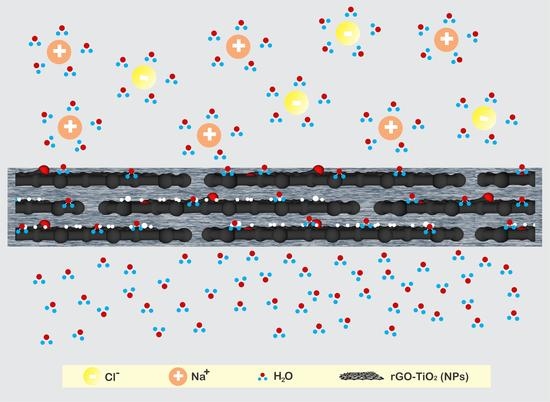
Pervaporation Membranes for Seawater Desalination Based on Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites. Part 1: Microstructure Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Geopolymer Paste
2.2. Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
2.3. Synthesis of Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposite
3. Results and Discussion
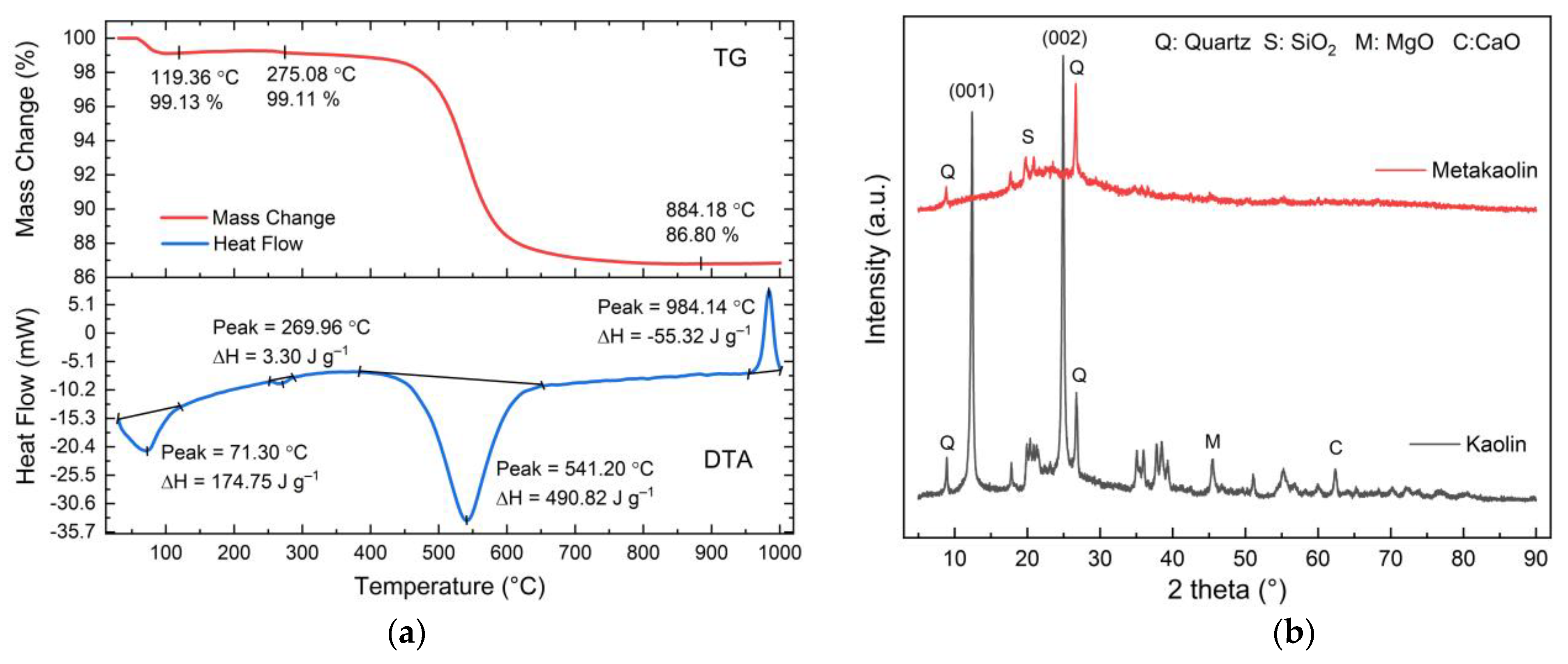
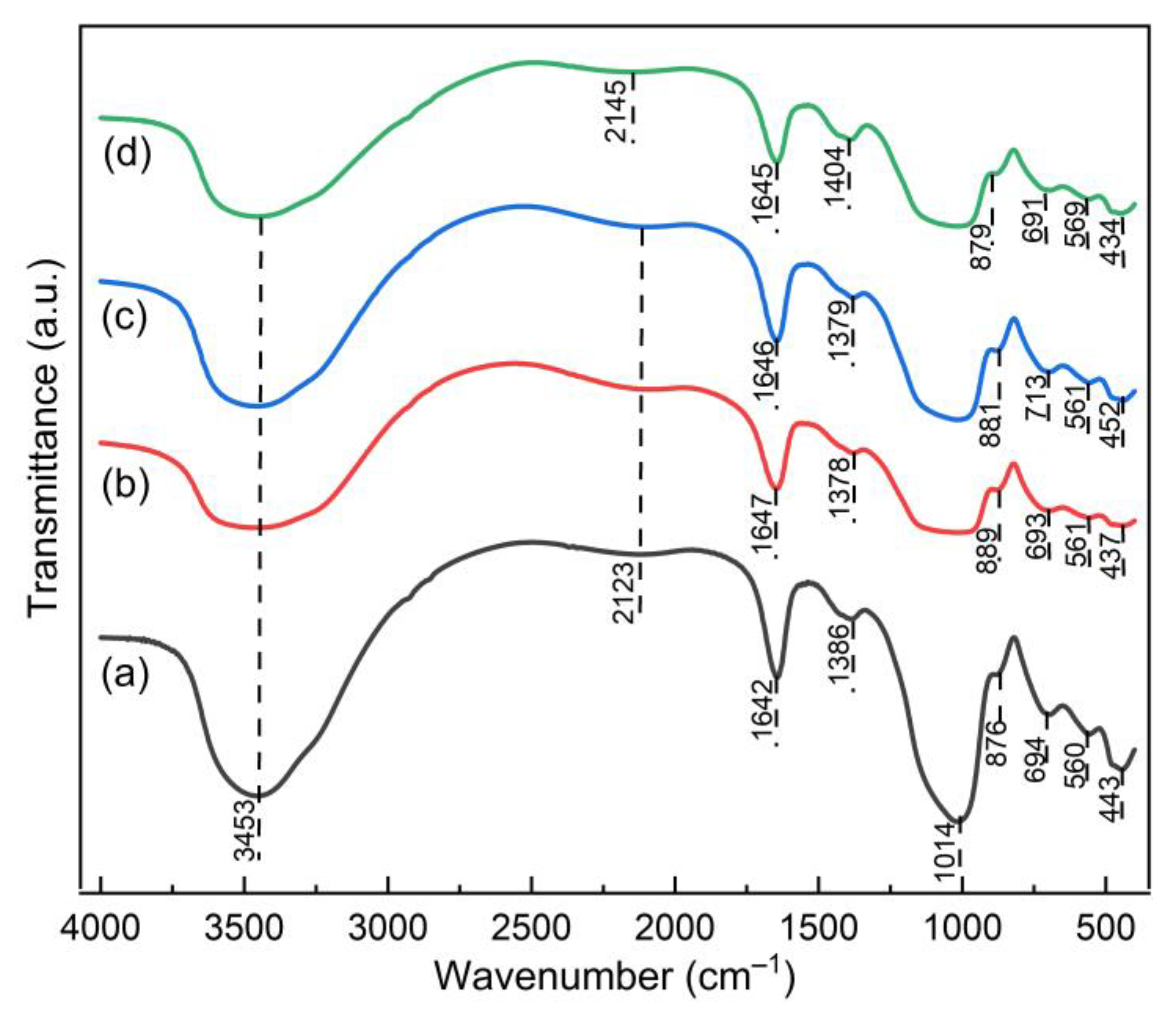
3.1. The Properties of Geopolymer Paste
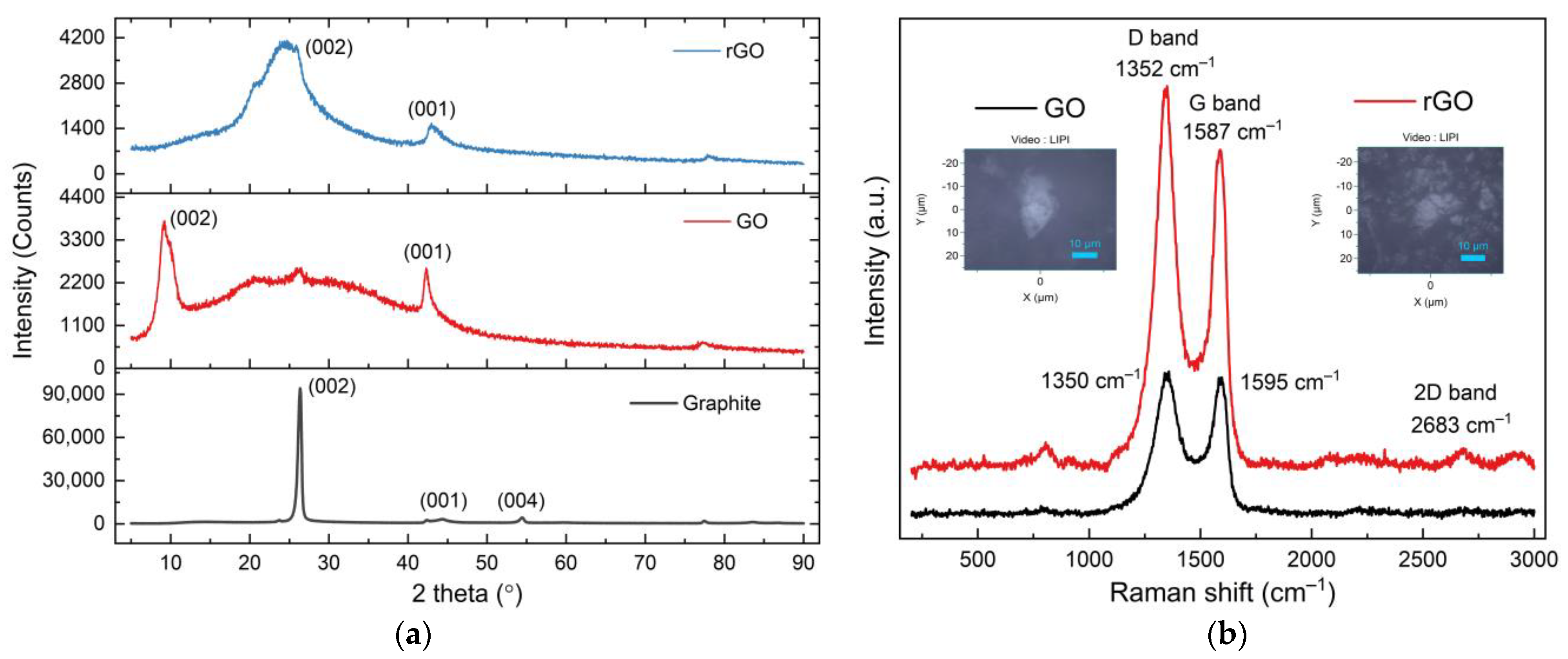
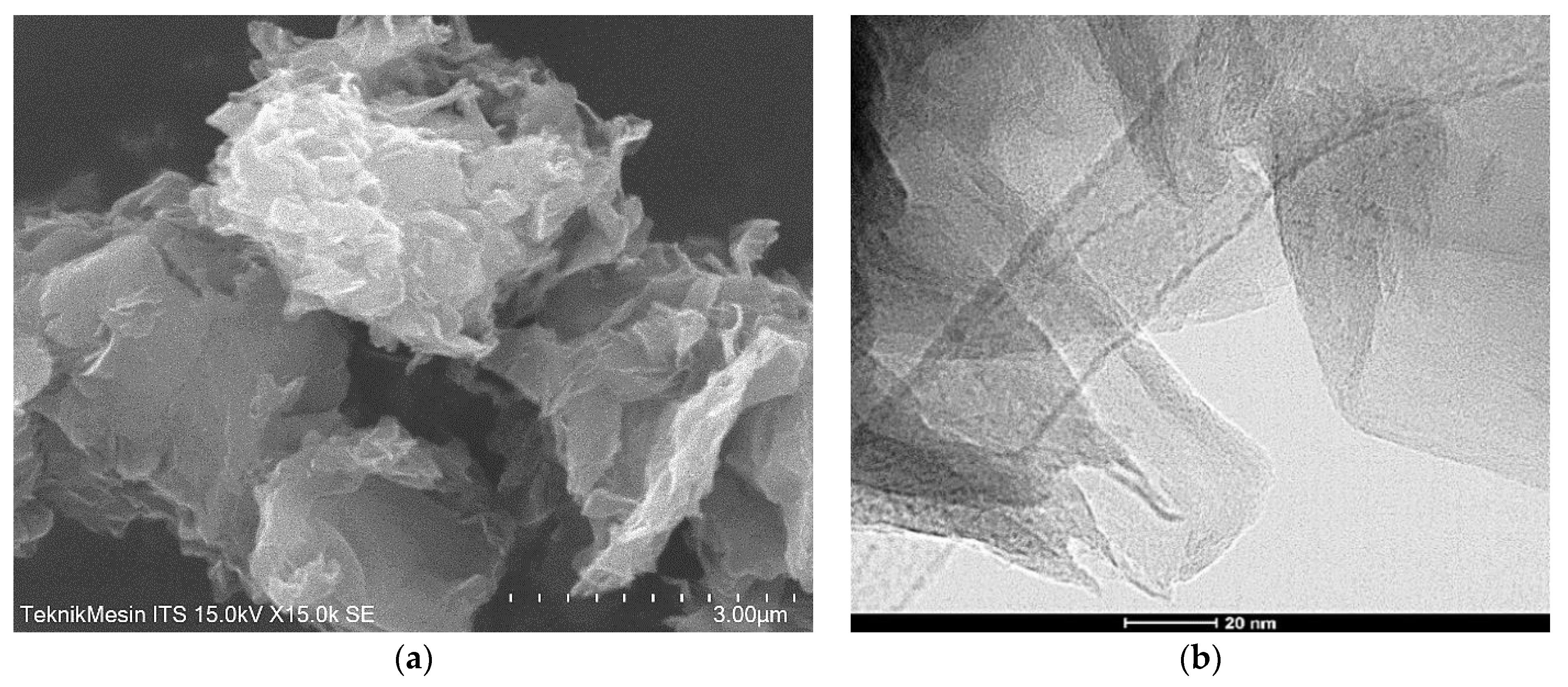
3.2. The Properties of rGO
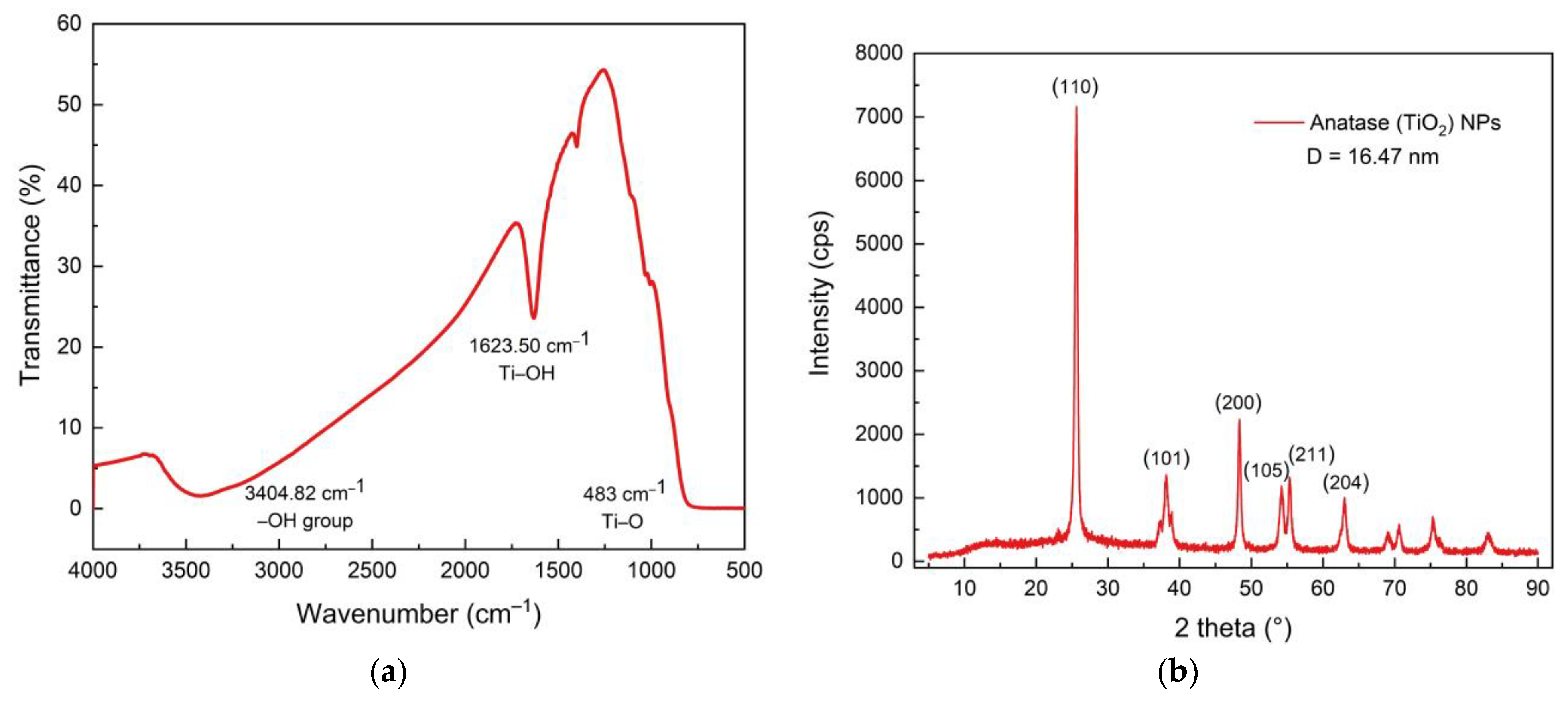
3.3. The Properties of TiO2 NPs
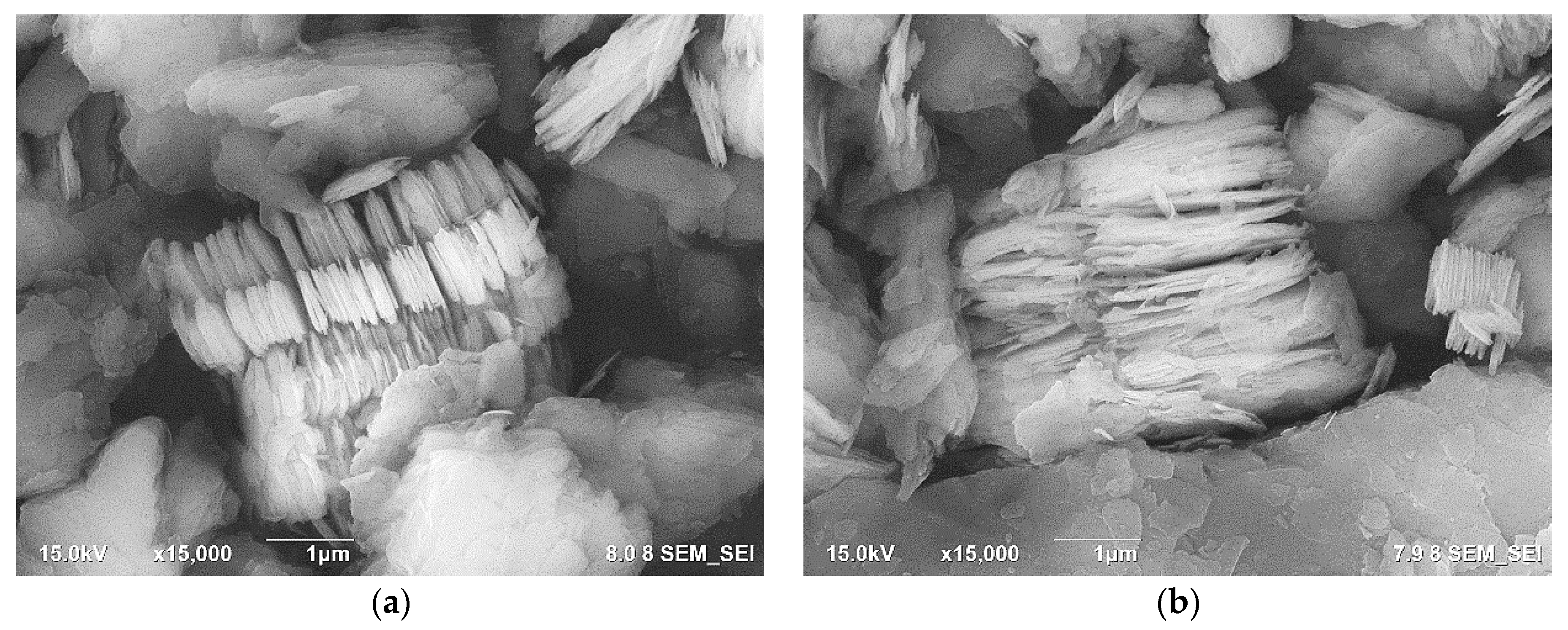
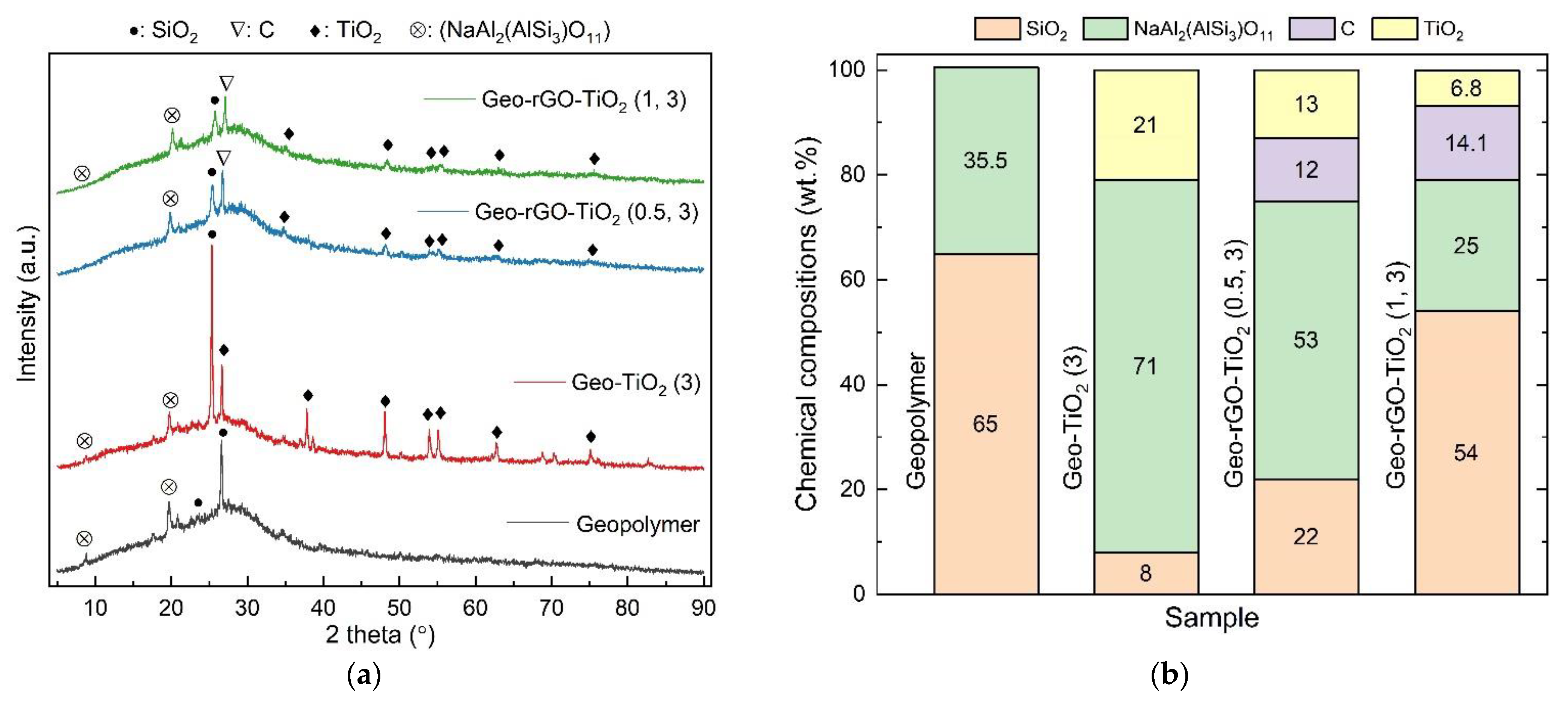
3.4. The Structure and Morphology of Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites (Pervaporation Membranes)
3.5. The Surface Area and Porosity of Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites (Pervaporation Membranes)
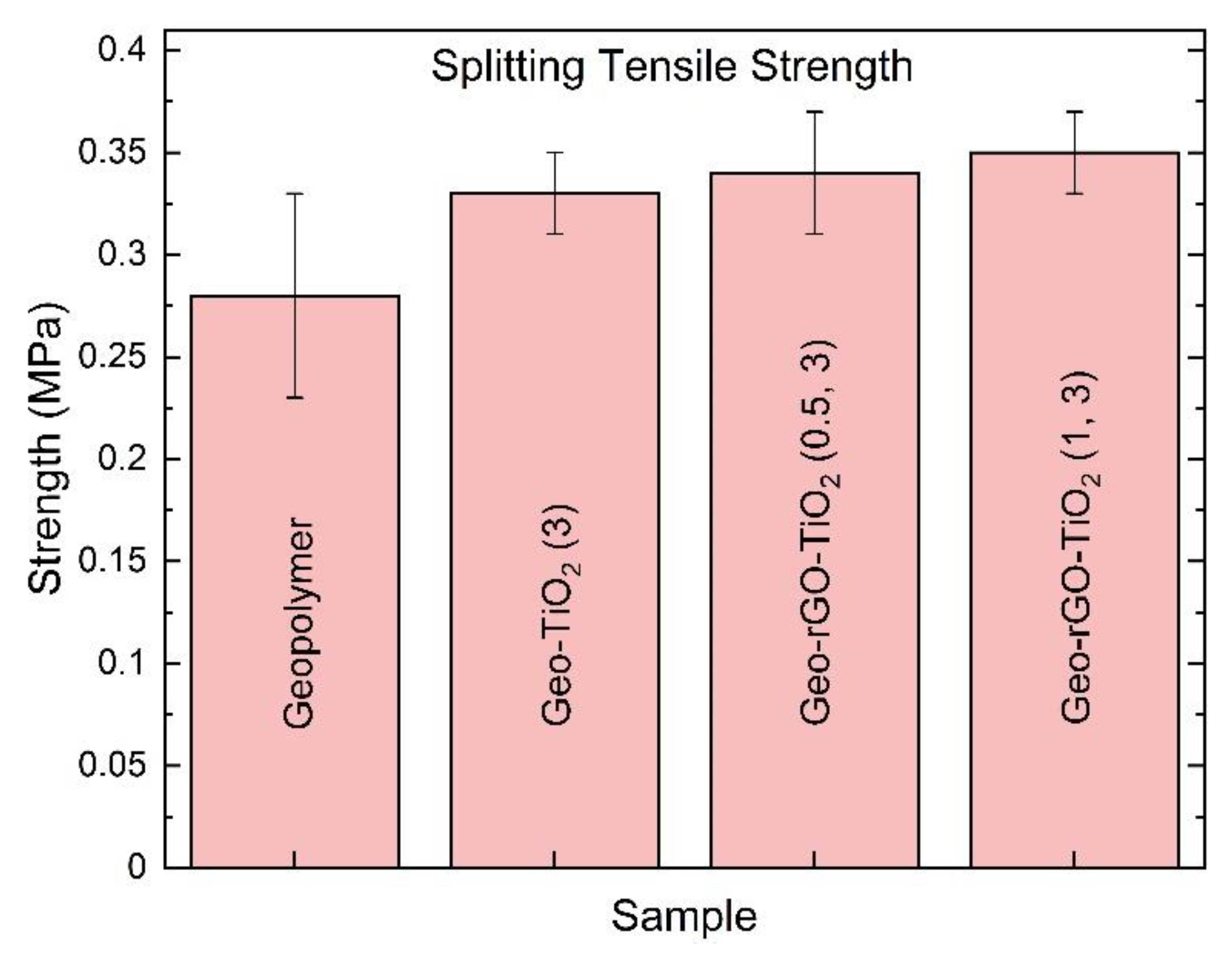
3.6. The Splitting Tensile Result of Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites (Pervaporation Membranes)
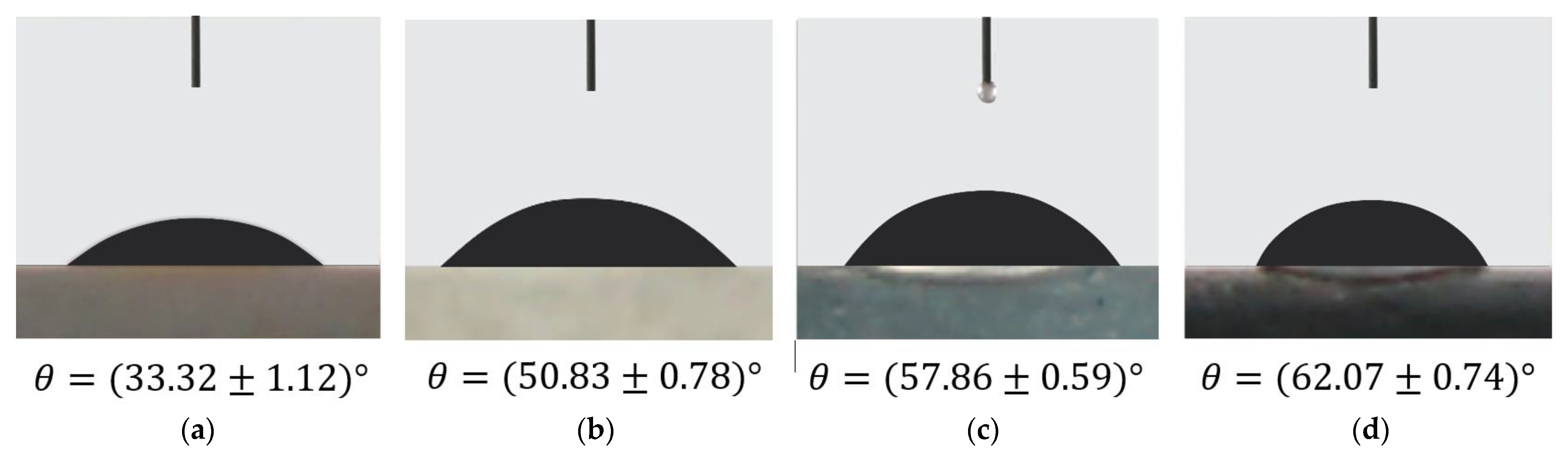
3.7. Contact Angle Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eljaddi, T.; Mendez, D.L.M.; Favre, E.; Roizard, D. Development of new pervaporation composite membranes for desalination: Theoretical and experimental investigations. Desalination 2021, 507, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Elbahri, M. Graphene membranes for water desalination. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Wen, B.; Su, Z. The Future of Freshwater Access: Functional Material-Based Nano-membranes for Desalination. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 22, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, G.; Ghaffour, N.; Li, Z.; Francis, L.; Linares, R.V.; Missimer, T.; Lattemann, S. Membrane-based seawater desalination: Present and future prospects. Desalination 2017, 401, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F.; Hilal, N. Recent trends in membranes and membrane processes for desalination. Desalination 2016, 391, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. A review on inorganic membranes for desalination and wastewater treatment. Desalination 2018, 434, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, W.; Marszalek, J.; Tomczak, E. Water