Microstructured Hollow Fiber Membranes: Potential Fiber Shapes for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
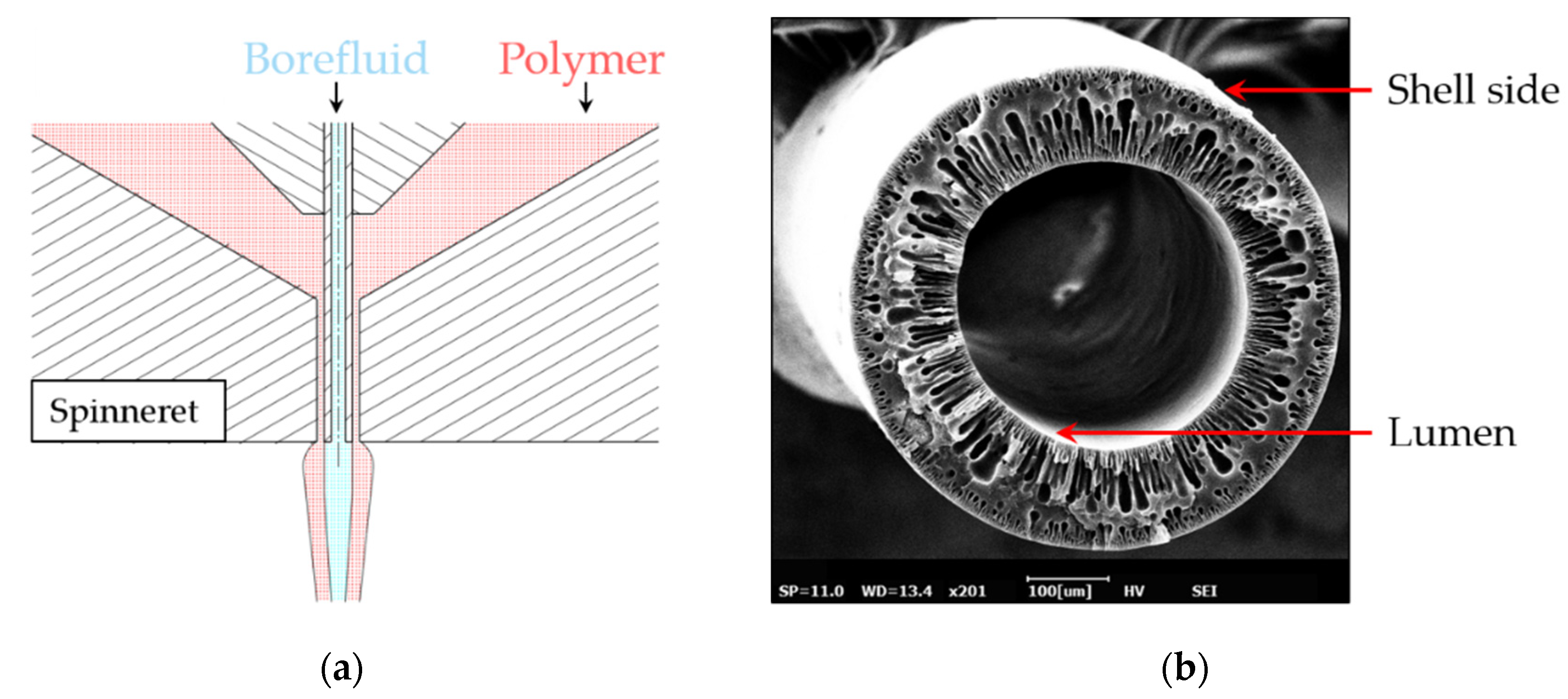
2.1. Non-Circular Fiber Shapes
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Velocity Measurement
2.4. Computational Fluid Dynamics
2.4.1. Flow Simulations
2.4.2. Sherwood Number Simulations
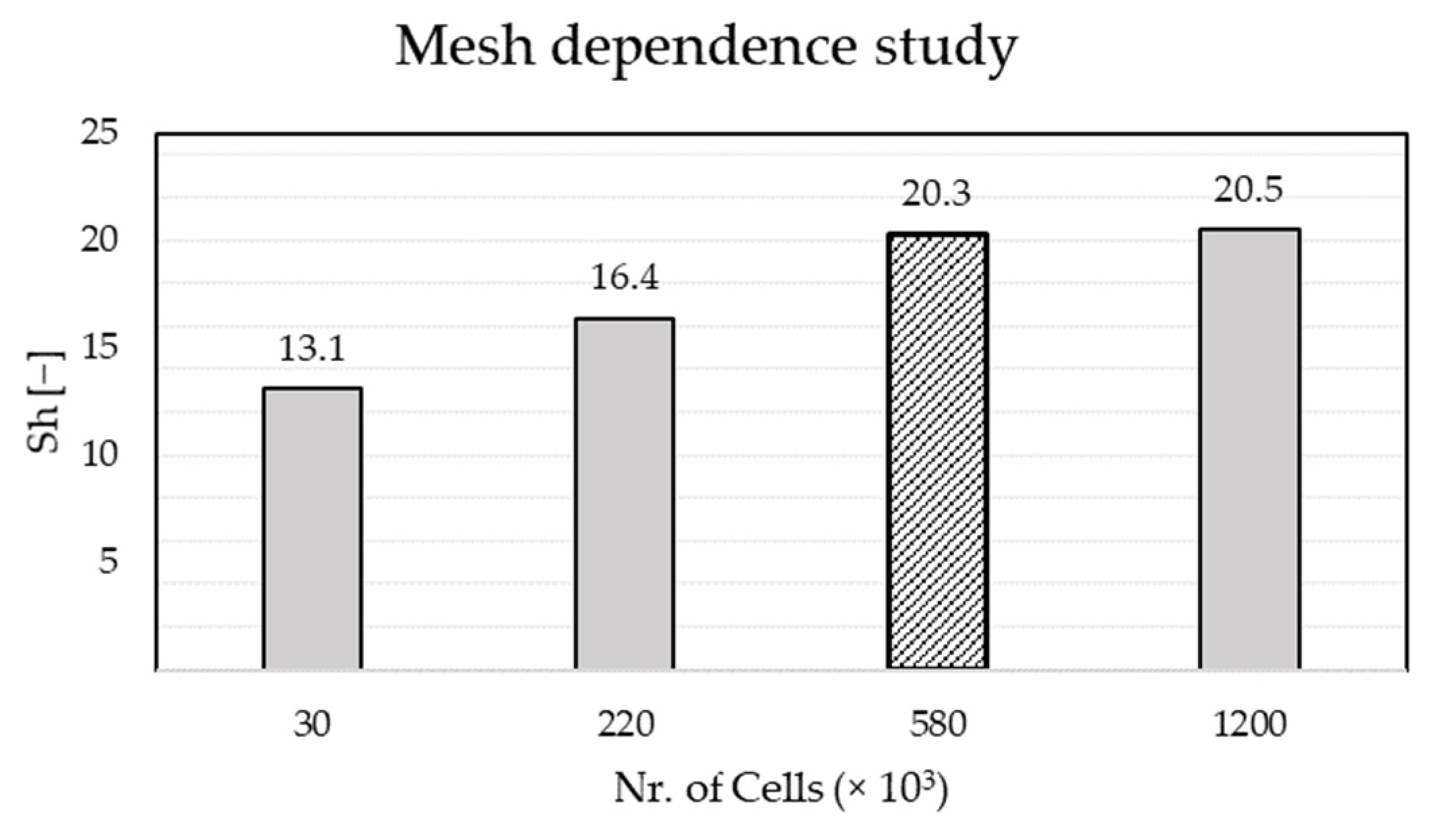
2.5. Evaluation of Results
3. Results
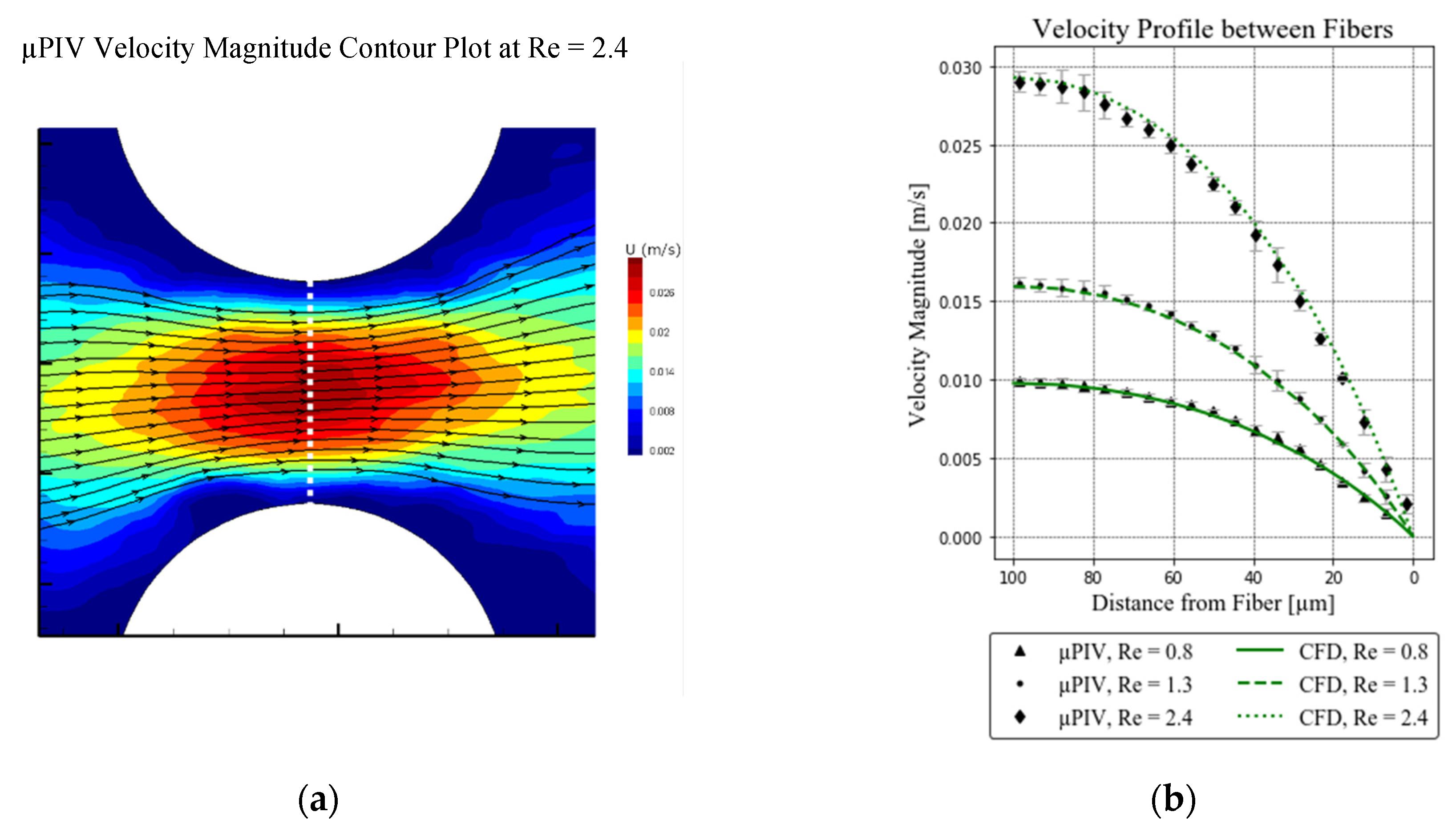
3.1. µPIV Measurements
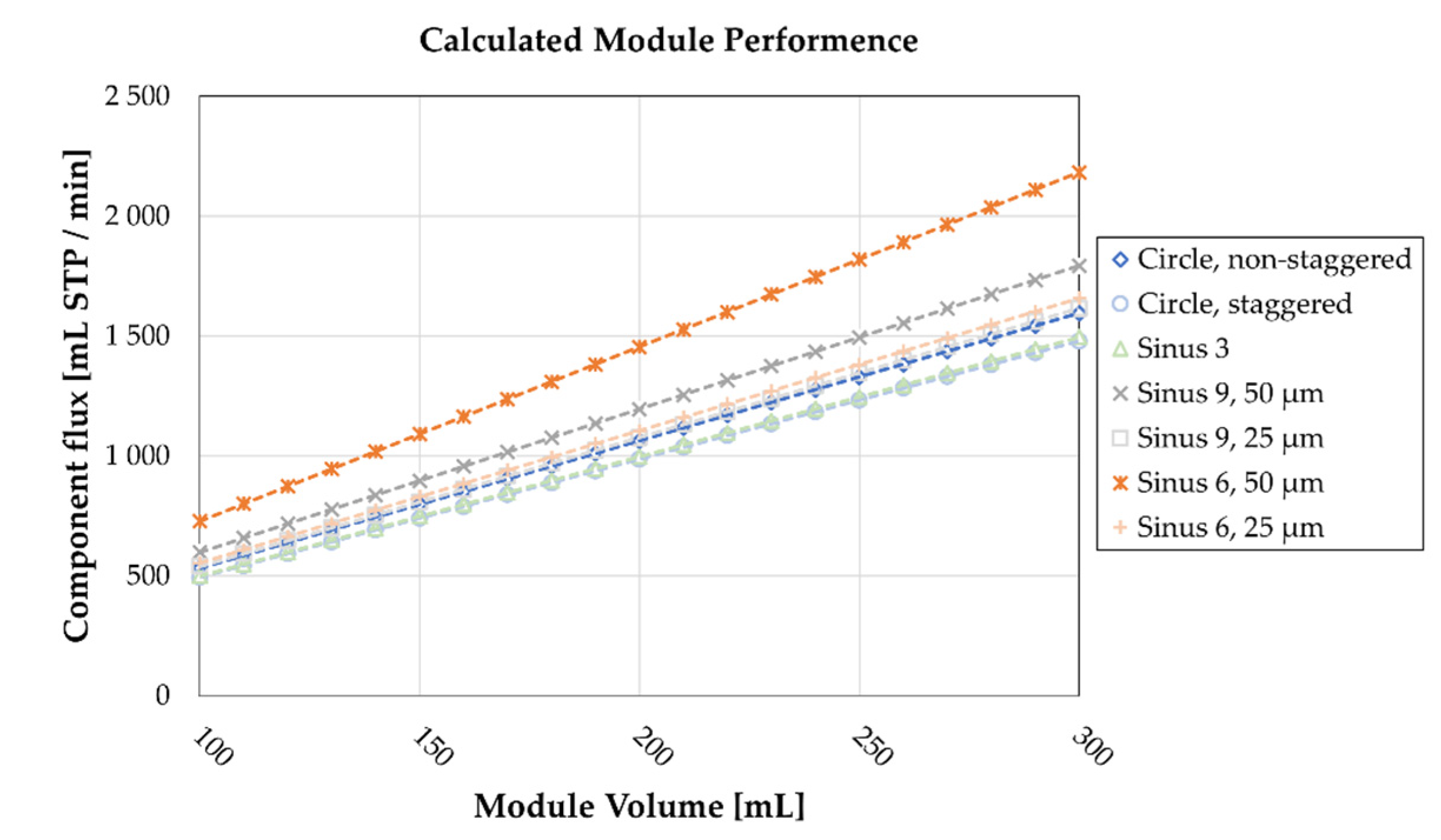
3.2. Computational Fluid Dynamics Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Acronyms | |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| µPIV | Micro- particle image velocimetry |
| DoC | Depth of correlation |
| Re | Reynolds number [−] |
| Sh | Local Sherwood number [−] |
| Mean Sherwood number [−] | |
| Latin Symbols | |
| A | Membrane surface area [m2] |
| JT | Component flux [mL/min] |
| S | Specific area [m2/m3] |
| T | Arbitrary species [m3/m3] |
| Tb | Bulk value of species T [−] |
| U | Velocity [m/s] |
| kc | Local mass transfer coefficient [m/s] |
| Mean mass transfer coefficient [m/s] | |
