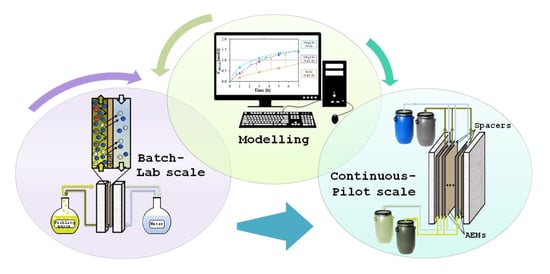
Diffusion Dialysis for Separation of Hydrochloric Acid, Iron and Zinc Ions from Highly Concentrated Pickling Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental
2.2. Batch and Continuous Diffusion Dialysis Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Zn Transport Behavior
3.2. HCl, Fe and Zn Test: Mutual Effects
4. Modelling Diffusion Dialysis with Multi-Metals Solutions
4.1. Modification in Model Constitutive Equations
4.2. Model Calibration
4.3. Model Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature and Abbreviations
| DD | - | diffusion dialysis |
| A | [] | area |
| c | molar concentration | |
| F | volumetric flow rate | |
| FeCl2 | [-] | iron chloride (II) |
| HCl | [-] | hydrochloric acid |
| molar flux | ||
| volumetric flux | ||
| i | [-] | Van´t Hoff coefficient |
| IN | [-] | initial |
| m | molality | |
| M | molecular weight | |
| diffusive permeability | ||
| osmotic permeability | ||
| R | gas constant | |
| RR | [%] | recovery ratio |
| T | [K] | temperature |
| U | overall mass transfer coefficient | |
| V | volume | |
| v | linear velocity | |
| ZnCl2 | [-] | zinc chloride |
| [-] | hydration number | |
| η | [%] | recovery efficiency |
| molar volume | ||
| [bar] | osmotic pressure | |
| [-] | osmotic coefficient | |
| Subscripts and Superscripts | ||
| ch | channel | |
| d | diffusate | |
| dr | drag | |
| exp | experimental | |
| f | feed | |
| i | ith component (HCl or FeCl2 or ZnCl2) | |
| m | membrane | |
| max | maximum | |
| mod | modelling | |
| os | osmotic | |
| r | retentate | |
| s | solvent | |
| t | time | |
| tot | total | |
| w | water | |
References
- Regel-Rosocka, M.; Cieszyńska, A.; Wiśniewski, M. Methods of Regeneration of Spent Pickling Solutions from Steel Treatment Plants. Polish J. Chem. Technol. 2007, 9, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, H.M. Standard Handbook of Hazardous Waste Treatment and Disposal, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, G.; White, R. Toward Cleaner Production of Hot Dip Galvanizing Industry in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regel-Rosocka, M. A Review on Methods of Regeneration of Spent Pickling Solutions from Steel Processing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bascone, D.; Cipollina, A.; Morreale, M.; Randazzo, S.; Santoro, F.; Micale, G. Simulation of a Regeneration Plant for Spent Pickling Solutions via Spray Roasting. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 23405–23419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladnig, W. New Development of Acid Regeneration in Steel Pickling Plants. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2008, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K.K. An Overview of the Recovery of Acid from Spent Acidic Solutions from Steel and Electroplating Industries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csicsovszki, G.; Kékesi, T.; Török, T.I. Selective Recovery of Zn and Fe from Spent Pickling Solutions by the Combination of Anion Exchange and Membrane Electrowinning Techniques Ga. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Román, M.F.; Ortiz-Gándara, I.; Bringas, E.; Ibañez, R.; Ortiz, I. Membrane Selective Recovery of HCl, Zinc and Iron from Simulated Mining Effluents. Desalination 2018, 440, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, Y.; Xu, T. Diffusion Dialysis Processes of Inorganic Acids and Their Salts: The Permeability of Different Acidic Anions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 78, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lu, S.; Fu, D. Recovery of Hydrochloric Acid from the Waste Acid Solution by Diffusion Dialysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strathmann, H. Ion Exchange Membrane Separation Processes. In Membrane Science and Technology Series; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 9, pp. 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Black, J.R.; Kavner, A.; Schauble, E.A. Calculation of Equilibrium Stable Isotope Partition Function Ratios for Aqueous Zinc Complexes and Metallic Zinc. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wu, C.; Wu, Y.; Xu, T. Diffusion Dialysis of Hydrochloric Acid with Their Salts: Effect of Co-Existence Metal Ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatý, Z.; Bendová, H. Separation of HCl + FeCl2 Mixture by Anion-Exchange Membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatý, Z.; Žáková, A. Competitive Transport of Hydrochloric Acid and Zinc Chloride through Polymeric Anion-Exchange Membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouad, F.; Lindheimer, A.; Gavach, C. Transport Properties of Electrodialysis Membranes in the Presence of Zn2+ complexes with Cl−. J. Memb. Sci. 1997, 123, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouad, F.; Lindheimer, A.; Chaouki, M.; Gavach, C. Loss of Permselectivity of Anion Exchange Membranes in Contact with Zinc Chloride Complexes. Desalination 1999, 121, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung Oh, S.; Moon, S.H.; Davis, T. Effects of Metal Ions on Diffusion Dialysis of Inorganic Acids. J. Memb. Sci. 2000, 169, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueccia, R.; Randazzo, S.; Chillura Martino, D.