desalination by pervaporation—Comparison of energy consumption. Desalination 2018, 433, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almarzooqi, K.; Ashrafi, M.; Kanthan, T.; Elkamel, A.; Pope, M.A. Graphene Oxide Membranes for High Salinity, Produced Water Separation by Pervaporation. Membranes 2021, 11, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.H.; Joshi, R.K.; De Silva, K.K.H.; Badam, R.; Yoshimura, M. Fabrication of reduced graphene oxide membranes for water desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, J. Graphene oxide based materials for desalination. Carbon 2019, 146, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Feng, B. Synthesis of novel graphene oxide-polyimide hollow fiber membranes for seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, Z. Preparation of nano-composites membranes with graphic oxides and polylactic acid. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 2018, 33, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, K.R.; Hardian, R.; Kumar, V.D.; Viswanatha, R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, A.; Santosh, M.S.; Szekely, G. Composite nanofiltration membrane comprising one-dimensional erdite, two-dimensional reduced graphene oxide, and silkworm pupae binder. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bery, H.M.; Matsushita, Y.; Abdel-moneim, A. Fabrication of efficient TiO2-RGO heterojunction composites for hydrogen generation via water-splitting: Comparison between RGO, Au and Pt reduction sites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Lei, M.; Wang, Y. One-step synthesis of easy-recycling TiO2-rGO nanocomposite photocatalysts with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 132, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, M.; Álvarez, M.G.; Contreras, S.; Medina, F.; Clarizia, L.; Vitiello, G.; Llorca, J.; Marotta, R. Treatment of saline produced water through photocatalysis using rGO-TiO2 nanocomposites. Catal. Today 2018, 315, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, X.; Li, N.; Wang, Q.; Ji, S. Chitosan/graphene oxide mixed matrix membrane with enhanced water permeability for high-salinity water desalination by pervaporation. Desalination 2018, 438, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, N.; Aziz, F.; Jamaludin, N.A.; Mutalib, M.