Effect of Initial Water Flux on the Performance of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor: Constant Flux Mode versus Varying Flux Mode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
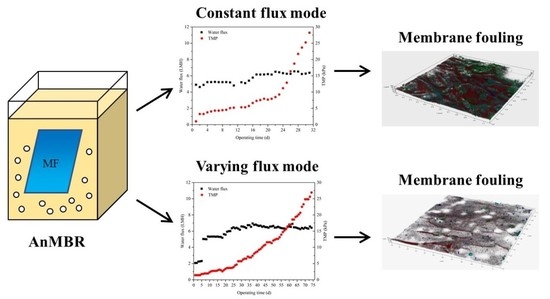
3.1. Performances at Different Operating Modes
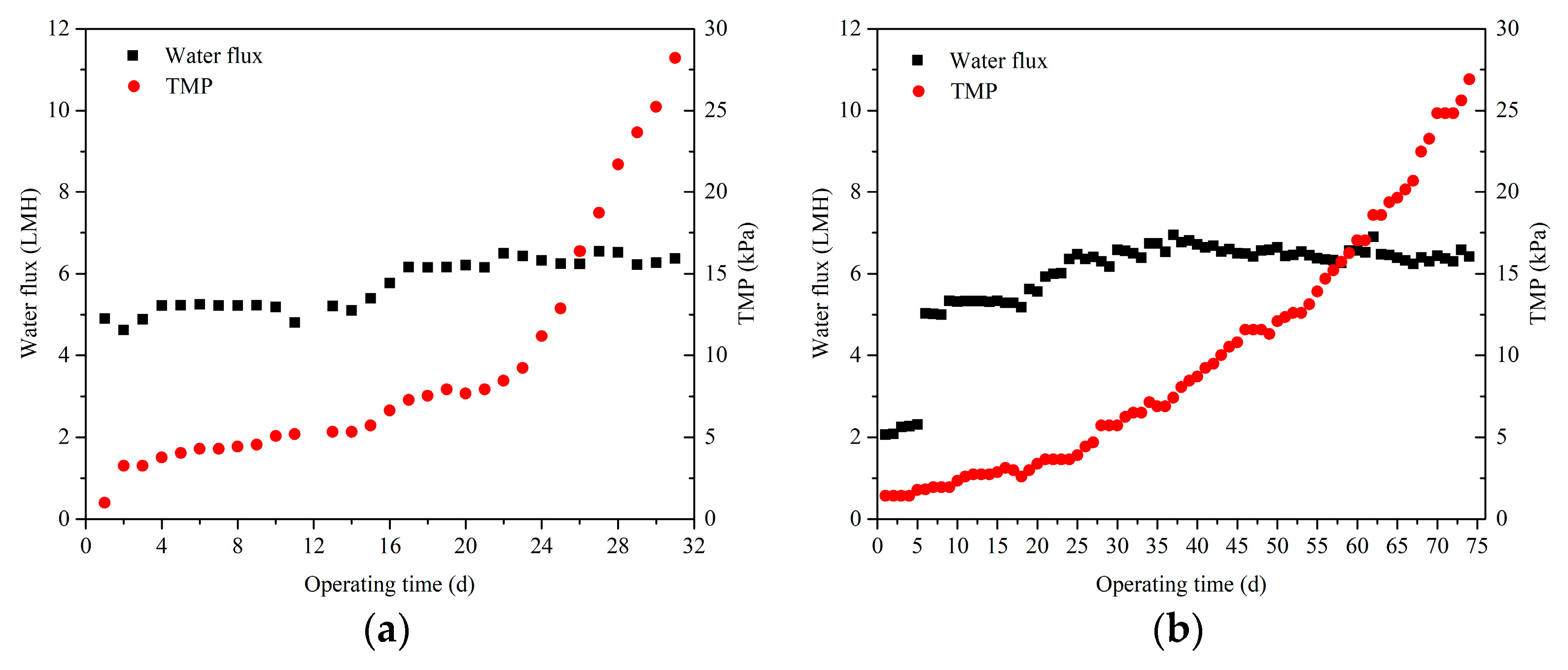
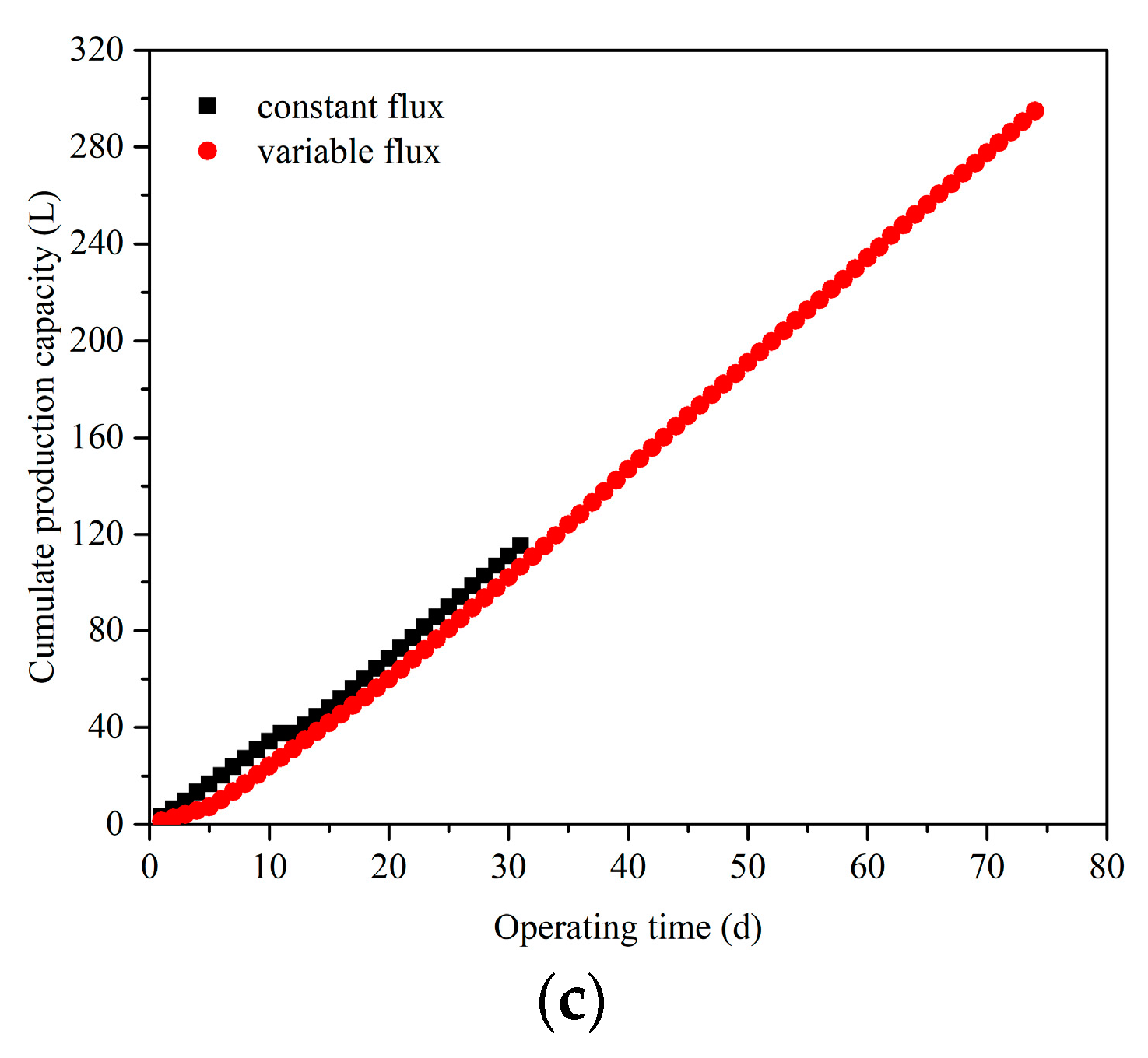
3.2. The Development of TMP and Cumulative Water Production at Different Operating Modes
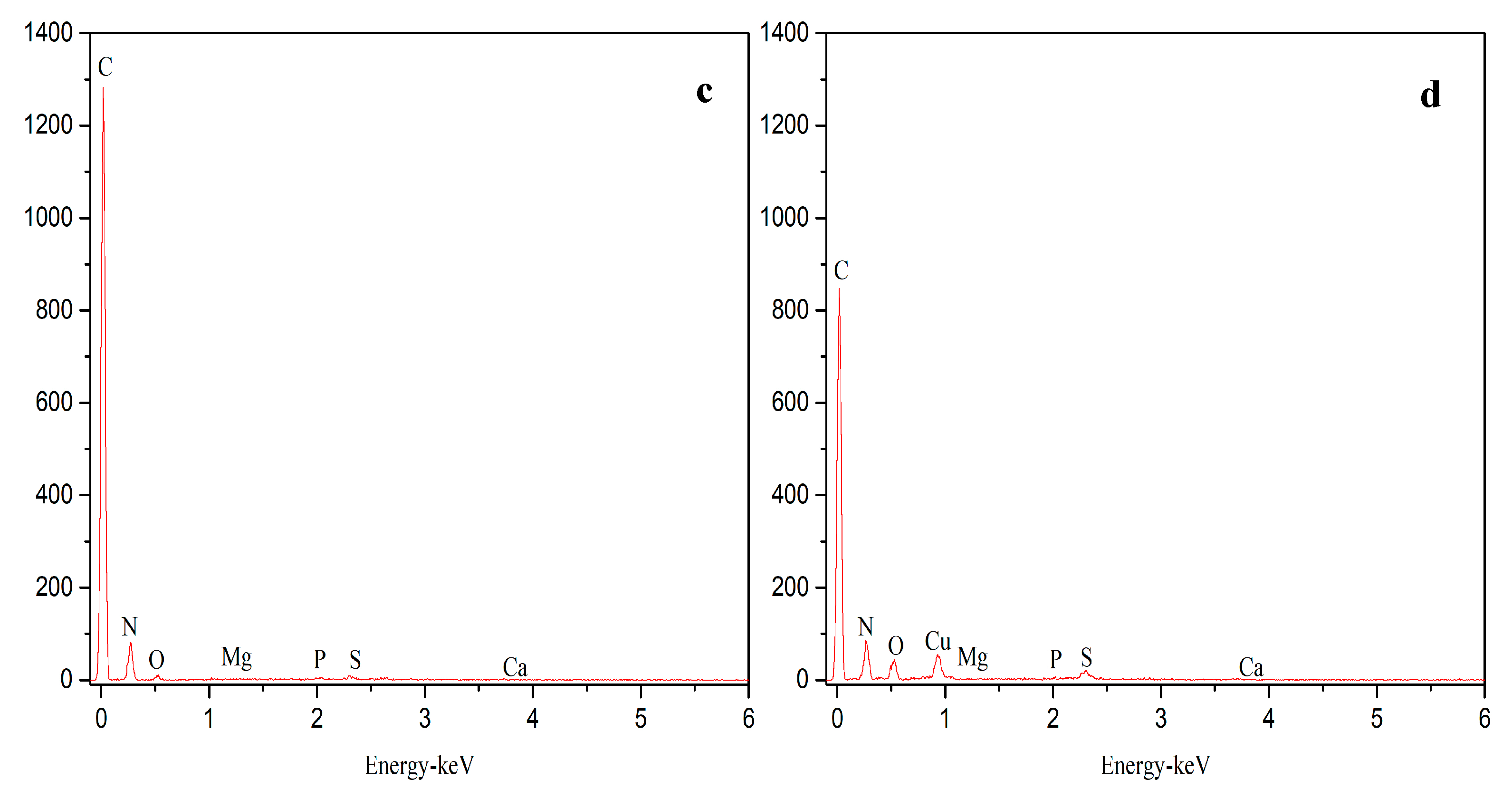
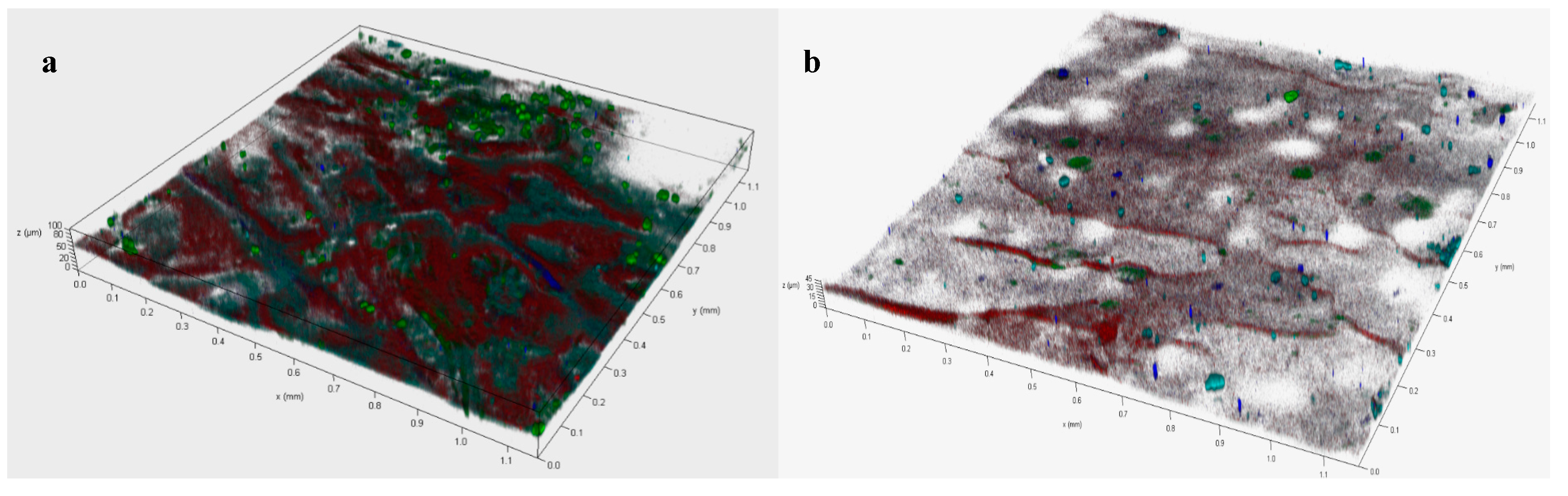
3.3. Fouling Characteristics at Different Operating Modes
3.4. Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, B.-Q.; Kraemer, J.T.; Bagley, D.M. Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors: Applications and Research Directions. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 489–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeison, D.; Vanlier, J. Thermophilic treatment of acidified and partially acidified wastewater using an anaerobic submerged MBR: Factors affecting long-term operational flux. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3868–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor for low-strength wastewater treatment: Effect of HRT and SRT on treatment performance and membrane fouling. Water Res. 2011, 45, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, Á.; Ruano, M.V.; García-Usach, F.; Ferrer, J. Sub-critical filtration conditions of commercial hollow-fibre membranes in a submerged anaerobic MBR (HF-SAnMBR) system: The effect of gas sparging intensity. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Ozturk, I.; Jeison, D.; Van Der Zee, F.; Van Lier, J.B. Potentials of anaerobic membrane bioreactors to overcome treatment limitations induced by industrial wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozgun, H.; Dereli, R.K.; Ersahin, M.E.; Kinaci, C.