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G. Experimental Investigation and Modeling of Diffusion Dialysis for HCl Recovery from Waste Pickling Solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culcasi, A.; Gueccia, R.; Randazzo, S.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G. Design of a Novel Membrane-Integrated Waste Acid Recovery Process from Pickling Solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gauwbergen, D.; Baeyens, J.; Creemers, C. Modeling Osmotic Pressures for Aqueous Solutions for 2-1 and 2-2 Electrolytes. Desalination 1997, 109, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitzer, K.S.; Kim, J.J. Thermodynamics of Electrolytes. IV. Activity and Osmotic Coefficients for Mixed Electrolytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 5701–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tialowska-mocharla, H.; Manohar, S. Activity Coefficient Measurements of the System HCI-ZnCl2-H2O at 25 and 35 °C. System 1992, 21, 545–546. [Google Scholar]
- Marion, G.M.; Catling, D.C.; Kargel, J.S. Modeling Aqueous Ferrous Iron Chemistry at Low Temperatures with Application to Mars. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 4251–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A. MEMBRANE SEPARATIONS/Diffusion Dialysis. In Encyclopedia of Separation Science, 1st ed.; Wilson, I.D., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 1693–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann, H. Membrane Separation Processes: Current Relevance and Future Opportunities. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 ) 5 (
) 5 ( ), 10 (
), 10 ( ) and 20 g/L (
) and 20 g/L ( ). Initial acid concentration: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) (empty symbols) and 73 g/L (2 mol/L) (solid symbols). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) HCl solution (empty symbols) and deionized water (solid symbol). Batch experimental-set-up.
). Initial acid concentration: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) (empty symbols) and 73 g/L (2 mol/L) (solid symbols). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) HCl solution (empty symbols) and deionized water (solid symbol). Batch experimental-set-up.
 ) 5 (
) 5 ( ), 10 (
), 10 ( ) and 20 g/L (
) and 20 g/L ( ). Initial acid concentration: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) (empty symbols) and 73 g/L (2 mol/L) (solid symbols). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) HCl solution (empty symbols) and deionized water (solid symbol). Batch experimental-set-up.
). Initial acid concentration: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) (empty symbols) and 73 g/L (2 mol/L) (solid symbols). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: 3.6 g/L (0.1 mol/L) HCl solution (empty symbols) and deionized water (solid symbol). Batch experimental-set-up.
 ); 5 (
); 5 ( ), 10 (
), 10 ( ) and 20 (
) and 20 ( ) g/L. Initial HCl concentration: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.
) g/L. Initial HCl concentration: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.
 ); 5 (
); 5 ( ), 10 (
), 10 ( ) and 20 (
) and 20 ( ) g/L. Initial HCl concentration: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.
) g/L. Initial HCl concentration: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.
 ,
,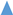 ) and 10 (
) and 10 (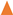 ,
, ) g/L. Initial Fe conc.: 0 (
) g/L. Initial Fe conc.: 0 ( ,
,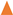 ); 100 (
); 100 (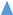 ,
, ) g/L. Initial acid conc.: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + FeCl2 + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.
) g/L. Initial acid conc.: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + FeCl2 + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.
 ,
,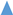 ) and 10 (
) and 10 (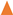 ,
, ) g/L. Initial Fe conc.: 0 (
) g/L. Initial Fe conc.: 0 ( ,
,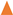 ); 100 (
); 100 (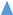 ,
, ) g/L. Initial acid conc.: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + FeCl2 + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.
