Contraindications to the Initiation of Veno-Venous ECMO for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Practical Approach Based on the Current Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
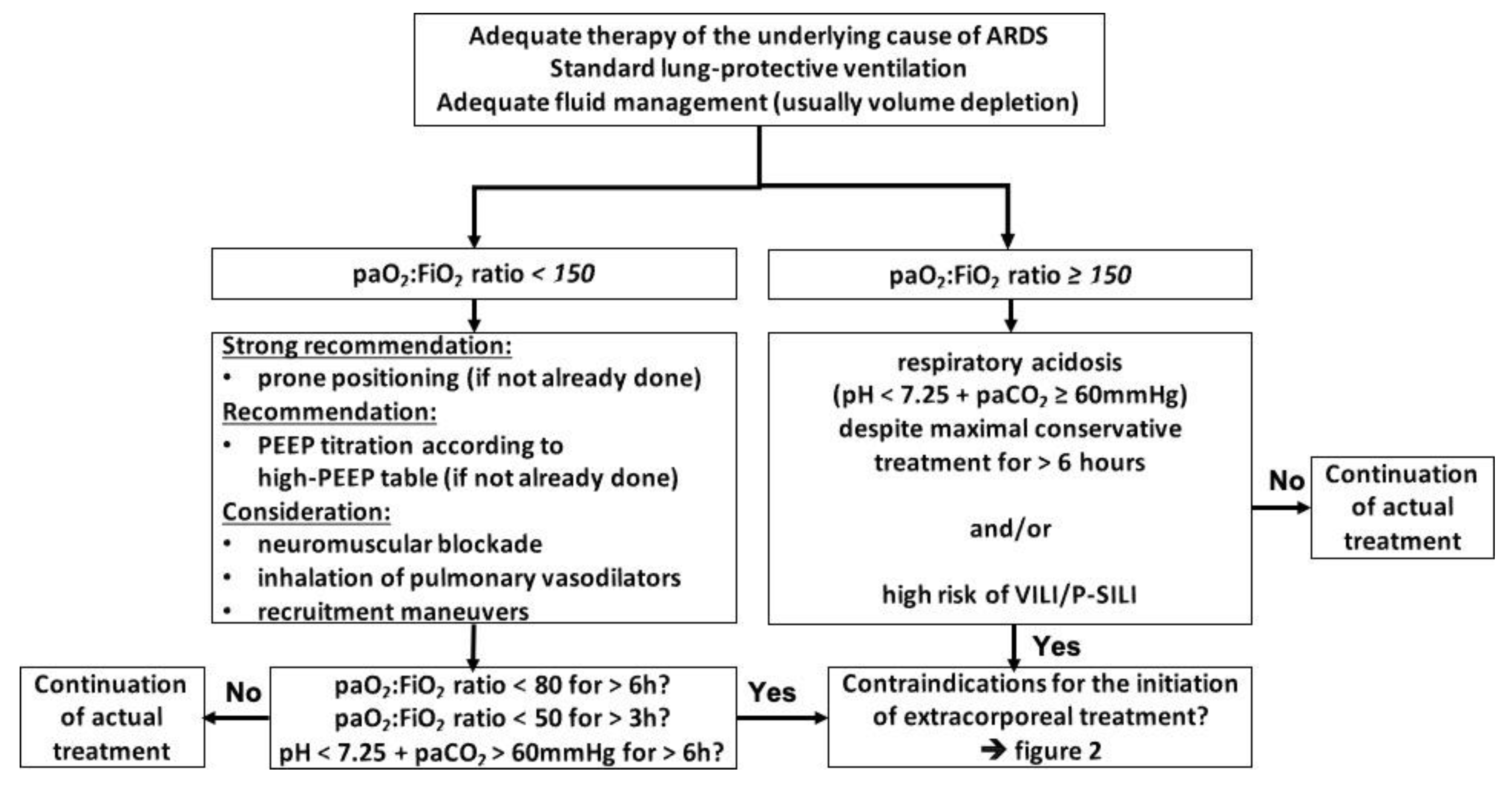
3. Indications for the Initiation of ECMO
4. Absolute Contraindications to the Initiation of ECMO
4.1. Refusal of the Use of Extracorporeal Techniques by the Patient
4.2. Advanced Stage of Cancer
4.3. Fatal Intracerebral Hemorrhage/Cerebral Herniation/Intractable Intracranial Hypertension
4.4. Irreversible Destruction of the Lung Parenchyma without the Option of Transplantation
4.5. Contraindications to Transplantation without the Option of Sufficient Lung Healing
5. Relative Contraindications to the Initiation of ECMO
5.1. Advanced Age >70 Years
5.2. Immunocompromized Patients/Pharmacological Immunosuppression
5.3. Time on Injurious Ventilator Settings >7 Days
5.4. Right-Heart Failure
5.5. Hematologic Malignancies, Especially Bone Marrow Transplantation and Graft-Versus-Host Disease
| Study | ICU Mortality | Hospital Mortality | Bone Marrow Transplant/HSCT Mortality (Hospital) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gow et al. 2010 [117] | 61% | 68% | 50% |
| Wohlfarth et al. 2014 [76] | 50% | 50% | 100% |
| Kang et al. 2015 [118] | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Choi et al. 2016 [80] | n/a | 80.9% | n/a |
| Wohlfarth et al. 2017 [119] | n/a | 81% | 100% (GvHD) |
| Stecher et al. 2018 [124] | n/a | 80% | 100% |
| Cho et al. 2019 [121] | 66% | 88% | 66.7% |
| Park et al. 2021 [122] | n/a | 86% (OR 42.25 (9.53, 187.22)) | 85.7% (OR 64) |
5.6. SAPS II Score ≥ 60 Points
5.7. SOFA Score >12 Points (mSOFA Score >8 Points)
5.8. PRESERVE Score ≥ 5 Points
5.9. RESP Score Worse Than −2 Points
5.10. PRESET Score ≥ 6 Points
5.11. “Do Not Attempt Resuscitation Order” (DN(A)R Status)
6. Factors Excluded as Contraindications/Additional Contraindications Only
6.1. Jehovah’s Witness/Refusal for Blood Transfusions
6.2. Fixed Pupils/Missing Brainstem Reflexes in Acute Settings
6.3. Nonfatal Intracranial Hemorrhage/Restrictions on Therapeutic Anticoagulation
6.4. Traumatic Bain Injury/Diffuse Axonal Injury
6.5. Use of Vasopressors
6.6. Obesity
6.7. Trauma/Polytrauma
6.8. Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC) after Cardiac Arrest Due to Hypoxemia/Hypercarbia
7. Factor Excluded for the Termination of ECMO
ECMO Runtime
8. Special Consideration
COVID-19
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fichtner, F.; Moerer, O.; Laudi, S.; Weber-Carstens, S.; Nothacker, M.; Kaisers, U.; the Guideline Group on Mechanical Ventilation; Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Acute Respiratory Insufficiency. Mechanical Ventilation and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygena tion in Acute Respiratory Insufficiency. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2018, 115, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner, F.; Moerer, O.; Weber-Carstens, S.; Nothacker, M.; Kaisers, U.; Laudi, S.; Guideline, G. Clinical Guideline for Treating Acute Respiratory Insufficiency with Invasive Ventilation and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Evidence-Based Recommendations for Choosing Modes and Setting Parameters of Mechanical Ventilation. Respiration 2019, 98, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapol, W.M.; Snider, M.T.; Hill, J.D.; Fallat, R.J.; Bartlett, R.H.; Edmunds, L.H.; Morris, A.H.; Peirce, E.C., 2nd; Thomas, A.N.; Proctor, H.J.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe acute respiratory failure. A randomized prospective study. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1979, 242, 2193–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, G.J.; Mugford, M.; Tiruvoipati, R.; Wilson, A.; Allen, E.; Thalanany, M.M.; Hibbert, C.L.; Truesdale, A.; Clemens, F.; Cooper, N.; et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009, 374, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, A.; Hajage, D.; Capellier, G.; Demoule, A.; Lavoue, S.; Guervilly, C.; Da Silva, D.; Zafrani, L.; Tirot, P.; Veber, B.; et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1965–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, A.; Peek, G.J.; Hajage, D.; Hardy, P.; Abrams, D.; Schmidt, M.; Dechartres, A.; Elbourne, D. ECMO for severe ARDS: Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Xing, X.; Zhang, G. Is Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation the Standard Care for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannidis, C.; Brodie, D.; Strassmann, S.; Stoelben, E.; Philipp, A.; Bein, T.; Muller, T.; Windisch, W. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: Evolving epidemiology and mortality. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, C.M.; Yuh, D.D.; Bonde, P. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation use has increased by 433% in adults in the United States from 2006 to 2011. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2015, 61, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betit, P. Are contraindications to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation slowly vanishing? Respir. Care 2011, 56, 1054–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ontaneda, A.; Annich, G.M. Novel Surfaces in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Circuits. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.R.; Garren, M.R.S.; Handa, H.; Batchinsky, A.I. Toward an artificial endothelium: Development of blood-compatible surfaces for extracorporeal life support. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2020, 89, S59–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, G.; Panarello, G.; Occhipinti, G.; Raffa, G.; Tuzzolino, F.; Capitanio, G.; Carollo, T.; Lino, G.; Bertani, A.; Vitulo, P.; et al. Impact of cannula design on packed red blood cell transfusions: Technical advancement to improve outcomes in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 5813–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robak, O.; Lakatos, P.K.; Bojic, A.; Hermann, A.; Laczika, K.F.; Chiari, A.; Hiesmayr, J.M.; Staudinger, T.; Locker, G.J. Influence of different oxygenator types on changing frequency, infection incidence, and mortality in ARDS patients on veno-venous ECMO. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2014, 37, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, D.; Pham, T.; Burns, K.E.A.; Combes, A.; Curtis, J.R.; Mueller, T.; Prager, K.M.; Serra, A.; Slutsky, A.S.; Brodie, D.; et al. Practice Patterns and Ethical Considerations in the Management of Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Patients: An International Survey. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.; Chatterjee, S.; Davignon, S.; Herlihy, J.P. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation as rescue therapy for severe hypoxemic respiratory failure. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, S1688–S1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, R.G.; Lanken, P.N.; MacIntyre, N.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; National Heart, L.; Blood Institute, A.C.T.N. Higher versus lower positive end-expiratory pressures in patients with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moerer, O.; Tonetti, T.; Quintel, M. Rescue therapies for acute respiratory distress syndrome: What to try first? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2017, 23, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnisch, L.O.; Moerer, O. ECMO therapy for ARDS: When, how, and how is the outcome? In DIVI Jahrbuch 2020/2021; Kluge, S., Heringlake, M., Janssens, U., Rieckels, E., Eds.; Medizinisch Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Patroniti, N.; Bonatti, G.; Senussi, T.; Robba, C. Mechanical ventilation and respiratory monitoring during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory support. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitzke, G.; Burchardi, H.; Duttge, G.; Hartog, C.; Erchinger, R.; Gretenkort, P.; Michalsen, A.; Mohr, M.; Nauck, F.; Salomon, F.; et al. Limits to the appropriateness of intensive care. Med. Klin. Intensivmed. Notfmed. 2019, 114, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felli, A.; Skhirtladze-Dworschak, K.; Opfermann, P.; Dworschak, M. Limitations of Cerebral Oximetry in a Patient With an Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Brain Edema on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Case Report. AA Pract. 