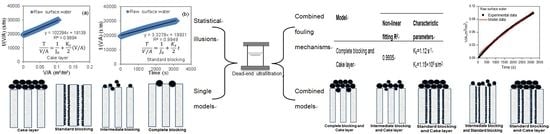
Fouling Mechanisms Analysis via Combined Fouling Models for Surface Water Ultrafiltration Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Surface Water
2.2. Coagulation Pretreatment
2.3. UF Experiments
2.4. Water Quality Analysis
2.5. Membrane Fouling Mechanism Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rejection Performance by UF for the Surface Water Treatment
3.2. Membrane Fouling of UF for the Surface Water Treatment
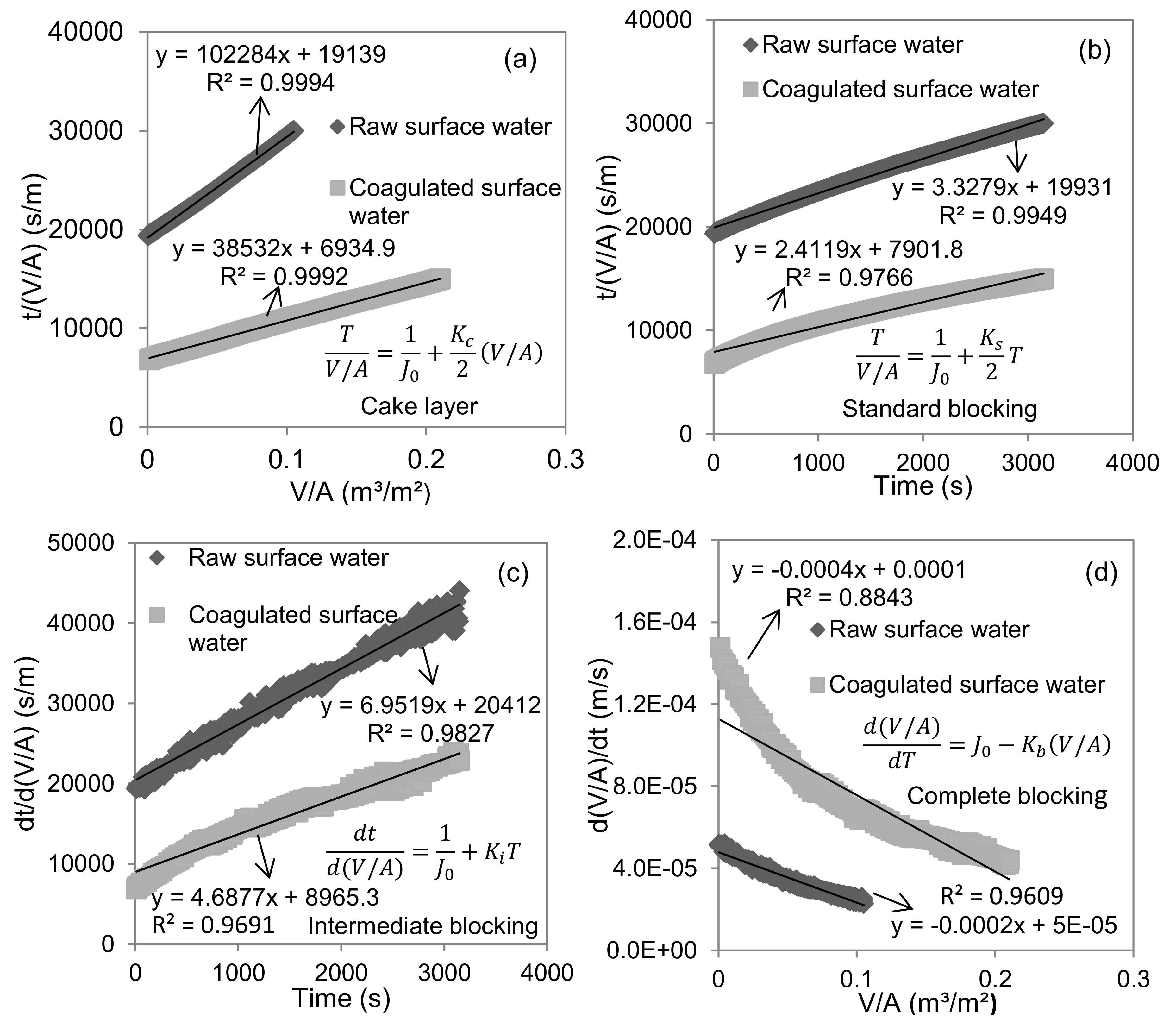
3.3. Analysis of UF Membrane Fouling Mechanisms Based on Single Models
3.4. Analysis of UF Membrane Fouling Mechanisms Based on Combined Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bei, E.; Wu, X.M.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.J. A Tale of Two Water Supplies in China: Finding Practical Solutions to Urban and Rural Water Supply Problems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Liang, H.; Ma, J.; Han, M.; Chen, Z.L.; Han, Z.S.; Li, G.B. Membrane fouling control in ultrafiltration technology for drinking water production: A review. Desalination 2011, 272, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritani, E. A Review on Modeling of Pore-Blocking Behaviors of Membranes During Pressurized Membrane Filtration. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, P.H.; Brede′e, H.L. Principles of the mathematical treatment of constant-pressure filtration. J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 1936, 55T, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, H. Structure and performance of filter media. II. Performance of filter media in liquid service. Aiche J. 1956, 2, 316–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermia, J. Constant pressure blocking filtration laws–application to power-law non-Newtonian fluids. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1982, 60, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, W.R.; Hall, N.J. Properties of microfiltration membranes: Mechanisms of flux loss in the recovery of an enzyme. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 46, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Amy, G.; Yoon, Y.; Sohn, J. Predictive models and factors affecting natural organic matter (NOM) rejection and flux decline in ultrafiltration (UF) membranes. Desalination 2002, 142, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.C.; Zydney, A.L. A Combined Pore Blockage and Cake Filtration Model for Protein Fouling during Microfiltration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, G.; LaCasse, D.; Kuriyel, R. Combined models of membrane fouling: Development and application to microfiltration and ultrafiltration of biological fluids. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 277, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Young, T.A.; Jacangelo, J.G. Unified Membrane Fouling Index for Low Pressure Membrane Filtration of Natural Waters: Principles and Methodology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.H.; Laborie, S.; Ben Aim, R.; Amy, G. Full Utilization of Silt Density Index (SDI) Measurements for Seawater Pre-Treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 405, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qu, F.S.; Liang, H.; Bruggen, B.V.D.; Cheng, X.X.; Yu, H.R.; Xu, G.R.; Li, G.B. Microcystis aeruginosa-laden surface water treatment using ultrafiltration: Membrane fouling, cell integrity and algogenic organic matter removal. Water Res. 2017, 112, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.H.; Sun, J.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.Y.