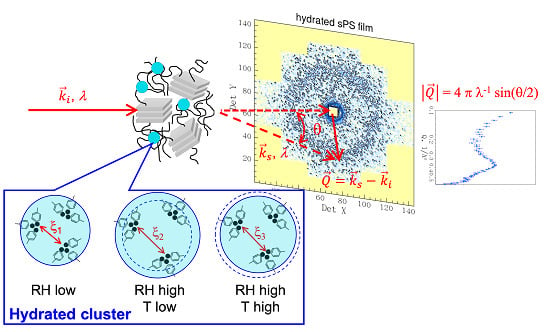
The Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Microstructure of Sulfonated Syndiotactic–polystyrene Ionic Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
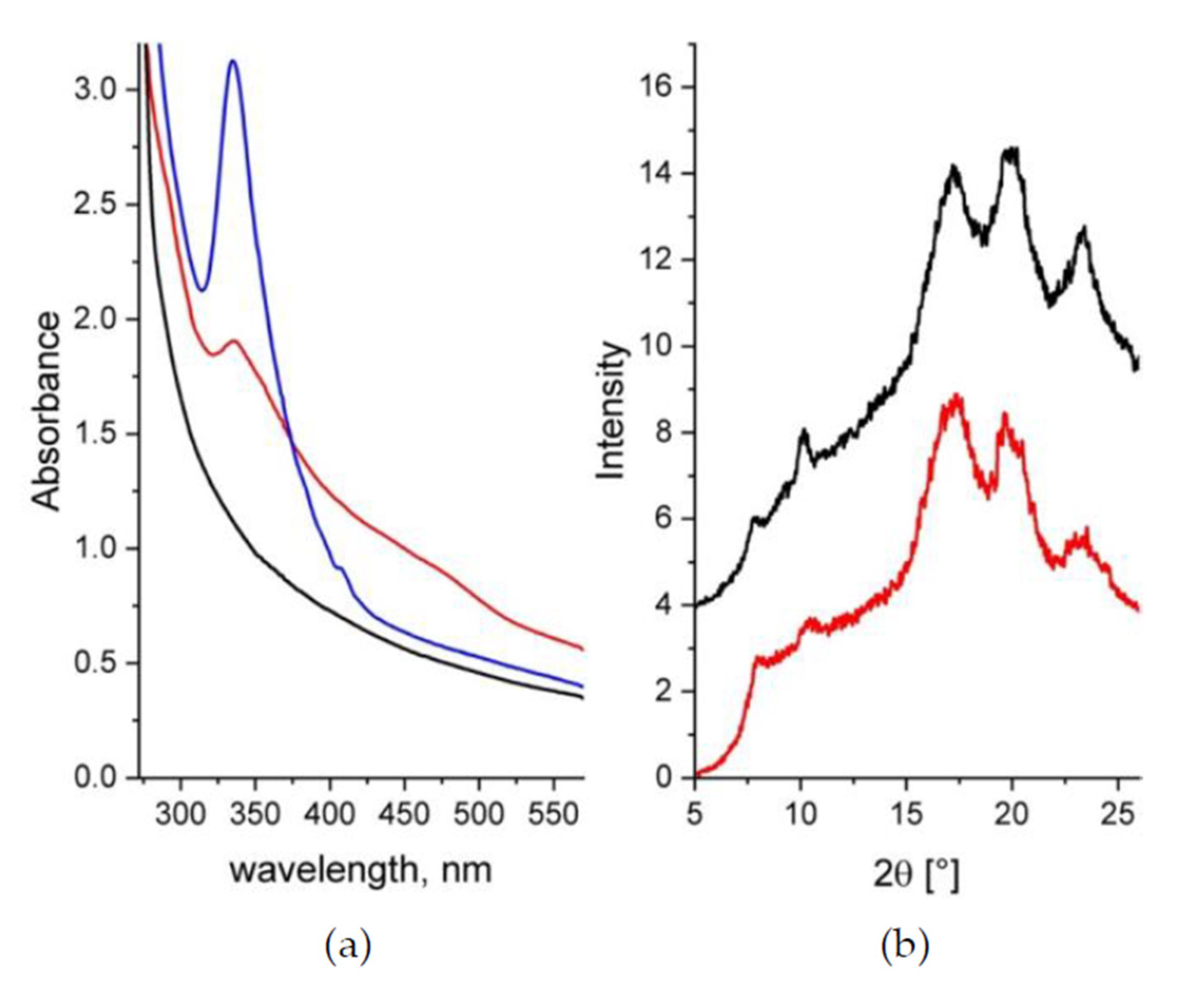
3.1. Composition Characterization
3.2. Water Uptake and Conductivity
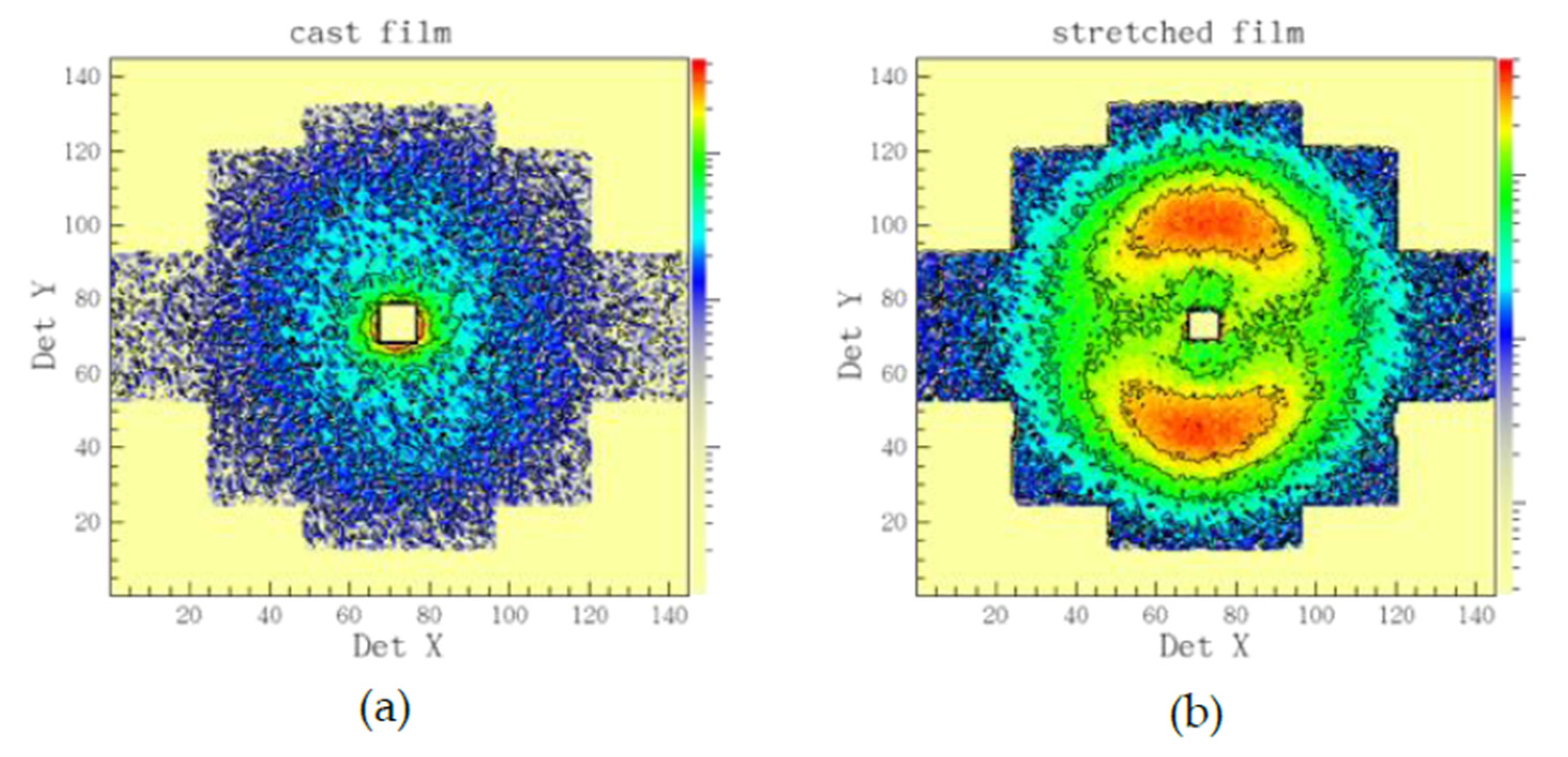
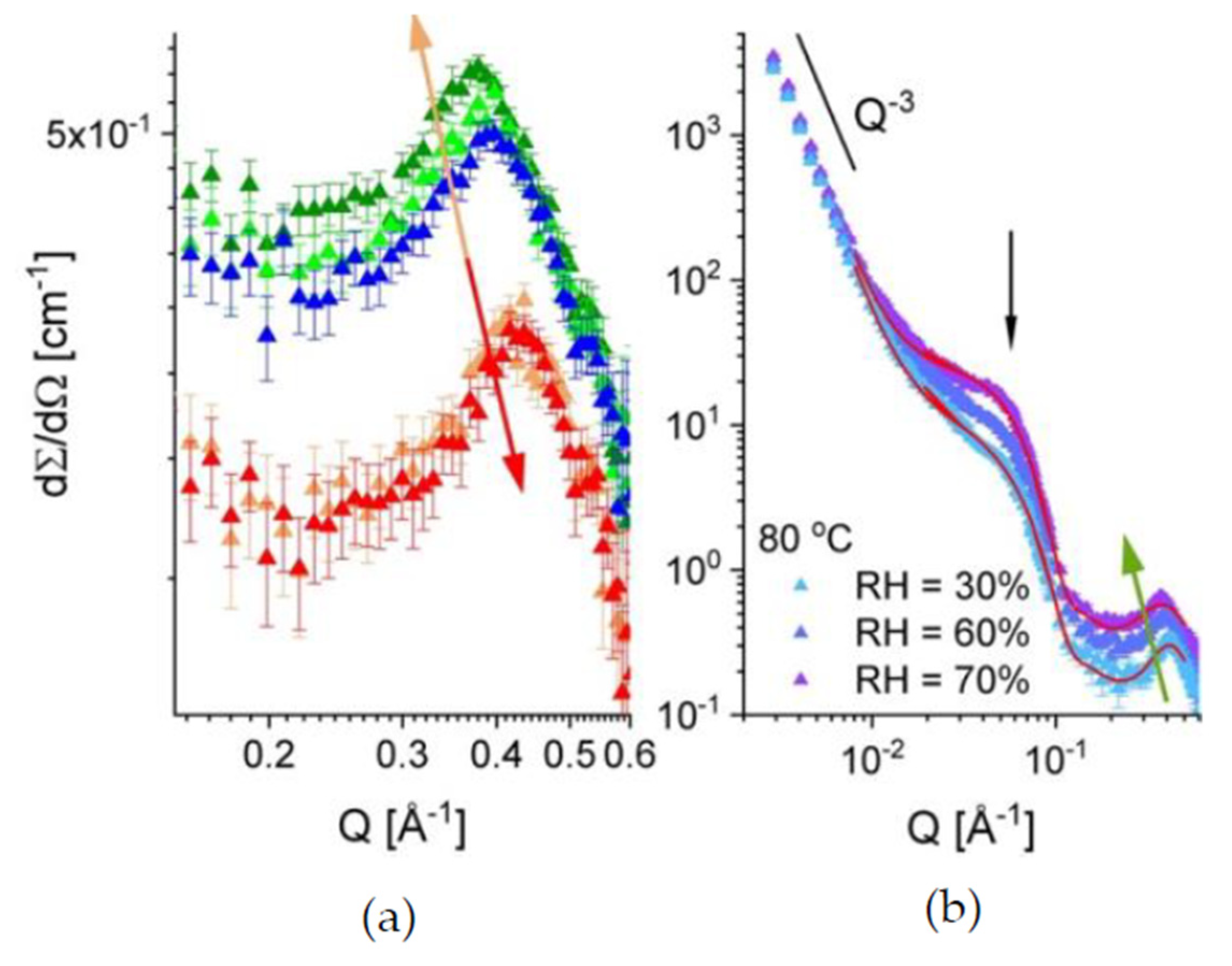
3.3. Microstructure Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Review of Advanced Materials for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7303–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Nishihara, M.; Matsuda, J.; Sasaki, K. Polymer electrolyte Fuel Cells (PEFCs). In Hydrogen Energy Engineering. Green Energy and Technology; Sasaki, K., Li, H.-W., Hayashi, A., Yamabe, J., Ogura, T., Lyth, S.M., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; pp. 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Kreuer, K.-D.; Paddison, S.J.; Spohr, E.; Schuster, M. Transport in Proton Conductors for Fuel-Cell Applications: Simulations, Elementary Reactions, and Phenomenology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4637–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusoglu, A.; Weber, A.Z. New Insights into Perfluorinated Sulfonic-Acid Ionomers. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 987–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smitha, B.; Sridhar, A.; Khan, A.A. Solid Polymer Electrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications—A Review. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 259, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Jalajakshi, A.; Pitchumani, S.; Shridhar, P.; Shukla, A.K. Endurance of Nafion-Composite Membranes in PEFCs Operating at Elevated Temperature under Low Relative-Humidity. J. Chem. Sci. 2012, 124, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Hariprasad, R.