2019, 12, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokes, B.T.; Vaszar, L.; Jahanyar, J.; Swanson, K.L. VV-ECMO-Assisted High-Risk Endobronchial Stenting as Rescue for Asphyxiating Mediastinal Mass. J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2018, 25, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurer, B.; Kertmen, H.; Yilmaz, E.R.; Dolgun, H.; Hasturk, A.E.; Sekerci, Z. The Surgical Outcome of Traumatic Extraaxial Hematomas Causing Brain Herniation. Turk. Neurosurg. 2017, 27, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakalov, I.; Harnisch, L.O.; Meyer, A.C.; Moerer, O. Preemptive veno-venous ECMO support in a patient with anticipated difficult airway: A case report. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 30, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K.; Vajpeyee, A.; Phadke, R.V.; Handique, A.; Salwani, V. Brain herniations in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2009, 119, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gower, D.J.; Lee, K.S.; McWhorter, J.M. Role of subtemporal decompression in severe closed head injury. Neurosurgery 1988, 23, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaab, M.R.; Rittierodt, M.; Lorenz, M.; Heissler, H.E. Traumatic brain swelling and operative decompression: A prospective investigation. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1990, 51, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polin, R.S.; Shaffrey, M.E.; Bogaev, C.A.; Tisdale, N.; Germanson, T.; Bocchicchio, B.; Jane, J.A. Decompressive bifrontal craniectomy in the treatment of severe refractory posttraumatic cerebral edema. Neurosurgery 1997, 41, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.P.; Volpin, L.; Fornezza, U.; Cervellini, P.; Zanusso, M.; Casentini, L.; Curri, D.; Piacentino, M.; Bozzato, G.; Colombo, F. The role of decompressive craniectomy in the treatment of uncontrollable post-traumatic intracranial hypertension. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2000, 76, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.; Butt, W.; Rosenfeld, J.; Shann, F.; Ditchfield, M.; Lewis, E.; Klug, G.; Wallace, D.; Henning, R.; Tibballs, J. A randomized trial of very early decompressive craniectomy in children with traumatic brain injury and sustained intracranial hypertension. Child’s Nerv. Syst. ChNS Off. J. Int. Soc. Pediatric Neurosurg. 2001, 17, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, P.C.; Patel, H.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Czosnyka, M.; Parry, D.; Menon, D.; Pickard, J.D.; Kirkpatrick, P.J. Bifrontal decompressive craniectomy in the management of posttraumatic intracranial hypertension. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 15, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, G.H.; Bardt, T.; Lanksch, W.R.; Unterberg, A. Decompressive craniectomy following traumatic brain injury: ICP, CPP and neurological outcome. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2002, 81, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, J.; Leone, M.; Alliez, J.R.; Kaya, J.M.; Antonini, F.; Alliez, B.; Martin, C. Decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury: Evaluation of the effects at one year. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 2535–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarabi, B.; Hesdorffer, D.C.; Ahn, E.S.; Aresco, C.; Scalea, T.M.; Eisenberg, H.M. Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant swelling due to severe head injury. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 104, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettervik, T.S.; Lenell, S.; Nyholm, L.; Howells, T.; Lewen, A.; Enblad, P. Decompressive craniectomy in traumatic brain injury: Usage and clinical outcome in a single centre. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakai, K.; Iwahashi, K.; Terada, K.; Gohda, Y.; Sakurai, M.; Matsumoto, Y. Outcome after external decompression for massive cerebral infarction. Neurol. Med. Chir. 1998, 38, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Geocadin, R.G.; Suarez, J.I.; Ulatowski, J.A. Long-term outcome after medical reversal of transtentorial herniation in patients with supratentorial mass lesions. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, M.A.; Bryan, M.; Lewin, J.L., 3rd; Mirski, M.A.; Geocadin, R.G.; Stevens, R.D. Reversal of transtentorial herniation with hypertonic saline. Neurology 2008, 70, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoglund, T.; Nellgard, B. Long-time outcome after transient transtentorial herniation in patients with traumatic brain injury. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2005, 49, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Park, J.K.; Kang, S.G.; Cho, K.S.; Yoo, D.S.; Jang, D.K.; Huh, P.W.; Kim, D.S. Comparison of the effect of decompressive craniectomy on different neurosurgical diseases. Acta Neurochir 2009, 151, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Richard, S.A.; Li, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, R.; Yang, C. Outcomes of patients undergoing craniotomy and decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury with brain herniation: A retrospective study. Medicine 2020, 99, e22742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcourt, C.; Zheng, D.; Chen, X.; Hackett, M.; Arima, H.; Hata, J.; Heeley, E.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Woodward, M.; Huang, Y.; et al. Associations with health-related quality of life after intracerebral haemorrhage: Pooled analysis of INTERACT studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Anderson, C.S.; Robinson, T.; Lavados, P.M.; Lindley, R.I.; Chalmers, J.; Delcourt, C. Infratentorial Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2019, 50, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, M.T.; Fonville, A.F.; Al-Shahi Salman, R. Long-term prognosis after intracerebral haemorrhage: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, J.; Costa, A.S.; Araujo, J.M.; Amorim, J.M.; Ferreira, C. Intracerebral hemorrhage outcome: A comprehensive update. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 398, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giangreco, A.; Arwert, E.N.; Rosewell, I.R.; Snyder, J.; Watt, F.M.; Stripp, B.R. Stem cells are dispensable for lung homeostasis but restore airways after injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9286–9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, M.V.; Abreu, S.C.; Padilha, G.A.; Rocha, N.N.; Maia, L.A.; Takiya, C.M.; Xisto, D.G.; Suki, B.; Silva, P.L.; Rocco, P.R. Characterization of a Mouse Model of Emphysema Induced by Multiple Instillations of Low-Dose Elastase. Front. Physiol 2016, 7, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meltzer, E.B.; Noble, P.W. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2008, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harnisch, L.O.; Moerer, O. Sequential use of extracorporeal devices to avoid mechanical ventilation in a patient with complicated pulmonary fibrosis. J. Artif. Organs Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Artif. Organs 2017, 20, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umei, N.; Ichiba, S.; Sakamoto, A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis patient supported with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for 403 days while waiting for a lung transplant: A case report. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2018, 24, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakwaya, Y.; Brown, K.K. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis andOutcomes. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, K.K.; Cherikh, W.S.; Chambers, D.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Hayes, D., Jr.; Hsich, E.; Meiser, B.; Potena, L.; Robinson, A.; Rossano, J.W.; et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-sixth adult heart transplantation report-2019; focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J. Heart Lung Transplant. Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Heart Transplant. 2019, 38, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, S.; Vos, R.; Van Raemdonck, D.E.; Verleden, G.M. Survival in adult lung transplantation: Where are we in 2020? Curr. Opin. Organ. Transpl. 2020, 25, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, D. Lung transplantation: Indications and contraindications. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 4574–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rooij, S.E.; Govers, A.; Korevaar, J.C.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Levi, M.; de Jonge, E. Short-term and long-term mortality in very elderly patients admitted to an intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, Y.S.; Jung, H.; Shin, T.R.; Kim, D.G.; Park, S.M. Mortality and outcomes in very elderly patients 90 years of age or older admitted to the ICU. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendiratta, P.; Tang, X.; Collins, R.T., 2nd; Rycus, P.; Brogan, T.V.; Prodhan, P. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory failure in the elderly: A review of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization registry. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2014, 60, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, S.; Sertic, F.; Valchanov, K.; De Silva, R. Use veno-venous extra corporeal membrane oxygenation in elderly patients with post-cardiotomy hypoxia: The changing paradigm of respiratory support in adult respiratory distress syndrome. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayanga, J.A.; Murphy, E.; Girgis, R.E.; Jansma, S.; Khaghani, A. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation as a Bridge to Lung Transplantation in Patients Over Age 70 Years: A Case Report. Transpl. Proc. 2017, 49, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deatrick, K.B.; Mazzeffi, M.A.; Galvagno, S.M., Jr.; Tesoriero, R.B.; Kaczoroswki, D.J.; Herr, D.L.; Dolly, K.; Rabinowitz, R.P.; Scalea, T.M.; Menaker, J. Outcomes of Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation When Stratified by Age: How Old Is Too Old? ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2020, 66, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giani, M.; Forlini, C.; Fumagalli, B.; Rona, R.; Pesenti, A.; Foti, G. Indication for Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Is 65 Years Old, Too Old? ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2021, 67, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, E.; Russell, L.; Van de Louw, A.; Metaxa, V.; Bauer, P.; Povoa, P.; Montero, J.G.; Loeches, I.M.; Mehta, S.; Puxty, K.; et al. Diagnosis of severe respiratory infections in immunocompromised patients. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azoulay, E.; Mokart, D.; Pene, F.; Lambert, J.; Kouatchet, A.; Mayaux, J.; Vincent, F.; Nyunga, M.; Bruneel, F.; Laisne, L.M.; et al. Outcomes of critically ill patients with hematologic malignancies: Prospective multicenter data from France and Belgium--a groupe de recherche respiratoire en reanimation onco-hematologique study. J. Clin. Oncol 2013, 31, 2810–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawcutt, K.; Gallo De Moraes, A.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.G.; Schears, G.J.; Nemergut, M.E. The use of ECMO in HIV/AIDS with Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia: A case report and review of the literature. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2014, 60, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Schellongowski, P.; Patroniti, N.; Taccone, F.S.; Reis Miranda, D.; Reuter, J.; Prodanovic, H.; Pierrot, M.; Dorget, A.; Park, S.; et al. Six-Month Outcome of Immunocompromised Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Rescued by Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. An International Multicenter Retrospective Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huprikar, N.A.; Peterson, M.R.; DellaVolpe, J.D.; Sams, V.G.; Lantry, J.H.; Walter, R.J.; Osswald, M.B.; Chung, K.K.; Mason, P.E. Salvage extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in induction-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome in acute leukemia patients: A case series. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 42, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. ELSO Guidelines for Adult Respiratory Failure. 2017. Available online: https://www.elso.org/Portals/0/ELSO%20Guidelines%20For%20Adult%20Respiratory%20Failure%201_4.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Pranikoff, T.; Hirschl, R.B.; Steimle, C.N.; Anderson, H.L., 3rd; Bartlett, R.H. Mortality is directly related to the duration of mechanical ventilation before the initiation of extracorporeal life support for severe respiratory failure. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 25, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mols, G.; Loop, T.; Geiger, K.; Farthmann, E.; Benzing, A. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A ten-year experience. Am. J. Surg. 2000, 180, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmila, M.R.; Rowe, S.A.; Boules, T.N.; Miskulin, J.; McGillicuddy, J.W.; Schuerer, D.J.; Haft, J.W.; Swaniker, F.; Arbabi, S.; Hirschl, R.B.; et al. Extracorporeal life support for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiderlinden, M.; Eikermann, M.; Boes, T.; Breitfeld, C.; Peters, J. Treatment of severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: Role of extracorporeal gas exchange. Intensive Care Med. 2006, 32, 1627–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patroniti, N.; Zangrillo, A.; Pappalardo, F.; Peris, A.; Cianchi, G.; Braschi, A.; Iotti, G.A.; Arcadipane, A.; Panarello, G.; Ranieri, V.M.; et al. The Italian ECMO network experience during the 2009 influenza A(H1N1) pandemic: Preparation for severe respiratory emergency outbreaks. Intensive Care Med. 2011, 37, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Tachon, G.; Devilliers, C.; Muller, G.; Hekimian, G.; Brechot, N.; Merceron, S.; Luyt, C.E.; Trouillet, J.L.; Chastre, J.; et al. Blood oxygenation and decarboxylation determinants during venovenous ECMO for respiratory failure in adults. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enger, T.; Philipp, A.; Videm, V.; Lubnow, M.; Wahba, A.; Fischer, M.; Schmid, C.; Bein, T.; Muller, T. Prediction of mortality in adult patients with severe acute lung failure receiving veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohlfarth, P.; Ullrich, R.; Staudinger, T.; Bojic, A.; Robak, O.; Hermann, A.; Lubsczyk, B.; Worel, N.; Fuhrmann, V.; Schoder, M.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adult patients with hematologic malignancies and severe acute respiratory failure. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, M.; Stewart, C.; Bailey, M.; Nieszkowska, A.; Kelly, J.; Murphy, L.; Pilcher, D.; Cooper, D.J.; Scheinkestel, C.; Pellegrino, V.; et al. Mechanical ventilation management during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute respiratory distress syndrome: A retrospective international multicenter study. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klinzing, S.; Wenger, U.; Steiger, P.; Starck, C.T.; Wilhelm, M.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Maggiorini, M. External validation of scores proposed for estimation of survival probability of patients with severe adult respiratory distress syndrome undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy: A retrospective study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Wu, M.Y.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, P.J. Developing a simple preinterventional score to predict hospital mortality in adult venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A pilot study. Medicine 2016, 95, e4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.B.; Kim, H.W.; Jo, K.H.; Kim do, Y.; Choi, H.J.; Hong, S.B. Extracorporeal Life Support in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies: A Single Center Experience. Korean J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2016, 49, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Li, T.; Xu, L.; Hu, X.M.; Duan, D.W.; Li, Z.B.; Gao, X.J.; Li, J.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.W.; et al. Performance of Multiple Risk Assessment Tools to Predict Mortality for Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome with Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Therapy: An External Validation Study Based on Chinese Single-center Data. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1688–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, C.H.; Wu, M.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Kao, K.C.; Lin, P.J. Venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adult respiratory failure: Scores for mortality prediction. Medicine 2016, 95, e3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yeo, H.J.; Yoon, S.H.; Lee, S.E.; Cho, W.H.; Jeon, D.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Son, B.S.; Kim do, H. Validity of Outcome Prediction Scoring Systems in Korean Patients with Severe Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Therapy. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serpa Neto, A.; Schmidt, M.; Azevedo, L.C.; Bein, T.; Brochard, L.; Beutel, G.; Combes, A.; Costa, E.L.; Hodgson, C.; Lindskov, C.; et al. Associations between ventilator settings during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for refractory hypoxemia and outcome in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A pooled individual patient data analysis: Mechanical ventilation during ECMO. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Wu, T.I.; Wang, C.L.; Lin, P.J. Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Adults: Prognostic Factors for Outcomes. Medicine 2016, 95, e2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilder, M.; Herbstreit, F.; Adamzik, M.; Beiderlinden, M.; Burschen, M.; Peters, J.; Frey, U.H. Comparison of mortality prediction models in acute respiratory distress syndrome undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and development of a novel prediction score: The PREdiction of Survival on ECMO Therapy-Score (PRESET-Score). Crit. Care 2017, 21, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kon, Z.N.; Bittle, G.J.; Pasrija, C.; Pham, S.M.; Mazzeffi, M.A.; Herr, D.L.; Sanchez, P.G.; Griffith, B.P. Venovenous Versus Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Adult Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Requiring Precannulation Hemodynamic Support: A Review of the ELSO Registry. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.Y.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, C.C.; Wu, T.I.; Lin, P.J. The impacts of baseline ventilator parameters on hospital mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome treated with venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posluszny, J.; Engoren, M.; Napolitano, L.M.; Rycus, P.T.; Bartlett, R.H.; centers, E.m. Predicting Survival of Adult Respiratory Failure Patients Receiving Prolonged (>/=14 Days) Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2020, 66, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, R.; Legouis, D.; Assouline, B.; De Charriere, A.; Decosterd, D.; Brunner, M.E.; Moret-Bochatay, M.; Fumeaux, T.; Bendjelid, K. Timing of VV-ECMO therapy implementation influences prognosis of COVID-19 patients. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supady, A.; DellaVolpe, J.; Taccone, F.S.; Scharpf, D.; Ulmer, M.; Lepper, P.M.; Halbe, M.; Ziegeler, S.; Vogt, A.; Ramanan, R.; et al. Outcome Prediction in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Requiring Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation-A Retrospective International Multicenter Study. Membranes 2021, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekontso Dessap, A.; Boissier, F.; Charron, C.; Begot, E.; Repesse, X.; Legras, A.; Brun-Buisson, C.; Vignon, P.; Vieillard-Baron, A. Acute cor pulmonale during protective ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome: Prevalence, predictors, and clinical impact. Intensive Care Med. 2016, 42, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, D.J.; Fabbri, A.; Falvo, A.; Powell-Tuck, J.; Desai, N.; Vasques, F.; Meadows, C.; Ioannou, N.; Glover, G.; Brame, A.; et al. Assessment of Right Ventricular Function With CT and Echocardiography in Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzeri, C.; Cianchi, G.; Bonizzoli, M.; Batacchi, S.; Terenzi, P.; Bernardo, P.; Valente, S.; Gensini, G.F.; Peris, A. Right ventricle dilation as a prognostic factor in refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome requiring veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Minerva Anestesiol. 2016, 82, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Price, L.C.; McAuley, D.F.; Marino, P.S.; Finney, S.J.; Griffiths, M.J.; Wort, S.J. Pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension in acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L803–L815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, M.C.; Freden, F.; Larsson, A.; Wiklund, P.; Bergquist, M.; Hambraeus-Jonzon, K. Hypercapnic acidosis transiently weakens hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction without affecting endogenous pulmonary nitric oxide production. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekontso Dessap, A.; Charron, C.; Devaquet, J.; Aboab, J.; Jardin, F.; Brochard, L.; Vieillard-Baron, A. Impact of acute hypercapnia and augmented positive end-expiratory pressure on right ventricle function in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanos, G.M.; Talbot, N.P.; Dorrington, K.L.; Robbins, P.A. Human pulmonary vascular response to 4h of hypercapnia and hypocapnia measured using Doppler echocardiography. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 94, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vieillard-Baron, A.; Schmitt, J.M.; Augarde, R.; Fellahi, J.L.; Prin, S.; Page, B.; Beauchet, A.; Jardin, F. Acute cor pulmonale in acute respiratory distress syndrome submitted to protective ventilation: Incidence, clinical implications, and prognosis. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieillard-Baron, A.; Loubieres, Y.; Schmitt, J.M.; Page, B.; Dubourg, O.; Jardin, F. Cyclic changes in right ventricular output impedance during mechanical ventilation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdorp, B.; Hofhuizen, C.; van Lavieren, M.; van Swieten, H.; Lemson, J.; van Putten, M.J.; van der Hoeven, J.G.; Pickkers, P. Mechanical ventilation-induced intrathoracic pressure distribution and heart-lung interactions*. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 42, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.G.; Wadia, S.K.; Kovach, J.; Fogg, L.; Tandon, R. Echocardiographic parameters of right ventricular function predict mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome: A pilot study. Pulm. Circ. 2016, 6, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boissier, F.; Katsahian, S.; Razazi, K.; Thille, A.W.; Roche-Campo, F.; Leon, R.; Vivier, E.; Brochard, L.; Vieillard-Baron, A.; Brun-Buisson, C.; et al. Prevalence and prognosis of cor pulmonale during protective ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, D.; Monnet, X.; Castelain, V.; Anguel, N.; Warszawski, J.; Teboul, J.L.; Richard, C.; the French Pulmonary Artery Catheter Study Group. Incidence and prognostic value of right ventricular failure in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, R.; Banfi, C.; Siegenthaler, N.; Bendjelid, K. Massive pulmonary embolism leading to cardiac arrest: One pathology, two different ECMO modes to assist patients. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2016, 30, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis Miranda, D.; van Thiel, R.; Brodie, D.; Bakker, J. Right ventricular unloading after initiation of venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumy, A.; Liaudet, L.; Rusca, M.; Marcucci, C.; Kirsch, M. Pulmonary complications associated with veno-arterial extra-corporeal membrane oxygenation: A comprehensive review. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangrillo, A.; Landoni, G.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Greco, M.; Greco, T.; Frati, G.; Patroniti, N.; Antonelli, M.; Pesenti, A.; Pappalardo, F. A meta-analysis of complications and mortality of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit. Care Resusc. 2013, 15, 172–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bunge, J.J.H.; Caliskan, K.; Gommers, D.; Reis Miranda, D. Right ventricular dysfunction during acute respiratory distress syndrome and veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S674–S682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecuyer, L.; Chevret, S.; Guidet, B.; Aegerter, P.; Martel, P.; Schlemmer, B.; Azoulay, E. Case volume and mortality in haematological patients with acute respiratory failure. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benoit, D.D.; Vandewoude, K.H.; Decruyenaere, J.M.; Hoste, E.A.; Colardyn, F.A. Outcome and early prognostic indicators in patients with a hematologic malignancy admitted to the intensive care unit for a life-threatening complication. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, E.; Thiery, G.; Chevret, S.; Moreau, D.; Darmon, M.; Bergeron, A.; Yang, K.; Meignin, V.; Ciroldi, M.; Le Gall, J.R.; et al. The prognosis of acute respiratory failure in critically ill cancer patients. Medicine 2004, 83, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, E.; Lemiale, V.; Mokart, D.; Pene, F.; Kouatchet, A.; Perez, P.; Vincent, F.; Mayaux, J.; Benoit, D.; Bruneel, F.; et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with malignancies. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, E.; Mokart, D.; Kouatchet, A.; Demoule, A.; Lemiale, V. Acute respiratory failure in immunocompromised adults. Lancet Respir Med. 2019, 7, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemiale, V.; Resche-Rigon, M.; Mokart, D.; Pene, F.; Rabbat, A.; Kouatchet, A.; Vincent, F.; Bruneel, F.; Nyunga, M.; Lebert, C.; et al. Acute respiratory failure in patients with hematological malignancies: Outcomes according to initial ventilation strategy. A groupe de recherche respiratoire en reanimation onco-hematologique (Grrr-OH) study. Ann. Intensive Care 2015, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina, R.; Bernal, T.; Borges, M.; Zaragoza, R.; Bonastre, J.; Granada, R.M.; Rodriguez-Borregan, J.C.; Nunez, K.; Seijas, I.; Ayestaran, I.; et al. Ventilatory support in critically ill hematology patients with respiratory failure. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gow, K.W.; Lao, O.B.; Leong, T.; Fortenberry, J.D. Extracorporeal life support for adults with malignancy and respiratory or cardiac failure: The Extracorporeal Life Support experience. Am. J. Surg. 2010, 199, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Rhee, C.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Kwon, S.S.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, J.W. Clinical outcomes of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support in patients with hematologic malignancies. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2015, 30, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wohlfarth, P.; Beutel, G.; Lebiedz, P.; Stemmler, H.J.; Staudinger, T.; Schmidt, M.; Kochanek, M.; Liebregts, T.; Taccone, F.S.; Azoulay, E.; et al. Characteristics and Outcome of Patients After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Treated With Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e500–e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, M.; Shanley, T.P.; Moler, F.W. Extracorporeal life support for severe respiratory failure in children with immune compromised conditions. Pediatric Crit. Care Med. A J. Soc. Crit. Care Med. World Fed. Pediatric Intensive Crit. Care Soc. 2008, 9, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Cho, W.C.; Lim, J.Y.; Kang, P.J. Extracorporeal Life Support in Adult Patients with Hematologic Malignancies and Acute Circulatory and/or Respiratory Failure. Korean J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 52, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Ko, U.W.; Ko, R.E.; Na, S.J.; Yang, J.H.; Jeon, K.; Suh, G.Y.; Sung, K.; Cho, Y.H. Outcomes of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adults with active hematologic and nonhematologic malignancy. Artif. Organs 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggewiss, R.; Einsele, H. Immune reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation and expanding options for immunomodulation: An update. Blood 2010, 115, 3861–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, S.S.; Beyer, G.; Goni, E.; Tischer, J.; Herold, T.; Schulz, C.; Op den Winkel, M.; Stemmler, H.J.; Lippl, S. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Predominantly Leuco- and Thrombocytopenic Haematologic/Oncologic Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome-a Single-Centre Experience. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2018, 41, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, J.R.; Lemeshow, S.; Saulnier, F. A New Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPSII) Based on a European/ North American Multicenter Study. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1993, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; Ha, S.O.; Kim, H.S.; Park, S.; Han, S.J.; Lee, S.H. The Simplified Acute Physiology Score II as a Predictor of Mortality in Patients Who Underwent Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Septic Shock. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.I.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.S.; Ha, S.O.; Lee, W.Y.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, T.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Choi, H.H.; et al. The pre-ECMO simplified acute physiology score II as a predictor for mortality in patients with initiation ECMO support at the emergency department for acute circulatory and/or respiratory failure: A retrospective study. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2015, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisser, C.; Rincon-Gutierrez, L.A.; Enger, T.B.; Taccone, F.S.; Broman, L.M.; Belliato, M.; Nobile, L.; Pappalardo, F.; Malfertheiner, M.V. Validation of Prognostic Scores in Extracorporeal Life Support: A Multi-Centric Retrospective Study. Membranes 2021, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonca, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, C.K.; Suter, P.M.; Thijs, L.G. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.L.; Bota, D.P.; Bross, A.; Melot, C.; Vincent, J.L. Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2001, 286, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Grooth, H.J.; Geenen, I.L.; Girbes, A.R.; Vincent, J.L.; Parienti, J.J.; Oudemans-van Straaten, H.M. SOFA and mortality endpoints in randomized controlled trials: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raith, E.P.; Udy, A.A.; Bailey, M.; McGloughlin, S.; MacIsaac, C.; Bellomo, R.; Pilcher, D.V.; the Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Centre for Outcomes and Resource Evaluation (CORE). Prognostic Accuracy of the SOFA Score, SIRS Criteria, and qSOFA Score for In-Hospital Mortality Among Adults With Suspected Infection Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2017, 317, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minne, L.; Abu-Hanna, A.; de Jonge, E. Evaluation of SOFA-based models for predicting mortality in the ICU: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2008, 12, R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safari, S.; Shojaee, M.; Rahmati, F.; Barartloo, A.; Hahshemi, B.; Forouzanfar, M.M.; Mohammadi, E. Accuracy of SOFA score in prediction of 30-day outcome of critically ill patients. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 16, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, R.; Martin, C.; Mattie, H.; Gichoya, J.W.; Stone, D.J.; Celi, L.A. Performance of intensive care unit severity scoring systems across different ethnicities in the USA: A retrospective observational study. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e241–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissom, C.K.; Brown, S.M.; Kuttler, K.G.; Boltax, J.P.; Jones, J.; Jephson, A.R.; Orme, J.F., Jr. A modified sequential organ failure assessment score for critical care triage. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2010, 4, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Zogheib, E.; Roze, H.; Repesse, X.; Lebreton, G.; Luyt, C.E.; Trouillet, J.L.; Brechot, N.; Nieszkowska, A.; Dupont, H.; et al. The PRESERVE mortality risk score and analysis of long-term outcomes after extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.R.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Jheon, S.; Lee, C.T.; Lee, Y.J. A Comparative Analysis of Survival Prediction Using PRESERVE and RESP Scores. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, M.; Bailey, M.; Sheldrake, J.; Hodgson, C.; Aubron, C.; Rycus, P.T.; Scheinkestel, C.; Cooper, D.J.; Brodie, D.; Pellegrino, V.; et al. Predicting survival after extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory failure. The Respiratory Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Survival Prediction (RESP) score. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabai, A.; Ghneim, M.H.; Kaczorowski, D.J.; Shah, A.; Dave, S.; Haase, D.J.; Vesselinov, R.; Deatrick, K.B.; Rabin, J.; Rabinowitz, R.P.; et al. Mortality Risk Assessment in COVID-19 Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, S.; Slutsky, A.S.; Schmidt, M. The PRESET-Score: The extrapulmonary predictive survival model for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S2040–S2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniack, E.P. Increasing use of DNR orders in the elderly worldwide: Whose choice is it? J. Med. Ethics 2002, 28, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollock, B.D.; Herrin, J.; Neville, M.R.; Dowdy, S.C.; Moreno Franco, P.; Shah, N.D.; Ting, H.H. Association of Do-Not-Resuscitate Patient Case Mix With Publicly Reported Risk-Standardized Hospital Mortality and Readmission Rates. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2010383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetsch, G.; Uhehlinger, D.; Zircher-Zenklusen, R. DNR orders at a tertiary care hospital–are they appropriate? Swiss Med. Wkly. 2002, 132, 190–196. [Google Scholar]
