Physical and Mechanical Properties of Hollow Fiber Membranes and Technological Parameters of the Gas Separation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
- The selective layer on the inner or outer surface of the fiber;
- The initial gas mixture which is fed into or outside the fiber;
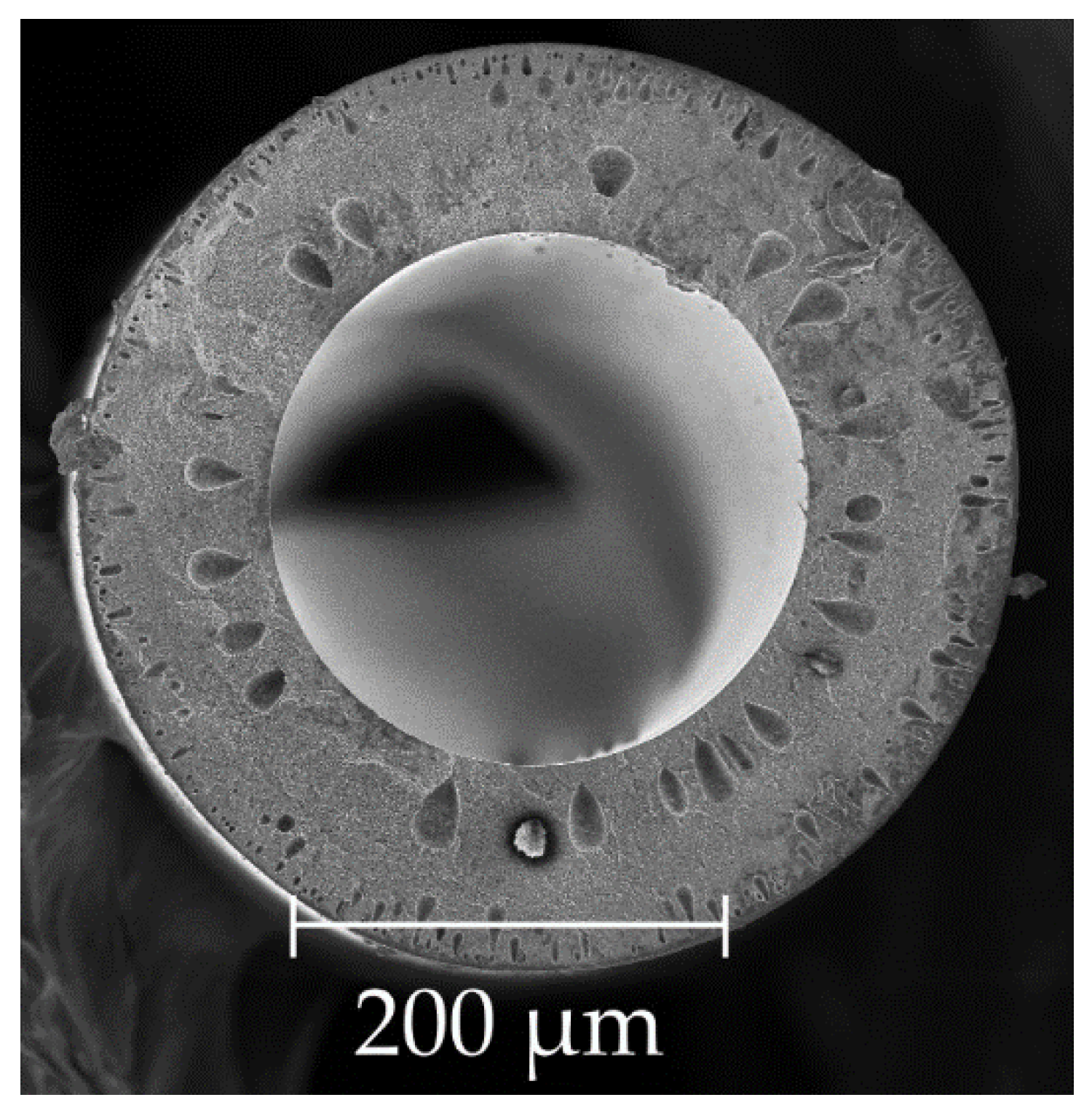
- Inner diameter = 100 microns;
- Selective layer thickness δ = 100 nm;
- Membrane material: Ultrason E6020P (PES);
- Young’s modulus for the selective layer and the porous substrate layer: , , respectively;
- Poisson’s ratio for both layers equal to 0.35 [25].