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Jaafar, J.; Yusof, N.; Ludin, N.A. A review of integrated photocatalyst adsorbents for wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7411–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alammar, A.; Park, S.H.; Williams, C.J.; Derby, B.; Szekely, G. Oil-in-water separation with graphene-based nanocomposite membranes for produced water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guzman, M.R.; Andra, C.K.A.; Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Dizon, G.V.C.; Caparanga, A.R.; Huang, S.H.; Lee, K.R. Increased performance and antifouling of mixed-matrix membranes of cellulose acetate with hydrophilic nanoparticles of polydopamine-sulfobetaine methacrylate for oil-water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Cheng, Y. Advances in geopolymer materials: A comprehensive review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021, 8, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaer; Haris, A.; Nurfadilla; Amalia, N.S.; Akifah, N. The prospect of geopolymers-Cu nanoparticles as antibacterial and antifungal composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2030, 020173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saafi, M.; Tang, L.; Fung, J.; Rahman, M.; Liggat, J. Enhanced properties of graphene/fly ash geopolymeric composite cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.; He, P.; Jia, D.; Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Effects of treatment temperature on the reduction of GO under alkaline solution during the preparation of graphene/geopolymer composites. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 18181–18188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Pan, K.; Li, L.; Giannelis, E.P.; Cao, B. High performance hydrophilic pervaporation composite membranes for water desalination. Desalination 2014, 347, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Gao, A.; Zhao, H.; Feng, X. Pervaporative desalination of high-salinity water. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Lu, Y.; Li, N.; Zeng, F.; Wang, Q.; Bai, H.; Xie, Z. Hyperbranch-Crosslinked S-SEBS Block Copolymer Membranes for Desalination by Pervaporation. Membranes 2020, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W. New generation nanomaterials for water desalination: A review. Desalination 2019, 451, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Cui, X.M.; Liu, X.D.