| DT | Diffusion coefficient [m2/s] |
| UFrac | Velocity magnitude fraction [−] |
| vi | Cell volume [m3] |
| VP | Packing volume [m3] |
| d | Fiber diameter [m] |
| ai | Cell face area [m2] |
| x | Amplitude [m] |
| n | Number of periods [−] |
| Greek Symbols | |
| ρ | Density [kg/m3] |
| μ | Dynamic viscosity [mPas] |
| ν | Kinematic viscosity [m2/s] |
| ϕ | Angle [rad] |
Appendix A

Appendix B
References
- Federspiel, W.; Henchir, K.L. Artificial: Basic Principles and Current Applications. In Encyclopedia of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering, 2nd ed.; Wnek, G., Bowlin, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 1661–1672. ISBN 978-1-4200-7802-2. [Google Scholar]
- Makdisi, G.; Wang, I. Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) Review of a Lifesaving Technology. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, E166–E176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.P.; Hote, M.P. Ventilatory Management of Patients on ECMO. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melin, T.; Rautenbach, R. (Eds.) Gaspermeation. In Membranverfahren: Grundlagen der Modul—Und Anlagenauslegung; VDI-Buch; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 447–506. ISBN 978-3-540-34328-8. [Google Scholar]
- Çulfaz, P.Z.; Wessling, M.; Lammertink, R.G.H. Hollow Fiber Ultrafiltration Membranes with Microstructured Inner Skin. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.L.; Kim, D.; Nunes, S.P. Evolution of Regular Geometrical Shapes in Fiber Lumens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, H.; Alders, M.; Luelf, T.; Emonds, S.; Mueller, S.I.; Tepper, M.; Wessling, M. Chemistry in a Spinneret—Sinusoidal-Shaped Composite Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 585, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luelf, T.; Tepper, M.; Breisig, H.; Wessling, M. Sinusoidal Shaped Hollow Fibers for Enhanced Mass Transfer. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 533, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luelf, T.; Rall, D.; Wypysek, D.; Wiese, M.; Femmer, T.; Bremer, C.; Michaelis, J.U.; Wessling, M. 3D-Printed Rotating Spinnerets Create Membranes with a Twist. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çulfaz, P.Z.; Rolevink, E.; van Rijn, C.