Bacterial Infection-Mimicking Three-Dimensional Phagocytosis and Chemotaxis in Electrospun Poly(?-caprolactone) Nanofibrous Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrospinning and Fabrication of the PCL Nanofibers
2.3. Preparation of Phagocytes from Bone Marrow
2.4. Preparation of Peritoneal Neutrophils and Macrophages
2.5. MLE-12 Cell Culture
2.6. Bacterial Culture and Adhesion Assay
2.7. Laser Confocal Microscopy
2.8. SEM
2.9. FACS Analysis of Phagocytosis
2.10. Live Imaging of Phagocytosis
2.11. Migration Assay in PCL-NM-Based Two-Layer System
2.12. Cytokine Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
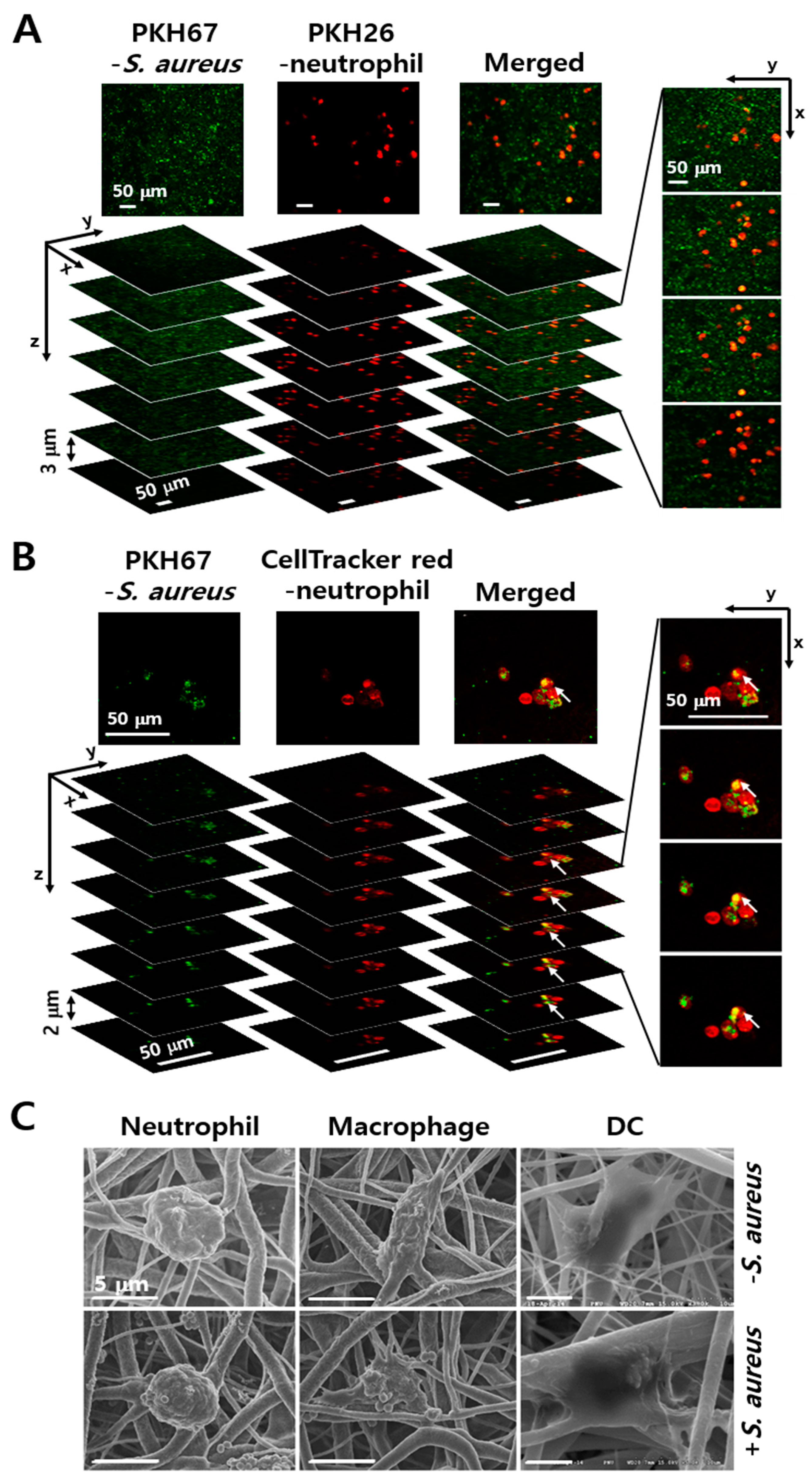
3.1. Culture of S. aureus and Phagocytes in Electrospun PCL-NM
3.2. Engulfment of S. aureus by Phagocytes in the PCL-NM
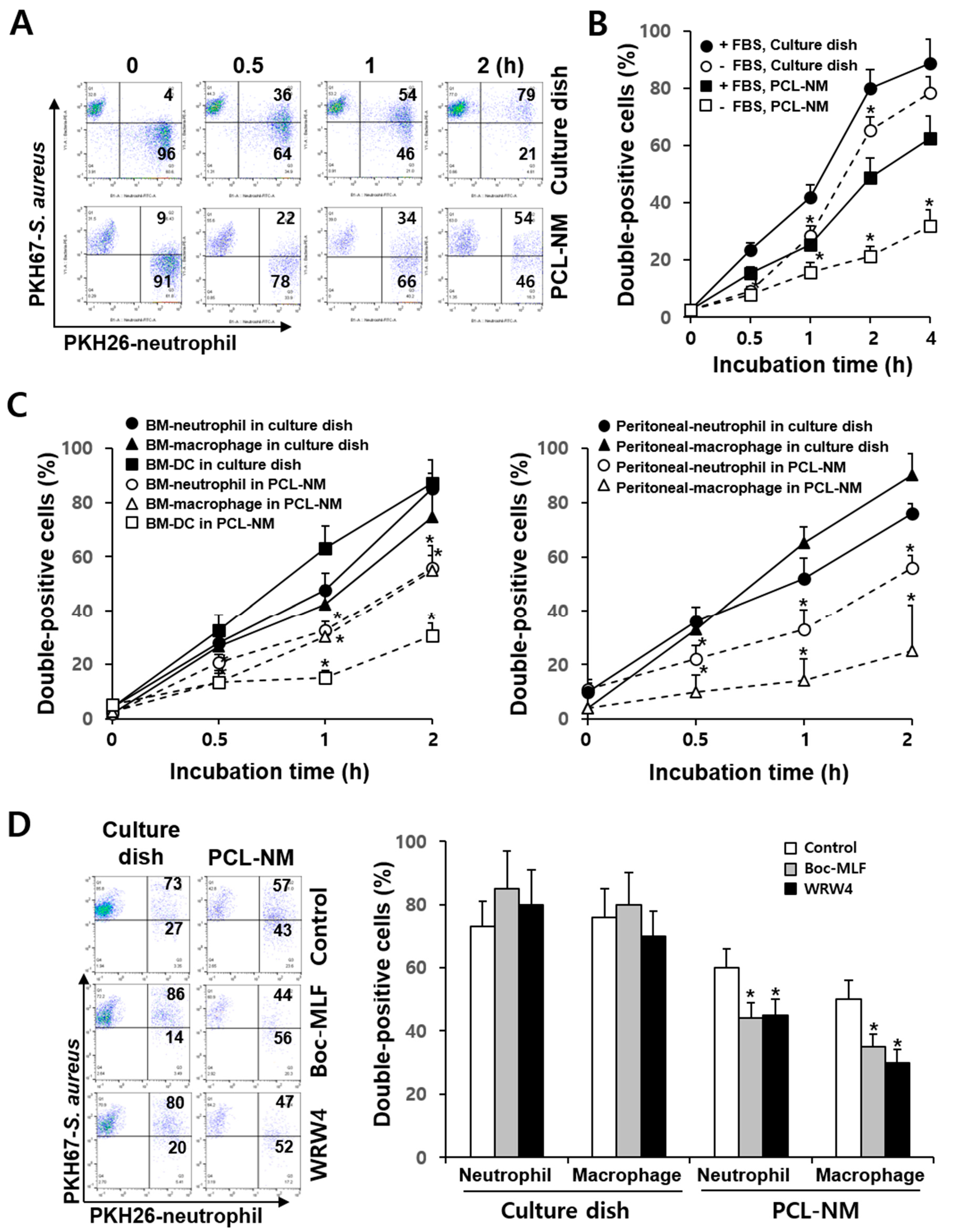
3.3. Differential Rate of Phagocytosis in 2D and 3D Culture Conditions
3.4. Effects of FPR Inhibitors on the Phagocytosis of S. aureus in 2D and 3D Culture Conditions
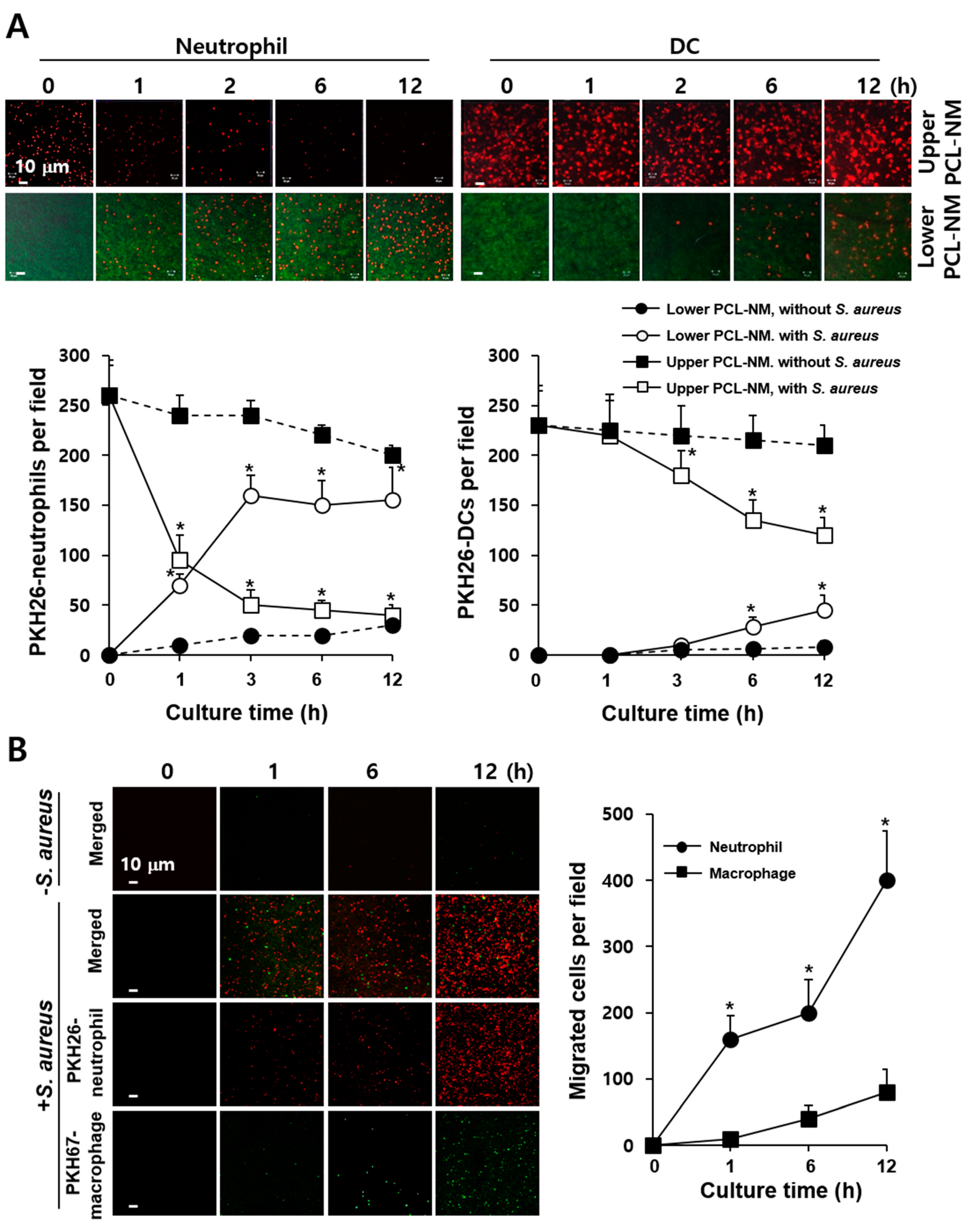
3.5. 3D Migration of Phagocytes to S. aureus in PCL-NM-Based Two-Layer Culture System
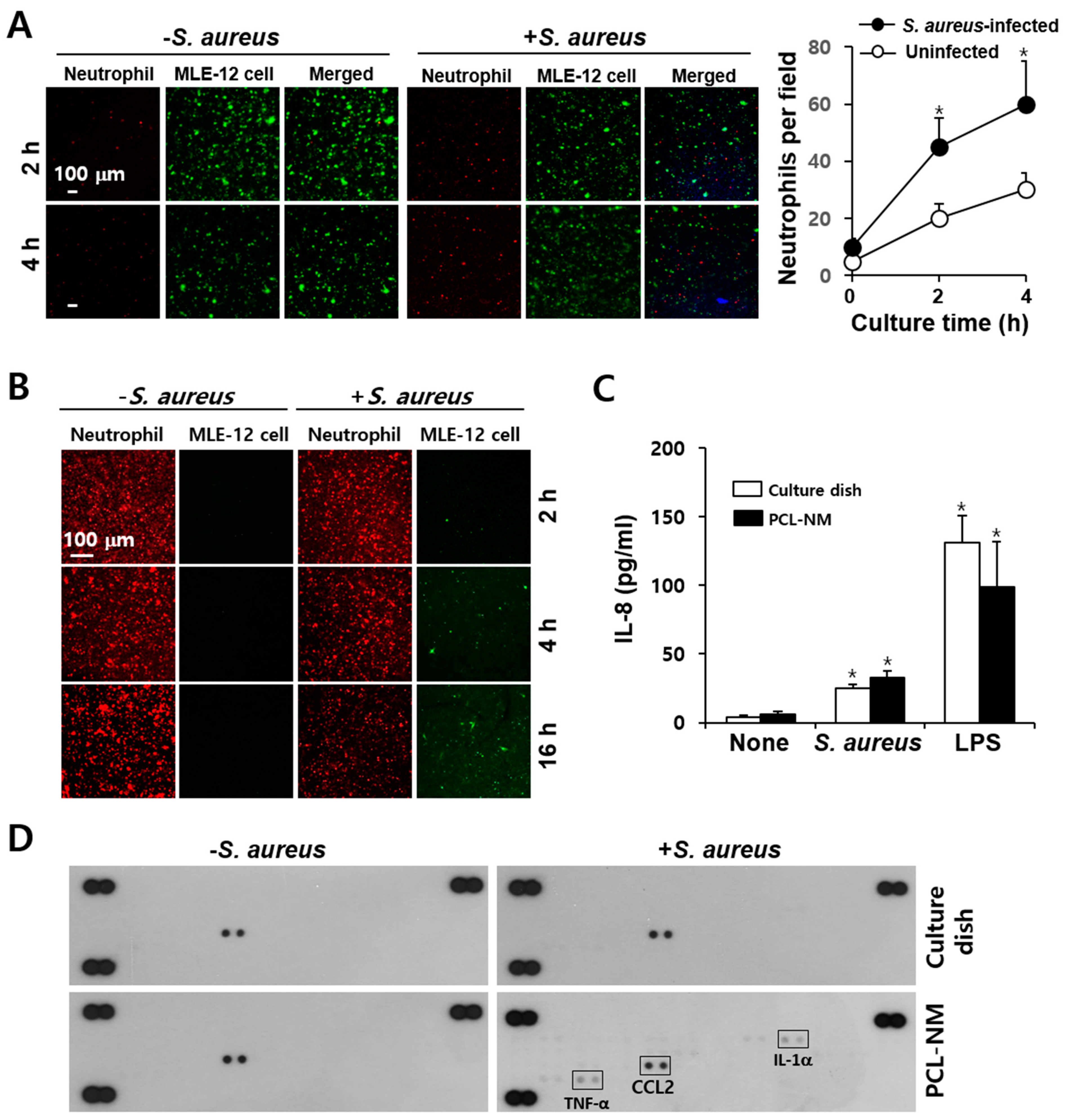
3.6. Neutrophil-Induced Recruitment of More Neutrophils to S. aureus in PCL-NM-Based Two-Layer Culture System
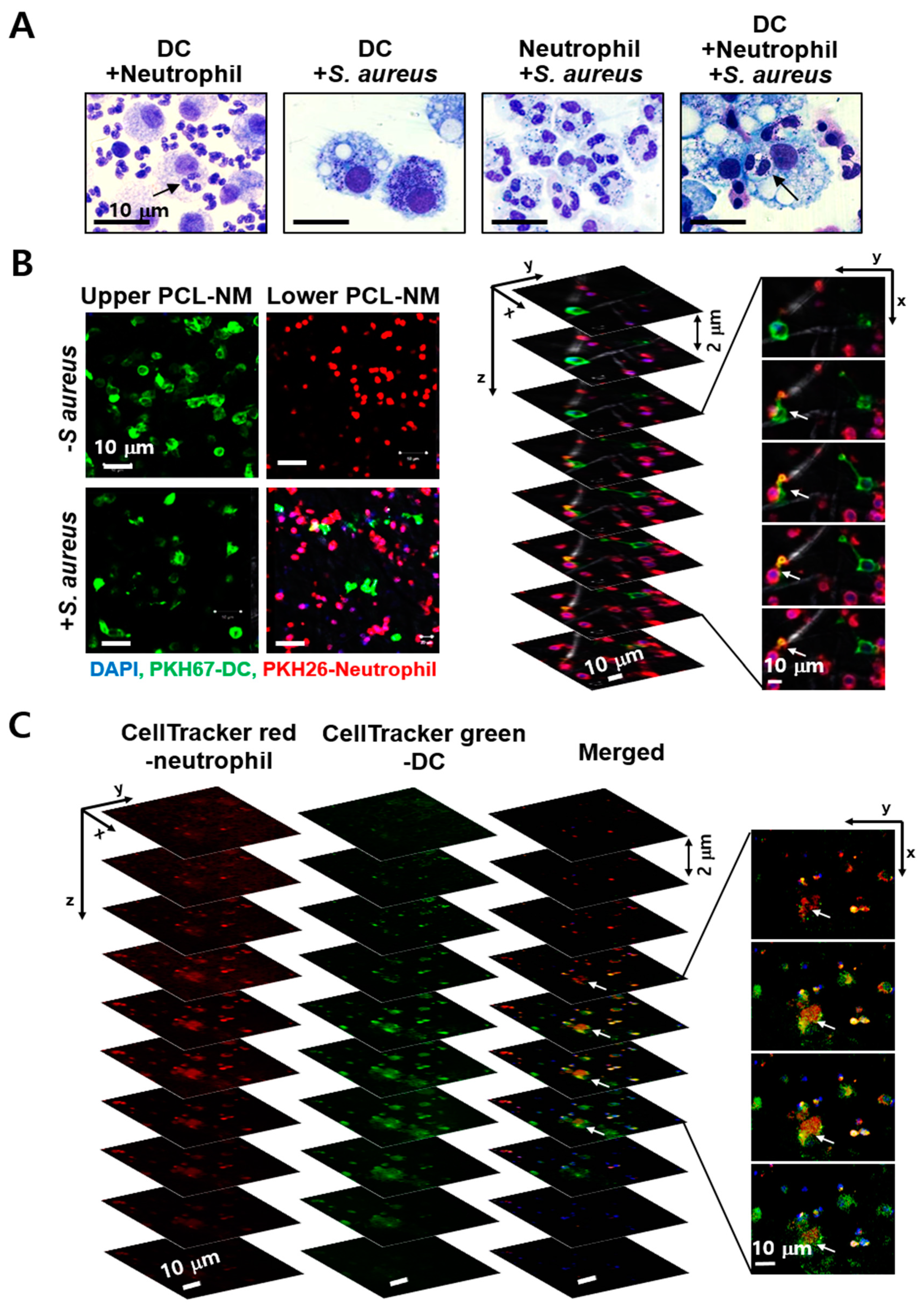
3.7. Engulfment of Neutrophils by DCs in the Presence of S. aureus in PCL-NM-Based Co-Culture Condition
3.8. Migration of Phagocytes to S. aureus–Infected Epithelial Cells in PCL-NM-Based Two-Layer Culture System
