Express Method of Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membrane Samples for Spinning Solution Optimization: Polysulfone as Example
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- -
- polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) K 30 with a molecular weight of 40,000 g/mol produced by Sigma Aldrich Co. LLC, St. Louis, MO, USA, presented as a white powder; and
- -
- polyethylene glycol (PEG400) in the form of a yellowish liquid with a molecular weight of 400 g/mol and a dynamic viscosity of 120 MPa s produced by Acros Organics, Waltham, MA, USA.
2.2. Preparation of Casting Solutions
- Group I: PSf-NMP;
- Group II: PSf-NMP—5 wt% PVP; and
- Group III: PSf-NMP—5 wt% PEG400.
2.3. Study of the Casting Solution
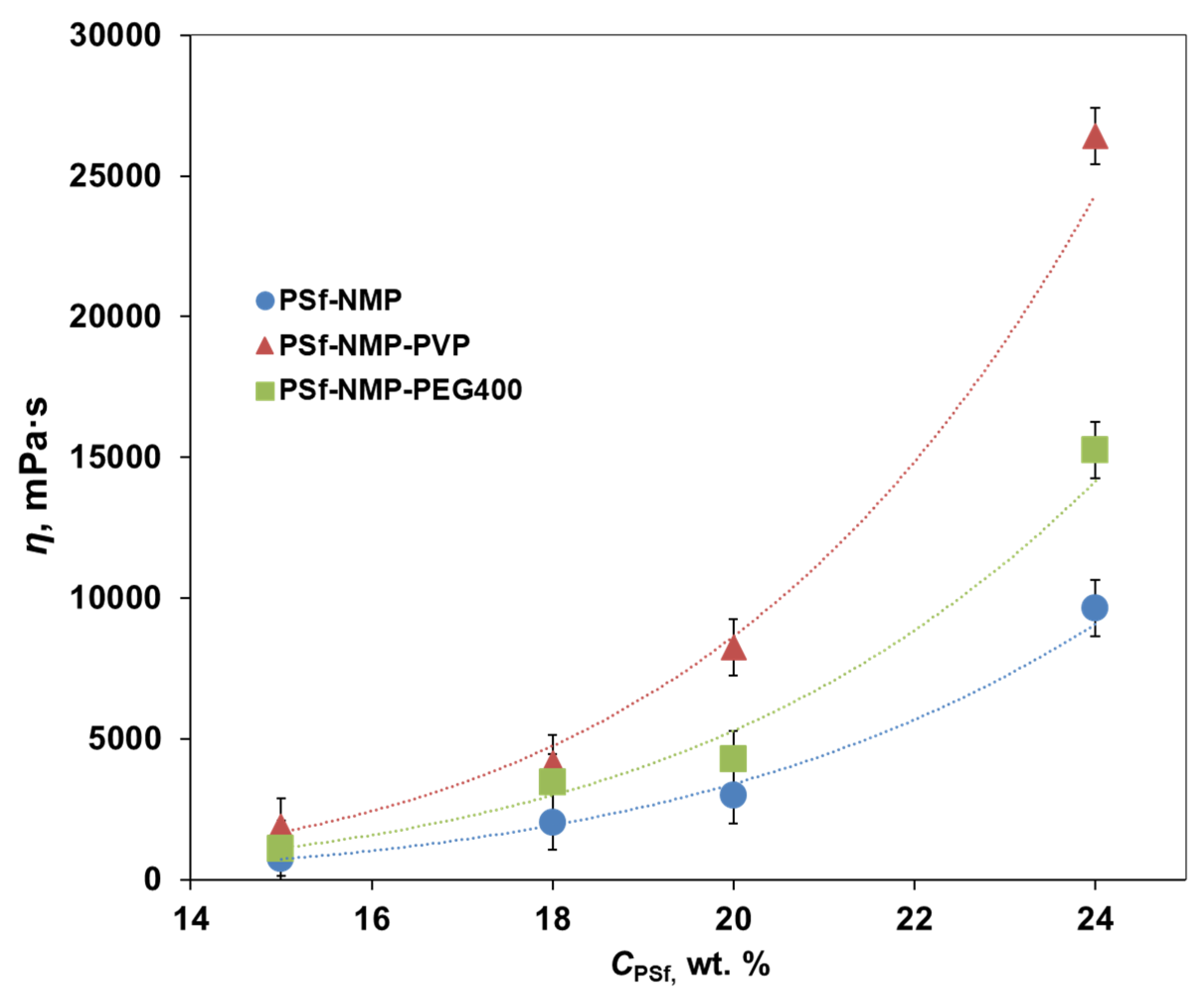
