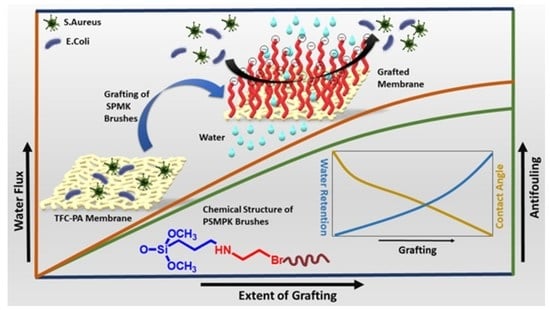
Antifouling and Flux Enhancement of Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Grafting Poly (3-Sulfopropyl Methacrylate) Brushes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Modification of Membrane
2.3. Characterization of Membranes
2.3.1. Evaluation of Grafting Yield
2.3.2. Antibacterial Testing of Membrane Samples
2.3.3. Biofilm Formation Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Microscopy
3.2. Functional Group Evaluation by FTIR
3.3. Morphological Observation
3.4. Contact Angle Measurements
3.5. Surface Roughness
3.6. Evaluation of Membrane Performance
3.7. Antibacterial Activity
3.8. Resistance to Biofilm Formation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, G.-D.; Cao, Y. Development of antifouling reverse osmosis membranes for water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, C.; Chen, R.; Li, J.; Li, J. Novel ionic liquid-type Gemini surfactants: Synthesis, surface property and antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 395, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ragunath, S. Emerging Membrane Technologies for Water and Energy Sustainability: Future Prospects, Constrains and Challenges. Energies 2018, 11, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, R.S.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Deshmukh, K.; Mehta, A.; Basu, S.; Meshram, J.S.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.A.; Karim, A. Natural polymer based composite membranes for water purification: A review. Polym. Technol. Mater. 2019, 58, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1043–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Arnot, T.C.; Mattia, D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination—Development to date and future potential. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-R.; Wang, J.; Li, C. Strategies for improving the performance of the polyamide thin film composite (PA-TFC) reverse osmosis (RO) membranes: Surface modifications and nanoparticles incorporations. Desalination 2013, 328, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Rui, X.; Zhang, Z. A Review on Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membranes for Water Purification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Elimelech, M. Influence of colloidal fouling and feed water recovery on salt rejection of RO and NF membranes. Desalination 2004, 160, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Elimelech, M.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling membranes for sustainable water purification: Strategies and mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5888–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.R.; Gohil, J.M.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Antifouling, fouling release and antimicrobial materials for surface modification of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahkaramipour, N.; Tran, T.; Ramanan, S.; Lin, H. Membranes with Surface-Enhanced Antifouling Properties for Water Purification. Membranes 2017, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, I.; Pangule, R.C.; Kane, R.S. Antifouling Coatings: Recent Developments in the Design of Surfaces That Prevent Fouling by Proteins, Bacteria, and Marine Organisms. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 690–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.S.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Misdan, N.; Ismail, A.F. Nanomaterials for biofouling and scaling mitigation of thin film composite membrane: A review. Desalination 2016, 393, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Lü, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Gao, C. Surface modification of thin-film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes by coating N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid copolymers for improved membrane properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Chi, W.S.; Ahn, S.H.; Park, C.H.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, J.H. Synthesis of poly(vinyl chloride)-g-poly(3-sulfopropyl methacrylate) graft copolymers and their use in pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 247, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xue, J.; Ran, F.; Sun, S. Modification of polyethersulfone membranes—A review of methods. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 76–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, J.; Kowalewski, T.; Matyjaszewski, K. Synthesis of Polymer Brushes Using Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2003, 24, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lee, J.; Ma, J.; Elimelech, M. Antifouling Thin-Film Composite Membranes by Controlled Architecture of Zwitterionic Polymer Brush Layer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.; Matyjaszewski, K. Solvent Effects on the Activation Rate Constant in Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 3350–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coessens, V.; Pintauer, T.; Matyjaszewski, K. Functional polymers by atom transfer radical polymerization. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 337–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fristrup, C.J.; Jankova, K.; Hvilsted, S. Surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization—A technique to develop biofunctional coatings. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbey, R.; Lavanant, L.; Paripovic, D.; Schüwer, N.; Sugnaux, C.; Tugulu, S.; Klok, H.-A. Polymer Brushes via Surface-Initiated Controlled Radical Polymerization: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5437–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiu, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Improving the performance of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane by incorporation of modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Takahara, A. Tribological properties of hydrophilic polymer brushes under wet conditions. Chem. Rec. 2010, 10, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Wickramasinghe, S. Photo-induced graft polymerization of N-isopropyl acrylamide on thin film composite membrane: Produced water treatment and antifouling properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 90, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.A.; Mushtaq, S.; Cheema, W.A.; Qiblawey, H.