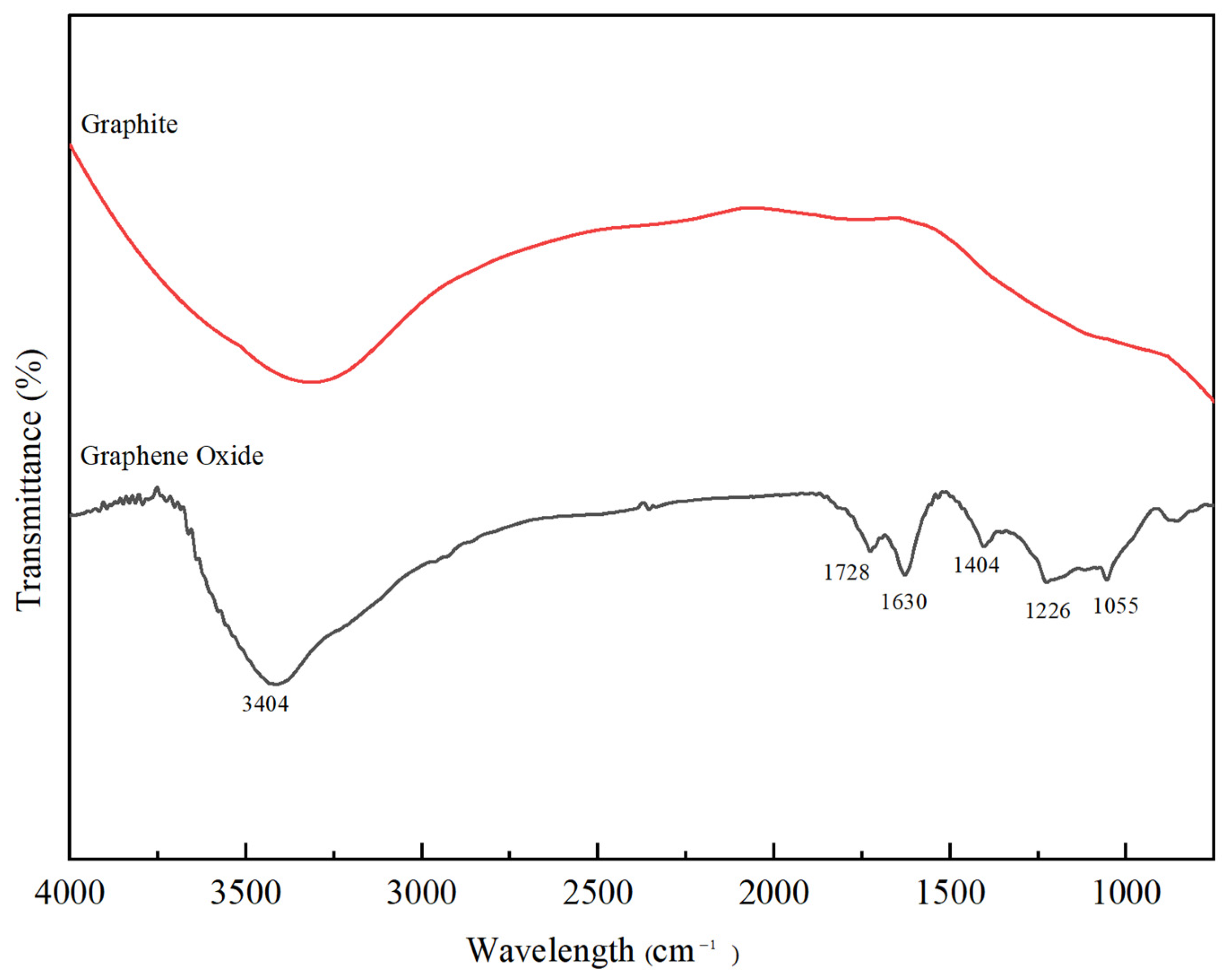
2.3. Characterisation of GO
2.4. Preparation of TFN-GO Membrane
2.5. Characterisation of the TFN-GO Membrane
2.5.1. Morphology, Surface Roughness, Functional Group and Contact Angle
2.5.2. Reverse Osmosis Test for Intrinsic Transport Properties of TFN-GO Membranes
2.5.3. Porosity and Average Pore Size of the TFN-GO Membranes
2.6. FO and PRO Membrane Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterisation of GO
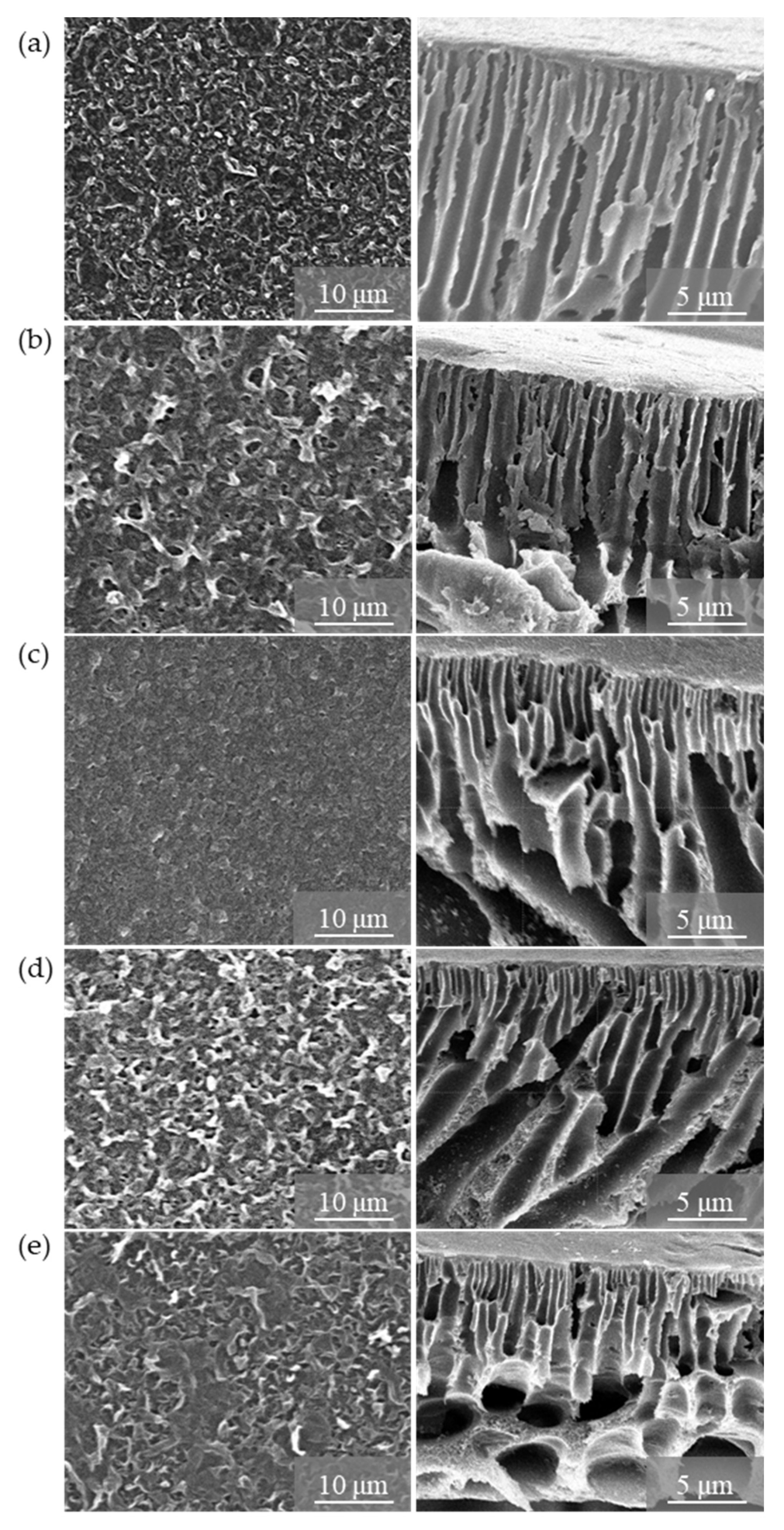
3.2. Characterisation of TFN-GO Membranes
3.3. Intrinsic Transport Properties, Porosity and Average Pore Sizes of TFN-GO Membranes
3.4. Forward Osmosis Performance
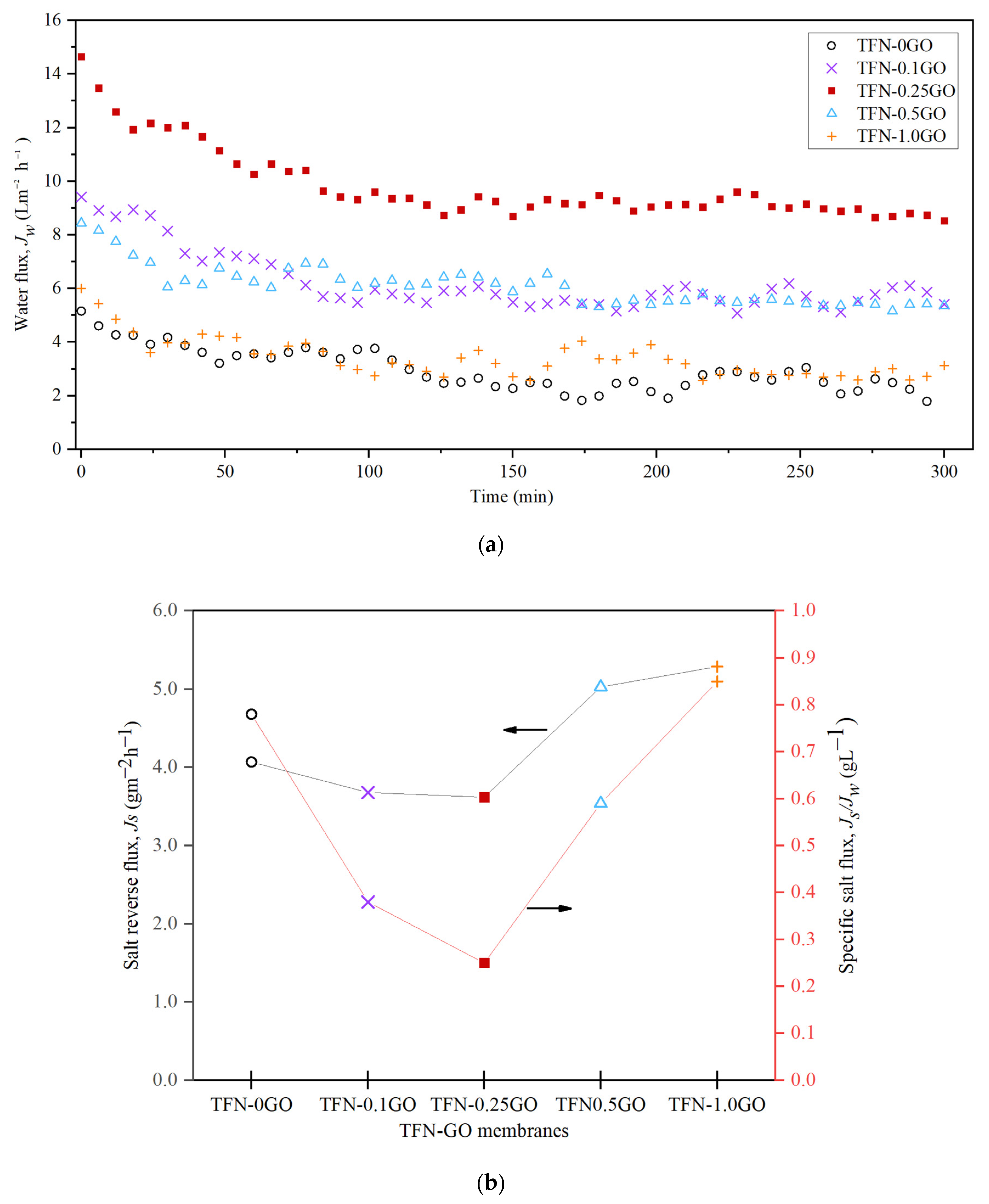
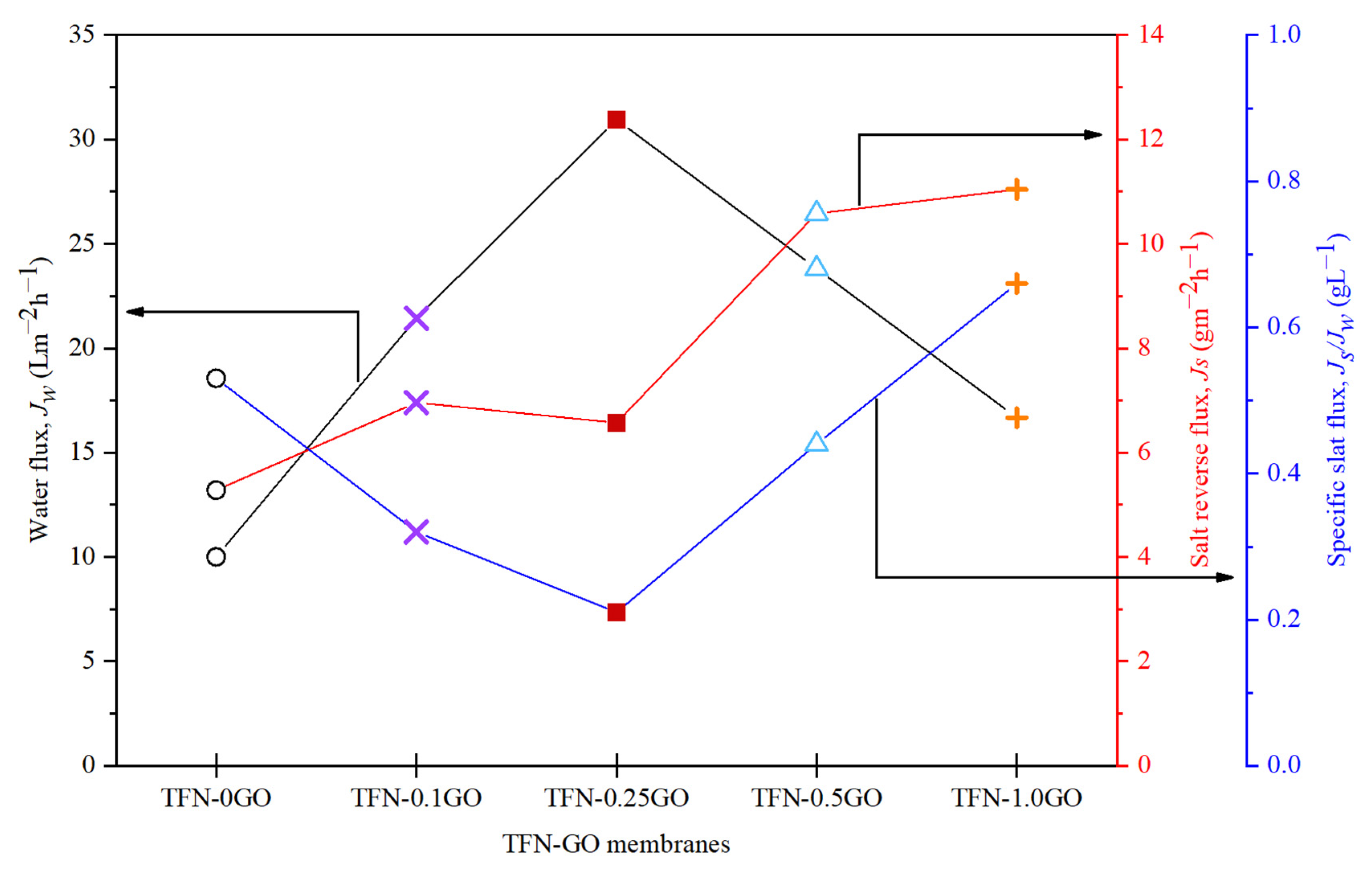
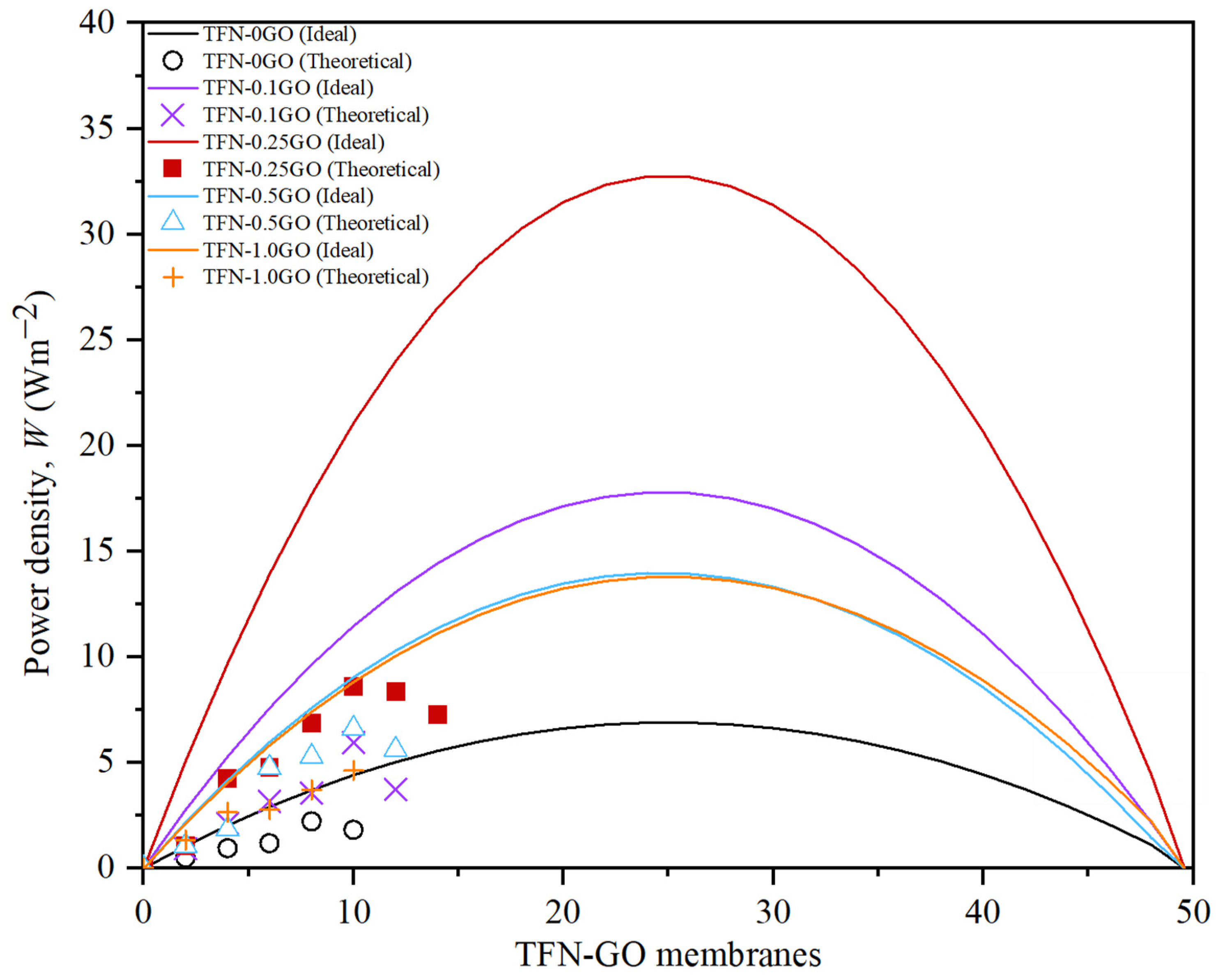
3.5. Pressure Retarded Osmosis Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skilhagen, S.E. Osmotic power—A new, renewable energy source. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 15, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.; Kim, D.I.; Hong, S. Evaluation of apparent membrane performance parameters in pressure retarded osmosis processes under varying draw pressures and with draw solutions containing organics. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Yasukawa, M.; Goda, S.; Higa, M.; Matsuyama, H. Optimization of Pressure-Retarded Osmosis with Hollow-Fiber Membrane Modules by Numerical Simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 6687–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Zhou, J.; Alanezi, A.A.; Zaragoza, G. Pressure retarded osmosis process for power generation: Feasibility, energy balance and controlling parameters. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touati, K.; Tadeo, F. Study of the Reverse Salt Diffusion in pressure retarded osmosis: Influence on concentration polarization and effect of the operating conditions. Desalination 2016, 389, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Qi, S.; Tang, C. Structural stability and mass transfer properties of pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) membrane under high operating pressures. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 488, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fu, F.; Chung, T.-S. Substrate modifications and alcohol treatment on thin film composite membranes for osmotic power, Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 87, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Wang, H.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M. A highly robust and water permeable thin film composite membranes for pressure retarded osmosis generating 26 W·m−2 at 21 bar. Desalination 2020, 483, 114409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Sultana, S.; Adhikary, S.; Rahaman, M.S. Highly effective organic draw solutions for renewable power generation by closed-loop pressure retarded osmosis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 171, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Ueyama, T.; Irie, M.; Matsuyama, K.; Tanioka, A.; Saito, K.; Kumano, A. Energy recovery by PRO in sea water desalination plant. Desalination 2016, 389, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Goh, K.; Liao, Y.; Fane, A.G. Synthesis and characterization of high-performance novel thin film nanocomposite PRO membranes with tiered nanofiber support reinforced by functionalized carbon nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 486, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.N.; McCutcheon, J.R. Nanofiber supported thin-film composite membrane for pressure-retarded osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4129–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Rahimpour, A. Synthesis of novel thin film nanocomposite (TFN) forward osmosis membranes using functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 435, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.R.; Park, M.J.; Bae, T.H.; Yang, Y.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Melamine-based covalent organic framework-incorporated thin film nanocomposite membrane for enhanced osmotic power generation. Desalination 2019, 459, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Wei, J.; Qi, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Nanocomposite substrates for controlling internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 441, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, T.M.; Peyravi, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Lau, W.J.; Rad, A.S. Impacts of zeolite nanoparticles on substrate properties of thin film nanocomposite membranes for engineered osmosis. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Lim, S.; Gonzales, R.R.; Phuntsho, S.; Han, D.S.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Adham, S.; Shon, H.K. Thin-film composite hollow fiber membranes incorporated with graphene oxide in polyethersulfone support layers for enhanced osmotic power density. Desalination 2019, 464, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Park, M.J.; Phuntsho, S.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Murphy, A.B.; Seo, D.; Shon, H. Dual-layered nanocomposite membrane incorporating graphene oxide and halloysite nanotube for high osmotic power density and fouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Lv, Y.; Dong, C.; Sreeprasad, T.S. Graphene and graphene oxide: Advanced membranes for gas separation and water purification. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, K.A.; Mansoor, B.; Mansour, A.; Khraisheh, M. Functional graphene nanosheets: The next generation membranes for water desalination. Desalination 2015, 356, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.K.; Alwarappan, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Sahajwalla, V.; Nishina, Y. Graphene oxide: The new membrane material. Appl. Mater. Today 2015, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamvura, T.A.; Simate, G.S. The