2.3.1. Investigation of the Viscosity of Casting Solutions
2.3.2. Kinetics of Precipitation of Casting Solutions
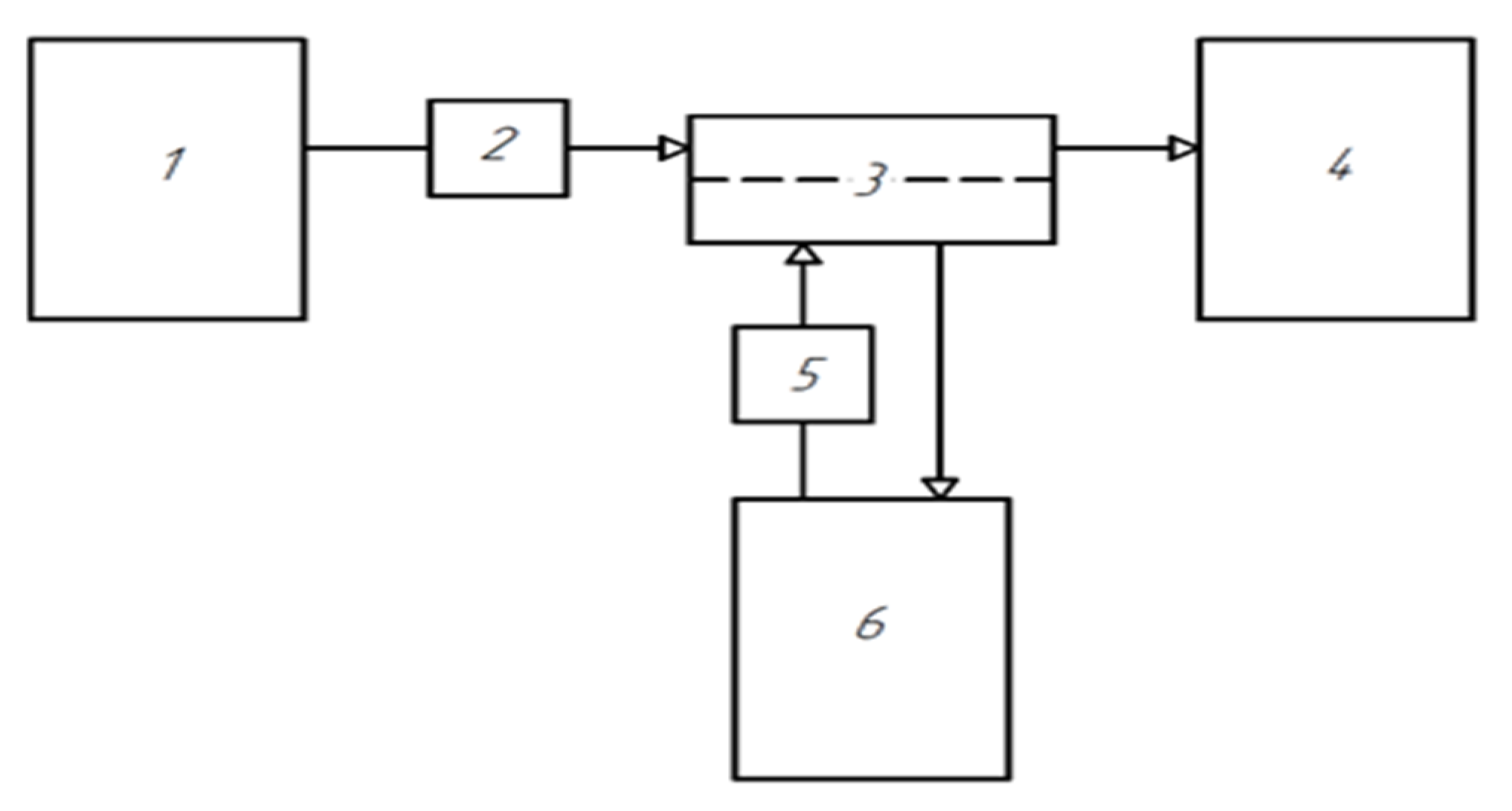
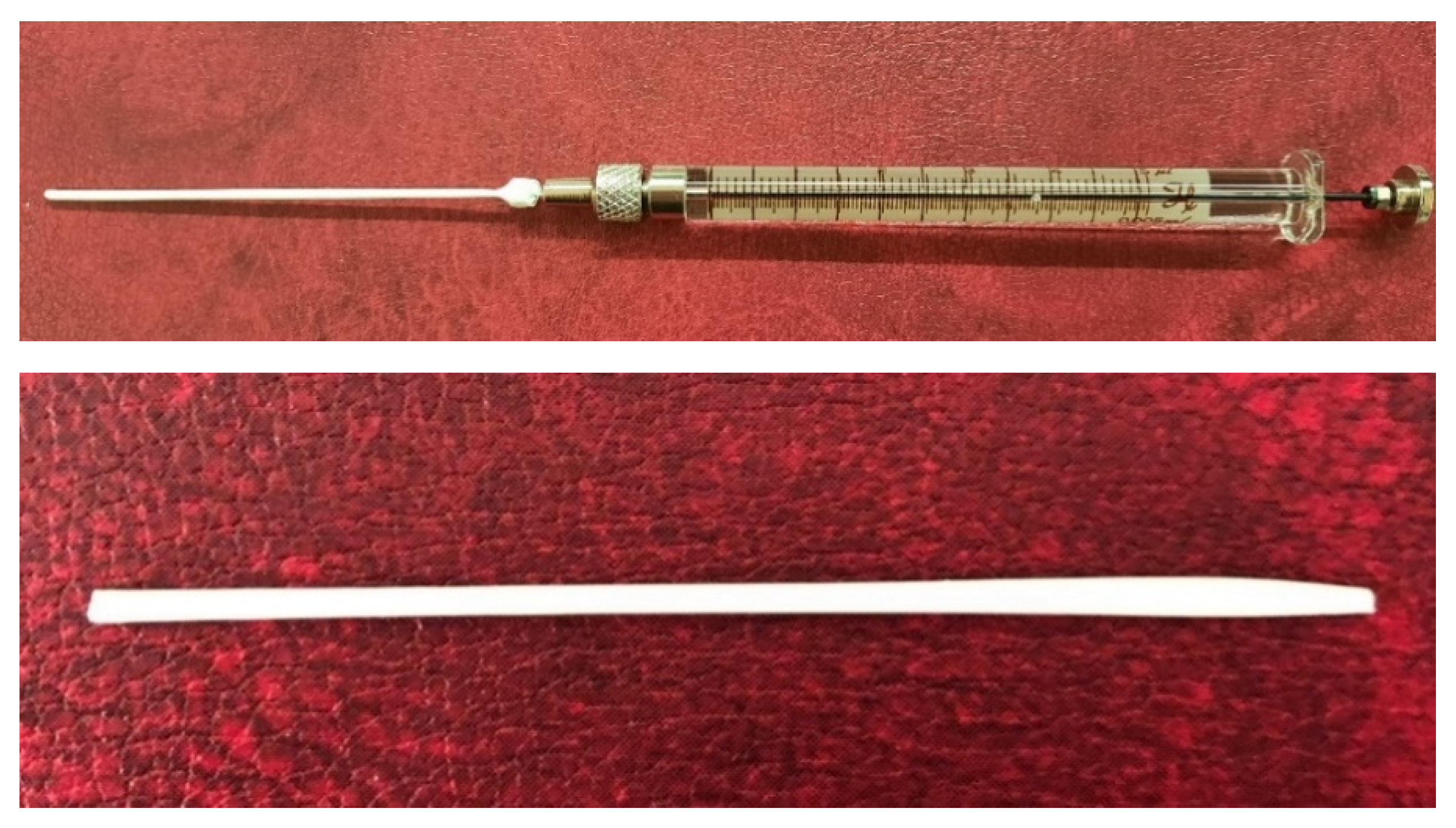
2.4. Preparation of Short-Samples of Hollow Fiber Membranes
- home—placing the unit with the carrier needle and the platform with the weighing bottles in the starting position.