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Sadiq, R.; et al. Surface Modification of TFC-PA RO Membrane by Grafting Hydrophilic pH Switchable Poly(Acrylic Acid) Brushes. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 8281058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Cui, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Song, L.-S.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Han, B.; Zhu, J. Poly(acrylic acid) brushes pattern as a 3D functional biosensor surface for microchips. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 266, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.G.; Uthirakumar, P.; Nahm, K.S.; Elizabeth, R.N. Fabrication and electro chemical properties of poly vinyl alcohol/para toluene sulfonic acid membranes for the applications of DMFC. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry -IInterpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2004, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, B.; Ma, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X. Permanently antistatic and high transparent PMMA terpolymer: Compatilizer, antistatic agent, and the antistatic mechanism. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstedt, M.; Cheng, N.; Azzaroni, O.; Mossialos, D.; Mathieu£, A.H.J.; Huck, W.T. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(3-Sulfopropylmethacrylate) Brushes for Potential Antibacterial Applications. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yameen, B.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Langner, A.; Duran, H.; Müller, F.; Gösele, U.; Azzaroni, O.; Knoll, W. Facile Large-Scale Fabrication of Proton Conducting Channels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13140–13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, Y.; Inukai, S.; Araki, T.; Cruz-Silva, R.; Ortiz-Medina, J.; Morelos-Gomez, A.; Tejima, S.; Yamanaka, A.; Obata, M.; Nakaruk, A.; et al. Effective Antiscaling Performance of Reverse-Osmosis Membranes Made of Carbon Nanotubes and Polyamide Nanocomposites. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6047–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, H.H.; Saha, N.K.; Jewrajka, S.K.; Reddy, A. Low fouling and improved chlorine resistant thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes by cerium(IV)/polyvinyl alcohol mediated surface modification. Desalination 2015, 357, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Desalination and Water Treatment Preparation and characterization of surface-modified zeolite-polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes for desalination Preparation and characterization of surface-modifi ed zeolite-polyamide. Desalin. Water Treat 2012, 34, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesalski, M.; Rühe, J. Swelling of a Polyelectrolyte Brush in Humid Air. Langmuir 2000, 16, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and Characterization of Membranes Formed by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.S. Theoretical Study of the Effective Parameters for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation in Hollow Fiber Modules. Mater. Sci. 2014, 32, 2949–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Subedi, D.P. Contact Angle Measurement for The Surface Characterization of Solids. Himal. Phys. 2011, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.E.; Nor, N.A.M.; Jaafar, J.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Qtaishat, M.R.; Samitsu, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Aziz, F.; Yusof, N. Performance of PES/LSMM-OGCN Photocatalytic Membrane for Phenol Removal: Effect of OGCN Loading. Membranes 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisamy, R.; Berry, D.; Holder, D.; Raskin, L.; Lepak, L.; Jones, K.L. Development of reactive thin film polymer brush membranes to prevent biofouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, P.; Shu-Biao, X.; Liu, J.-J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, F. Anti-Fouling and Anti-Bacterial Modification of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Membrane by Blending with the Capsaicin-Based Copolymer. Polymers 2019, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Hua, Z.; Tian, K.; Kou, R.; Zhang, J.; Ye, S.; Luo, Y.; Craig, V.S.J.; et al. Reorganization of hydrogen bond network makes strong polyelectrolyte brushes pH-responsive. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, 1600579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, N.; Gallego, S.; Del Vigo, F.; Chesters, S. Evaluating impact of fouling on reverse osmosis membranes performance. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 51, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, J.; Harrisson, S.; Chen, V. Strategies for controlling biofouling in membrane filtration systems: Challenges and opportunities. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4567–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.A.; Goh, P.S.; Zulhairun, A.K.; Ismail, A.F. Antifouling Property of Oppositely Charged Titania Nanosheet Assembled on Thin Film Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane for Highly Concentrated Oily Saline Water Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Fantin, M.; Ramakrishna, S.N.; Spencer, N.D.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Benetti, E.M. Growing Polymer Brushes from a Variety of Substrates under Ambient Conditions by Cu0-Mediated Surface-Initiated ATRP. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 27470–27477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Surface Modifications for Antifouling Membranes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2448–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.J.; Khan, E.S.; Del Campo, A.; Hinterdorfer, P.; Li, B. Nanoscale Characteristics and Antimicrobial Properties of (SI-ATRP)-Seeded Polymer Brush Surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 29312–29319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Ling, Q.; Zhao, W.; Ma, Y.; Bai, P.