Potential Application of Graphene Nanotechnology for Renewable Energy Systems; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Alam, J.; Alhoshan, M.; Dass, L.A.; Muthumareeswaran, M.R. Development of a nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane based on polyphenylsulfone blended with graphene oxide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Phuntsho, S.; He, T.; Nisola, G.M.; Tijing, L.D.; Li, X.M.; Chen, G.; Chung, W.J.; Shon, H.K. Graphene oxide incorporated polysulfone substrate for the fabrication of flat-sheet thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Xiong, S.; Wang, Y. Graphene oxide incorporated thin-film composite membranes for forward osmosis applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 143, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Mi, B. Polyamide-crosslinked graphene oxide membrane for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Kohlhaas, K.M.; Zimney, E.J.; Stach, E.A.; Piner, R.D.; Nguyen, S.B.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based composite materials. Nature 2006, 442, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, J.R.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 2011, 52, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.S.; Li, D.L.; Doong, R.A. Unveiling the hydrodechlorination of trichloroethylene by reduced graphene oxide supported bimetallic Fe/Ni nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, X. A low-cost and high-performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane based on an SPSU/PVC substrate. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Gwak, G.; Hong, S. Review on methodology for determining forward osmosis (FO) membrane characteristics: Water permeability (A), solute permeability (B), and structural parameter (S). Desalination 2017, 422, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.M.