- move—movement to the bottle with polymer solution. The speed of movement along axes X, Y is 0–50 mm/s.
- moveZ—lowering the unit with the carrier needle into a weighing bottle with a polymer solution. The speed of movement along the Z axis is 0–20 mm/z.
- dwell—holding the carrier needle in a bottle with a polymer solution to form a polymer solution on it. The holding time of the carrier needle is 20 s.
- moveZ—lifting the carrier needle with polymer solution. The speed of movement along the Z axis is 0–20 mm/s.
- dwell—holding the carrier needle over the bottle. On average, one sample requires 46 s.
- move—movement of the carrier needle with the polymer solution to the weighing bottle with the precipitant. The speed of movement along the X, Y axes is 0–50 mm/s.
- moveZ—lowering the carrier needle with the polymer solution into the weighing bottle with the precipitant. The speed of movement along the Z axis is 0–20 mm/s
- dwell—holding the carrier needle in a weighing bottle with a precipitant. On average, one sample requires 33 s.
- moveZ—raising the carrier needle to a starting height of 0 mm. The speed of movement along the Z axis is 0–20 mm/s.
- home—return to the starting position to replace the carrier needle from the membrane with a new one. The speed of movement along the X, Y axes is 0–50 mm/s.
2.5. Investigation of the Properties of Short-Samples of Hollow Fiber Membranes
2.5.1. Study of the Morphology of Short-Samples of HF PSf Membranes
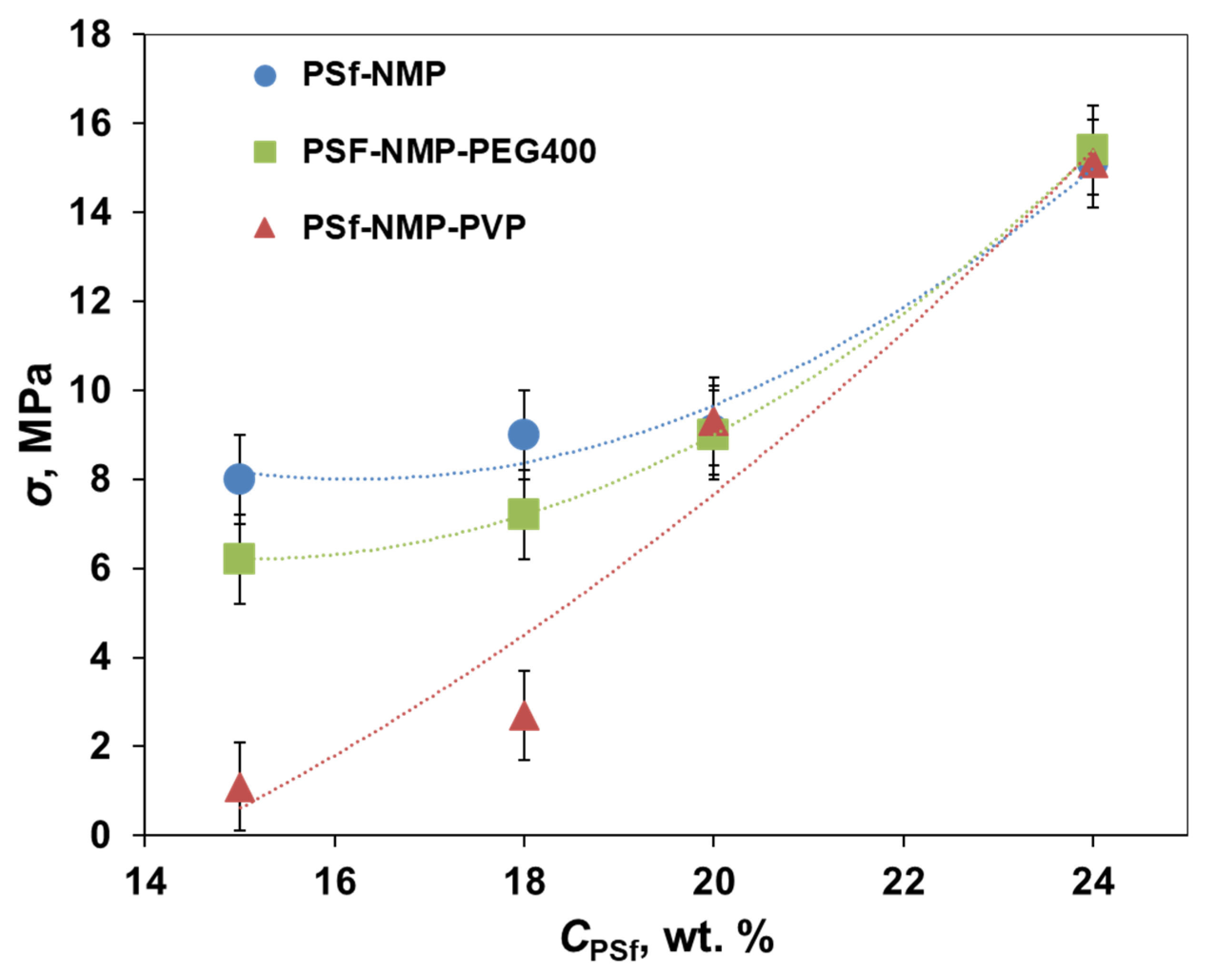
2.5.2. Investigation of Mechanical Properties of Short-Samples of HF PSF Membranes
2.5.3. Investigation of Transport and Separation Properties of Short-Samples of Hollow Fiber PSF Membranes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscosity and Precipitation Rate of Polymer Casting Solutions
3.2. The Porous Structure of Short-Samples of Hollow Fiber Membranes Formed on the Needle Carrier of the Manipulator
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Short-Samples of Hollow Fiber Membranes
3.4. Transport and Separation Properties of Short-Samples of Hollow Fiber PSF Membranes
3.5. Analysis of Economic and Time Costs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, R.W. Overview of membrane science and technology. Membr. Technol. Appl. 2004, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cassano, A.; Basile, A. Membranes for industrial microfiltration and ultrafiltration. In Advanced Membrane Science and Technology for Sustainable Energy and Environmental Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 647–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Montigny, D.; Tontiwachwuthikul, P.; Chakma, A. Using polypropylene and polytetrafluoroethylene membranes in a membrane contactor for CO2 absorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 277, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildyukevich, A.V.; Plisko, T.V.; Usosky, V.V. The formation of polysulfone hollow fiber membranes by the free fall spinning method. Pet. Chem. 2016, 56, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. A review on membrane fabrication: Structure, properties and performance relationship. Desalination 2013, 326, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalhy, Q.F.; Salih, H.A.; Simone, S.; Zablouk, M.