) g/L. Initial acid conc.: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Solutions flow rate fixed at 48 mL/min. Feed solution: HCl + FeCl2 + ZnCl2. Inlet diffusate: deionized water. Batch experimental-set-up.

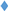 ,
,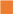 ) and 10 (
) and 10 ( ,
,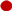 ) g/L. Initial Fe concentrations: 100 (
) g/L. Initial Fe concentrations: 100 ( ,
, ) and 150 (
) and 150 (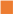 ,
, ) g/L. Initial acid concentrations: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Flow rate: 48 mL/min. Feed: HCl, FeCl2, ZnCl2 solution. Diffusate IN: deionized water. Theoretical curves (—) obtained by using the model.
) g/L. Initial acid concentrations: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Flow rate: 48 mL/min. Feed: HCl, FeCl2, ZnCl2 solution. Diffusate IN: deionized water. Theoretical curves (—) obtained by using the model.
 ,
, ) and 10 (
) and 10 ( ,
, ) g/L. Initial Fe concentrations: 100 (
) g/L. Initial Fe concentrations: 100 ( ,
, ) and 150 (
) and 150 ( ,
, ) g/L. Initial acid concentrations: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Flow rate: 48 mL/min. Feed: HCl, FeCl2, ZnCl2 solution. Diffusate IN: deionized water. Theoretical curves (—) obtained by using the model.
) g/L. Initial acid concentrations: 73 g/L (2 mol/L). Flow rate: 48 mL/min. Feed: HCl, FeCl2, ZnCl2 solution. Diffusate IN: deionized water. Theoretical curves (—) obtained by using the model.

 ,
, ) and 10 (
) and 10 ( ,
,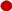 ) g/L, and Fe at 100 (
) g/L, and Fe at 100 (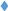 ,
, ) and 150 (
) and 150 (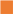 ,
,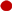 ) g/L. (c)&(d) species concentration and flow rates in retentate and diffusate streams for tests 1 (
) g/L. (c)&(d) species concentration and flow rates in retentate and diffusate streams for tests 1 ( ) 2 (
) 2 ( ), 3 (
), 3 ( ), and 4 (
), and 4 ( ) named in Table 2.
) named in Table 2.
 ,
, ) and 10 (
) and 10 ( ,
, ) g/L, and Fe at 100 (