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F. Enhanced hydrophilicity and salt rejection study of graphene oxide-polysulfone mixed matrix membrane. Desalination 2013, 313, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhu, G.; Deng, B. Graphene oxide (GO) enhanced polyamide (PA) thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane for water purification. Desalination 2016, 379, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuila, T.; Bose, S.; Khanra, P.; Mishra, A.K.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Recent advances in graphene-based biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4637–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Li, S.; Liu, K.; Xu, L.; Wang, K.; Guo, W. Study on modified graphene/butyl rubber nanocomposites. I. Preparation and characterization. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriary, L.; Athawale, A.A. Graphene Oxide Synthesized by using Modified Hummers Approach. Int. J. Renew. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 2, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.J.; Tang, L.C.; Gong, L.X.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.B.; Wu, L.B.; Jiang, J.X.; Lai, G.Q. Grafting of epoxy chains onto graphene oxide for epoxy composites with improved mechanical and thermal properties. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 69, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannov, A.G.; Manakhov, A.; Shibaev, A.A.; Ukhina, A.V.; Polčák, J.; Maksimovskii, E.A. Synthesis dynamics of graphite oxide. Thermochim. Acta 2018, 663, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjani, A.; Nakhjiri, A.T.; Adimi, M.; Jirandehi, H.F.; Shirazian, S. Effect of graphene oxide on modifying polyethersulfone membrane performance and its application in wastewater treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Mi, B. Enabling graphene oxide nanosheets as water separation membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteserín, C.; Blanco, M.; Aranzabe, E.; Aranzabe, A.; Laza, J.M.; Larrañaga-Varga, A.; Vilas, J.L. Effects