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Waite, T.D. An extended standard blocking filtration law for exploring membrane pore internal fouling due to rate-determining adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schippers, J.; Verdouw, J. The modified fouling index, a method of determining the fouling characteristics of water. Desalination 1980, 32, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM. D8002-15, Standard Test. Method for Modified Fouling Index (MFI-0.45) of Water; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.X.; Ju, Y.G.; Lee, H.; Hong, S. Fouling potential evaluation by cake fouling index: Theoretical development, measurements, and its implications for fouling mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerlage, S.F.E.; Kennedy, M.D.; Aniye, M.P.; Abogream, E.M.; EI-Hodali, D.E.Y.; Tarawneh, Z.S.; Schippers, J.C. Modified Fouling Index ultrafiltration to compare pretreatment processes of reverse osmosis feedwater. Desalination 2000, 131, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, L.N.; Ye, Y.; Chen, V.; Fane, A.G. Crossflow Sampler Modified Fouling Index Ultrafiltration (C FS-MFIUF)—An alternative Fouling Index. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Qu, F.S.; Yu, H.R.; Tian, J.; Chen, W.; Liang, H.; Li, G.B.; Bruggen, B.V.D. Membrane fouling and rejection of organics during algae-laden water treatment using ultrafiltration: A comparison between in-situ oxidation with Fe(II)/persulfate and ozone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Gao, B.Y.; Cheng, D.D.; Yue, Q.Y. Evaluation of dynamic membrane formation and filtration models at constant pressure in a combined coagulation/dynamic membrane process in treating polluted river water. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2013, 13, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, C.; Tong, T.; Zhao, K.; Qu, J.; Liu, H.; Elimelech, M. Performance and Mechanisms of Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling Mitigation by Coupling Coagulation and Applied Electric Field in a Novel Electrocoagulation Membrane Reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 8544–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, G.; Hong, H.; Sun, T.; Liao, B.Q.; Lin, H. Membrane fouling by alginate in polyaluminum chloride (PACl) coagulation/microfiltration process: Molecular insights. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Jeong, S.H.; Im, S.J.; Jang, A. High turbidity water treatment by ceramic microfiltration membrane: Fouling identification and process optimization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Charfi, A.; Lee, J.; Park, B.; Jang, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J. Combined effect of periodic backwashing and forward flushing on fouling mitigation in a pressurized UF membrane process for high turbid surface water treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 101, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.H.; Amy, G. Membrane Fouling Potential of Secondary Effluent Organic Matter (EfOM) from Conventional Activated Sludge Process. J. Membr. Sep. Technol. 2012, 1, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbaton-Baguena, M.J.; Alvarez-Blanco, S.; Vincent-Vela, M.C. Fouling mechanisms of ultrafiltration membranes fouled with whey model solutions. Desalination 2015, 360, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gao, B.; Wang, W.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Y. Floc properties and membrane fouling in coagulation/ultrafiltration process for the treatment of Xiaoqing River: The role of polymeric aluminum-polymer dual-coagulants. Chemosphere 2020, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.J.; Liang, H.; Xu, S.Q.; Chuah, C.J.; Luo, X.S.; Wang, T.Y. Organic matter removal and membrane fouling mitigation during algae-rich surface water treatment by powdered activated carbon adsorption pretreatment: Enhanced by UV and UV/chlorine oxidation. Water Res. 2019, 159, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model | Equation * | Characteristic Parameters | Schematic Diagram | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cake layer | Kc (s/m2) |  | [4,6] | |