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Poly(ether sulfone) (PES) hollow-fiber membranes prepared from various spinning parameters. Desalination 2014, 345, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Ramon, G.Z.; Kavehpour, H.P.; Kaner, R.B.; Hoek, E.M. Direct microscopic observation of membrane formation by nonsolvent induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 431, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrzadeh, M.; Bhattacharjee, S. Rational design of phase inversion membranes by tailoring thermodynamics and kinetics of casting solution using polymer additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 441, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Khulbe, K.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A. Recent progresses in polymeric hollow fiber membrane preparation, characterization and applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 111, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Otitoju, T.A.; Ooi, B.S. Hollow fiber (HF) membrane fabrication: A review on the effects of solution spinning conditions on morphology and performance. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 70, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J. Progress on polymeric hollow fiber membrane preparation technique from the perspective of green and sustainable development. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirieh, S.; Asghari, M.; Afsari, M. Application and modification of polysulfone membranes. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2018, 34, 657–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyanaya, M.; Bazhenov, S.; Borisov, I.; Plisko, T.; Vasilevsky, V. Surface Modified Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes for Ethane/Ethylene Separation Using Gas-Liquid Membrane Contactors with Ionic Liquid-Based Absorbent. Fibers 2019, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roslan, R.A.; Lau, W.J.; Lai, G.S.; Zulhairun, A.K.; Yeong, Y.F.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. Impacts of Multilayer Hybrid Coating on PSF Hollow Fiber Membrane for Enhanced Gas Separation. Membranes 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plisko, T.V.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Usosky, V.V.; Volkov, V.V. Influence of the concentration and molecular weight of polyethylene glycol on the structure and permeability of polysulfone hollow fiber membranes. Pet. Chem. 2016, 56, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bil’Dyukevich, A.V.; Plisko, T.V.; Branitskii, G.A.; Semenkevich, N.G.; Zharkevich, I.L. Investigation of the morphology of polymer-inorganic capillary membranes based on polysulfone. Pet. Chem. 2013, 53, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.; Habert, A.; Borges, C. Membrane formation mechanism based on precipitation kinetics and membrane morphology: Flat and hollow fiber polysulfone membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 155, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, I.; Vasilevsky, V.; Matveev, D.; Ovcharova, A.; Volkov, A.; Volkov, V. Effect of Temperature Exposition of Casting Solution on Properties of Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes. Fibers 2019, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Cao, B.; Li, P. Fabrication of PMDA-ODA hollow fibers with regular cross-section morphologies and study on the formation mechanism. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Song, J.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Li, X.