of graphene oxide and chemically-reduced graphene oxide on the dynamic mechanical properties of epoxy amine composites. Polymers 2017, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi-Jurkuyeh, A.; Jafari, A.J.; Kalantary, R.R.; Esrafili, A. A novel synthetic thin-film nanocomposite forward osmosis membrane modified by graphene oxide and polyethylene glycol for heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 146, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, A.; Rajabi, M.; Zahedi, P. Effect of graphene oxide content on morphology and topography of polysulfone-based mixed matrix membrane for permeability and selectivity of carbon dioxide and methane. Materwiss. Werksttech. 2020, 51, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.M.; El-Aassar, A.H.M.; Kotp, Y.H.; Shawky, H.A.; Mottaleb, M.S.A.A. Performance assessment of prepared polyamide thin film composite membrane for desalination of saline groundwater at Mersa Alam-Ras Banas, Red Sea Coast. Egypt Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 4927–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misdan, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. Formation of thin film composite nanofiltration membrane: Effect of polysulfone substrate characteristics. Desalination 2013, 329, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Chung, T.S. High performance thin film composite pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) membranes for renewable salinity-gradient energy generation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 440, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.M.; Jee, K.Y.; Lee, Y.T. Preparation and characterization of a thin-film composite reverse osmosis membrane using a polysulfone membrane including metal-organic frameworks. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Mahmood, A.