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Potential Bifunctional Filler (CeO2-ACNTs) for Nafion Matrix toward Extended Electrochemical Power Density and Durability in Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells Operating at reduced Relative Humidity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12847–12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Narducci, R.; Di Vona, M.L.; Giancola, S. Annealing of Nafion 1100 in the Presence of an Annealing Agent: A Powerful Method for Increasing Ionomer Working Temperature in PEMFCs. Fuel Cells 2013, 13, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T. Theory for Water Management in Membranes for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells—Part 1 The Effect of Impurity Ions at the Anode Side on the Membrane Performance. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 465, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Pierre, J.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Knights, S.; Bos, M.L. Relationships between Water Management, Contamination and Lifetime Degradation in PEFC. J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst. 2000, 3, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Huguet, P.; Morin, A.; Gebel, G.; Deabate, S.; Sutor, A.K.; Peng, Z. In Situ Analysis of Water Management in Operating Fuell Cells by Confocal Raman Spectroscopy. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Di Vona, M.L.; Narducci, R. New results on the visco-elastic behaviour of ionomer membranes and relations between TeRH plots and proton conductivity decay of Nafion_117 in the range 50–140 °C. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 6302–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narducci, R.; Knauth, P.; Chailan, J.-F.; DiVona, M.L. How to Improve Nafion with Tailor Made Annealing. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 27268–27274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakandan, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Hu, M.; Wang, L. Highly Branched Poly (Arylene Ether)/Surface Functionalized Fullerene-based Composite Membrane Electrolyte for DMFC Applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 3756–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Gabunada, J.C.; Yoo, D.J. Amelioration in Physicochemical Properties and Single Cell Performance of Sulfonated Poly (ether ether ketone) Block Copolymer Composite Membrane using Sulfonated Carbon Nanotubes for Intermediate Humidity Fuel Cells. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 2974–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated Fluorinated Multi-Block Copolymer Hybrid Containing Sulfonated (Poly Ether Ether Ketone) and Graphene Oxide: A Ternary Hybrid Membrane Architecture for Electrolyte Applications in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Energy. Chem. 2018, 27, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Vinothkannan, M.; Park, C.J.; Yoo, D.J. Alleviating the Mechanical and Thermal Degradations of Highly Sulfonated Poly (Ether Ether Ketone) Blocks via Copolymerization with Hydrophobic Unit for Intermediate Humidity Fuel Cells. Polymers 2018, 10, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickner, M.A.; Ghassemi, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Einsla, B.R.; McGrath, J.E. Alternative Polymer System for Proton Exchange Membranes (PEMs). Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4587–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hihashihara, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Ueda, M. Sulfonated Aromatic Hydrocarbon Polymers as Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cells. Polymer 2009, 50, 5341–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Cai, W.; Cheng, H. Recent Developments on Alternative Proton Exchange Membranes: Strategies for Systematic Performance Improvement. Energy Technol. 