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schiffmann, E.; Corcoran, B.A.; Wahl, S.M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gouwy, M.; Struyf, S.; Proost, P.; Van Damme, J. Synergy in cytokine and chemokine networks amplifies the inflammatory response. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.D.; Luster, A.D. The role of tissue resident cells in neutrophil recruitment. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyden, S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1962, 115, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sackmann, E.K.; Berthier, E.; Young, E.W.; Shelef, M.A.; Wernimont, S.A.; Huttenlocher, A.; Beebe, D.J. Microfluidic kit-on-a-lid: A versatile platform for neutrophil chemotaxis assays. Blood 2012, 120, e45–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faure-André, G.; Vargas, P.; Yuseff, M.I.; Heuzé, M.; Diaz, J.; Lankar, D.; Steri, V.; Manry, J.; Hugues, S.; Vascotto, F.; et al. Regulation of dendritic cell migration by CD74, the MHC class II-associated invariant chain. Science 2008, 322, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heuzé, M.L.; Collin, O.; Terriac, E.; Lennon-Duménil, A.M.; Piel, M. Cell migration in confinement: A micro-channel-based assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 769, 415–434. [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak, A.N.; Irvine, D.J. Inverse opal hydrogel-collagen composite scaffolds as a supportive microenvironment for immune cell migration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, D.; Matthews, B.D.; Mammoto, A.; Montoya-Zavala, M.; Hsin, H.Y.; Ingber, D.E. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science 2010, 328, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.E.