Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes for Non-Polar Solvents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials for TFC Membrane
2.1. Support Membranes
- Preparation of the polymer dope solution using polar aprotic solvents such as dimethylformamide (DMF), N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and degassing
- Casting the polymer film on the highly porous non-woven fabric using a casting knife
- Immersing the cast film in the non-solvent (usually water) bath
2.2. Selective Layers
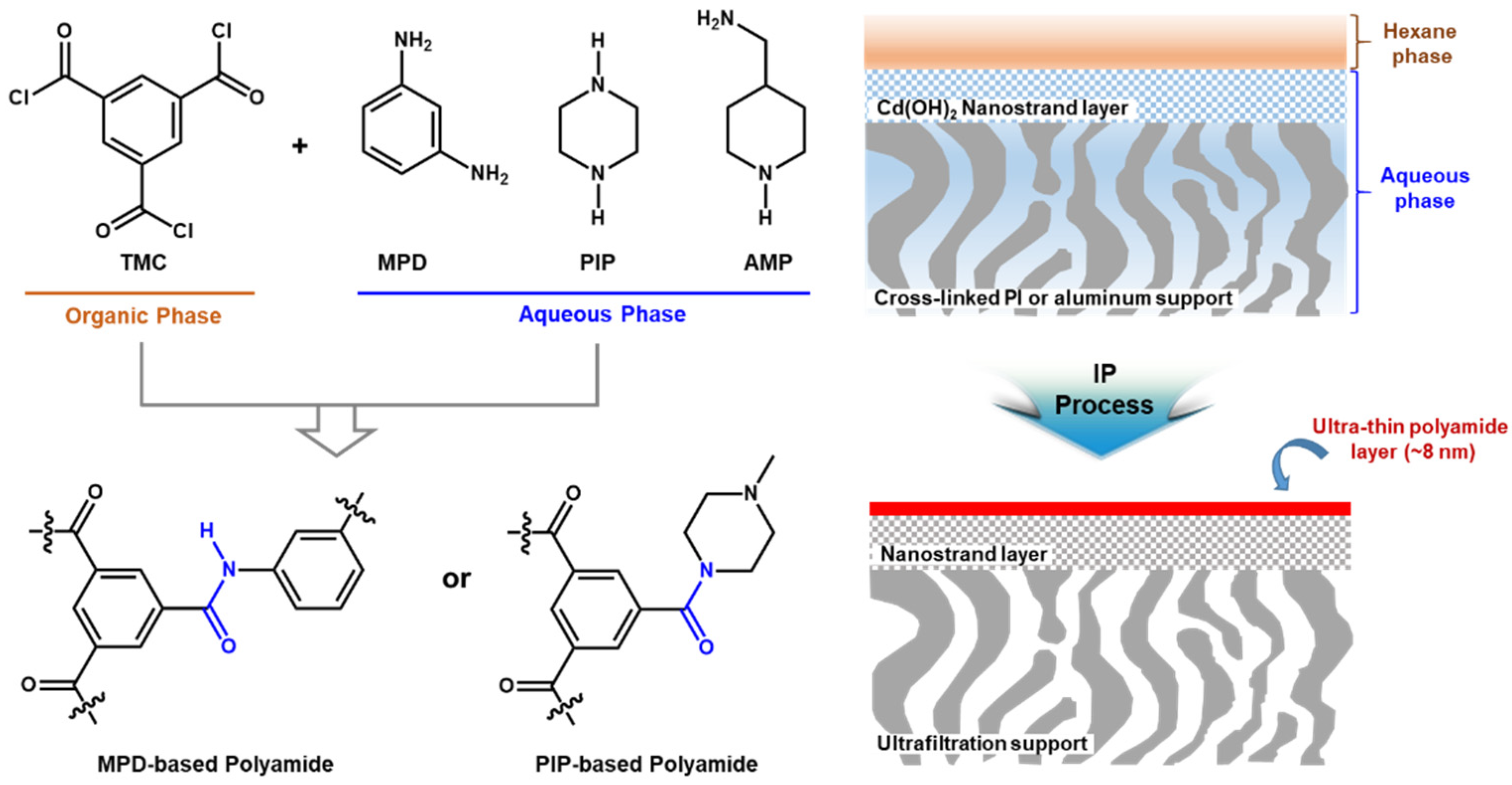
- Preparation of two immiscible monomer solutions (MPD and TMC commonly dissolved in water and n-hexane, respectively)
- First step: immersing the porous support membrane in MPD aqueous solution for a few minutes (3~30 min)
- Second step: contacting MPD-immersed support membrane in TMC organic solution for a few minutes (1~5 min) after removing excess MPD solution on the porous support membrane using a gummous roller.