2015, 3, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Oshima, T.; Koizumi, S.; Rikukawa, M.; Szekely, N.; Radulescu, A.; Richter, D. Elucidation of the Morphology of the Hydrocarbon Multiblock Copolymer Electrolyte Membranes for Proton Exchange Fuel Cells. Polymer 2016, 86, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Kondo, S.; Kaseyama, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Selyanchyn, R.; Fujikawa, S.; Christiani, L.; Sasaki, K.; Nishihara, M. Development of Polymer-Polymer Type Charge-Transfer Blend Membranes for Fuel Cell Application. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Narducci, R.; Compan, V.; Constantino, F. Proton Conductivity of Composite Polyelectrolyte Membranes with Metal-Organic Frameworks for Fuel Cell Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-D.; Ohira, A.; Nakao, N. Chemically Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyphenylsulfone (CSPPSU) Membranes for PEM Fuel Cells. Membranes 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serbanescu, O.S.; Voicu, S.I.; Thakur, V.K. Polysulfone Functionalized Membranes: Properties and Challenges. Mater. Today Chem. 2020, 17, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriello, A.; Agoretti, P.; Ambrosio, L.; Fasano, G.; Pellegrino, M.; Venditto, V.; Guerra, G. Syndiotactic Polystyrene Films with Sulfonated Amorphous Phase and Nanoporous Crystalline Phase. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saga, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Saito, K.; Minagawa, M.; Tanioka, A. Polyelectrolyte Membranes Based on Hydrocarbon Polymer Containing Fullerenes. J. Power Sources 2008, 176, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, G.; Califano, R.; Pellegrino, M.; Venditto, V.; Guerra, G.; Boriello, A.; Ambrosio, L.; Sansone, L. Semicrystalline proton-conductive membranes with sulfonated amorphous phases. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 8038–8044. [Google Scholar]
