Direct Purification of Digestate Using Ultrafiltration Membranes: Influence of Pore Size on Filtration Behavior and Fouling Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Digestate Pretreatment
2.2. UF System and Separation Process
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Membrane Performance
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Operating Parameters on Membrane Flux
3.1.1. Operating Temperature
3.1.2. Transmembrane Pressure
3.1.3. Cross-Flow Velocity
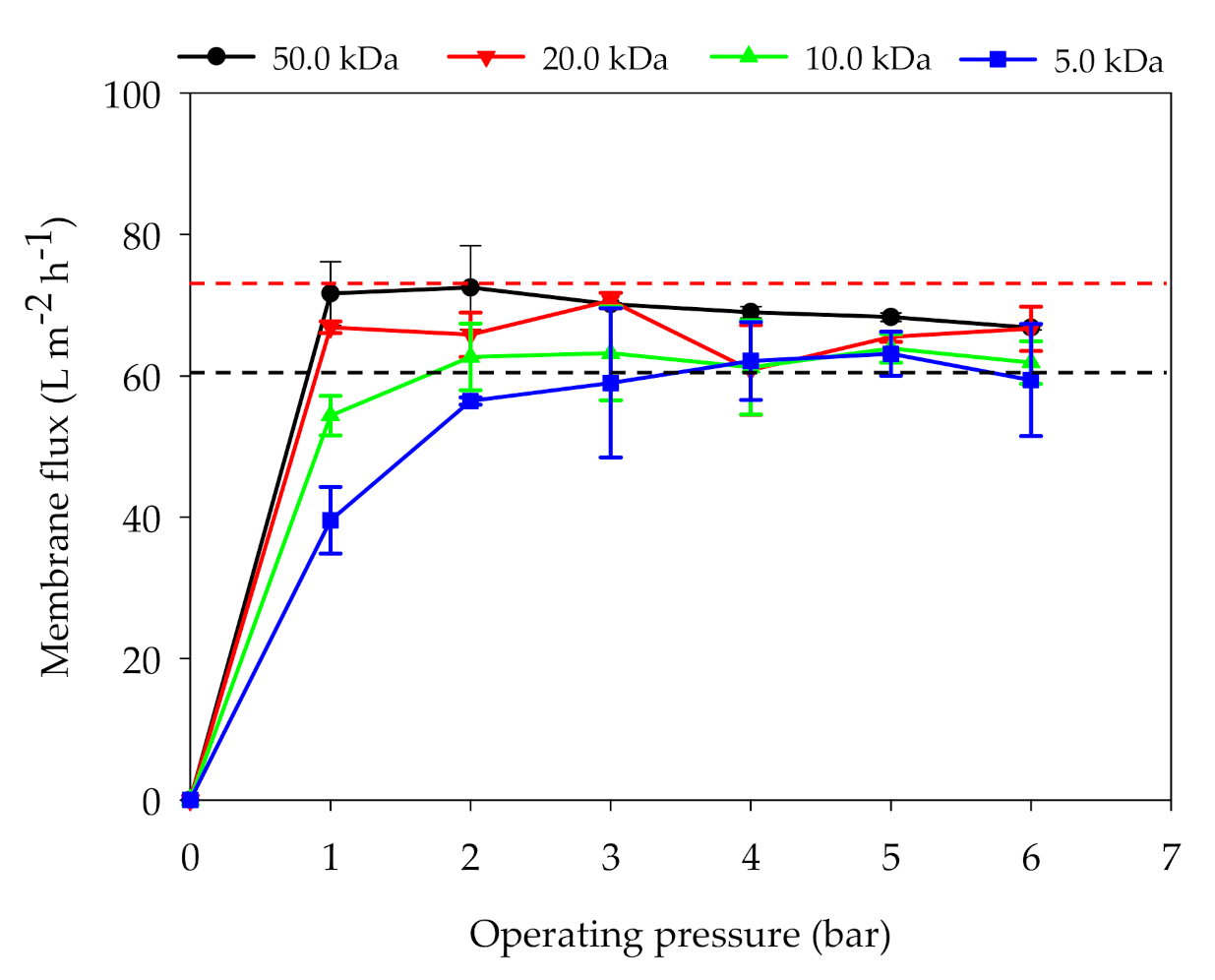
3.1.4. Membrane Flux Variation
3.2. Purification Effect of UF on Digestate
3.2.1. Changes in Physicochemical Characteristics
3.2.2. Antibiotics Removal
3.2.3. Dissolved Organic Matter
3.3. Membrane Fouling Characteristics
3.3.1. SEM-EDS
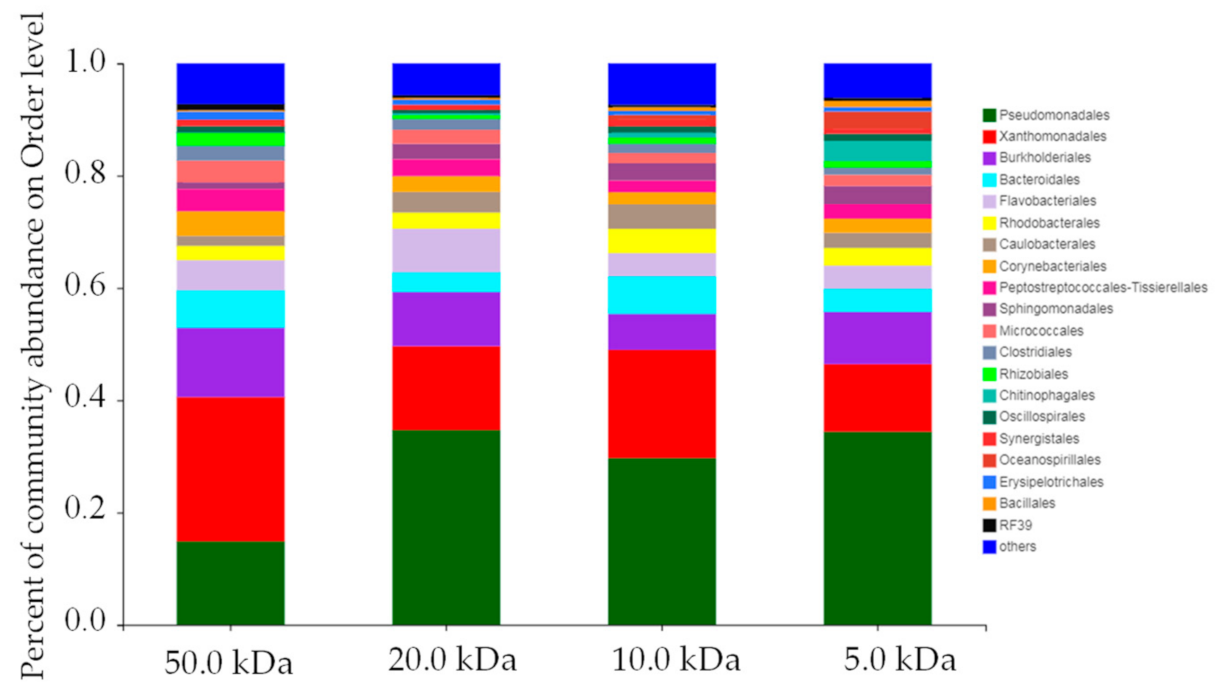
3.3.2. Bacterial Community Analysis
3.3.3. Membrane Cleaning
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| AD | anaerobic digestion |
| CTC | chlorotetracycline |
| CFV | cross-flow velocity (m s−1) |
| DOTC | doxycycline |
| EPS | extracellular polymeric substances |
| FRR | membrane flux recovery rate (%) |
| J | membrane flux (L m−2 h−1) |
| MWCO | molecule weight cut off |
| NF | nanofiltration |
| UF | ultrafiltration |
| OTC | oxytetracycline |
| PES | polyethersulfone |
| RO | reverse osmosis |
| SEM-EDS | scanning electron microscope-energy spectroscopy |
| SMP | soluble microbial products |
| TET | tetracycline |
| TMP | transmembrane pressure |
| 3D-EEM | three-dimensional excitation emission matrix |
References
- Dai, X.; Gai, X.; Dong, B. Rheology evolution of sludge through high-solid anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 174, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ersahin, M.E.; Ghasimi, D.S.; Ozgun, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, M.; Yang, Y.; Stuckey, D.C.; Van Lier, J.B. Biogas productivity of anaerobic digestion process is governed by a core bacterial microbiota. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Wang, D. Impact of molecular structure and charge property of chitosan based polymers on flocculation conditioning of advanced anaerobically digested sludge for dewaterability improvement. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 670, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilayn, F.; Jimenez, J.; Rouez, M.; Crest, M.; Patureau, D. Digestate mechanical separation: Efficiency profiles based on anaerobic digestion feedstock and equipment choice. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masse, L.; Massé, D.I.; Beauséjour, R. Effects of Polymer Charge Density and Molecular Weight on Flocculation Treatment of Swine Manure at Various Dry Matter Contents. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, C. The potential contribution of separation technologies to the management of livestock manure. Livest. Sci. 2007, 112, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Dong, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Yin, F.; Wang, S. Effects of Membrane Concentration Processes on Flux, Nutrient Recovery, and Antibiotic Isolation for Anaerobically Digested Slurry from Swine Manure. Trans. ASABE 2020, 63, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Duan, L.; Zhu, S.; Ye, Z.; Yu, H. The electrocoagulation pretreatment of biogas digestion slurry from swine farm prior to nanofiltration concentration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, L.; Massé, D.; Pellerin, Y. The use of membranes for the treatment of manure: A critical literature review. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 98, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.A.; Mladenov, N.; Wasswa, J. Fluorescent compounds retained by ultrafiltration membranes for water reuse. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 600, 117867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ihara, M.; Yamashita, N.; Tanaka, H. Improvement of virus removal by pilot-scale coagulation-ultrafiltration process for wastewater reclamation: Effect of optimization of pH in secondary effluent. Water Res. 2017, 114, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri-Rumbau, M.; Norddahl, B.; Wei, J.; Christensen, K.; Søtoft, L.F. Microfiltration and ultrafiltration as a post-treatment of biogas plant digestates for producing concentrated fertilizers. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 55, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkina, A.; Zacharof, M.-P.; Hery, G.; Nouvel, T.; Lovitt, R.W. Formulation and utilisation of spent anaerobic digestate fluids for the growth and product formation of single cell algal cultures in heterotrophic and autotrophic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Jin, X. Treatment of Anaerobically Digested Cattle Manure Wastewater by Tubular Ultrafiltration Membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Xue, W.; Li, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Integrated Fe-based floc-membrane process for alleviating ultrafiltration membrane fouling by humic acid and reservoir water. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-P.; Zhang, L.-Z. Conjugate heat and mass transfer in a cross-flow hollow fiber membrane bundle used for seawater desalination considering air side turbulence. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 533, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugere, R.; Mameri, N.; Gallot, J.; Comeau, Y. Treatment of pig farm effluents by ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 255, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Yang, Z.; Lin, J.; Shen, J.; Ji, J.; Gao, C.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Biogas slurry concentration hybrid membrane process: Pilot-testing and RO membrane cleaning. Desalination 2015, 368, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.; Lau, W.; Othman, M.; Ismail, A. Membrane fouling in desalination and its mitigation strategies. Desalination 2018, 425, 130–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Yin, F.; Yue, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zou, M.; Dong, H. Effect of Pretreatment on Hydraulic Performance of the Integrated Membrane Process for Concentrating Nutrient in Biogas Digestate from Swine Manure. Membranes 2020, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, A.Y.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Paul, D.R.; Field, R.W.; Freeman, B.D. Fouling mechanisms in constant flux crossflow ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X. Study of membrane morphology by microscopic image analysis and membrane structure parameter model. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, M.; Yasin, M.; Aslam, M.; Kumar, G.; Atabani, A.; Idrees, M.; Anjum, F.; Jamil, F.; Ahmad, R.; Khan, A.L.; et al. Anaerobic membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment: Novel configurations, fouling control and energy considerations. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 283, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfort, G.; Davis, R.H.; Zydney, A.L. The behavior of suspensions and macromolecular solutions in crossflow microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 96, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waeger, F.; Delhaye, T.; Fuchs, W. The use of ceramic microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes for particle removal from anaerobic digester effluents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alresheedi, M.T.; Basu, O.D. Interplay of water temperature and fouling during ceramic ultrafiltration for drinking water production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.S.; Dunstan, D.E.; Martin, G.J. Influence of processing temperature on flux decline during skim milk ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Lin, S.; Zhou, X.; Dong, H.; Zhan, Y. Fate of antibiotics during membrane separation followed by physical-chemical treatment processes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 759, 143520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Lei, Y.-H.; Chen, Z.-A.; Deng, L.-W. The effects of temperature, organic matter and time-dependency on rheological properties of dry anaerobic digested swine manure. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, M.; Bernat, K.; Mikucka, W. Membrane Bioreactor Technology: The Effect of Membrane Filtration on Biogas Potential of the Excess Sludge. Membranes 2020, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobbo, A.; Bernardes, A.M.; Rosa, M.J.F.; De Pinho, M.N. Concentration Polarization in Ultrafiltration/Nanofiltration for the Recovery of Polyphenols from Winery Wastewaters. Membranes 2018, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, K.-J.; Sz, P.-Y. Effect of membrane pore size on the performance of cross-flow microfiltration of BSA/dextran mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, M.; Schiffer, S.; Heidebrecht, H.-J.; Dumpler, J.; Kulozik, U. Milk protein fractionation by custom-made prototypes of spiral-wound microfiltration membranes operated at extreme crossflow velocities. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 605, 118110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Heat transfer intensification and scaling mitigation in bubbling-enhanced membrane distillation for brine concentration. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gienau, T.; Ehrmanntraut, A.; Kraume, M.; Rosenberger, S. Influence of Ozone Treatment on Ultrafiltration Performance and Nutrient Flow in a Membrane Based Nutrient Recovery Process from Anaerobic Digestate. Membranes 2020, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Livestock and Poultry Breeding. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/swrwpfbz/200301/t20030101_66550.shtml (accessed on 28 January 2021).