- Final step: cleaning the prepared PA TFC membrane using a pure n-hexane to stop the reaction and then drying.
2.2.1. Conventional MPD-based Selective Layer
2.2.2. Selective Layer with Enhanced Microporosity
2.2.3. Selective Layer Prepared by Sustainable Sources
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchetti, P.; Solomon, M.F.J.; Szekely, G.; Livingston, A.G. Molecular Separation with Organic Solvent Nanofiltration: A Critical Review. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10735–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Ma, D.; Ardakani, P.N. Nanocomposite membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2018, 49, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, P.; Peeva, L.; Livingston, A. The Selectivity Challenge in Organic Solvent Nanofiltration: Membrane and Process Solutions. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2017, 8, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekely, S.; Solomon, M.F.J.; Marchetti, P.; Kim, J.F.; Livingston, A.G. Sustainability assessment of organic solvent nanofiltration: From fabrication to application. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4431–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tashvigh, A.A.; Feng, Y.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C.; Chung, T.S. 110th Anniversary: Selection of Cross-Linkers and Cross-Linking Procedures for the Fabrication of Solvent-Resistant Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review. Ind. End. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 10678–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, S.; Marien, H.; Goethem, C.V.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Recent developments in thin film (nano)composite membranes for solvent resistant nanofiltration. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2015, 8, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandezande, P.; Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Solvent resistant nanofiltration: Separating on a molecular level. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 365–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgojo, P.; Karan, S.; Wong, H.C.; Solomon, M.F.J.; Cabral, J.T.; Livingston, A.G. Ultrathin Polymer Films with Intrinsic Microporosity: Anomalous Solvent Permeation and High Flux Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4729–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroko, I.; Livingston, A. Impact of TiO2 nanoparticles on morphology and performance of crosslinked polyimide organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 343, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.F.J.; Bhole, Y.; Livingston, A.G. High flux membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN)—Interfacial polymerization with solvent activation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroko, I.; Lopes, M.P.; Livingston, A. The effect of membrane formation parameters on performance of polyimide membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN): Part A. Effect of polymer/solvent/non-solvent system choice. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroko, I.; Makowski, M.; Spill, F.; Livingston, A. The effect of membrane formation parameters on performance of polyimide membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). Part B: Analysis of evaporation step and the role of a co-solvent. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroko, I.; Sairam, M.; Livingston, A.G. The effect of membrane formation parameters on performance of polyimide membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). Part C. Effect of polyimide characteristics. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishmanesh, S.; Tasselli, F.; Jansen, J.C.; Tocci, E.; Bazzarelli, F.; Bernado, P.; Luis, P.; Degrève, J.; Drioli, E.; Van der Bruggen, B.J. Preparation of solvent stable polyphenylsulfone hollow fiber nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishmanesh, S.; Jansen, J.C.; Tasselli, F.; Tocci, E.; Luis, P.; Degrève, J.; Drioli, E.; Van der Bruggen, B.J. Novel polyphenylsulfone membrane for potential use in solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holda, A.K.; Aernouts, B.; Saeys, W.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.J. Study of polymer concentration and evaporation time as phase inversion parameters for polysulfone-based SRNF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holda, A.K.; De Roeck, M.; Hendrix, K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.J. The influence of polymer purity and molecular weight on the synthesis of integrally skinned polysulfone membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.J. Integrally skinned PSf-based SRNF-membranes prepared via phase inversion—Part A: Influence of high molecular weight additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.J. Integrally skinned PSf-based SRNF-membranes prepared via phase inversion—Part B: Influence of low molecular weight additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.S.; Nitsch, A.R. Solvent recovery from lube oil filtrates with a polyimide membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 179, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Greens, J.; Vandecasteele, C. Fluxes and rejections for nanofiltration with solvent stable polymeric membranes in water, ethanol and n-hexane. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Burgal, J.; Peeva, L.; Livingston, A. Negligible ageing in poly(ether-ether-ketone) membranes widens application range for solvent processing. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Burgal, J.; Peeva, L.G.; Kumbharkar, S.; Livingston, A. Organic solvent resistant poly(ether-ether-ketone) nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Burgal, J.; Peeva, L.; Marchetti, P.; Livingston, A. Controlling molecular weight cut-off of PEEK nanofiltration membranes using a drying method. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalwani, M.; Benes, N.E.; Bargeman, G.; Stamatialis, D.; Wessling, M. Effect of pH on the performance of polyamide/polyacrylonitrile based thin film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; McCutcheon, J.R. Polyacrylonitrile supported thin film composite hollow fiber membranes for forward osmosis. Desalination 2015, 372, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yu, Q.; Deng, B. Preparation and characterization of polyamide thin-film composite (TFC) membranes on plasma-modified polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 344, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Seo, J.A.; Lee, H.H.; Jeong, S.K.; Park, H.S.; Min, B.R. Simple method for preparing thin film composite polyamide nanofiltration membrane based on hydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride support membrane. Thin Solid Films 2017, 624, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, M.; Goethem, C.V.; Thijs, M.; Koeckelberghs, G.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Crosslinked PVDF-membranes for solvent resistant nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 566, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Chung, T.S. Polyelectrolyte functionalized lamellar graphene oxide membranes on polypropylene support for organic solvent nanofiltration. Carbon 2017, 122, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Kim, S.S. Plasma treatment of polypropylene and polysulfone supports for thin film composite reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korikov, A.P.; Kosaraju, P.B.; Sirkar, K.K. Interfacially polymerized hydrophilic microporous thin film composite membranes on porous polypropylene hollow fibers and flat films. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 279, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaraju, P.B.; Sirkar, K.K. Interfacially polymerized thin film composite membranes on microporous polypropylene supports for solvent-resistant nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 321, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, B.A.; Habboub, O.S.; Aristizabal, S.L.; Szekely, G.; Nunes, S.P. Recycled Poly(ethylene terephthalate) for High Temperature Solvent Resistant Membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdellah, M.H.; Perez-Manriquez, L.; Puspasari, T.; Scholes, C.A.; Kentish, S.E.; Peinemann, K.-V. A catechin/cellulose composite membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 567, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Kwon, S.J.; Shin, M.G.; Park, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Park, C.H.; Park, H.; Lee, J.H. Polyethylene-supported high performance reverse osmosis membranes with enhanced mechanical and chemical durability. Desalination 2018, 436, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtcheva, I.B.; Marchetti, P.; Livingston, A.G. Crosslinked polybenzimidazole membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN): Analysis of crosslinking reaction mechanism and effects of reaction parameters. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tashvigh, A.A.; Chung, T.S. Facile fabrication of solvent resistant thin film composite membranes by interfacial crosslinking reaction between polyethylenimine and dibromo-pxylene on polybenzimidazole substrates. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 560, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; He, R. Fabrication of crosslinked polybenzimidazole membranes by trifunctional crosslinkers for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.L.; Chou, Y.C.; Yu, T.L.; Lai, S.W. Poly(benzimidazole)-epoxide crosslink membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Chung, T.S. A novel crosslinking technique towards the fabrication of high-flux polybenzimidazole (PBI) membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanherck, K.; Odena, A.C.; Koeckelberghs, G.; Dedroog, T.; Vankelecom, I. A simplified diamine crosslinking method for PI nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 353, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroko, I.; Bhole, Y.; Livingston, A.G. Environmentally friendly route for the preparation of solvent resistant polyimide nanofiltration membranes. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Kim, J.F.; Ignacz, G.; Pogany, P.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Bio-Inspired Robust Membranes Nanoengineered from Interpenetrating Polymer Networks of Polybenzimidazole/Polydopamine. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.D.; Zhao, L.L.; Yong, W.F.; Wang, Q.; Duan, L.; Sun, S.P. Highly solvent-durable thin-film molecular sieve membranes with insoluble polyimide nanofibrous substrate. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128206–128215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Moon, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Cook, M.; Livingston, A.G.; Lee, Y.M. A robust thin film composite membrane incorporating thermally rearranged polymer support for organic solvent nanofiltration and pressure retarded osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The Future of Seawater Desalination: Energy, Technology, and the Environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Japip, S.; Chung, T.S. Organic solvent resistant membranes made from a cross-linked functionalized polymer with intrinsic microporosity (PIM) containing thioamide groups. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.R.; Steffes, J.; Huey, B.D.; McCutcheon, J.R. 3D printed polyamide membranes for desalination. Science 2018, 361, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tijing, L.D.; Dizon, J.R.C.; Ibrahim, I.; Nisay, A.R.N.; Shon, H.K.; Advincula, R.C. 3D printing for membrane separation, desalination and water treatment. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Gu, J.E.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.; Bang, J.; Baek, K.Y.; Park, B.; Lee, J.S.; Chan, E.P.; Lee, J.H. Tailor-Made Polyamide Membranes for Water Desalination. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.E.; Stafford, C.M.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, W.; Kim, B.Y.; Beak, K.Y.; Chan, E.P.; Chung, J.Y.; Bang, J.; Lee, J.H. Molecular Layer-by-Layer Assembled Thin-Film Composite Membranes for Water Desalination. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4778–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Constructing interlayer to tailor structure and performance of thin-film composite polyamide membranes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 282, 102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karan, S.; Jiang, Z.; Livingston, A.G. Sub–10 nm polyamide nanofilms with ultrafast solvent transport for molecular separation. Science 2015, 348, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.G.; Park, S.H.; Kwon, S.J.; Kwon, H.E.; Park, J.B.; Lee, J.H. Facile performance enhancement of reverse osmosis membranes via solvent activation with benzyl alcohol. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 578, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, S.J.; Shin, M.G.; Nam, S.E.; Cho, Y.H.; Park, Y.I.; Kim, J.F.; Lee, J.H. Polyethylene Battery Separator as a Porous Support for Thin Film Composite Organic Solvent Nanofiltration Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44050–44058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Geise, G.M.; Freeman, B.D.; Lee, H.S.; Byun, G.; McGrath, J.E. Polyamide interfacial composite membranes prepared from m-phenylene diamine, trimesoyl chloride and a new disulfonated diamine. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 403–404, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Park, C.H.; Park, S.H.; Shin, M.G.; Kim, H.J.; Baek, K.Y.; Chan, E.P.; Bang, J.; Lee, J.H. Star polymer-assembled thin film composite membranes with high separation performance and low fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroush, A.; Barzin, J.; Barikani, M.; Fathizadeh, M. Interfacially polymerized polyamide thin film composite membranes: Preparation, characterization and performance evaluation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 287, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.F.J.; Song, Q.; Jelfs, K.E.; Ibanez, M.M.; Livingston, A.G. Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fritsch, D.; Merten, P.; Heinrich, K.; Lazar, M.; Priske, M. Ultrathin Polymer Films with Intrinsic Microporosity: Anomalous Solvent Permeation and High Flux Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Feng, W.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, L. PIM-1 pore-filled thin film composite membranes for tunable organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.; Gaffney, P.R.J.; Peeva, L.G.; Livingston, A.G. Roll-to-roll dip coating of three different PIMs for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 558, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, K.A.; Mathias, R.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Rangnekar, N.; Johnson, J.R.; Hoy, S.J.; Bechis, I.; Tarzia, A.; Jelfs, K.E.; et al. N-Aryl–linked spirocyclic polymers for membrane separations of complex hydrocarbon mixtures. Science 2020, 369, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Xiao, A.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Growing covalent organic frameworks on porous substrates for moleculesieving membranes with pores tunable from ultra- to nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaun, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Puyvelde, P.V.; Bruggen, B.V.D. Covalent organic frameworks for membrane separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) for Membrane Separation: A Mini Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 15394–15406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandambeth, S.; Biswal, B.P.; Chaudhari, H.D.; Rout, K.C.; Kunjattu H., K.; Mitra, S.; Karak, S.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Kharul, U.K.; et al. Selective Molecular Sieving in Self-Standing Porous Covalent-Organic-Framework Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603945–1603953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Lin, R.B.; Chen, B. Conjugated Microporous Polymers with Rigid Backbones for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. Chem 2018, 4, 2260–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinde, D.B.; Sheng, G.; Li, X.; Ostwal, M.; Emwas, A.H.; Huang, K.W.; Lai, Z. Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for High-Flux Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14342–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uribe, R.F.J.; Doonan, C.J.; Furukawa, H.; Oisaki, K.; Yaghi, O.M. Crystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks with Hydrazone Linkages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11478–11481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Wu, H.; Pan, F. High-efficiency water-selective membranes from the solution-diffusion synergy of calcium alginate layer and covalent organic framework (COF) layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, X.; Xiao, A.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y. Interfacial polymerization of covalent organic frameworks (COFs) on polymeric substrates for molecular separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 566, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Valentino, L.; Stiehl, G.M.; Balch, H.B.; Corcos, A.R.; Wang, F.; Ralph, D.C.; Marinas, B.J.; Dichtel, W.R. Lewis-Acid-Catalyzed Interfacial Polymerization of Covalent Organic Framework Films. Chem 2018, 4, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, B.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Shen, B.; He, X.; Ghazi, Z.A.; Khan, N.A.; Sin, H.; Khattak, A.M.; Li, L.; et al. Microporous membranes comprising conjugated polymers with rigid backbones enable ultrafast organic-solvent nanofiltration. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Alammar, A.; Fulop, Z.; Pulido, B.A.; Nunes, S.P.; Szekely, G. Hydrophobic thin film composite nanofiltration membranes derived solely from sustainable sources. Green Chem. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Sun, H.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Niu, Q.J. Non-organic solvent prepared nanofiltration composite membrane from natural product tannic acid (TA) and cyclohexane-1,4-diamine (CHD). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ma, X.; Wng, J.; Tang, C.Y. A One-Step Rapid Assembly of Thin Film Coating Using Green Coordination Complexes for Enhanced Removal of Trace Organic Contaminants by Membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12638–12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Yang, H.C.; Du, Y.; Xu, Z.K. Polyphenol Coating as an Interlayer for Thin-Film Composite Membranes with Enhanced Nanofiltration Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32512–32519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.L.; Neelakanda, P.; Peinemann, K.V. Tannin-based thin-film composite membranes for solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdellah, M.H.; Perez, M.L.; Puspasari, T.; Scholes, C.A.; Kentish, S.E.; Peinemann, K.V. Effective Interfacially Polymerized Polyester Solvent Resistant Nanofiltration Membrane from Bioderived Materials. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 2, 1800043–1800049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.L.; Neelakanda, P.; Peinemann, K.V. Morin-based nanofiltration membranes for organic solvent separation processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Hua, D.; Zhang, Y.; Japip, S.; Chung, T.S. Precise Molecular Sieving Architectures with Janus Pathways for Both Polar and Nonpolar Molecules. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705933–1705939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, L.F.; Huang, T.; Peinemann, K.V. Cyclodextrin Films with Fast Solvent Transport and Shape-Selective Permeability. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606641–1606647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.J.; Shen, Q.; Xu, Z.L.; Dong, Z.Q. Novel designed TFC membrane based on host-guest interaction for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117227–117237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Salehi, H.; Rastgar, M. Chitosan-based thin active layer membrane for forward osmosis desalination. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Almijbilee, M.M.A.; Zheng, J.; Wang, L. A thin film composite membrane prepared from monomers of vanillin and trimesoyl chloride for organic solvent nanofiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 263, 118394–118400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, H.A.L.; Blanford, C.F.; Szekely, G. Reporting the unreported: The reliability and comparability of the literature on organic solvent nanofiltration. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3397–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, H.; Peeva, L.G.; Stoikos, K.; Pasparakis, G.; Vamvakaki, M.; Livingston, A.G. Membranes for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration Based on Preassembled Nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Jacobs, P.A. Solvent-resistant nanofiltration with filled polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanherck, K.; Aerts, A.; Martens, J.; Vankelecom, I. Hollow filler based mixed matrix membranes. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2492–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, S.M.F.; Gorgojo, P.; Munoz, I.M.; Livingston, A.G. Beneath the surface: Influence of supports on thin film composite membranes by interfacial polymerization for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 448, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, G.