- Lavorgna, M.; Fusco, L.; Piscitelli, F.; Mensitieri, G.; Agoretti, P.; Borriello, A.; Mascia, L. Control of morphology of sulfonated syndio-polystyrene membranes through constraints imposed by siloxane netwroks. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 2389–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, A.; Napolitano, T. Proton conductivity and methanol permeability of sulfonated syndiotactic polystyrene membranes. Soft Mater. 2011, 9, 224–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, M.-M.; Tarallo, O.; Di Girolamo, R.; Caporaso, L.; Appavou, M.-S.; Revay, Z.; Radulescu, A. Structure and Morphology of Model Polymer Electrolyte Membranes based on Sulfonated Syndiotactic-Polystyrene in the Co-crystalline Phase Resolved by Small-Angle Neutron Scattering. Solid State Ion. 2018, 320, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, M.-M.; Iwase, H.; Takata, S.; Radulescu, A. The multilevel structure of syndiotactic-polystyrene model polyelectrolyte membranes resolved by extended Q-range contrast variation SANS. Membranes 2019, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, F.; Radulescu, A.; Ute, K. Time-resolved SANS Studies on Guest Exchange Processes in Co-Crystals of Syndiotactic Polytyrene. Polymer 2013, 54, 3145–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandele, A.M.; Neacsu, P.; Cimpean, A.; Staras, A.I.; Miculescu, F.; Iordache, A.; Voicu, S.I.; Thakur, V.K.; Toader, O.D. Cellulose Acetate Membranes Functionalized with Resveratrol by Covalent Immobilization for Improved Osseointegration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 438, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revay, Z.; Kudejova, P.; Kleszczm, K.; Sölradl, S.; Genreith, C. In-beam activation analysis at Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum, Garching. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2015, 799, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, P.H.; Weidinger, A. Quantitative Investigation of the X-Ray Diffraction Picture of Some Typical Rayon Specimens Part, I. Textil. Res. 1961, 31, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, A.; Szekely, N.K.; Appavou, M.