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Wessling, M. Microstructured Hollow Fibers for Ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 347, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenbach, R. Membranverfahren: Grundlagen der Modul—und Anlagenauslegung; Chemische Technik Verfahrenstechnik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; ISBN 978-3-662-08655-1. [Google Scholar]
- Raffini, L. Anticoagulation with VADs and ECMO: Walking the Tightrope. Hematology 2017, 2017, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Optimization of Microstructured Hollow Fiber Design for Membrane Distillation Applications Using CFD Modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 421–422, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaesler, A.; Schlanstein, P.C.; Hesselmann, F.; Büsen, M.; Klaas, M.; Roggenkamp, D.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Steinseifer, U.; Arens, J. Experimental Approach to Visualize Flow in a Stacked Hollow Fiber Bundle of an Artificial Lung with Particle Image Velocimetry. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.L.C.; Geraldes, V.; Velizarov, S.; Crespo, J.G. Investigation of Flow Patterns and Mass Transfer in Membrane Module Channels Filled with Flow-Aligned Spacers Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD). J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 305, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukitsch, B.; Ecker, P.; Elenkov, M.; Janeczek, C.; Haddadi, B.; Jordan, C.; Krenn, C.; Ullrich, R.; Gfoehler, M.; Harasek, M. Computation of Global and Local Mass Transfer in Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raffel, M.; Willert, C.E.; Scarano, F.; Kähler, C.; Wereley, S.T.; Kompenhans, J. Particle Image Velocimetry: A Practical Guide, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-3-319-68851-0. [Google Scholar]
- OpenFOAM|Free CFD Software|The OpenFOAM Foundation. Available online: https://openfoam.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Ahrens, J.; Geveci, B.; Law, C. ParaView: An end-user tool for large-data visualization. In The Visualization Handbook; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 717–731. ISBN 9780123875822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenFOAM: User Guide: Cyclic. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/latest/doc/guide-bcs-coupled-cyclic.html (accessed on 30 March 2021).