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- the physico-chemical nature of the membrane polymer;
- physico-chemical properties (morphology, structure, permeability, selectivity) of the skin layer;
- physico-mechanical properties (Young’s modulus, elastic limit, etc.) of membrane layers;
- the porosity of the membrane support layer;
- hollow fiber dimensions—outer and inner diameters, length, and their influence on each other.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbol | Description |
| inner fiber diameter | |
| outer fiber diameter | |
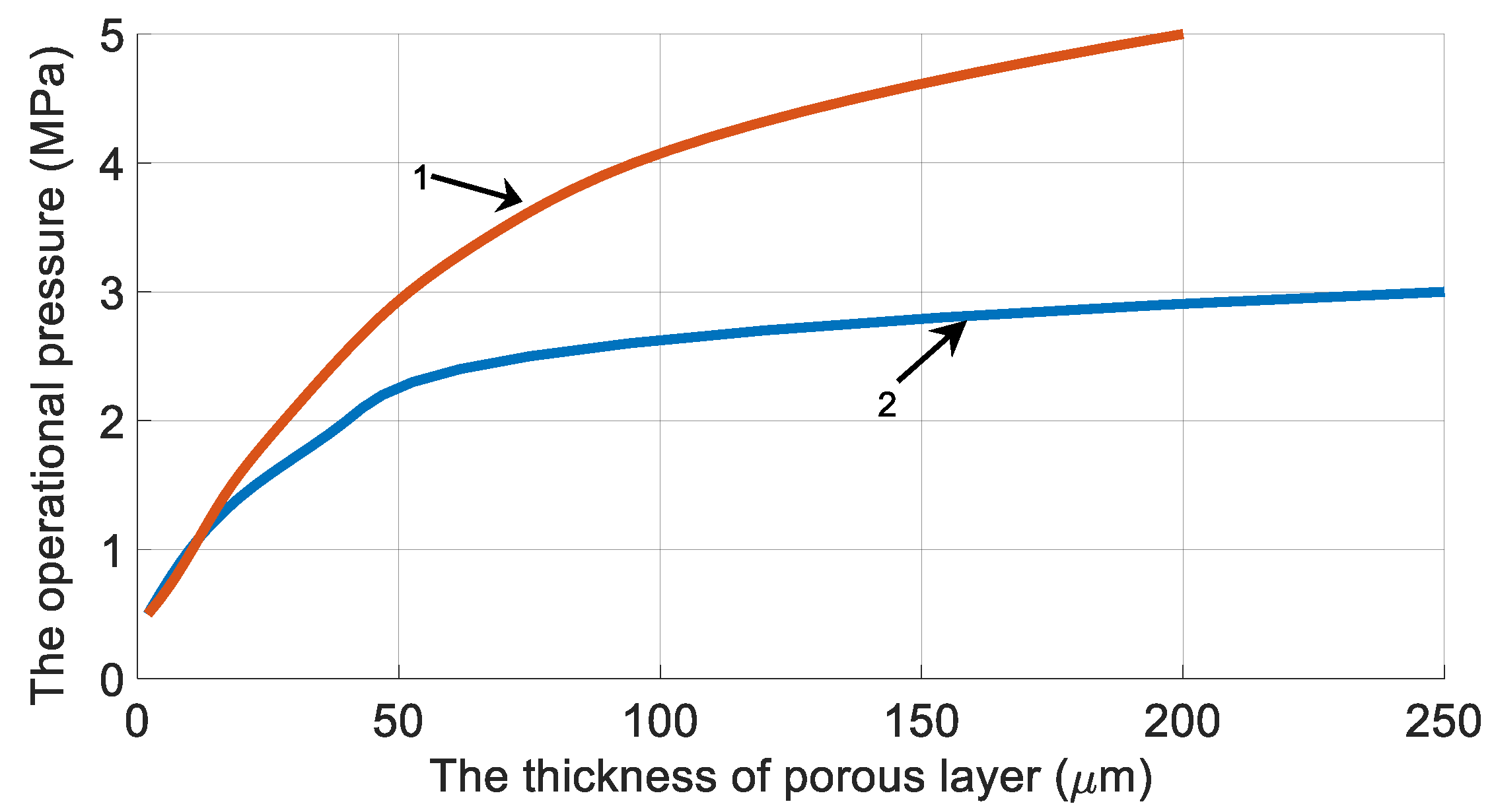
| pressure inside the fiber | |
| pressure outside the fiber | |
| selective layer thickness | |
| radial stress | |
| circumferential stress | |
| cylinder radius | |
| displacement vector | |
| integration constant | |
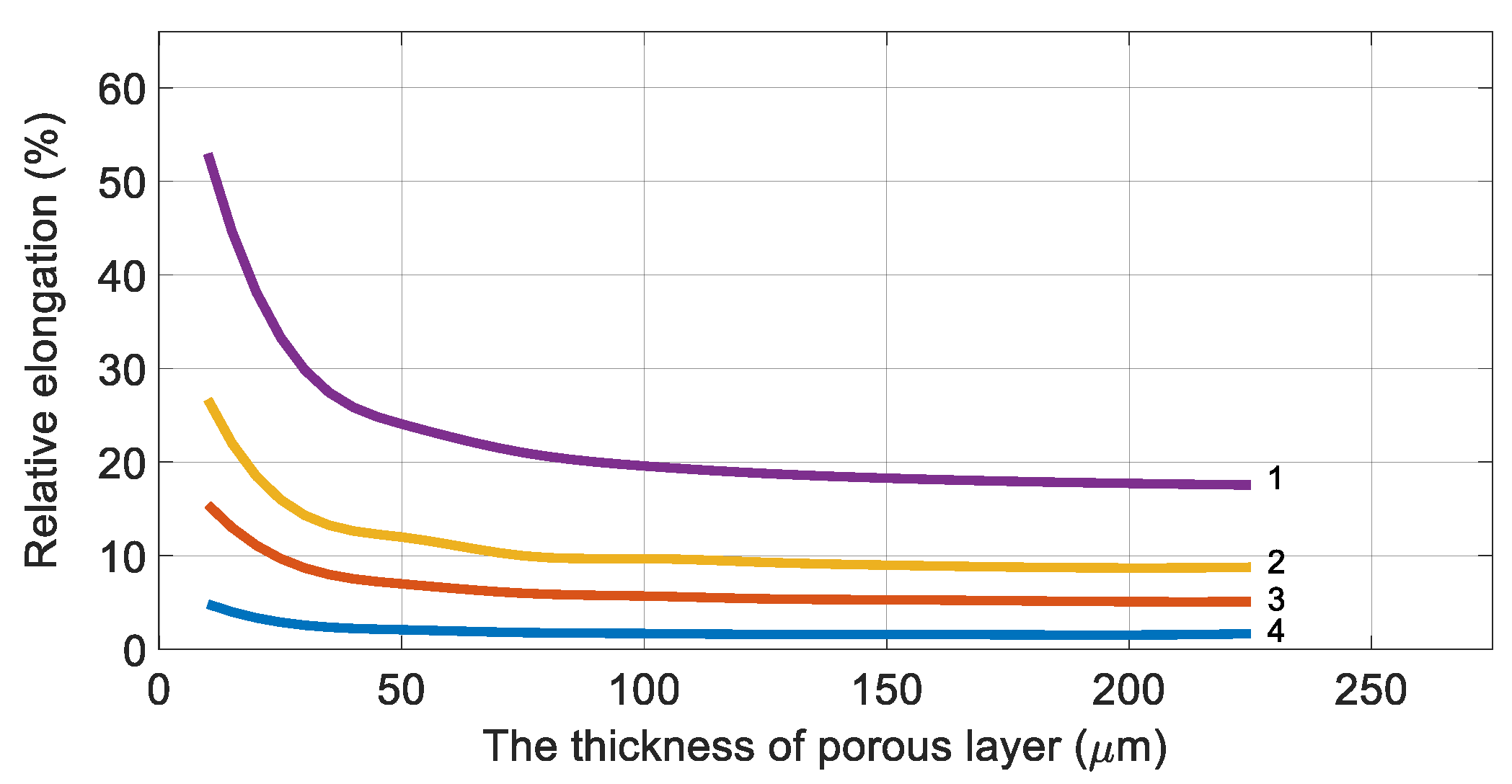
| relative elongation (strain) | |
| stress | |
| Young’s modulus | |
| Poisson’s ratio | |
| radial strain | |
| circumferential strain | |
| the density of the porous material | |
| density of dense matter | |
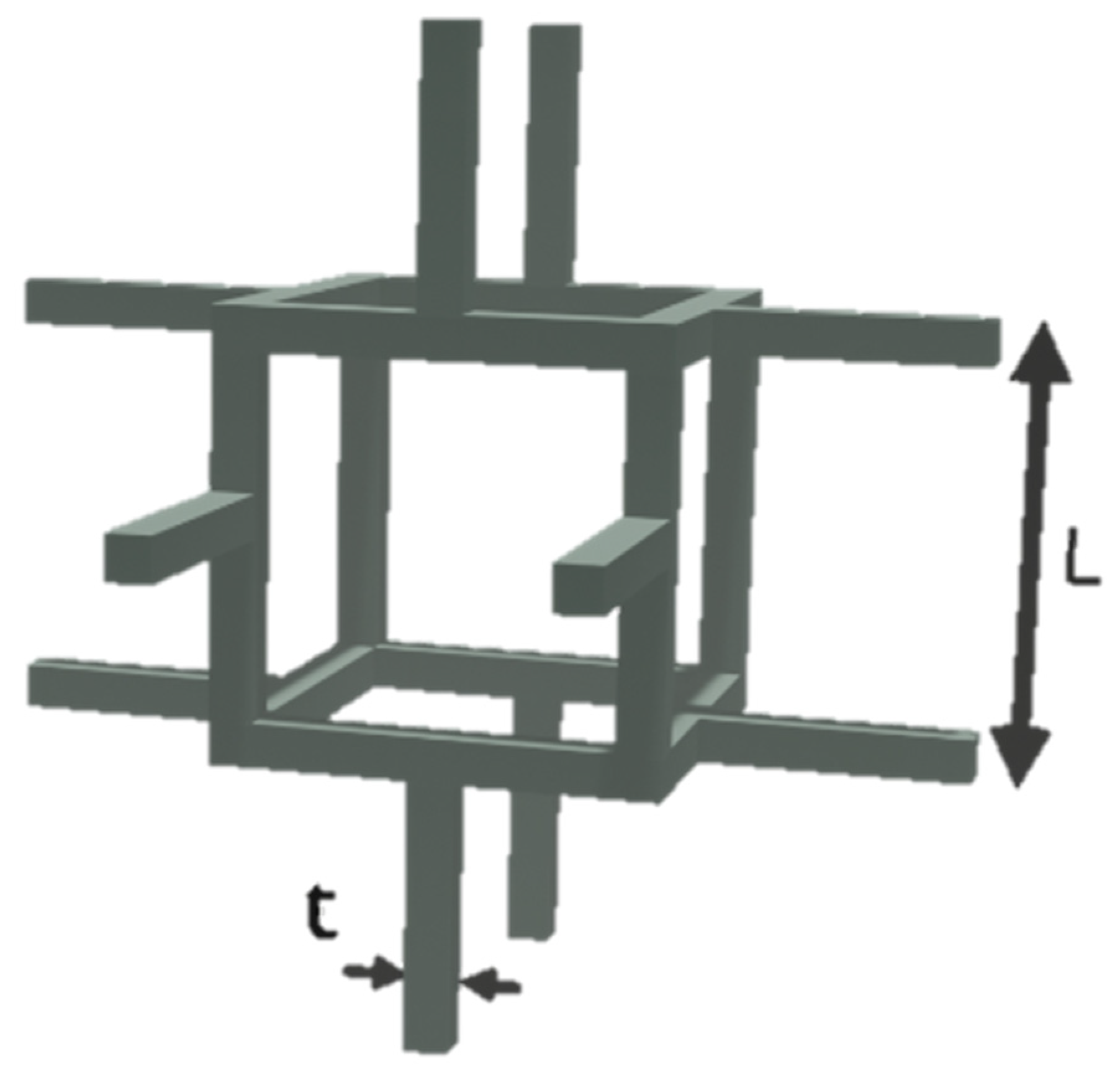
| cell size | |
| the thickness of the cell’s edges | |
| Young’s modulus of porous material | |
| Young’s modulus of dense matter |
References
- Kim, T.; Koros, W.; Husk, G.; O’Brien, K. Relationship between gas separation properties and chemical structure in a series of aromatic polyimides. J. Membr. Sci. 1988, 37, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartenev, G.M.; Zelenev, Y.V. Physics and Mechanics of Polymers; Vysshaya Shkola: Moscow, Russia, 1983. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E.; Golemme, G. Membrane gas separation: A review/state of the art. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4638–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausi, D.T.; McKelvey, S.A.; Koros, W.J. Characterization of substructure resistance in asymmetric gas separation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 160, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononova, S.V.; Kuznetsov, Y.P.; Romashkova, K.A.; Kudryavtsev, V.V. Relationship between the conditions of formation and structure of asymmetric membranes based on poly-diphenyloxide amido-N-phenylphthalimide. High Mol. Compd. 2006, 9, 1647–1654. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Matveev, D.N.; Vasilevsky, V.P.; Borisov, I.L.; Volkov, V.V.; Volkov, A.V. Influence of the parameters of dry-wet formation on the properties of half-fiber membranes from polysulphone. J. Appl. Chem. 2020, 4, 545–555. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Yeow, M.L.; Liu, Y.T.; Li, K. Morphological study of poly(vinylidene fluoride) asymmetric membranes: Effects of the solvent, additive, and dope temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kaliaguine, S.; Rodrigue, D. A comparison between several commercial polymer hollow fiber membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sep. Technol. 2017, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.S.; Xu, Z.L. Asymmetric hollow fiber membranes prepared from miscible polybenzimidazole and polyetherimide blends. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 1, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.T.; Kammermeyer, K. Membrane Separation Processes; Chemistry: Moscow, Russian, 1981. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dytnersky, Y.I.; Brykov, V.P.; Kagramanov, G.G. Membrane Separation of Gases; Chemistry: Moscow, Russian, 1991. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagramanov, G.G.; Farnosova, E.N. Scientific and engineering principles of membrane gas separation systems development. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2017, 51, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibrov, G.; Ivanov, M.; Semyashkin, M.; Sudin, V.; Kagramanov, G. High-pressure aging of asymmetric Torlon® hollow fibers for helium separation from natural gas. Fibers 2018, 6, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolov, A.P.; Mikhailovsky, K.V.; Shchetinin, V.N.; Sapelkin, A.S.; Presnyakov, V.V. Numerical determination of effective elastic-strength characteristics of composite embedments of gas separation membrane modules. In Proceedings of the XI International Conference on Nonequilibrium Processes in Nozzles and Jets (NPNJ’2016), Alushta, Crimea, 25–31 May 2016; pp. 387–389. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Elele, E.; Shen, Y.; Tang, J.; Lei, Q.; Khusid, B.; Tkacik, G.; Carbrello, C. Mechanical properties of polymeric microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgreccia, E.; Chailan, J.F.; Khadhraoui, M.; Di Vona, M.L.; Knauth, P. Mechanical properties of proton-conducting sulfonated aromatic polymer membranes: Stress-strain tests and dynamic analysis. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 7770–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iio, S.; Yonezu, A.; Yamamura, H.; Chen, X. Deformation modeling of polyvinylidenedifluoride (PVDF) symmetrical microfiltration hollow-fiber (HF) membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokolov, A.P.; Pershin, A.Y.; Kozov, A.V.; Kirillov, N.D. Homogenization of multi-level multicomponent heterogeneous structures for determining the physical and mechanical characteristics of composite materials. Phys. Mesomech. 2018, 21, 90–107. [Google Scholar]
- Rabotnov, Y.N. Strength of Materials; Fizmatgiz: Moscow, Russia, 1963. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gotsev, D.V.; Perunov, N.S. Mathematical model of the stress-strain state of an elastic cylindrical body with a porous filler. Vestn. Tomsk. Gos. Univ. Mat. Mekhanika 2017, 47, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tager, A.A. Physical Chemistry of Polymers; Ripol Classic: Moscow, Russia, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Schulte, K.; Friedrich, K.; Horstenkamp, G. Temperature-dependent mechanical behaviour of PI and PES resins used as matrices for short-fibre reinforced laminates. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 3561–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F. The properties of foams and lattices. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 1838, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanditov, B.D.; Tsydypov, S.B.; Sanditov, D.S.; Mantatov, V.V. Gruneisen parameter and Poisson’s ratio of glassy organic polymers and inorganic glasses. High Mol. Compd. Ser. B 2006, 7, 173–176. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ross, C.T.F.; Chilver, A. Strength of Materials and Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]