) g/L, and Fe at 100 ( ,
, ) and 150 (
) and 150 ( ,
, ) g/L. (c)&(d) species concentration and flow rates in retentate and diffusate streams for tests 1 (
) g/L. (c)&(d) species concentration and flow rates in retentate and diffusate streams for tests 1 ( ) 2 (
) 2 ( ), 3 (
), 3 ( ), and 4 (
), and 4 ( ) named in Table 2.
) named in Table 2.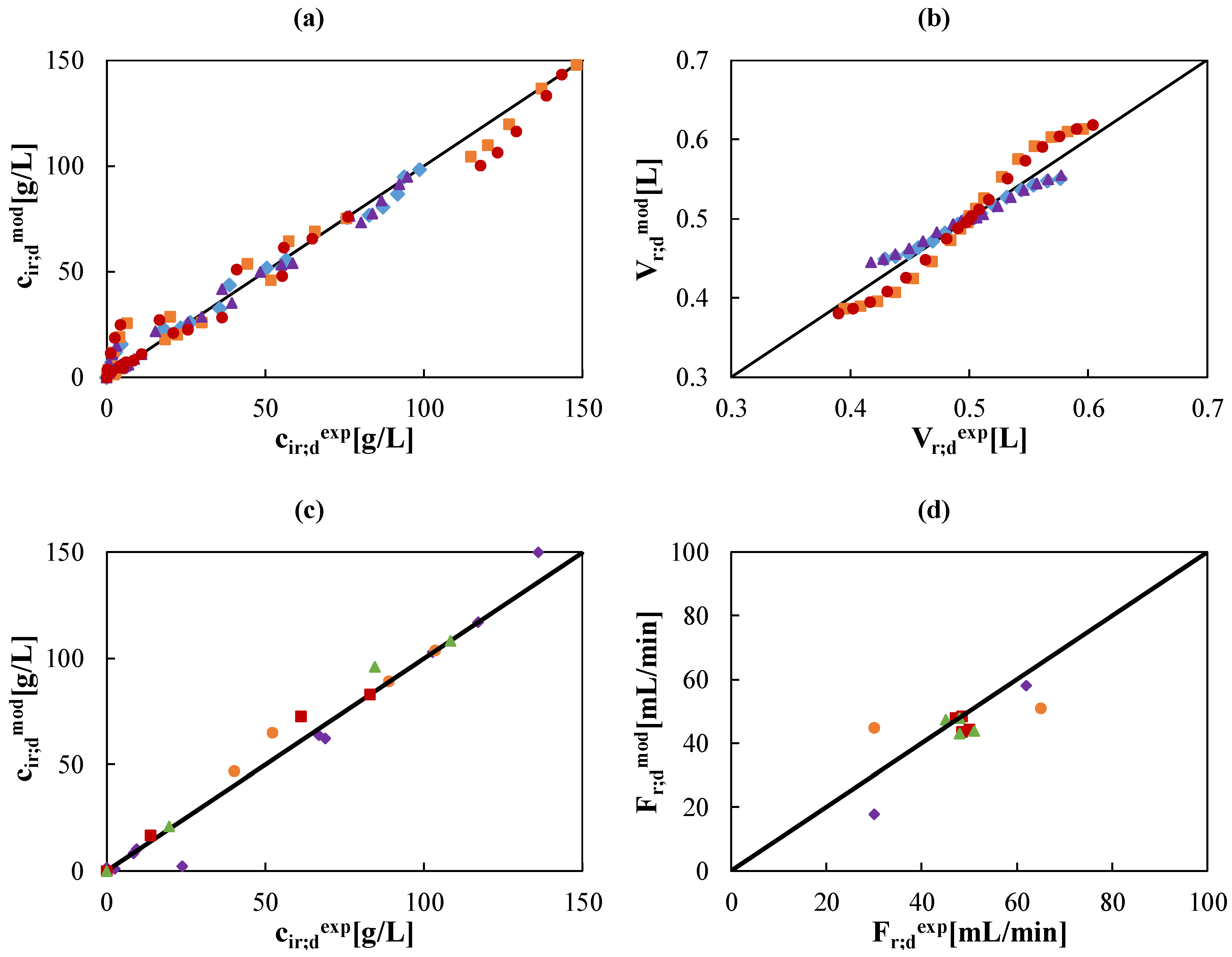
| Component | Unit | Mean |
|---|---|---|
| Free acidity (HCl) | g/L | 20–150 |
| Fe | g/L | 50–150 |
| Zn | g/L | 1–20 |
| № Test Identification | № of Repetitions | Flowrate mL/min | CHCl,f g/L | CFe,f g/L | CZn,f g/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 48 | 73 | - | - |
| 2 | 3 | 100 | - | - | |
| 3 | 1 | 100 | 117 | - | |
| 4 | 3 | 100 | 117 | 8 |
| № Test Identification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 76 | - | - |
| 2 | 80 (± 1.8%) | - | - |
| 3 | 87 | 35 | - |
| 4 | 79 (± 6.0%) | 30 (± 7.8%) | 60 (± 7.7%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gueccia, R.; Aguirre, A.R.; Randazzo, S.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G. Diffusion Dialysis for Separation of Hydrochloric Acid, Iron and Zinc Ions from Highly Concentrated Pickling Solutions. Membranes 2020, 10, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060129
Gueccia R, Aguirre AR, Randazzo S, Cipollina A, Micale G. Diffusion Dialysis for Separation of Hydrochloric Acid, Iron and Zinc Ions from Highly Concentrated Pickling Solutions. Membranes. 2020; 10(6):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060129
Chicago/Turabian StyleGueccia, Rosa, Alba Ruiz Aguirre, Serena Randazzo, Andrea Cipollina, and Giorgio Micale. 2020. "Diffusion Dialysis for Separation of Hydrochloric Acid, Iron and Zinc Ions from Highly Concentrated Pickling Solutions" Membranes 10, no. 6: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060129
APA StyleGueccia, R., Aguirre, A. R., Randazzo, S., Cipollina, A., & Micale, G. (2020). Diffusion Dialysis for Separation of Hydrochloric Acid, Iron and Zinc Ions from Highly Concentrated Pickling Solutions. Membranes, 10(6), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060129