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, J.S.; Jin, S.; Yoon, S.; Bae, H.R.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kwak, J.Y. Three-dimensional culture and interaction of cancer cells and dendritic cells in an electrospun nano-submicron hybrid fibrous scaffold. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 823–835. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Park, T.M.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, J.S.; Le, B.D.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kwak, J.Y.; Yoon, S. Three-dimensional migration of neutrophils through an electrospun nanofibrous membrane. Biotechniques 2015, 58, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodruff, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. The Return of a Forgotten Polymer-Polycaprolactone in the 21st Century. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1217–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mountcastle, S.E.; Cox, S.C.; Sammons, R.L.; Jabbari, S.; Shelton, R.M.; Kuehne, S.A. A review of co-culture models to study the oral microenvironment and disease. J. Oral Microbiol. 2020, 12, 1773122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, L.; Kovalski, J.; Grandi, G.; Bagnoli, F.; Amieva, M.R. Three-dimensional human skin models to understand Staphylococcus aureus skin colonization and infection. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parente, R.; Possetti, V.; Schiavone, M.L.; Campodoni, E.; Menale, C.; Loppini, M.; Doni, A.; Bottazzi, B.; Mantovani, A.; Sandri, M. 3D cocultures of osteoblasts and Staphylococcus aureus on biomimetic bone scaffolds as a tool to