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. A review of anaerobic membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment: Integration options, limitations and expectations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersahin, M.E.; Gimenez, J.B.; Ozgun, H.; Tao, Y.; Spanjers, H.; van Lier, J.B. Gas-lift anaerobic dynamic membrane bioreactors for high strength synthetic wastewater treatment: Effect of biogas sparging velocity and HRT on treatment performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 305, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Meng, F.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; She, Q. Effect of driving force on the performance of anaerobic osmotic membrane bioreactors: New insight into enhancing water flux of FO membrane via controlling driving force in a two-stage pattern. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 569, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chang, V.W.; She, Q.; Tang, C.Y. Removal of cytostatic drugs from wastewater by an anaerobic osmotic membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xinhua, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Permeability recovery of fouled forward osmosis membranes by chemical cleaning during a long-term operation of anaerobic osmotic membrane bioreactors treating low-strength wastewater. Water Res. 2017, 123, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Q.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Membrane fouling in osmotically driven membrane processes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, V.W.; Tang, C.Y. Osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Advances, challenges, and prospects for the future. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Comparison of biofouling mechanisms between cellulose triacetate (CTA) and thin-film composite (TFC) polyamide forward osmosis membranes in osmotic membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 202, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.Y.; Hu, T.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Development of a novel anaerobic membrane bioreactor simultaneously integrating microfiltration and forward osmosis membranes for low-strength wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wicaksana, F.; Tang, C.Y.; Fane, A.G. Direct Microscopic Observation of Forward Osmosis Membrane Fouling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7102–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Xie, M.