-M.; He, T. Impact of SPEEK on PEEK membranes: Demixing, morphology and performance enhancement in lithium membrane extraction. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 615, 118448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anokhina, T.; Borisov, I.; Yushkin, A.; Vaganov, G.; Didenko, A.; Volkov, A. Phase Separation within a Thin Layer of Polymer Solution as Prompt Technique to Predict Membrane Morphology and Transport Properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, H. Preparation of poly (vinyl butyral) hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane via wet-spinning method using PVP as additive. Desalination 2011, 278, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, C.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of non-solvent additives on the morphology and separation performance of poly( m -phenylene isophthalamide) (PMIA) hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2015, 365, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-J. Thermodynamic and rheological variation in polysulfone solution by PVP and its effect in the preparation of phase inversion membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 202, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shi, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C. Effect of PEG additive on the morphology and performance of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2011, 272, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.-F.; Sublet, J.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Schaetzel, P. Formation and morphology studies of different polysulfones-based membranes made by wet phase inversion process. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.-S.; Qin, J.-J.; Gu, J.; Chung, N.T.-S. Effect of shear rate within the spinneret on morphology, separation performance and mechanical properties of ultrafiltration polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, W.; Weigel, T.; Schossig-Tiedemann, M.; Kneifel, K.; Peinemann, K.-V.; Paul, D. Formation of hollow fiber membranes from poly(ether imide) at wet phase inversion using binary mixtures of solvents for the preparation of the dope. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 192, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Du, Q.; Yang, Y. The phase diagrams of mixtures of EVAL and PEG in relation to membrane formation. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 180, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; p. 544. [Google Scholar]
- Ohya, H.; Shiki, S.; Kawakami, H. Fabrication study of polysulfone hollow-fiber microfiltration membranes: Optimal dope viscosity for nucleation and growth. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhu, G.; Deng, B. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs)/polysulfone (PSU) mixed matrix hollow fiber membranes for enhanced water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptel, P.; Abidine, N.; Ivaldi, F.; Lafaille, J. Polysulfone hollow fibers—Effect of spinning conditions on ultrafiltration properties. J. Membr. Sci. 1985, 22, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, S.; Hamanaka, K. Pore size control technique in the spinning of polysulfone hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 1991, 80, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Sourirajan, S. Solution-Spun Hollow Fiber Polysulfone and Polyethersulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1992, 27, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveev, D.N.; Kutuzov, K.A.; Vasilevsky, V.P. Effect of Draw Ratio on the Morphology of Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2020, 2, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveev, D.N.; Vasilevsky, V.P.; Kutuzov, K.A. Properties of Polysulfone Hollow Fiber Membranes Depending on the Method of the Spinning Solution Preparing. Key Eng. Mater. 