-S.; Pipich, V.; Kohnke, T.; Ossovyi, V.; Staringer, S.; Schneider, G.J.; Amann, M.; Zhang-Haagen, B.; et al. Studying Soft-Matter and Biological Systems over a Wide Length-Scale from Nanometer and Micrometer Sizes at the Small-Angle Neutron Diffractometer KWS-2. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 118, 54639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyses, S.; Spells, S.J. Conformationally Sensitive Infrared Vibrations of the Syndiotactic Polystyrene/Ethylbenzene Complex. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 2684–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, F.; Seto, N.; Radulescu, A.; Schiavone, M.-M.; Allgaier, J.; Ute, K. Development of a Simultaneous SANS/FTIR Measuring System. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Jin, B.; Peng, R.F.; Chen, C.D.; Zheng, R.Z.; He, Y.; Chu, S.J. Synthesis and Characterization of [60]Fullerenes-Glycidyl Azide Polymer and Its Thermal Decomposition. Polymers 2015, 7, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ruan, L.; Chang, X.-L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.-T.; Guo, X.; Yuan, H.; Guo, C.; Shi, W.; Sun, B.; et al. The Isotopic Effect of 13C-Labeled Large Carbon Cage (C70) Fullerens and Their Formation Process. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 76949–76956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.C.; Jelski, D.A.; George, T.F. Vibrational motions of Buckminsterfullerenes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1987, 137, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törpe, A.; Belton, D.J. Improved Spectrophotometric Analysis of Fullerenes C60 and C70 in High-solubility Organic Solvents. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bensasson, R.V.; Bienvenue, E.; Dellinger, M.; Leach, S.; Seta, P. C60 in model Biological Systems. A Visible-UV Absorption Study of Solvent-Dependent Parameters and Solute Aggregation. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 3492–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, S.; Alargova, R.G.; Tsujii, K. Stable dispersions of fullerenes, C60 and C70, in water. Preparation and Characterization. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6013–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, C.; Guerra, G.; Petraccone, V.; Pirozzi, B. Crystal Structure of the Emptied Clathrate Form (e Form) of Syndiotactic Polystyrene. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 4147–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Malik, S.; Guenet, J.-M. Syndiotactic Polystyrene/Fullerene Composites: Elucidation of Structural Aspect. Macromol. Symp. 2011, 303, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Hayamizu, K.; Okada, T. Temperature Dependence of Ion and Water Transport in Perfluorinated Ionomer Membranes for Fuel Cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3112–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, B.R.; Goulart, C.A.; Santiago, E.I.; Muccillo, R.; Fonseca, F.C. Proton Conductivity of Perfluorosulfonate Ionomers at High Temperature and High Relative Humidity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 091904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieke, P.R.; Vanderborgh, N.E. Temperature Dependence of Water Content and Proton Conductivity in Polyperfluorosulfonic Acid Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 32, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, J.J.; Creager, S.E.; Ma, J.J.; DesMarteau, D.D. Proton Conductivity in Nafion® 117 and in a Novel BisE (perfluoroalkyl)sulfonylimide lonomer Membrane. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaki, K.; DeSousa, R.; Wang, H.; Gasa, J.; Venkatesan, A.; Pugazhendhi, P.; Loutfy, R.O. Fullerene Composite Proton Conducting Membranes for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Operating under Low Humidity Conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