investigate the host–pathogen interface in osteomyelitis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Wu, H.; Fang, L.; Wu, M.; Liu, R. Transmigration and phagocytosis of macrophages in an airway infection model using four-dimensional techniques. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.S.; Choi, M.H.; Shin, J.I.; Maza, P.A.M.A.; Kwak, J.Y. Co-culturing of endothelial and cancer cells in a nanofibrous scaffold-based two-layer system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 11, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamydas, M.; Luo, Y.; Dorf, M.E.; Lionakis, M.S. Isolation of mouse neutrophils. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2015, 110, 3.20.1–3.20.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maza, P.A.M.A.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Sun, G.M.; Sung, Y.J.; Ponomarenko, L.P.; Stonik, V.A.; Ryu, M.; Kwak, J.Y. Inotodiol from Inonotus obliquus chaga mushroom induces atypical maturation in dendritic cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 650841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Torra, I.; Gage, M.; de Juan, A.; Pello, O.M. Isolation, culture, and polarization of murine bone marrow-derived and peritoneal macrophages. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1339, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Kurokawa, K.; Zheng, L.; Jung, D.J.; Tateishi, K.; Jin, J.O.; Ha, N.C.; Kang, H.J.; Matsushita, M.; Kwak, J.Y.; et al. Human serum mannose-binding lectin senses wall teichoic acid glycopolymer of Staphylococcus aureus, which is restricted in infancy. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27167–27175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raybourne, R.B.; Bunning, V.K. Bacterium-host cell interactions at the cellular level: Fluorescent labeling of bacteria and analysis of short-term bacterium-phagocyte interaction by flow cytometry. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Porter, A.R.; Kennedy, A.D.; Kobayashi, S.D.; DeLeo, F.R. Phagocytosis and killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human neutrophils. J. Innate Immun. 2014, 6, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.D.; Boulay, F.; Wang, J.M.; Dahlgren, C.; Gerard, C.; Parmentier, M.; Serhan, C.N.; Murphy, P.M. International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXIII. Nomenclature for the formyl peptide receptor (FPR) family. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 119–161. [Google Scholar]
- Skovbakke, S.L.; Winther, M.; Gabl, M.; Holdfeldt, A.; Linden, S.; Wang, J.M.; Dahlgren, C.; Franzyk, H.; Forsman, H. The peptidomimetic Lau-(Lys-βNSpe)6-NH2 antagonizes formyl peptide receptor 2 expressed in mouse neutrophils. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 119, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.E.; Armstrong, A.; Hamilton, M.K.; Mao, D.P.; Leaf, I.A.; Miao, E.A.; Aderem, A. Cutting Edge: Cytosolic bacterial DNA activates the inflammasome via Aim2. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alfaro, C.; Suarez, N.; Oñate, C.