2020, 869, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. Groups | No. Membrane | Polymer | Cpol, (%) | Solvent | Csol, (%) | Pore-Forming Agent | Cagent, (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | PSf-15 | PSf | 15 | NMP | 85 | - | - |
| PSf-18 | 18 | 82 | |||||
| PSf-20 | 20 | 80 | |||||
| PSf-24 | 24 | 76 | |||||
| II | PSf-PVP-15 | 15 | 80 | PVP | 5 | ||
| PSf-PVP-18 | 18 | 77 | |||||
| PSf-PVP-20 | 20 | 75 | |||||
| PSf-PVP-24 | 24 | 71 | |||||
| III | PSf-PEG-15 | 15 | 80 | PEG400 | 5 | ||
| PSf-PEG-18 | 18 | 77 | |||||
| PSf-PEG-20 | 20 | 75 | |||||
| PSf-PEG-24 | 24 | 71 |
| v, (μm/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cpol, (%) | PSf-NMP | PSf-NMP-PVP | PSf-NMP-PEG400 |
| 15 | 24.5 ± 0.6 | 14.8 ± 0.7 | 20.9 ± 0.5 |
| 18 | 18.7 ± 0.5 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | 18.3 ± 0.5 |
| 20 | 8.7 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 8.7 ± 0.2 |
| 24 | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 7.2 ± 0.2 |
| Membrane No. | H (mPa s) | tpr (s) | ths (s) | vlifting (mm/s) | thp (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSf-15 | 730 | 11 | 0 | 20 | 11 |
| PSf-18 | 2040 | 15 | 30 | 15 | 15 |
| PSf-20 | 2980 | 38 | 40 | 15 | 38 |
| PSf-24 | 9630 | 41 | 60 | 10 | 41 |
| PSf-PVP-15 | 1870 | 20 | 30 | 15 | 20 |
| PSf-PVP-18 | 4130 | 24 | 60 | 14 | 24 |
| PSf-PVP-20 | 8260 | 61 | 70 | 12 | 61 |
| PSf-PVP-24 | 26,420 | 76 | 73 | 10 | 76 |
| PSf-PEG-15 | 1110 | 15 | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| PSf-PEG-18 | 3470 | 18 | 60 | 15 | 18 |
| PSf-PEG-20 | 4270 | 36 | 60 | 14 | 36 |
| PSf-PEG-24 | 15,260 | 40 | 70 | 12 | 40 |
| Group Solution | Membrane No. | SEM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | PSf-15 | 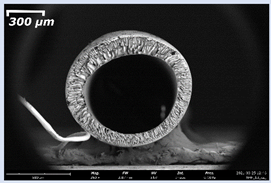 |  |
| PSf-18 |  |  | |
| PSf-20 |  |  | |
| PSf-24 |  |  | |
| II | PSf-PVP-15 |  |  |
| PSf-PVP-18 |  | 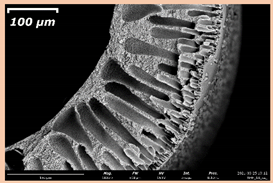 | |
| PSf-PVP-20 |  |  | |
| PSf-PVP-24 | 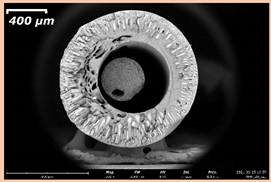 | 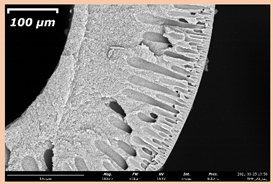 | |
| III | PSf-PEG-15 |  | 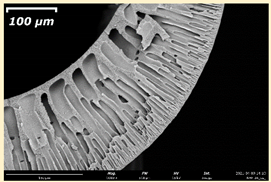 |
| PSf-PEG-18 | 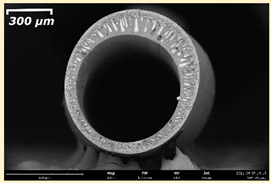 |  | |
| PSf-PEG-20 | 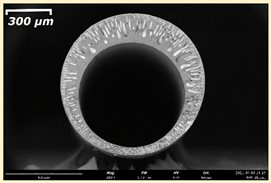 | 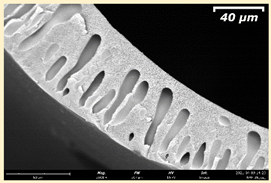 | |
| PSf-PEG-24 |  | 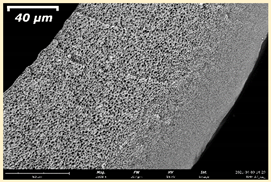 | |
| δd (MPa)1/2 | δp (MPa)1/2 | δh (MPa)1/2 | δt (MPa)1/2 | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG400 | 16.6 | 3.7 | 13.3 | 21.6 | [29] |
| PVP | 15.5 | 11.7 | 8.6 | 21.2 | [22] |
| NMP | 18.0 | 12.3 | 7.2 | 22.9 | [30] |
| Water | 15.6 | 16.0 | 42.3 | 47.8 |
| P (L/m2 h Bar) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cp, (%) | No Additive | PVP | PEG400 |
| 15 | 17.1 | 178.7 | 475.6 |
| 18 | 5.7 | 94.3 | 89.7 |
| 20 | 2.9 | 82.4 | 28.6 |
| 24 | 0.5 | 35.0 | 0.1 |