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.H. Graphene oxide modified polyamide nanofiltration membrane with improved flux and antifouling properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Qiblawey, H. Novel polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes incorporating polydopamine functionalized graphene oxide with enhanced flux and fouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 2020, 118900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wang, P.; Chung, T.S. Highly robust thin-film composite pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) hollow fiber membranes with high power densities for renewable salinity-gradient energy generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8070–8077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Setiawan, L.; Chou, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, R. Identification of safe and stable operation conditions for pressure retarded osmosis with high performance hollow fiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 503, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, J.; Laflamme, C.B.; Pillay, P. Experimental investigation of pressure retarded osmosis for renewable energy conversion: Towards increased net power. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E. Power generation with pressure retarded osmosis: An experimental and theoretical investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 343, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Membrane | Water Permeability, A (Lm−2h−1bar−1) | Salt Permeability, B (Lm−2h−1) | B/A (bar) | Salt Rejection, R (%) | Structural Parameter, S (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFN-0GO | 0.40 ± 0.25 | 0.70 ± 0.02 | 1.75 | 89.2 ± 0.15 | 2712 |
| TFN-0.1GO | 1.04 ± 0.33 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 0.36 | 96.23 ± 0.08 | 1012 |
| TFN-0.25GO | 1.91 ± 0.34 | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.13 | 98.67 ± 0.13 | 726 |
| TFN-0.5GO | 0.82 ± 0.38 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0.59 | 93.96 ± 0.06 | 1027 |