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; He, M. Modification of polyethersulfone membrane by grafting bovine serum albumin on the surface of polyethersulfone/poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid) blended membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 329, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmarghany, M.R.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Salem, M.S.; Shouman, M.A.; Sabry, M.N.; Matsuyama, H.; Nady, N. Triple-Layer Nanocomposite Membrane Prepared by Electrospinning Based on Modified PES with Carbon Nanotubes for Membrane Distillation Applications. Membranes 2020, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, X.; Gao, C. Surface modification of thin-film-composite polyamide membranes for improved reverse osmosis performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W.; Sun, H.; Wu, L.; Chen, S. A facile method for polyamide membrane modification by poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) to improve fouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-F.; Wu, H.; Li, R.-H.; Yu, C.; Zhao, X.; Gao, C.-J. Modification of poly(amide-urethane-imide) (PAUI) thin film composite reverse osmosis membrane with nano-silver particles. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37817–37827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Logan, E.B. Bacterial adhesion to glass and metal-oxide surfaces. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2004, 36, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, Z.; Khan, S.J.; Ahmad, N.M.; Shahzad, H.M.A.; Jamal, Y.; Hashmi, I. Antibacterial behaviour of surface modified composite polyamide nanofiltration (NF) membrane by immobilizing Ag-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 3657–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Davenport, D.M.; Ormsbee, L.; Bhattacharyya, D. Polymerization and Functionalization of Membrane Pores for Water Related Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4174–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, B.A.; Harms, H.; Zehnder, A.J. Adhesion of the positively charged bacterium Stenotrophomonas (Xanthomonas) maltophilia 70401 to glass and Teflon. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5472–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-H.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Wee, K.-H.; Bai, R. Achieving Highly Effective Non-biofouling Performance for Polypropylene Membranes Modified by UV-Induced Surface Graft Polymerization of Two Oppositely Charged Monomers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 2422–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, P.; Tramonti, A.; De Biase, D. Coping with low pH: Molecular strategies in neutralophilic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 1091–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, R.; Belfer, S.; Freger, V. Bacterial Attachment to RO Membranes Surface-Modified by Concentration-Polarization-Enhanced Graft Polymerization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5973–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia-Semião, A.J.C.; Habimana, O.; Casey, E. Bacterial adhesion onto nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: Effect of permeate flux. Water Res. 2014, 63, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, A.; Okuyama, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Tsuneda, S.; Hosomi, M. The effect of surface charge property on Escherichia coli initial adhesion and subsequent biofilm formation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1745–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcíková, M.; Tkac, J.; Kasak, P. Switchable Materials Containing Polyzwitterion Moieties. Polymers 2015, 7, 2344–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagandran, S.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Wong, T.-W.; Dagang, W.R.Z.B.W. The Recent Progress in Modification of Polymeric Membranes Using Organic Macromolecules for Water Treatment. Symmetry 2020, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddinti, B.S.T.; Scholle, F.; Vargas, M.G.; Smith, S.D.; Ghiladi, R.A.; Spontak, R.J. Inherently self-sterilizing charged multiblock polymers that kill drug-resistant microbes in minutes. Mater. Horizons 2019, 6, 2056–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Material for ATRP | Membrane Sample Codes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MH1 | MH2 | MH3 | |
| SPMK (mmol) | 4.06 | 8.12 | 12.185 |
| DMF (mL) | 1.25 | 2.50 | 3.75 |
| Water (mL) | 0.75 | 1.5 | 2.25 |
| Bipy (mmol) | 2.0 | 3.248 | 4.874 |
| CuBr I (mmol) | 0.4 | 0.649 | 0.974 |
| CuBr II (mmol) | 0.4 | 0.649 | 0.974 |
| EBIB (mmol) | 0.1 | 0.162 | 0.243 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mushtaq, R.; Abbas, M.A.; Mushtaq, S.; Ahmad, N.M.; Khan, N.A.; Khan, A.U.; Hong, W.; Sadiq, R.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling and Flux Enhancement of Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Grafting Poly (3-Sulfopropyl Methacrylate) Brushes. Membranes 2021, 11, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030213
Mushtaq R, Abbas MA, Mushtaq S, Ahmad NM, Khan NA, Khan AU, Hong W, Sadiq R, Jiang Z. Antifouling and Flux Enhancement of Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Grafting Poly (3-Sulfopropyl Methacrylate) Brushes. Membranes. 2021; 11(3):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030213
Chicago/Turabian StyleMushtaq, Reema, Muhammad Asad Abbas, Shehla Mushtaq, Nasir M. Ahmad, Niaz Ali Khan, Asad U. Khan, Wu Hong, Rehan Sadiq, and Zhongyi Jiang. 2021. "Antifouling and Flux Enhancement of Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Grafting Poly (3-Sulfopropyl Methacrylate) Brushes" Membranes 11, no. 3: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030213
APA StyleMushtaq, R., Abbas, M. A., Mushtaq, S., Ahmad, N. M., Khan, N. A., Khan, A. U., Hong, W., Sadiq, R., & Jiang, Z. (2021). Antifouling and Flux Enhancement of Reverse Osmosis Membrane by Grafting Poly (3-Sulfopropyl Methacrylate) Brushes. Membranes, 11(3), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030213