| Groups | CPSf (%) | Added | Cadd (%) | CNMP (%) | Laboratory Facility | Manipulator | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consumption (PSf/Add/NMP) (g) | Cost ($) | Consumption (PSf/Add/NMP) (g) | Cost ($) | |||||
| I | 15 | - | - | 85 | 45/-/255 | 81 | 1.5/-/8.5 | 2.7 |
| 18 | 82 | 54/-/246 | 88 | 1.8/-/8.2 | 2.9 | |||
| 20 | 80 | 60/-/240 | 92 | 2.0/-/8.0 | 3.1 | |||
| 24 | 76 | 72/-/228 | 111 | 2.4/-/7.6 | 3.4 | |||
| II | 15 | PVP | 5 | 80 | 45/15/240 | 106 | 1.5/0.5/8.0 | 3.5 |
| 18 | 77 | 54/15/231 | 118 | 1.8/0.5/7.7 | 3.9 | |||
| 20 | 75 | 60/15/225 | 126 | 2.0/0.5/7.5 | 4.2 | |||
| 24 | 71 | 72/15/213 | 142 | 2.4/0.5/7.1 | 4.7 | |||
| III | 15 | PEG400 | 5 | 80 | 45/15/240 | 81 | 1.5/0.5/8.0 | 2.7 |
| 18 | 77 | 54/15/231 | 89 | 1.8/0.5/7.7 | 3.0 | |||
| 20 | 75 | 60/15/225 | 94 | 2.0/0.5/7.5 | 3.1 | |||
| 24 | 71 | 72/15/213 | 103 | 2.4/0.5/7.1 | 3.4 | |||
| Amount $: | ≈1230 | ≈41 | ||||||
| Groups | CPSf (%) | Added | Laboratory Facility | Manipulator | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tmix (h) | tdegas/filtration (h) | tspinning (h) | tmix/degas (h) | tfiltration (h) | tspinning 3 samples (h) | |||
| I | 15 | - | 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 24 | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| 18 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | ||||
| 20 | 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | |||
| 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | ||||
| II | 15 | 5 wt% PVP | 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | |
| 18 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | ||||
| 20 | 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | |||
| 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | ||||
| III | 15 | 5 wt% PEG400 | 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | |
| 18 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | ||||
| 20 | 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | |||
| 24 | 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.15 | ||||
| Time spent on 12 solutions, h | 144 | 288 | 6 | 24 | 3 | 1.8 | ||
| Total time, h | 438 | 28.8 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anokhina, T.; Raeva, A.; Makaev, S.; Borisov, I.; Vasilevsky, V.; Volkov, A. Express Method of Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membrane Samples for Spinning Solution Optimization: Polysulfone as Example. Membranes 2021, 11, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060396
Anokhina T, Raeva A, Makaev S, Borisov I, Vasilevsky V, Volkov A. Express Method of Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membrane Samples for Spinning Solution Optimization: Polysulfone as Example. Membranes. 2021; 11(6):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060396
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnokhina, Tatyana, Alisa Raeva, Sergey Makaev, Ilya Borisov, Vladimir Vasilevsky, and Alexey Volkov. 2021. "Express Method of Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membrane Samples for Spinning Solution Optimization: Polysulfone as Example" Membranes 11, no. 6: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060396
APA StyleAnokhina, T., Raeva, A., Makaev, S., Borisov, I., Vasilevsky, V., & Volkov, A. (2021). Express Method of Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membrane Samples for Spinning Solution Optimization: Polysulfone as Example. Membranes, 11(6), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060396









