Using Additives for Fouling Control in a Lab-Scale MBR; Comparing the Anti-Fouling Potential of Coagulants, PAC and Bio-Film Carriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lab-Scale MBR Operation and Additives
2.2. Fouling Estimation
2.3. Determination of Effluent Quality Parameters
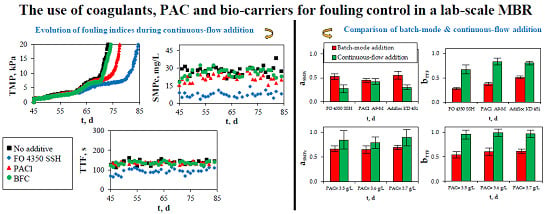
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fouling Investigation
3.1.1. Batch-Mode Addition of Coagulants and PAC
3.1.2. Continuous-Flow Addition of Coagulants, PAC, and Bio-Carriers
3.2. Effluent Quality
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| bEPS | Cound Extracellular Polymeric Substances |
| BFC | Bio-Film Carriers |
| BOD5 | Biochemical Oxygen Demand |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
| EPS | Extracellular Polymeric Substances |
| MBR | Membrane Bio-Reactor |
| MLSS | Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids |
| OECD | Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development |
| PAC | Powdered Activated Carbon |
| PLC | Programmable Logic Controller |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
| sEPS | Soluble Extracellular Polymeric Substances |
| SMP | Soluble Microbial Products |
| SMPc | Carbohydrate Fraction of Soluble Microbial Products |
| SRT | Solids Retention Time |
| TMP | Trans-Membrane Pressure |
| TN | Total Nitrogen |
| TOC | Total Organic Carbon |
| TTF | Time-To-Filter |
References
- Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Oh, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shin, H.-S.; Chae, S.-R. Fouling in membrane bioreactors: An updated review. Water Res. 2017, 114, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Meng, F.; Liao, B.-Q.; Hong, H.; Chen, J.; Gao, W. A critical review of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) in membrane bioreactors: Characteristics, roles in membrane fouling and control strategies. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. Extracellular polymeric substances. In The MBR book. Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.-H. Membrane Fouling in Membrane Bioreactor (Methods to reduce fouling). In Membrane Bioreactor Processes: Principles and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Banti, D.C.; Peleka, E.N.; Zouboulis, A.I.; Samaras, P.E. Fouling Issues in Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) for Wastewater Treatment: Major Mechanisms, Prevention and Control Strategies. Processes 2014, 2, 795–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Zhou, H.; Husain, H. Identification of wastewater sludge characteristics to predict critical flux for membrane bioreactor processes. Water Res. 2006, 40, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Zuthi, M.F.R.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Membrane fouling reduction and improvement of sludge characteristics by bioflocculant addition in submerged membrane bioreactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. The use of bio-carriers and zeolite in a lab-scale MBR for membrane fouling mitigation. Glob. NEST J. 2019, 21, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Skouteris, G.; Saroj, D.; Melidis, P.; Hai, F.I.; Ouki, S. The effect of activated carbon addition on membrane bioreactor processes for wastewater treatment and reclamation—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Gkotsis, P.K.; Zamboulis, D.X.; Mitrakas, M.G. Application of powdered activated carbon (PAC) for membrane fouling control in a pilot-scale MBR system. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Leslie, G.; Waite, T. Effect of ferric and ferrous iron addition on phosphorus removal and fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2015, 69, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shang, R.; Deng, H.; Heijman, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. Effect of PAC dosage in a pilot-scale PAC-MBR treating micro-polluted surface water. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Song, K.-G.; Ahn, K.-H. The activated sludge and microbial substances influences on membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactor: Unstirred batch cell test. Desalination 2005, 183, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamis, S.; Andreadakis, A. Fractionation of proteins and carbohydrates of extracellular polymeric substances in a membrane bioreactor system. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Activated Sludge, Respiration Inhibition Test (Carbon and Ammonium Oxidation); OECD: Paris, France, 2010; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Mitrakas, M.M.; Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Batch and continuous dosing of conventional and composite coagulation agents for fouling control in a pilot-scale MBR. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.; Rebers, P.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre, T.; Lesjean, B.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M. Monitoring of transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) and correlation with other fouling indicators. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, S.; Kraume, M. Filterability of activated sludge in membrane bioreactors. Desalination 2002, 151, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.A.; Sun, D.; Fane, A.G. Operation of membrane bioreactor with powdered activated carbon addition. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1447–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Remy, M.; Van Der Marel, P.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Rulkens, W.; Temmink, H. Low dose powdered activated carbon addition at high sludge retention times to reduce fouling in membrane bioreactors. Water Res. 2009, 43, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyawali, Y.; Balakrishnan, M. Effect of PAC addition on sludge properties in an MBR treating high strength wastewater. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1577–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA (American Public Health Association); AWWA (American Water Works Association); WEF (Water Environment Federation). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; The Water Environment Federation (WEF): Alexandria, VA, USA, 2005; p. 541. [Google Scholar]
- Kitanou, S.; Tahri, M.; Bachiri, B.; Mahi, M.; Hafsi, M.; Taky, M.; Elmidaoui, A. Comparative study of membrane bioreactor (MBR) and activated sludge processes in the treatment of Moroccan domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 78, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayi-Ucar, N.; Sarioglu, M.; Insel, G.; Cokgor, E.U.; Orhon, D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Long-term study on the impact of temperature on enhanced biological phosphorus and nitrogen removal in membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2015, 84, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Substance * | Concentration, mg/L |
|---|---|
| Peptone water | 0.4 |
| Meat extract | 0.275 |
| Urea | 0.075 |
| K2HPO4 | 0.07 |
| NaCl | 0.0175 |
| CaCl2∙2H2O | 0.01 |
| MgSO4∙7H2O | 0.005 |
| Characterization Parameter | |
| COD = 611.1 ± 26.3 mg/L | |
| BOD5 = 313.1 ± 19.2 mg/L | |
| TN = 96.7 ± 12.8 mg/L | |
| NH4+ = 59.6 ± 8.1 mg/L | |
| NO3− = 2.9 ± 0.5 mg/L | |
| pH = 7.76 ± 0.1 | |
| Conductivity = 0.983 ± 0.04 mS/cm | |
| Simple metallic salts FeCl3∙6H2O | |
| Pre-polymerized coagulation agents PACl-10 (5 wt.% Al) PACl-16 (8 wt.% Al) PACl-18 (9 wt.% Al) PACl A9-L (4.5 wt.% Al) 5% Polyamine of low MW 1 (poly-dimethylamine-co-epichlorohydrin-co-ethylenediamine) PACl A9-M (4.5 wt.% Al): 5% Polyamine of medium MW (poly-dimethylamine-co-epichlorohydrin-co-ethylenediamine) | |
| Organic Polymers (cationic polyelectrolytes) | |
| Polyacrylamides | Polymers of diallyldimethylammonium chloride |
| FO 4290 SSH (20% cationic) | Adifloc KD 550 (average M.W.) |
| FO 4350 SSH (25% cationic) | Adifloc KD 451 (high M.W.) |
| FO 4490 SSH (40% cationic) | Adifloc KD 453 (very high M.W.) |
| FO 4650 SSH (55% cationic) | Adifloc KD 553 (very high M.W.) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gkotsis, P.; Zouboulis, A.; Mitrakas, M. Using Additives for Fouling Control in a Lab-Scale MBR; Comparing the Anti-Fouling Potential of Coagulants, PAC and Bio-Film Carriers. Membranes 2020, 10, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030042
Gkotsis P, Zouboulis A, Mitrakas M. Using Additives for Fouling Control in a Lab-Scale MBR; Comparing the Anti-Fouling Potential of Coagulants, PAC and Bio-Film Carriers. Membranes. 2020; 10(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleGkotsis, Petros, Anastasios Zouboulis, and Manassis Mitrakas. 2020. "Using Additives for Fouling Control in a Lab-Scale MBR; Comparing the Anti-Fouling Potential of Coagulants, PAC and Bio-Film Carriers" Membranes 10, no. 3: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030042
APA StyleGkotsis, P., Zouboulis, A., & Mitrakas, M. (2020). Using Additives for Fouling Control in a Lab-Scale MBR; Comparing the Anti-Fouling Potential of Coagulants, PAC and Bio-Film Carriers. Membranes, 10(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030042