| Complete blocking | Kb (s−1) |  | [4,6] | |
| Intermediate blocking | Ki (m−1) |  | [4,6] | |
| Standard blocking | Ks (m−1) |  | [4,6] | |
| Complete blocking and Cake layer | Kc (s/m2), Kb (s−1) |  | [10] | |
| Intermediate blocking and Cake layer | Kc (s/m2), Ki (m−1) |  | [10] | |
| Complete blocking and Standard blocking | Kb (s−1), Ks (m−1) |  | [10] | |
| Intermediate blocking and Standard blocking | Ki (m−1), Ks (m−1) |  | [10] | |
| Standard blocking and Cake layer | Kc (s/m2), Ks (m−1) |  | [10] |
| Model | Raw Surface Water | Coagulated Surface Water | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Linear/Linear Fitting R2 | Characteristic Parameters | Non-Linear/Linear Fitting R2 | Characteristic Parameters | |
| Complete blocking and Cake layer | 0.9935 | Kb = 1.12 s−1 Kc = 1.15 × 106 s/m2 | 0.9948 | Kb = 0.35 s−1 Kc = 1.94 × 105 s/m2 |
| Intermediate blocking and Cake layer | 0.9423 | Ki = 2.17 × 10−6 m−1 * Kc = 5.90 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9908 | Ki = 2.83 × 10−7 m−1* Kc = 1.08 × 105 s/m2 |
| Standard blocking and Cake layer | Fitting failed due to no convergence | Fitting failed due to no convergence | ||
| Complete blocking and Standard blocking | 0.6428 | Kb = 1.64 × 10−5 s−1 * Ks = 22.90 m−1 * | 0.9102 | Kb = 2.51 × 10−6 s−1 * Ks = 28.15 m−1 * |
| Intermediate blocking and Standard blocking | 0.7989 | Ki = 39.77 m−1 Ks = 1.77 m−1 * | 0.9503 | Ki = 11.65 m−1 Ks = 0.84 m−1 * |
| Cake layer | 0.9994 | Kc = 5.1 × 104 s/m2 | 0.9992 | Kc = 1.93 × 104 s/m2 |
| Intermediate blocking | 0.9827 | Ki = 6.95 m−1 | 0.9691 | Ki = 4.69 m−1 |
| Complete blocking | 0.9609 | Kb = 2 × 10−4 s−1 | 0.8843 | Kb = 4 × 10−4 s−1 |
| Standard blocking | 0.9949 | Ks = 1.66 m−1 | 0.9766 | Ks = 1.21 m−1 |
| Filtration Cycle | Raw Surface Water | Coagulated Surface Water | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic Parameter | R2 | KcJ0/(Kb/J0) | Characteristic Parameter | R2 | KcJ0/(Kb/J0) | |
| 1st | Kb = 0.27 s−1 Kc = 1.78 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9931 | 0.033 | Kb = 0.24 s−1 Kc = 9.70 × 104 s/m2 | 0.9938 | 0.021 |
| 2nd | Kb = 1.12 s−1 Kc = 1.15 × 106 s/m2 | 0.9945 | 0.052 | Kb = 0.35 s−1 Kc = 1.94 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9952 | 0.027 |
| 3rd | Kb = 0.61 s−1 Kc = 5.55 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9949 | 0.046 | Kb = 0.29 s−1 Kc = 1.55 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9954 | 0.027 |
| 4th | Kb = 0.71 s−1 Kc = 6.83 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9948 | 0.049 | Kb = 0.56 s−1 Kc = 4.10 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9953 | 0.037 |
| 5th | Kb = 0.65 s−1 Kc = 6.37 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9951 | 0.049 | Kb = 0.82 s−1 Kc = 4.93 × 105 s/m2 | 0.9951 | 0.031 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, B.; Gu, H.; Xiao, K.; Qu, F.; Yu, H.; Wei, C. Fouling Mechanisms Analysis via Combined Fouling Models for Surface Water Ultrafiltration Process. Membranes 2020, 10, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070149
Huang B, Gu H, Xiao K, Qu F, Yu H, Wei C. Fouling Mechanisms Analysis via Combined Fouling Models for Surface Water Ultrafiltration Process. Membranes. 2020; 10(7):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070149
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Bin, Hangkun Gu, Kang Xiao, Fangshu Qu, Huarong Yu, and Chunhai Wei. 2020. "Fouling Mechanisms Analysis via Combined Fouling Models for Surface Water Ultrafiltration Process" Membranes 10, no. 7: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070149
APA StyleHuang, B., Gu, H., Xiao, K., Qu, F., Yu, H., & Wei, C. (2020). Fouling Mechanisms Analysis via Combined Fouling Models for Surface Water Ultrafiltration Process. Membranes, 10(7), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10070149