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Martinez-Forero, I.; Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Rodriguez, I.; Perez, G.; Bolaños, E.; Palazon, A.; et al. Dendritic cells take up and present antigens from viable and apoptotic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.; François, P.P.; Nüsse, O.; Foti, M.; Hartford, O.M.; Vaudaux, P.; Foster, T.J.; Lew, D.P.; Herrmann, M.; Krause, K.H. Fibronectin-binding protein acts as Staphylococcus aureus invasin via fibronectin bridging to integrin α5β1. Cell. Microbiol. 1999, 1, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, C.J.; Burke, L.; Wright, C.J. Microbial interactions with nanostructures and their importance for the development of electrospun nanofibrous materials used in regenerative medicine and filtration. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2016, 8, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrigo, M.; Kingshott, P.; McArthur, S.L. Electrospun polystyrene fiber diameter influencing bacterial attachment, proliferation, and growth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7644–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.; Gutierrez, M.G.; Beineke, A.; Rauter, Y.; Rohde, M.; Foster, S.; Goldmann, O.; Medina, E. Dendritic cells are central coordinators of the host immune response to Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Park, B.G.; Wolf, A.J.; Brikos, C.; Goodridge, H.S.; Becker, C.A.; Reyes, C.N.; Miao, E.A.; Aderem, A.; Götz, F.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus evades lysozyme-based peptidoglycan digestion that links phagocytosis, inflammasome activation, and IL-1β secretion. Cell. Host Microbe 2010, 7, 38–49. [Google Scholar]