- Carbonell-Alcaina, C.; Soler-Cabezas, J.L.; Bes-Piá, A.; Vincent-Vela, M.C.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Pastor-Alcañiz, L.; Álvarez-Blanco, S. Integrated Membrane Process for the Treatment and Reuse of Residual Table Olive Fermentation Brine and Anaerobically Digested Sludge Centrate. Membranes 2020, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, L.; Massé, D.I.; Beaudette, V.; Muir, M. Size distribution and composition of particles in raw and anaerobically digested swine manure. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Marti, E.; Balcázar, J.L.; Boy-Roura, M.; Busquets, A.; Colón, J.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Lekunberri, I.; Borrego, C.M.; Ponsá, S.; et al. Fate of pharmaceuticals and antibiotic resistance genes in a full-scale on-farm livestock waste treatment plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part, I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Luo, W. Removal of antibiotics by sequencing-batch membrane bioreactor for swine wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Han, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Effect of extracellular polymer substances on the tetracycline removal during coagulation process. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 309, 123316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, J.; Massa, L.; Sperlich, A.; Gnirss, R.; Jekel, M. UV254 absorbance as real-time monitoring and control parameter for micropollutant removal in advanced wastewater treatment with powdered activated carbon. Water Res. 2016, 94, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Liu, C.; Song, L. Soluble microbial products in membrane bioreactor operation: Behaviors, characteristics, and fouling potential. Water Res. 2007, 41, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fane, A.; Fell, C.; Suki, A. The effect of ph and ionic environment on the ultrafiltration of protein solutions with retentive membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1983, 16, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongwong, W.; Goh, K.; Sethunga, D.; Bae, T.-H. Fouling formation in membrane contactors for methane recovery from anaerobic effluents. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, S.; Fukushima, T.; Ishii, S.; Okabe, S. Membrane fouling potentials and cellular properties of bacteria isolated from fouled membranes in a MBR treating municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2016, 100, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Wan, C.; Lee, D.-J. Understanding the role of extracellular polymeric substances in the rheological properties of aerobic granular sludge. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 705, 135948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Membrane Type | MWCO (Da) | Contact Angle (°) | Pure Water Flux (L m−2 h−1) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PES 5.0 | 5000 | 74.1 ± 6.9 | 151.4 ± 16.3 |
| PES 10.0 | 10,000 | 64.4 ± 1.7 | 203.8 ± 9.4 |
| PES 20.0 | 20,000 | 52.0 ± 4.8 | 309.6 ± 19.4 |
| PES 50.0 | 50,000 | 68.7 ± 2.2 | 593.6 ± 84.5 |
| Treatment | Types | COD/ (mg⋅L−1) | TP/ (mg⋅L−1) | NH3-N/ (mg⋅L−1) | TN/ (mg⋅L−1) | K/ (mg⋅L−1) | OTC/ (μg L−1) | CTC/ (μg L−1) | TET/ (μg L−1) | DOTC/ (μg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | 1345 ± 261.7 b | 100.6 ± 20.0 ab | 647.5 ± 31.8 a | 660 ± 254.6 a | 1092.8 ± 50.6 a | 89.1 ± 33.8 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 24.4 ± 9.6 b | 2.2 ± 0.1 | |