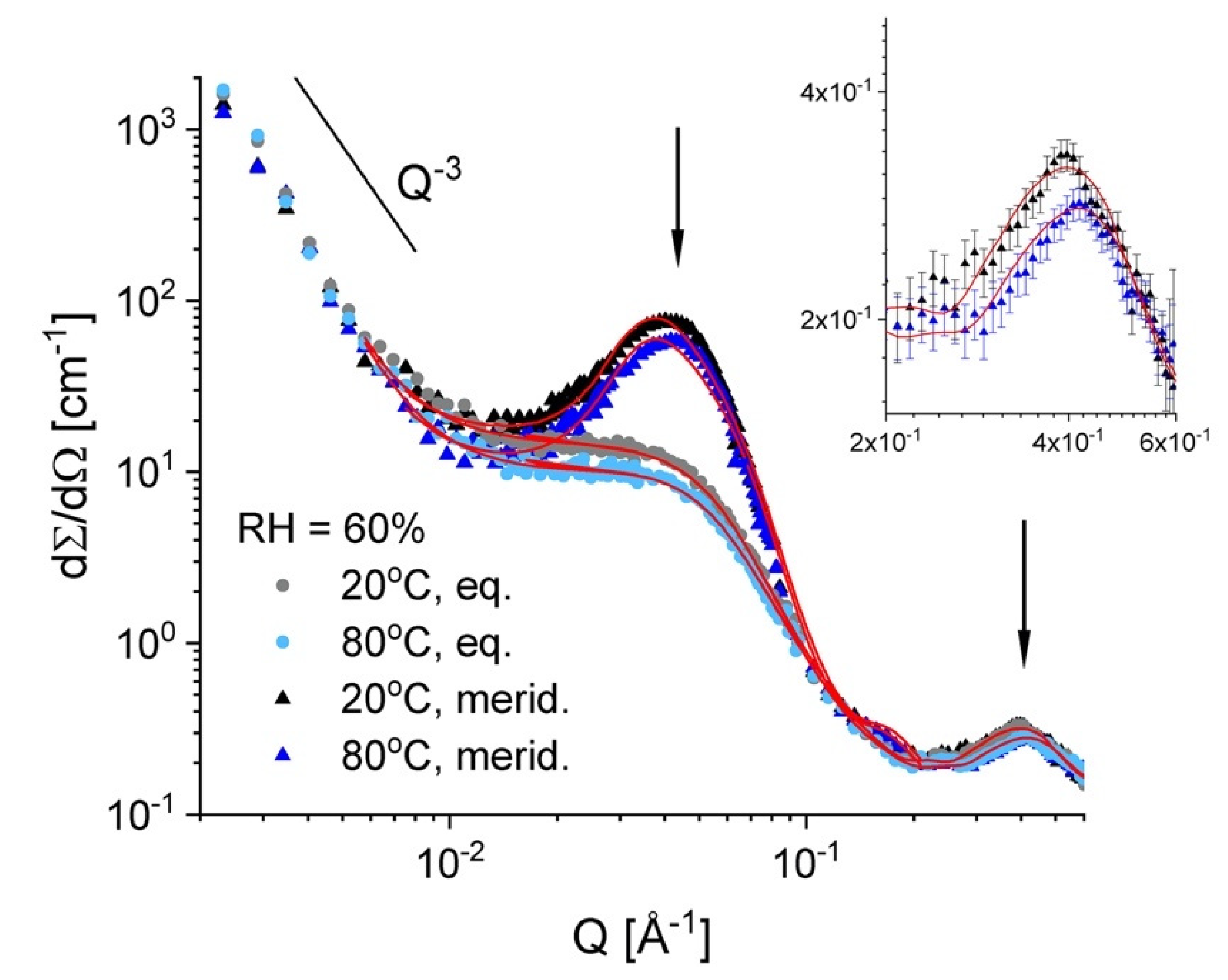
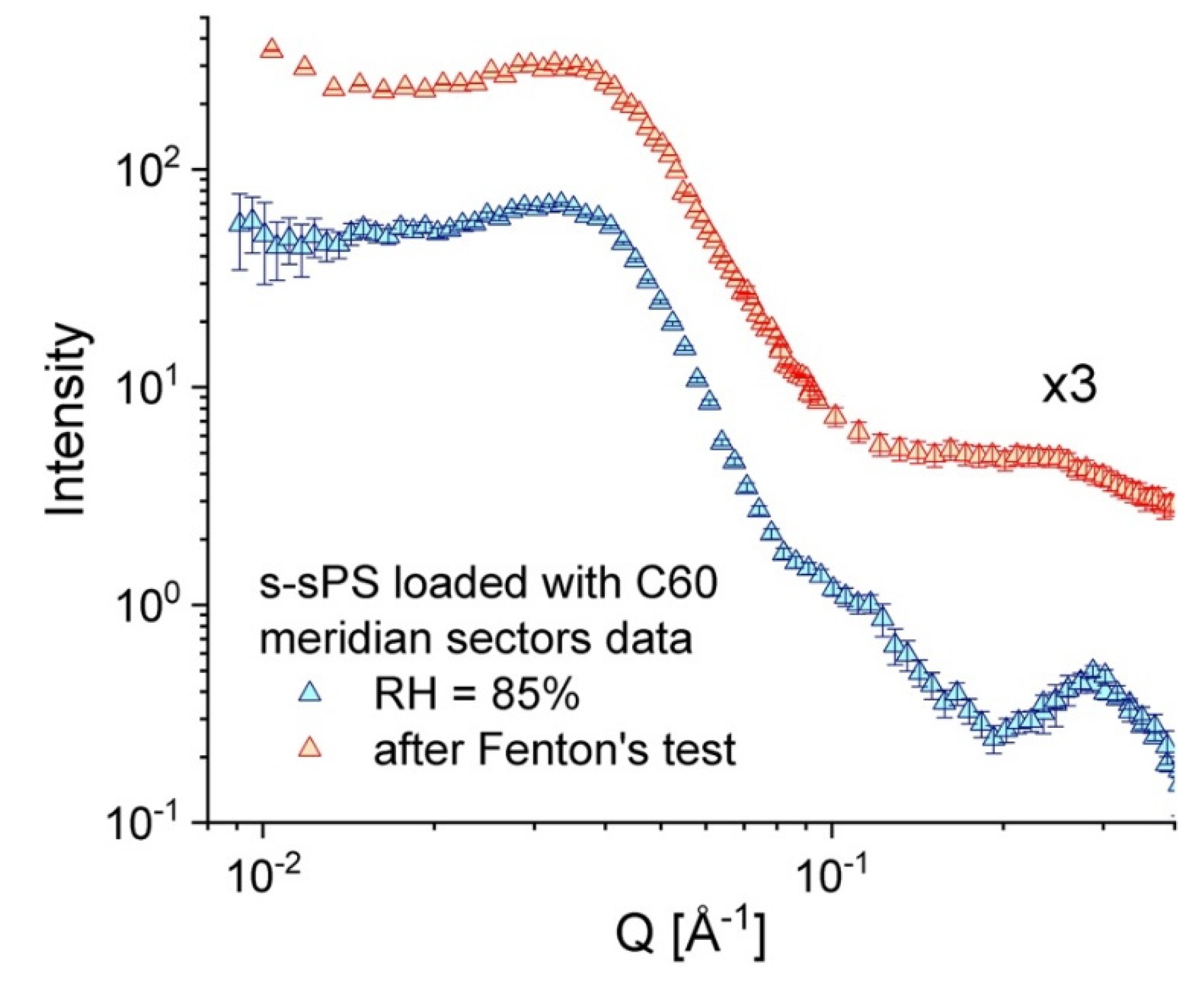
| Parameter | Sample A | Sample B |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfonation degree (%) | 46.3 | 41.5 |
| Crystallinity (%) | 33 | 31 |
| Water uptake at 25 °C (%) | 87.5 | 76.3 |
| Conductivity 25 °C (mS/cm) | 128.2 | 99.9 |
| Conductivity 80 °C (mS/cm) | 160.3 | 219.8 |
| Parameter | Sample A, RH = 60% | Sample B, 80 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 80 °C | RH = 30% | RH = 70% | |
| (φwater)amorphous (%) | 3.24 | 2.75 | 2.35 | 8.52 |
| Rsph (Å) | 50.3 | 45.1 | 41.5 | 38.2 |
| (φwater)inter-lam (%) | 3.21 | 2.87 | – | – |
| ξion (Å) | 16.10 | 14.95 | 16.75 | 15.06 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schiavone, M.-M.; Lamparelli, D.H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Revay, Z.; Radulescu, A. The Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Microstructure of Sulfonated Syndiotactic–polystyrene Ionic Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080187
Schiavone M-M, Lamparelli DH, Zhao Y, Zhu F, Revay Z, Radulescu A. The Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Microstructure of Sulfonated Syndiotactic–polystyrene Ionic Membranes. Membranes. 2020; 10(8):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080187
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchiavone, Maria-Maddalena, David Hermann Lamparelli, Yue Zhao, Fengfeng Zhu, Zsolt Revay, and Aurel Radulescu. 2020. "The Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Microstructure of Sulfonated Syndiotactic–polystyrene Ionic Membranes" Membranes 10, no. 8: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080187
APA StyleSchiavone, M.-M., Lamparelli, D. H., Zhao, Y., Zhu, F., Revay, Z., & Radulescu, A. (2020). The Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Microstructure of Sulfonated Syndiotactic–polystyrene Ionic Membranes. Membranes, 10(8), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080187