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, P. Nanoparticle-Assembled Thin Film with Amphipathic Nanopores for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17804–17813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Su, B.; Han, L.; Mandal, B. Graphene oxide (GO)-interlayered thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes with high solvent resistance for organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 13315–13330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Novel thin-film nanocomposite membranes filled with multi-functional Ti3C2Tx nanosheets for task-specific solvent transport. Compos. Part A 2017, 100, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.F.J.; Bhole, Y.; Livingston, A.G. High flux hydrophobic membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration(OSN)-Interfacial polymerization, surface modification and solvent activation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cui, Y.; Chung, T.S. Hydrophobic Perfluoropolyether-Coated Thin-Film Composite Membranes for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.M.R.; Oh, J.; Sett, S.; Feng, L.; Yan, X.; Hoque, M.J.; Liu, A.; Haasch, R.T.; Masoomi, M.; Bagheri, R.; et al. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Made from Naturally Derived Hydrophobic Materials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 11362–11370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltane, H.B.; Roizard, D.; Favre, E. Study of the rejection of various solutes in OSN by a composite polydimethylsiloxane membrane: Investigation of the role of solute affinity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 161, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.M.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Liu, J.Y.; Chung, T.-S. Separation of vegetable oil compounds and solvent recovery using commercial organic solvent nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Name | Structure | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Polysulfone (PSF) | 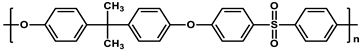 | [14] |
| Polyethersulfone (PES) | 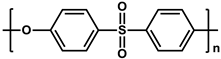 | [20] |
| Poly(ether ether ketone) (PEEK) | 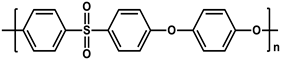 | [22] |
| Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) | 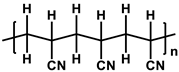 | [25] |
| Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) | 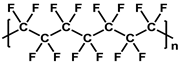 | [27] |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 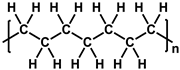 | [30] |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 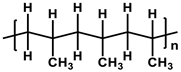 | [31] |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | 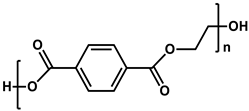 | [34] |
| Cellulose | 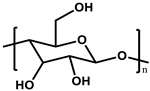 | [35] |
| Membrane No. | Fabrication | Performance | Reference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials (Selective Layer/ Support) | Method | Solvent System | Solvent | Permeance (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) | Solute | Solute MW (g mol−1) | Rejection (%) | ||
| 1 | Nanoparticle/PI | Coating | Methanol | Toluene | 0.6 | Styrene dimers | 220 | 90 | [89] |
| 2 | Zeolite-filled PDMS/PAN | Coating | Hexane/water | 0.58 | Wilkinson catalyst | 925 | >97 | [90] | |
| 3 | Silicalite-filled PDMS/PI | Coating | Hexane | 0.9 | Bromothymol blue | 624 | 80 | [91] | |
| 4 | Fluoro-functional PA/PEEK | IP (1) | Hexane/water | 2.0 | Styrene dimers | 236 | 98 | [92] | |
| 5 | PIM/PAN | Dip coating | Chloroform | 7.1 | Polystyrene | 800 | 90 | [63] | |
| 6 | QD-based PA/PAN | IP | Hexane/water | 2.5 | Acid yellow 14 | 450 | 90 | [93] | |
| 7 | TA-based polyimine/PET | IP | p-cymene/water | 3.5 | Styrene dimers | 235 | 75 | [76] | |
| 8 | CMP/PAN | Grafting | Toluene/triethylamine | n-Hexane | 31.7 | Protoporphyrin IX | 562 | 90 | [75] |
| 9 | GO-filled PA | IP | Hexane/water | 0.1 | Rhodamine B | 475 | 95 | [94] | |
| 10 | QD-based PA/PAN | IP | Hexane/water | 51 | AY79 Dyes | 1280 | 99 | [93] | |
| 11 | PIM/PAN | Spin coating | Chloroform | n-Heptane | 18 | Hexaphenylbenzene | 535 | 86~90 | [8] |
| 12 | Ti3C2Tx-filled PA/PAN | IP | Hexane/water | 1.8 | PEG | 200 | 92 | [95] | |
| 13 | PIM/PAN | Dip coating | Chloroform | 2.5 | polystyrene | 900 | 90 | [63] | |
| 14 | TA-based polyimine/PET | IP process | p-cymene/water | 2.5 | Styrene dimers | 235 | 91 | [76] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Kang, T.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.; Choi, S.H.; Yu, J.-Y.; Ok, S.; Park, S.-H. Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes for Non-Polar Solvents. Membranes 2021, 11, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030184
Lee S, Kang T, Lee JY, Park J, Choi SH, Yu J-Y, Ok S, Park S-H. Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes for Non-Polar Solvents. Membranes. 2021; 11(3):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030184
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seungmin, Taewon Kang, Jong Young Lee, Jiyu Park, Seoung Ho Choi, Jin-Yeong Yu, Serin Ok, and Sang-Hee Park. 2021. "Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes for Non-Polar Solvents" Membranes 11, no. 3: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030184
APA StyleLee, S., Kang, T., Lee, J. Y., Park, J., Choi, S. H., Yu, J.-Y., Ok, S., & Park, S.-H. (2021). Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes for Non-Polar Solvents. Membranes, 11(3), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030184