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. EDTA-based adsorption layer for mitigating FO membrane fouling via in situ removing calcium binding with organic foulants. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 578, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Kimura, K.; Wang, Q.; Han, X. Membrane cleaning in membrane bioreactors: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 468, 276–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, S.; Helmus, F.P.; Drews, A. Addition of Particles for Fouling Minimization in Membrane Bioreactors—Permeability Performance, Fluid Dynamics, and Rheology. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2015, 88, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-K.; Li, W.-W.; Sheng, G.-P.; Shi, B.-J.; Yu, H.-Q. In-situ utilization of generated electricity in an electrochemical membrane bioreactor to mitigate membrane fouling. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5794–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Columbia, M. Enzymatic control of alginate fouling of dead-end MF and UF ceramic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 381, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.; Li, Q. Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3931–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, S.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, H.; Hu, W.; Li, C.; Tong, L.; Kumar, R.R.; et al. Membrane fouling mitigation by coupling applied electric field in membrane system: Configuration, mechanism and performance. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 287, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ahn, W.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Comparison of the filtration characteristics between attached and suspended growth microorganisms in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.-R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.-S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Fane, A. Fouling transients in nominally sub-critical flux operation of a membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 209, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.; Liang, S.; Wei, C.; Wen, X.; Huang, X. Outlining the Roles of Membrane-Foulant and Foulant-Foulant Interactions in Organic Fouling During Microfiltration and Ultrafiltration: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.Y.; Peng, Y. Fouling of ultrafiltration membrane during secondary effluent filtration. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 30, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Environmental and Planning Agency. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Methods, 4th ed.; Chinese Environmental Science Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Li, X.; Yu, G. In situ observation of the growth of biofouling layer in osmotic membrane bioreactors by multiple fluorescence labeling and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Water Res. 2015, 75, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chua, H.; Zhou, J.; Fane, A. Factors affecting the membrane performance in submerged membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Nagai, Y.; Aizawa, T.; Kimura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Proteins causing membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyoshi, T.; Aizawa, T.; Kimura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Identification of proteins involved in membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors (MBRs) treating municipal wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 75, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peiris, R.; Jaklewicz, M.; Budman, H.; Legge, R.; Moresoli, C. Assessing the role of feed water constituents in irreversible membrane fouling of pilot-scale ultrafiltration drinking water treatment systems. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3364–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Hua, J. Membrane fouling mechanisms in the process of using flat-sheet membrane for simultaneous thickening and digestion of activated sludge. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Items | Performance | Constant Flux Mode | Varying Flux Mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| COD | MF permeate concentration (mg/L) | 193.55 ± 19.35 | 196.64 ± 16.26 |