| Materials | Glass Transition Temperature (°C) | Young’s Modulus, (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultem@ 1000 (PEI) | 217 | 3585 | 60 | 105 |
| Matrimid@ 5218 (PI) | 319 | 2896 | 49 | 86.9 |
| Ultrason E6020P (PES) | 225 | 2650 | 50–100 | 85 |
| Membranes (Materials) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Ultimate Strength (MPa) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U305 (Ultem@ 1000 (PEI)) | 132 | 44 | 58.5 | 55.9 |
| M264 (Matrimid@ 5218 (PI)) | 121 | 29 | 54.8 | 58.4 |
| PES28 (Ultrason E6020P (PES)) | 72 | 85 | 5.2 | 46.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kagramanov, G.; Gurkin, V.; Farnosova, E. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Hollow Fiber Membranes and Technological Parameters of the Gas Separation Process. Membranes 2021, 11, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080583
Kagramanov G, Gurkin V, Farnosova E. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Hollow Fiber Membranes and Technological Parameters of the Gas Separation Process. Membranes. 2021; 11(8):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080583
Chicago/Turabian StyleKagramanov, Georgy, Vladimir Gurkin, and Elena Farnosova. 2021. "Physical and Mechanical Properties of Hollow Fiber Membranes and Technological Parameters of the Gas Separation Process" Membranes 11, no. 8: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080583
APA StyleKagramanov, G., Gurkin, V., & Farnosova, E. (2021). Physical and Mechanical Properties of Hollow Fiber Membranes and Technological Parameters of the Gas Separation Process. Membranes, 11(8), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080583