| 50.0 kDa | Concentrate 2 | 2500 ± 1244.5 ab | 52.7 ± 69.6 ab | 597.5 ± 17.7 ab | 800 ± 141.4 a | 1106 ± 58.7 a | 156.1 ± 132.4 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 62.0 ± 0.1 | 13.7 ± 0.1 |
| Permeate | 290 ± 70.7 c | 25.6 ± 0.87 b | 517.5 ± 31.8 b | 530 ± 240.4 a | 1081.8 ± 10.3 a | 3.0 ± 0.1 | - 3 | - | - | |
| 20.0 kDa | Concentrate | 3470 ± 98.9 a | 189.2 ± 14.8 a | 610.0 ± 21.2 ab | 830 ± 42.4 a | 1148.3 ± 63.9 a | 247.7 ± 2.08 c | 4.4 ± 0.06 | 70.7 ± 7.9 | 12.6 ± 0.8 |
| Permeate | 175 ± 35.4 c | 30.5 ± 0.9 b | 625.0 ± 28.3b | 530 ± 183.8 a | 1087.3 ± 72.5 a | - | - | - | - | |
| 10.0 kDa | Concentrate | 3410 ± 240.4 a | 176.9 ± 28.7 a | 645.0 ± 7.1 a | 720 ± 226.3 a | 1094.8 ± 107.1 a | 283.2 ± 56.7 | 6.4 ± 2.7 | 84.7 ± 15.5 | 14.2 ± 5.2 |
| Permeate | 155.0 ± 21.2 c | 29.3 ± 2.6 b | 537.5 ± 53.0 b | 490 ± 14.1 a | 1053.3 ± 43.5 a | - | - | - | - | |
| 5.0 kDa | Concentrate | 2680.0 ± 551.5 ab | 190.5 ± 82.6 ab | 620.0 ± 14.1 ab | 810 ± 14.1 a | 1120.3 ± 63.9 a | 241.0 ± 12.4 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 57.6 ± 14.4 | 8.5 ± 2.7 |
| Permeate | 140.0 ± 0.01 c | 29.3 ± 1.7 b | 572.5 ± 24.7 ab | 510 ± 127.3 a | 1131 ± 105.4 a | - | - | - | - |
| Region | Organic | Ex(nm) | Em(nm) | Integral Standard Volume (au·nm2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | 50.0 kDa Effluent | 20.0 kDa Effluent | 10.0 kDa Effluent | 5.0 kDa Effluent | ||||
| I | Aromatic proteins I | 200~250 | 280–330 | 117,160 | 95,434 | 109,728 | 100,691 | 125,757 |
| II | Aromatic proteins II | 200~250 | 330–380 | 59,069 | 39,427 | 43,380 | 44,546 | 39,970 |
| Ⅲ | Fulvic acid-like | 200~250 | 380–550 | 381,601 | 285,436 | 283,485 | 276,636 | 357,423 |
| Ⅳ | SMBP | 250~340 | 280–380 | 492,550 | 387,255 | 356,757 | 357,817 | 357,841 |
| Ⅴ | Humic acid-like | 340~400 | 380–550 | 386,489 | 234,302 | 250,661 | 200,942 | 243,290 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, C.; Dong, H.; Chen, Y.; Shang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z. Direct Purification of Digestate Using Ultrafiltration Membranes: Influence of Pore Size on Filtration Behavior and Fouling Characteristics. Membranes 2021, 11, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030179
Yue C, Dong H, Chen Y, Shang B, Wang Y, Wang S, Zhu Z. Direct Purification of Digestate Using Ultrafiltration Membranes: Influence of Pore Size on Filtration Behavior and Fouling Characteristics. Membranes. 2021; 11(3):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030179
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Caide, Hongmin Dong, Yongxing Chen, Bin Shang, Yi Wang, Shunli Wang, and Zhiping Zhu. 2021. "Direct Purification of Digestate Using Ultrafiltration Membranes: Influence of Pore Size on Filtration Behavior and Fouling Characteristics" Membranes 11, no. 3: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030179
APA StyleYue, C., Dong, H., Chen, Y., Shang, B., Wang, Y., Wang, S., & Zhu, Z. (2021). Direct Purification of Digestate Using Ultrafiltration Membranes: Influence of Pore Size on Filtration Behavior and Fouling Characteristics. Membranes, 11(3), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030179