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K. Preparation of self-supporting NaA zeolite membranes using geopolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.X.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Cui, X.M. Preparation of a non-hydrothermal NaA zeolite membrane and defect elimination by vacuum-inhalation repair method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 158, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaer; Haris, A.; Irhamsyah, A.; Permatasari, A.D.; Desa, S.S.; Irfanita, R.; Wahyuni, S. Pervaporation membrane based on laterite zeolite-geopolymer for ethanol-water separation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subaer; Van Riessen, A. Thermo-mechanical and microstructural characterization of sodium-poly (sialate-siloxo)(Na-PSS) geopolymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 3117–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfo, K.K.; Dodoo-Arhin, D.; Agyei-Tuffou, B.; Nyankson, E.; Obada, D.O.; Damoah, L.N.; Annan, E.; Yaya, A.; Onwona-Agyeman, B.; Bediako, M. The physico-mechanical influence of dehydroxylized activated local kaolin: A supplementary cementitious material for construction applications. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 12, e00306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obada, D.O.; Dodoo-Arhin, D.; Dauda, M.; Anafi, F.O.; Ahmed, A.S.; Ajayi, O.A. The impact of kaolin dehydroxylation on the porosity and mechanical integrity of kaolin based ceramics using different pore formers. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, R.; Maffucci, L.; Santoro, L. Optimization of geopolymer synthesis by calcination and polycondensation of a kaolinitic residue. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 40, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Sagoe-Crentsil, K. Dissolution processes, hydrolysis and condensation reactions during geopolymer synthesis: Part I—Low Si/Al ratio systems. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2997–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayah, N.M.S.; Liu, W.W.; Lai, C.W.; Noriman, N.Z.; Khe, C.S.; Hashim, U.; Lee, H.C. Comparison on graphite, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide: Synthesis and characterization. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1892, 150002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, F.W.; Lai, C.W.; Abd Hamid, S.B. Easy preparation of ultrathin reduced graphene oxide sheets at a high stirring speed. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5798–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzyka, R.; Drewniak, S.; Pustelny, T.; Chrubasik, M.; Gryglewicz, G. Characterization of graphite oxide and reduced graphene oxide obtained from different graphite precursors and oxidized by different methods using Raman spectroscopy. Materials 2018, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- How, G.T.S.; Pandikumar, A.; Ming, H.N.; Ngee, L.H. Highly exposed {001} facets of titanium dioxide modified with reduced graphene oxide for dopamine sensing. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chougala, L.S.; Yatnatti, M.S.; Linganagoudar, R.K.; Kamble, R.R.; Kadadevarmath, J.S. A simple approach on synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles and its application in dye sensitized solar cells. J. Nano-Electron. Phys. 2017, 9, 04005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Rao, F.; Song, S.; Cholico-González, D.F.; Ortiz, N.L. Combination formation in the reinforcement of metakaolin geopolymers with quartz sand. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeni, O.; Onwualu, A.P.; Boakye, E. Characterization and mechanical performance of metakaolin-based geopolymer for sustainable building applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J. Preparation and properties of alkali activated metakaolin-based geopolymer. Materials 2016, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maiti, M.; Sarkar, M.; Maiti, S.; Malik, M.A.; Xu, S. Modification of geopolymer with size controlled TiO2 nanoparticle for enhanced durability and catalytic dye degradation under UV light. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertcumfu, N.; Jaita, P.; Thammarong, S.; Lamkhao, S.; Tandorn, S.; Randorn, C.; Tunkasiri, T.; Rujijanagul, G. Influence of graphene oxide additive on physical, microstructure, adsorption, and photocatalytic properties of calcined kaolinite-based geopolymer ceramic composites. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 602, 125080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Jiang, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, P. Effects of graphene oxide on microstructure and mechanical properties of graphene oxide-geopolymer composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; He, P.; Jia, D.; Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Effect of reduced graphene