| TFN-1.0GO | 0.80 ± 0.06 | 0.68 ± 0.01 | 0.85 | 91.50 ± 0.13 | 1659 |
| Membrane | Feed Solution | Draw Solution | Operation Pressure (bar) | Water Flux (Lm−2h−1) | Power Density (Wm−2) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFN-0.1GO | DI water | 1 M NaCl | 10 | 21.43 | 5.95 | Current study |
| TFN-0.25GO | DI water | 1 M NaCl | 12 | 30.95 | 8.36 | Current study |
| TFC-PAN | DI Water | 0.5 NaCl | 12.07 | 28.2 | 8 | [12] |
| Polyamide TFC-PRO | DI water | 1 M NaCl | 15 | 40 * − 90 ± 2 | 7–12 | [46] |
| Porifera, commercial FO | DI water | 58.44 g/L NaCl | 10.4 | 28.8 | 7.1 | [52] |
| HTI, commercial asymmetric CTA | DI water | 60 g/L NaCl | 9.72 | 18.76 | 5.06 | [53] |
| TFC-PEI-CNT | DI Water | 1 M NaCl | ~22 | 23.2 | 15 | [11] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Idris, S.N.A.; Jullok, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ong, H.L.; Dong, C.-D. Graphene Oxide Incorporated Polysulfone Substrate for Flat Sheet Thin Film Nanocomposite Pressure Retarded Osmosis Membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120416
Idris SNA, Jullok N, Lau WJ, Ong HL, Dong C-D. Graphene Oxide Incorporated Polysulfone Substrate for Flat Sheet Thin Film Nanocomposite Pressure Retarded Osmosis Membrane. Membranes. 2020; 10(12):416. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120416
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdris, Siti Nur Amirah, Nora Jullok, Woei Jye Lau, Hui Lin Ong, and Cheng-Di Dong. 2020. "Graphene Oxide Incorporated Polysulfone Substrate for Flat Sheet Thin Film Nanocomposite Pressure Retarded Osmosis Membrane" Membranes 10, no. 12: 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120416
APA StyleIdris, S. N. A., Jullok, N., Lau, W. J., Ong, H. L., & Dong, C.-D. (2020). Graphene Oxide Incorporated Polysulfone Substrate for Flat Sheet Thin Film Nanocomposite Pressure Retarded Osmosis Membrane. Membranes, 10(12), 416. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10120416