| Removal rate (%) | 94.05 ± 0.95 | 94.06 ± 2.66 | |
| NH4+-N | MF permeate concentration (mg/L) | 67.35 ± 1.53 | 62.10 ± 4.58 |
| Removal rate (%) | 25.62 ± 6.70 | 29.77 ± 3.81 | |
| TP | MF permeate concentration (mg/L) | 6.25 ± 1.48 | 14.18 ± 1.78 |
| Removal rate (%) | 4.38 ± 1.93 | 18.36 ± 1.13 |
| Operating Mode | Total Cells (μm3/μm2) | Proteins (μm3/μm2) | α-d-glucopyranose (μm3/μm2) | β-d-glucopyranose (μm3/μm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant flux | 7.71 ± 0.40 | 8.20 ± 0.25 | 8.29 ± 0.38 | 7.72 ± 0.49 |
| Varying flux | 6.64 ± 0.36 | 2.37 ± 0.29 | 5.60 ± 0.28 | 4.26 ± 0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, X.; Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Wang, X. Effect of Initial Water Flux on the Performance of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor: Constant Flux Mode versus Varying Flux Mode. Membranes 2021, 11, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030203
Yi X, Zhang M, Song W, Wang X. Effect of Initial Water Flux on the Performance of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor: Constant Flux Mode versus Varying Flux Mode. Membranes. 2021; 11(3):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030203
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Xiawen, Meng Zhang, Weilong Song, and Xinhua Wang. 2021. "Effect of Initial Water Flux on the Performance of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor: Constant Flux Mode versus Varying Flux Mode" Membranes 11, no. 3: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030203
APA StyleYi, X., Zhang, M., Song, W., & Wang, X. (2021). Effect of Initial Water Flux on the Performance of Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor: Constant Flux Mode versus Varying Flux Mode. Membranes, 11(3), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030203