oxide content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of graphene–geopolymer nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mailhiot, S.; Sreenivasan, H.; Kantola, A.M.; Illikainen, M.; Adesanya, E.; Kriskova, L.; Telkki, V.V.; Kinnunen, P. Curing process and pore structure of metakaolin-based geopolymers: Liquid-state 1H NMR investigation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 143, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Rao, F.; Song, S.; Zhang, Y. Immobilization forms of ZnO in the solidification/stabilization (S/S) of a zinc mine tailing through geopolymerization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5728–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.M.; Huang, L.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.C.; Tang, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hedayati, M.; Kipper, M.J.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Synthesis of graphene oxide/polyacrylamide composite membranes for organic dyes/water separation in water purification. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akifah, N.; Supoyo, K.N.A.; Subaer. The potential of geopolymers-TiO2 NPs composites as self-cleaning materials. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2030, 020180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapham, D.P.; Lapham, J.L. BET surface area measurement of commercial magnesium stearate by krypton adsorption in preference to nitrogen adsorption. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinoza-Gómez, H.; Wai Lin, S.; Rogel-Hernández, E. Nanofiltration membrane pore diameter determination. Rev. Soc. Quím. Méx. 2004, 48, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Qiu, W.Z.; Lv, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.K. Nanofiltration membranes with narrow pore size distribution via contra-diffusion-induced mussel-inspired chemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29696–29704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.J.; Sivakamasundari, S.; Nishanth, A. Study on partial replacement of silica fume based geopolymer concrete beam behavior under torsion. Procedia Eng. 2017, 173, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mašek, Z.; Diblíková, L. Hydrophobic impregnation of geopolymer composite by ethoxysilanes. Acta Polytech. 2018, 53, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jia, D.; Li, H.; Colombo, P. Porous geopolymer composites: A review. Compos.