- Moura, C.A.d.; Kubrusly, C.S. (Eds.) The Courant–Friedrichs–Lewy (CFL) Condition: 80 Years After Its Discovery; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2013; ISBN 978-0-8176-8393-1. [Google Scholar]
- Accessories for the CentriMag Acute Circulatory Support System. Available online: https://www.cardiovascular.abbott/us/en/hcp/products/heart-failure/mechanical-circulatory-support/centrimag-acute-circulatory-support-system/about/accessories.html (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Herbig, B.A.; Diamond, S.L. Thrombi Produced in Stagnation Point Flows Have a Core–Shell Structure. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2017, 10, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskin, M.E.; Fraser, K.H.; Zhang, T.; Griffith, B.P.; Wu, Z.J. Micro-Scale Modeling of Flow and Oxygen Transfer in Hollow-Fiber Membrane Bundle. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dierickx, P.W.; de Wachter, D.S.; Verdonck, P.R. Two-Dimensional Finite Element Model for Oxygen Transfer in Cross-Flow Hollow Fiber Membrane Artificial Lungs. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2001, 24, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddadi, B.; Jordan, C.; Miltner, M.; Harasek, M. Membrane Modeling Using CFD: Combined Evaluation of Mass Transfer and Geometrical Influences in 1D and 3D. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Numerical Simulation of Heat and Mass Transfer in Direct Membrane Distillation in a Hollow Fiber Module with Laminar Flow. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdi, G.P.; Rannacher, R.; Robertson, A.M.; Turek, S. Hemodynamical Flows: Modeling, Analysis and Simulation; Oberwolfach Seminars; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2008; ISBN 978-3-7643-7805-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Nolan, T.D.C.; Zhang, T.; Griffith, B.P.; Wu, Z.J. Characterization of Membrane Blood Oxygenation Devices Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenshields, C. OpenFOAM v6 User Guide: 7.3 Transport/Rheology Models. Available online: https://cfd.direct/openfoam/user-guide/v6-transport-rheology/ (accessed on 12 April 2021).






| Name | Unit | Sinus 3 | Sinus 6, 50 µm | Sinus 6, 25 µm | Sinus 9, 50 µm | Sinus 9, 25 µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross section | - |  |  |  |  |  |
| Average Diameter | µm | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| No. of Periods | - | 3 | 6 | 6 | 9 | 9 |
| Amplitude | µm | 50 | 50 | 25 | 50 | 25 |
| Specific Area | m2/m3 | 3810 | 4976 | 3920 | 5962 | 4482 |
| Boundary | Validation Simulation | Sherwood Simulation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velocity | Pressure | Velocity | Pressure | |
| Inlet | uniform value | zero gradient | uniform value | zero gradient |
| Outlet | zero gradient | uniform value | zero gradient | uniform value |
| Membrane | no-slip | zero gradient | no-slip | zero gradient |
| Side wall | no-slip | zero gradient | no-slip | zero gradient |
| Top and bottom wall | no-slip | zero gradient | cyclic | cyclic |
| Boundary | Specie, T |
|---|---|
| Inlet | uniform value, 1 |
| Outlet | zero gradient |
| Membrane | uniform value, 0 |
| Side wall | zero gradient |
| Top and bottom wall | cyclic |
| Geometry | Expected Increase Based on Area 1 | Actual Increase Based on Sherwood 1,2 | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| [%] | [%] | [%] | |
| Sinus 3 | 15 | 1 | −14 |
| Sinus 9, 50 µm | 79 | 21 | −58 |
| Sinus 9, 25 µm | 35 | 9 | −26 |
| Sinus 6, 50 µm | 50 | 48 | −2 |
| Sinus 6, 25 µm | 18 | 12 | −6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ecker, P.; Pekovits, M.; Yorov, T.; Haddadi, B.; Lukitsch, B.; Elenkov, M.; Janeczek, C.; Jordan, C.; Gfoehler, M.; Harasek, M. Microstructured Hollow Fiber Membranes: Potential Fiber Shapes for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenators. Membranes 2021, 11, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050374
Ecker P, Pekovits M, Yorov T, Haddadi B, Lukitsch B, Elenkov M, Janeczek C, Jordan C, Gfoehler M, Harasek M. Microstructured Hollow Fiber Membranes: Potential Fiber Shapes for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenators. Membranes. 2021; 11(5):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050374
Chicago/Turabian StyleEcker, Paul, Markus Pekovits, Tsvetan Yorov, Bahram Haddadi, Benjamin Lukitsch, Martin Elenkov, Christoph Janeczek, Christian Jordan, Margit Gfoehler, and Michael Harasek. 2021. "Microstructured Hollow Fiber Membranes: Potential Fiber Shapes for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenators" Membranes 11, no. 5: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050374
APA StyleEcker, P., Pekovits, M., Yorov, T., Haddadi, B., Lukitsch, B., Elenkov, M., Janeczek, C., Jordan, C., Gfoehler, M., & Harasek, M. (2021). Microstructured Hollow Fiber Membranes: Potential Fiber Shapes for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenators. Membranes, 11(5), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11050374