- Spaan, A.N.; Surewaard, B.G.; Nijland, R.; van Strijp, J.A. Neutrophils versus Staphylococcus aureus: A biological tug of war. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Chen, K.; Yoshimura, T.; Liu, Y.; Gong, W.; Wang, A.; Gao, J.; Murphy, P.M.; Wang, J.M. Formylpeptide receptors are critical for rapid neutrophil mobilization in host defense against Listeria monocytogenes. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, C.D.; Kim, N.D.; Luster, A.D. Neutrophils cascading their way to inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-J.; Maza, P.A.M.A.; Sun, G.-M.; Slama, P.; Lee, I.-J.; Kwak, J.-Y. Bacterial Infection-Mimicking Three-Dimensional Phagocytosis and Chemotaxis in Electrospun Poly(?-caprolactone) Nanofibrous Membrane. Membranes 2021, 11, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080569
Lee S-J, Maza PAMA, Sun G-M, Slama P, Lee I-J, Kwak J-Y. Bacterial Infection-Mimicking Three-Dimensional Phagocytosis and Chemotaxis in Electrospun Poly(?-caprolactone) Nanofibrous Membrane. Membranes. 2021; 11(8):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080569
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung-Jun, Perry Ayn Mayson A Maza, Gyu-Min Sun, Petr Slama, In-Jeong Lee, and Jong-Young Kwak. 2021. "Bacterial Infection-Mimicking Three-Dimensional Phagocytosis and Chemotaxis in Electrospun Poly(?-caprolactone) Nanofibrous Membrane" Membranes 11, no. 8: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080569
APA StyleLee, S.-J., Maza, P. A. M. A., Sun, G.-M., Slama, P., Lee, I.-J., & Kwak, J.-Y. (2021). Bacterial Infection-Mimicking Three-Dimensional Phagocytosis and Chemotaxis in Electrospun Poly(?-caprolactone) Nanofibrous Membrane. Membranes, 11(8), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080569