-A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 150, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Lin, K.L.; Wang, D.; Hwang, C.L.; Tuan, B.L.A.; Shiu, H.S.; Cheng, T.W. Effect of nano-SiO2 on the alkali-activated characteristics of metakaolin-based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Mehrali, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. Graphene nanoplatelet-fly ash based geopolymer composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 76, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.S.; Sarker, P.K.; Barbhuiya, S. Sorptivity and acid resistance of ambient-cured geopolymer mortars containing nano-silica. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 72, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Pang, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T. Synthesis of hydrophobic carbon nanotubes/reduced graphene oxide composite films by flash light irradiation. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, V.S. Carbon nanostructure-based superhydrophobic surfaces and coatings. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 518–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


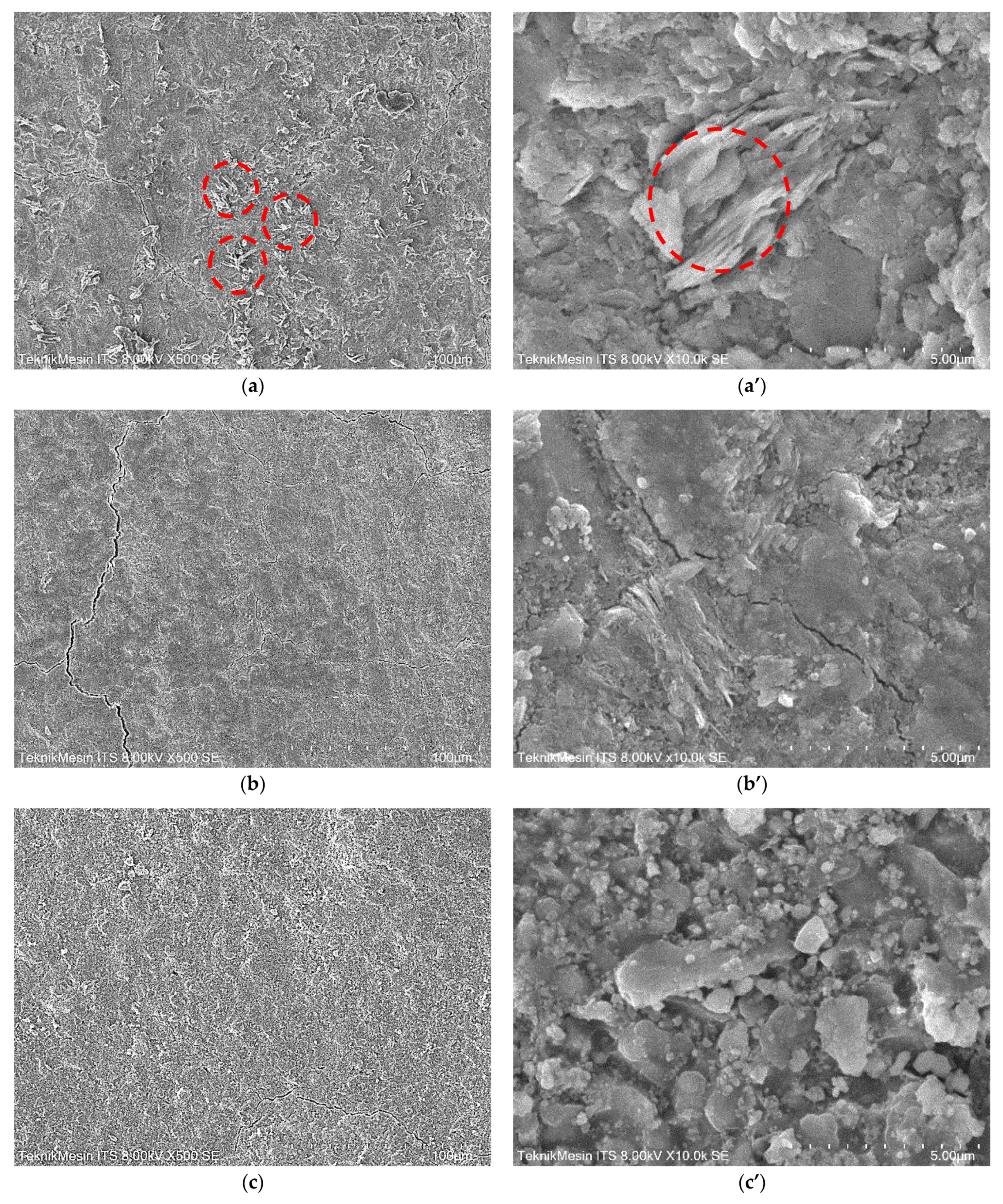
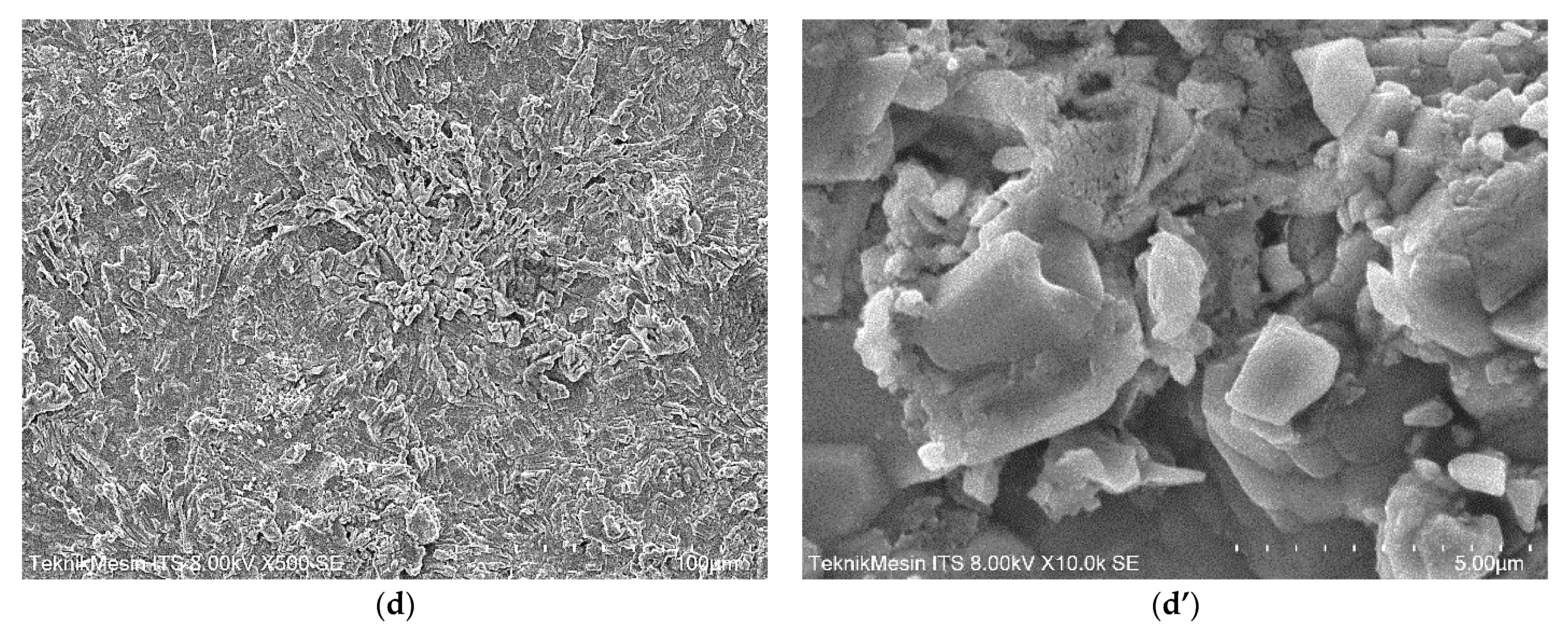



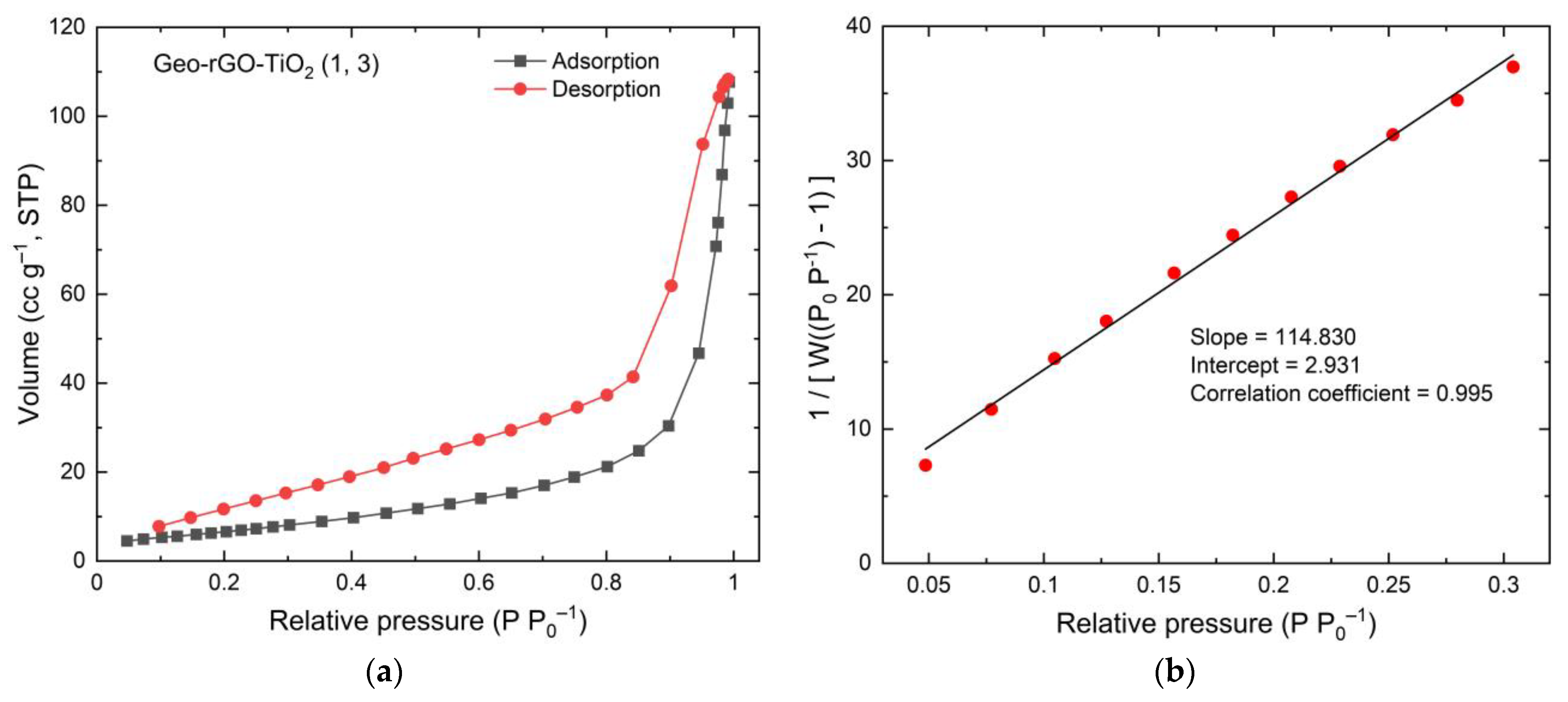
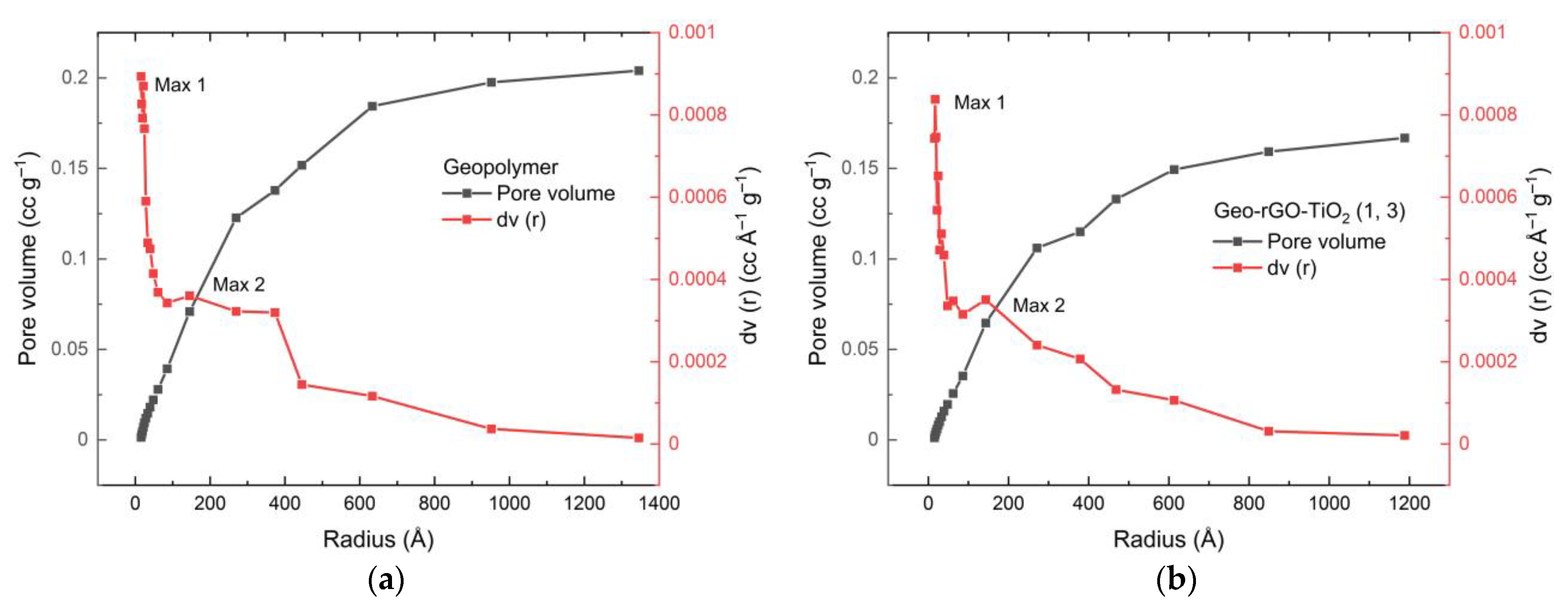
| Sample | Metakaolin | NaOH | Na2SiO3 | H2O | rGO | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geopolymer | 30 | 3 | 24 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Geo–TiO2 (3) | 30 | 3 | 24 | 9 | 0 | 3 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (0.5, 3) | 30 | 3 | 24 | 9 | 0.5 | 3 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (1, 3) | 30 | 3 | 24 | 9 | 1.0 | 3 |
| Sample | Mass (g) | Length (mm) | Outer Diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Density (g cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geopolymer | 28.304 | 101.1 | 19.5 | 2.2 | 1.04 |
| Geo–TiO2 (3) | 26.209 | 100.2 | 19.6 | 2.1 | 1.01 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (0.5, 3) | 25.426 | 100.2 | 19.7 | 2.3 | 0.98 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (1, 3) | 26.414 | 100.1 | 19.5 | 2.2 | 0.97 |
| Sample | Si | Al | Na | C | Ti | Si:Al | Na:Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geopolymer | 53.33 | 28.84 | 17.83 | 0 | 0 | 1.85 | 0.62 |
| Geo–TiO2 (3) | 46.91 | 28.00 | 13.44 | 0 | 11.64 | 1.67 | 0.48 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (0.5, 3) | 16.06 | 11.33 | 8.23 | 3.61 | 4.46 | 1.42 | 0.73 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (1, 3) | 3.86 | 2.77 | 28.82 | 6.48 | 1.04 | 1.39 | 10.40 |
| Sample | Si | Al | Na | C | Ti | Si:Al | Na:Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geopolymer | 52.38 | 29.45 | 18.17 | 0 | 0 | 1.78 | 0.62 |
| Geo–TiO2 (3) | 16.89 | 11.93 | 8.57 | 4.23 | 0 | 1.42 | 0.72 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (0.5, 3) | 14.65 | 9.60 | 9.05 | 2.79 | 9.22 | 1.53 | 0.94 |
| Geo–rGO–TiO2 (1, 3) | 14.05 | 10.32 | 4.55 | 3.20 | 11.30 | 1.36 | 0.44 |
| Parameter | Geopolymer | Geo–TiO2 (3) | Geo–rGO–TiO2 (0.5, 3) | Geo–rGO–TiO2 (1, 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface area (m2 g–1) | 26.031 | 35.590 | 29.573 | 25.549 |
| Total pore vol (cc g–1) | 0.2020 | 0.1583 | 0.1787 | 0.1666 |
| Average pore diameter (nm) | 15.52 | 7.99 | 12.90 | 13.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subaer, S.; Fansuri, H.; Haris, A.; Misdayanti; Irfanita, R.; Ramadhan, I.; Putri, Y.; Setiawan, A. Pervaporation Membranes for Seawater Desalination Based on Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites. Part 1: Microstructure Properties. Membranes 2021, 11, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120966
Subaer S, Fansuri H, Haris A, Misdayanti, Irfanita R, Ramadhan I, Putri Y, Setiawan A. Pervaporation Membranes for Seawater Desalination Based on Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites. Part 1: Microstructure Properties. Membranes. 2021; 11(12):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120966
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubaer, Subaer, Hamzah Fansuri, Abdul Haris, Misdayanti, Resky Irfanita, Imam Ramadhan, Yulprista Putri, and Agung Setiawan. 2021. "Pervaporation Membranes for Seawater Desalination Based on Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites. Part 1: Microstructure Properties" Membranes 11, no. 12: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120966
APA StyleSubaer, S., Fansuri, H., Haris, A., Misdayanti, Irfanita, R., Ramadhan, I., Putri, Y., & Setiawan, A. (2021). Pervaporation Membranes for Seawater Desalination Based on Geo–rGO–TiO2 Nanocomposites. Part 1: Microstructure Properties. Membranes, 11(12), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120966