- Salottolo, K.; Offner, P.J.; Orlando, A.; Slone, D.S.; Mains, C.W.; Carrick, M.; Bar-Or, D. The epidemiology of do-not-resuscitate orders in patients with trauma: A community level one trauma center observational experience. Scand. J. Trauma Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2015, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walkey, A.J.; Weinberg, J.; Wiener, R.S.; Cooke, C.R.; Lindenauer, P.K. Hospital Variation in Utilization of Life-Sustaining Treatments among Patients with Do Not Resuscitate Orders. Health Serv. Res. 2018, 53, 1644–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, J.L.; Harhay, M.O.; Gabler, N.B.; Ratcliffe, S.J.; Quill, C.M.; Halpern, S.D. Variability Among US Intensive Care Units in Managing the Care of Patients Admitted With Preexisting Limits on Life-Sustaining Therapies. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, M.C.; Morrison, R.S. The effect of do-not-resuscitate orders on physician decision-making. J. Am. Geriatr Soc. 2002, 50, 2057–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Puma, J.; Silverstein, M.D.; Stocking, C.B.; Roland, D.; Siegler, M. Life-sustaining treatment. A prospective study of patients with DNR orders in a teaching hospital. Arch. Intern. Med. 1988, 148, 2193–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Kostousov, V.; Teruya, J. Bleeding and Thrombotic Complications in the Use of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 44, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.; Zhang, D.; Nair, P.; Buscher, H. A Systematic Literature Review of Packed Red Cell Transfusion Usage in Adult Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. Membranes 2021, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, J.; Palmer, K.; Frenckner, B. Long-term ECMO treatment in Jehovah’s Witness patient without transfusions. Perfusion 2012, 27, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, T.J.; Olshove, V.F., Jr.; Chase, M. Bloodless extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the Jehovah’s Witness patient. J. Extra Corpor Technol. 2012, 44, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, M.J.; Merlo, A.; Eton, D.; Patel, P.J.; Fedson, S.; Anderson, A.; Shah, A.; Jeevanandam, V. Successful use of ECMO in a Jehovah’s Witness after complicated re-heart transplant. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2013, 59, 528–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Lee, B.; Kim, C.Y. Blood-sparing removal technique of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit in a Jehovah Witness patient: Case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e16740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.; Wang, J.; Zakaria, A.; Dinescu, D.; Bogar, L.; Singh, R.; Dalton, H.; Osborn, E. Fixed and dilated pupils, not a contraindication for extracorporeal support: A case series. Perfusion 2020, 35, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, K.T.; Kutcher, M.E.; Shake, J.G.; Panos, A.L.; Cochran, R.P.; Creswell, L.L.; Copeland, H. Heparin-Sparing Anticoagulation Strategies Are Viable Options for Patients on Veno-Venous ECMO. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 243, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willers, A.; Swol, J.; Kowalewski, M.; Raffa, G.M.; Meani, P.; Jiritano, F.; Matteucci, M.; Fina, D.; Heuts, S.; Bidar, E.; et al. Extracorporeal Life Support in Hemorrhagic Conditions: A Systematic Review. ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2021, 67, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, B.; Dobler, M.; Friedrich, R.; Stahl, K.; Kuhn, C.; Bauersachs, J.; Steinhagen, F.; Ehrentraut, S.F.; Schewe, J.C.; Putensen, C.; et al. Comparison of anticoagulation strategies for veno-venous ECMO support in acute respiratory failure. Crit. Care 2021, 24, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biderman, P.; Einav, S.; Fainblut, M.; Stein, M.; Singer, P.; Medalion, B. Extracorporeal life support in patients with multiple injuries and severe respiratory failure: A single-center experience? J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013, 75, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arlt, M.; Philipp, A.; Voelkel, S.; Rupprecht, L.; Mueller, T.; Hilker, M.; Graf, B.M.; Schmid, C. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe trauma patients with bleeding shock. Resuscitation 2010, 81, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonies, D.; Merkel, M. Advanced extracorporeal therapy in trauma. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2016, 22, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, A.; Schellongowski, P.; Bojic, A.; Robak, O.; Buchtele, N.; Staudinger, T. ECMO without anticoagulation in patients with disease-related severe thrombocytopenia: Feasible but futile? Artif. Organs 2019, 43, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muellenbach, R.M.; Redel, A.; Kustermann, J.; Brack, A.; Gorski, A.; Rosner, T.; Roewer, N.; Wurmb, T. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and severe traumatic brain injury. Is the ECMO-therapy in traumatic lung failure and severe traumatic brain injury really contraindicated? Der Anaesthesist 2011, 60, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muellenbach, R.M.; Kredel, M.; Kunze, E.; Kranke, P.; Kuestermann, J.; Brack, A.; Gorski, A.; Wunder, C.; Roewer, N.; Wurmb, T. Prolonged heparin-free extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in multiple injured acute respiratory distress syndrome patients with traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 72, 1444–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagaki, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ikeda, N.; Takeda, K.; Kasai, F.; Yahagi, K.; Kanzaki, S.; Mitsuyama, S.; Kadowaki, T.; Kotani, T. Post-cardiotomy venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation without heparinization. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg 2019, 67, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, C.; Oakes, M.; Kim, M.; Desai, A.; Olson, S.R.; Raghunathan, V.; Shatzel, J.J. Anticoagulation strategies in extracorporeal circulatory devices in adult populations. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, M.C.; Rattani, A.; Gupta, S.; Baticulon, R.E.; Hung, Y.C.; Punchak, M.; Agrawal, A.; Adeleye, A.O.; Shrime, M.G.; Rubiano, A.M.; et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kool, B.; Chelimo, C.; Ameratunga, S. Head injury incidence and mortality in New Zealand over 10 Years. Neuroepidemiology 2013, 41, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.H.; Meaney, D.F.; Shull, W.H. Diffuse axonal injury in head trauma. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2003, 18, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gennarelli, T.A.; Thibault, L.E.; Adams, J.H.; Graham, D.I.; Thompson, C.J.; Marcincin, R.P. Diffuse axonal injury and traumatic coma in the primate. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 12, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, K.G.; Brezova, V.; Skandsen, T.; Haberg, A.K.; Folvik, M.; Vik, A. Traumatic axonal injury: The prognostic value of lesion load in corpus callosum, brain stem, and thalamus in different magnetic resonance imaging sequences. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humble, S.S.; Wilson, L.D.; Wang, L.; Long, D.A.; Smith, M.A.; Siktberg, J.C.; Mirhoseini, M.F.; Bhatia, A.; Pruthi, S.; Day, M.A.; et al. Prognosis of diffuse axonal injury with traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018, 85, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eijck, M.M.; Schoonman, G.G.; van der Naalt, J.; de Vries, J.; Roks, G. Diffuse axonal injury after traumatic brain injury is a prognostic factor for functional outcome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, S.; Bhandari, S.; Ranabhat, K.; Agrawal, P. Does Diffuse Axonal Injury MRI Grade Really Correlate with Functional Outcome? World Neurosurg. 2020, 135, e424–e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Cao, F. Prognosis in prolonged coma patients with diffuse axonal injury assessed by somatosensory evoked potentia. Neural Regen Res. 2013, 8, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Eijck, M.; van der Naalt, J.; de Jongh, M.; Schoonman, G.; Oldenbeuving, A.; Peluso, J.; de Vries, J.; Roks, G. Patients with Diffuse Axonal Injury Can Recover to a Favorable Long-Term Functional and Quality of Life Outcome. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida Vieira, R.C.; Paiva, W.S.; de Oliveira, D.V.; de Paula Guirado, V.M.; Caetano Lanca, E.F.; de Sousa, R.M.C. Recovery of Patients with Pure Diffuse Axonal Injury Who Remained in a Coma for 6 Hours or More. World Neurosurg. 2018, 109, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henninger, N.; Compton, R.A.; Khan, M.W.; Carandang, R.; Hall, W.; Muehlschlegel, S. "Don’t lose hope early": Hemorrhagic diffuse axonal injury on head computed tomography is not associated with poor outcome in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury patients. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018, 84, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterakis, K.; Karantanas, A.H.; Komnos, A.; Volikas, Z. Outcome of patients with diffuse axonal injury: The significance and prognostic value of MRI in the acute phase. J. Trauma 2000, 49, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicuendez, M.; Castano-Leon, A.; Ramos, A.; Hilario, A.; Gomez, P.A.; Lagares, A. Prognostic value of corpus callosum injuries in severe head trauma. Acta Neurochir 2017, 159, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelly, H.; Chaari, A.; Daoud, E.; Dammak, H.; Medhioub, F.; Mnif, J.; Hamida, C.B.; Bahloul, M.; Bouaziz, M. Diffuse axonal injury in patients with head injuries: An epidemiologic and prognosis study of 124 cases. J. Trauma 2011, 71, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogan, T.V.; Thiagarajan, R.R.; Rycus, P.T.; Bartlett, R.H.; Bratton, S.L. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in adults with severe respiratory failure: A multi-center database. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayat, R.; Kalverkamp, S.; Grottke, O.; Durak, K.; Dreher, M.; Autschbach, R.; Marx, G.; Marx, N.; Spillner, J.; Kersten, A. Role of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in critically Ill COVID-19 patients and predictors of mortality. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, E158–E170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Kit, B.K.; Orpana, H.; Graubard, B.I. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 309, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bercault, N.; Boulain, T.; Kuteifan, K.; Wolf, M.; Runge, I.; Fleury, J.C. Obesity-related excess mortality rate in an adult intensive care unit: A risk-adjusted matched cohort study. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, O.W.; Bramley, A.; Fowlkes, A.; Freedman, D.S.; Taylor, T.H.; Gargiullo, P.; Belay, B.; Jain, S.; Cox, C.; Kamimoto, L.; et al. Morbid obesity as a risk factor for hospitalization and death due to 2009 pandemic influenza A(H1N1) disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlayjeh, H.; Arabi, Y.M.; Ferguson, N.D.; Zhou, Q.; Lamontagne, F.; Arroliga, A.; Danesh, V.; Dominguez-Cherit, G.; Jimenez, E.; Mullaly, A.; et al. Body Mass Index and Mortality in Subjects With ARDS: Post-hoc Analysis of the OSCILLATE Trial. Respir. Care 2019, 64, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Soufi, S.; Buscher, H.; Nguyen, N.D.; Rycus, P.; Nair, P. Lack of association between body weight and mortality in patients on veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swol, J.; Buchwald, D.; Dudda, M.; Strauch, J.; Schildhauer, T.A. Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in obese surgical patients with hypercapnic lung failure. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2014, 58, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, Z.N.; Dahi, S.; Evans, C.F.; Byrnes, K.A.; Bittle, G.J.; Wehman, B.; Rector, R.P.; McCormick, B.M.; Herr, D.L.; Sanchez, P.G.; et al. Class III Obesity is Not a Contraindication to Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 1855–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubani, A.O.; Chen, W.; Jang, H. The outcome of acute respiratory distress syndrome in relation to body mass index and diabetes mellitus. Heart Lung J. Crit. Care 2015, 44, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri, C.; Bonizzoli, M.; Cianchi, G.; Batacchi, S.; Terenzi, P.; Cozzolino, M.; Bernardo, P.; Peris, A. Body mass index and echocardiography in refractory ARDS treated with veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J. Artif. Organs Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Artif. Organs 2017, 20, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swol, J.; Buchwald, D.; Strauch, J.T.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Ull, C. Effect of body mass index on the outcome of surgical patients receiving extracorporeal devices (VV ECMO, pECLA) for respiratory failure. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2017, 40, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salna, M.; Chicotka, S.; Biscotti, M., 3rd; Agerstrand, C.; Liou, P.; Brodie, D.; Bacchetta, M. Morbid obesity is not a contraindication to transport on extracorporeal support. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 53, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keyser, A.; Philipp, A.; Zeman, F.; Lubnow, M.; Lunz, D.; Zimmermann, M.; Schmid, C. Percutaneous Cannulation for Extracorporeal Life Support in Severely and Morbidly Obese Patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvagno, S.M., Jr.; Pelekhaty, S.; Cornachione, C.R.; Deatrick, K.B.; Mazzeffi, M.A.; Scalea, T.M.; Menaker, J. Does Weight Matter? Outcomes in Adult Patients on Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation When Stratified by Obesity Class. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 131, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, K.; Andruszkow, H.; Weber, C.D.; Pishnamaz, M.; Herren, C.; Zhi, Q.; Knobe, M.; Lefering, R.; Hildebrand, F.; Pape, H.C. Thoracic trauma now and then: A 10 year experience from 16,773 severely injured patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.O.; Kang, D.H.; Moon, S.H.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Byun, J.H. Risk Factors for Pneumonia in Ventilated Trauma Patients with Multiple Rib Fractures. Korean J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 50, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swol, J.; Brodie, D.; Napolitano, L.; Park, P.K.; Thiagarajan, R.; Barbaro, R.P.; Lorusso, R.; McMullan, D.; Cavarocchi, N.; Hssain, A.A.; et al. Indications and outcomes of extracorporeal life support in trauma patients. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018, 84, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerer, O.; Huber-Petersen, J.F.; Schaeper, J.; Binder, C.; Wand, S. Factor XIII Activity Might Already Be Impaired before Veno-Venous ECMO in ARDS Patients: A Prospective, Observational Single-Center Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, S.; Huber-Petersen, J.F.; Schaeper, J.; Binder, C.; Moerer, O. Platelet Function Disturbance During Veno-Venous ECMO in ARDS Patients Assessed by Multiple Electrode Aggregometry-A Prospective, Observational Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosarge, P.L.; Raff, L.A.; McGwin, G., Jr.; Carroll, S.L.; Bellot, S.C.; Diaz-Guzman, E.; Kerby, J.D. Early initiation of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation improves survival in adult trauma patients with severe adult respiratory distress syndrome. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2016, 81, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, A.A.; Hart, V.J.; Lineen, E.B.; Lai, C.; Ginzburg, E.; Houghton, D.; Schulman, C.I.; Vianna, R.; Patel, A.N.; Casalenuovo, A.; et al. The Impact of an Advanced ECMO Program on Traumatically Injured Patients. Artif. Organs 2018, 42, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robba, C.; Ortu, A.; Bilotta, F.; Lombardo, A.; Sekhon, M.S.; Gallo, F.; Matta, B.F. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for adult respiratory distress syndrome in trauma patients: A case series and systematic literature review. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 82, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strumwasser, A.; Tobin, J.M.; Henry, R.; Guidry, C.; Park, C.; Inaba, K.; Demetriades, D. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in trauma: A single institution experience and review of the literature. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 41, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ull, C.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Strauch, J.T.; Swol, J. Outcome measures of extracorporeal life support (ECLS) in trauma patients versus patients without trauma: A 7-year single-center retrospective cohort study. J. Artif. Organs Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Artif. Organs 2017, 20, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ried, M.; Bein, T.; Philipp, A.; Muller, T.; Graf, B.; Schmid, C.; Zonies, D.; Diez, C.; Hofmann, H.S. Extracorporeal lung support in trauma patients with severe chest injury and acute lung failure: A 10-year institutional experience. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.C.; Chen, W.T.; Lin, H.H.; Fu, C.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Lo, H.C.; Cheng, H.T.; Tzeng, C.W. Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe traumatic lung injury with respiratory failure. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 33, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirand, D.M.; Okoye, O.T.; Schmidt, B.S.; Mansfield, N.J.; Aden, J.K.; Martin, R.S.; Cestero, R.F.; Hines, M.H.; Pranikoff, T.; Inaba, K.; et al. Venovenous extracorporeal life support improves survival in adult trauma patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014, 76, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Qin, T.; Xi, Z.; Sun, L.; Wu, H.; Li, D. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in trauma patients: A systematic review. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2020, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.B.; Menaker, J.; Kufera, J.; O’Connor, J.; Scalea, T.M.; Stein, D.M. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation after traumatic injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 82, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.L., 3rd; Shapiro, M.B.; Delius, R.E.; Steimle, C.N.; Chapman, R.A.; Bartlett, R.H. Extracorporeal life support for respiratory failure after multiple trauma. J. Trauma 1994, 37, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.K.; Liu, K.S.; Lu, M.S.; Wu, M.Y.; Tsai, F.C.; Lin, P.J. Extracorporeal life support in post-traumatic respiratory distress patients. Resuscitation 2009, 80, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacchi, M.; Spina, R.; Torracchi, L.; Harmelin, G.; Sani, G.; Peris, A. Extracorporeal life support in patients with severe trauma: An advanced treatment strategy for refractory clinical settings. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 145, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, S.H.; Kim, K.N.; Jung, J.J.; Park, J.H.; Byun, J.H. Heparin-free veno-venous ECMO applied to a patient with severe lung contusion and hypovolemic shock due to trauma. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2018, 24, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, F.; Sakai, T.; Takahashi, K.; Kato, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Okazaki, S.; Abe, T.; Iwashita, M.; Takeuchi, I. A case report: Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe blunt thoracic trauma. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.C.; Fang, J.F.; Chen, M.F. Treatment of endobronchial hemorrhage after blunt chest trauma with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). J. Trauma 2008, 65, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senunas, L.E.; Goulet, J.A.; Greenfield, M.L.; Bartlett, R.H. Extracorporeal life support for patients with significant orthopaedic trauma. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1997, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell-Smith, J.A.; Roberts, N.; Peek, G.J.; Firmin, R.K. Traumatic lung injury treated by extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Injury 2006, 37, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, C.R.; Dellavolpe, J.; Chung, K.K.; Cancio, L.C.; Mason, P. Revisiting extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for ARDS in burns: A case series and review of the literature. Burns 2018, 44, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotra, S.; Nallamothu, B.K.; Spertus, J.A.; Li, Y.; Krumholz, H.M.; Chan, P.S. Trends in survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1912–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Miano, T.; Geller, B.; Milewski, R.C.; Williams, M.; Bermudez, C.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Patel, P.; Mackay, E.; Vernick, W.; et al. Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Patients With Return of Spontaneous Circulation After Cardiac Arrest Owing to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 2216–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Baik, H.J.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.H.; Chung, R.K.; Han, J.I.; Joo, H.; Woo, J.H. Heparin-free veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a multiple trauma patient: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e19070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camboni, D.; Philipp, A.; Lubnow, M.; Bein, T.; Haneya, A.; Diez, C.; Schmid, C.; Muller, T. Support time-dependent outcome analysis for veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Eur J. Cardiothorac Surg 2011, 40, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kon, Z.N.; Dahi, S.; Evans, C.F.; Byrnes, K.A.; Bittle, G.J.; Wehman, B.; Rector, R.P.; McCormick, B.M.; Herr, D.L.; Sanchez, P.G.; et al. Long-Term Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreier, E.; Malfertheiner, M.V.; Dienemann, T.; Fisser, C.; Foltan, M.; Geismann, F.; Graf, B.; Lunz, D.; Maier, L.S.; Muller, T.; et al. ECMO in COVID-19-prolonged therapy needed? A retrospective analysis of outcome and prognostic factors. Perfusion 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaker, J.; Rabinowitz, R.P.; Tabatabai, A.; Tesoriero, R.B.; Dolly, K.; Cornachione, C.; Stene, E.; Buchner, J.; Kufera, J.; Kon, Z.N.; et al. Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Respiratory Failure: How Long Is Too Long? ASAIO J. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1992. 2019, 65, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, V.; Ranieri, M.V.; Mancebo, J.; Moerer, O.; Quintel, M.; Morley, S.; Moran, I.; Parrilla, F.; Costamagna, A.; Gaudiosi, M.; et al. Feasibility and safety of low-flow extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal to facilitate ultra-protective ventilation in patients with moderate acute respiratory distress sindrome. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Combes, A.; Fanelli, V.; Pham, T.; Ranieri, V.M.; European Society of Intensive Care Medicine Trials Group and the “Strategy of Ultra-Protective lung ventilation with Extracorporeal CO2 Removal for New-Onset moderate to severe ARDS” (SUPERNOVA) investigators. Feasibility and safety of extracorporeal CO2 removal to enhance protective ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome: The SUPERNOVA study. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mang, S.; Kalenka, A.; Broman, L.M.; Supady, A.; Swol, J.; Danziger, G.; Becker, A.; Horsch, S.I.; Mertke, T.; Kaiser, R.; et al. Extracorporeal life support in COVID-19-related acute respiratory distress syndrome: A EuroELSO international survey. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, J.; Dean, R.K.; Landsberg, D. Right Atrial Perforation Leading to Cardiac Tamponade Following Veno-Venous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Cannulation. Cureus 2021, 13, e13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnisch, L.O.; Riech, S.; Mueller, M.; Gramueller, V.; Quintel, M.; Moerer, O. Longtime Neurologic Outcome of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Non Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Survivors. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Study | Pathological Condition | Mortality | Worse Outcome (GOS ≤ 3 or Equal) |
| Gurer et al. 2017 [24] | SDH/EDH | 49.1% (ICU) | 66.7% (6 months) |
| Gower et al. 1988 [27] | swelling after TBI | 23% (ICU) | 60% (≥ 2 years) |
| Gaab et al. 1990 [28] | swelling after TBI | 14% (ICU) | 22% (n/a) |
| Polin et al. 1997 [29] | swelling after TBI | 23% (hospital) | 63% (discharge) |
| De Luca et al. 2000 [30] | swelling after TBI | 18% (n/a) | 59% (n/a) |
| Taylor et al. 2001 [31] | swelling after TBI (children) | DC: 33% (1 week) medical: 42% (1 week) | 46% (6 months) |
| Whitfield et al. 2001 [32] | swelling after TBI | 23% (10 months) | 31% (10 months) |
| Schneider et al. 2002 [33] | swelling after TBI | 22.5% (6 months) | 71% (6 months) |
| Albanèse et al. 2003 [34] | swelling after TBI | early DC: 52% (1 year) late DC: 23% | 62% (1 year) |
| Aarabi et al. 2006 [35] | swelling after TBI | 32.4% (30 days) | 48.7% (30 days) |
| Wettervik et al. 2018 [36] | swelling after TBI | DC: 17% (6 months) Thiopental: 4% no specific treatment: 11% | DC: 60% (6 months) Thiopental: 48% no specific treatment: 27% |
| Sakai et al. 1998 [37] | cerebral infraction/malignant swelling | 33% (2 months) | 67% (2 months) |
| Qureshi et al. 2000 [38] | medical reversal of supratentorial masses | 54% (hospital) | 46% (Barthel & Rankin) (≥6 months) |
| Koenig et al. 2008 [39] | medical reversal of transtentorial herniation | 67.6% (hospital) | 77% (GOS 4 & 5) |
| Skoglund et al. 2005 [40] | transtentorial herniation after TBI | 26% (≥6 months) | 41% (≥6 months) |
| Kim et al. 2009 [41] | DC for TBI/ICH/infarction | TBI: 21.4% (6 months) ICH: 25% (6 months) Infarction: 60.9% (6 months) | TBI: 42.9% (6 months) ICH: 50% (6 months) Infarction: 69.6% (6 months) |
| Lan et al. 2020 [42] | DC for herniation after TBI | 30.4% (6 months) | 66% (6 months) |
| Delcourt et al. 2017 [43] | ICH | 12% (90 days) | 45.4% (90 days) |
| Chen et al. 2019 [44] | infratentorial ICH | 8% (90 days) | 28% (90 days) |
| Poon et al. 2014 [45] (metaanalysis) | ICH | 46% (1 year) | up to 24% (1 year) |
| Pinho et al. 2019 [46] (metaanalysis) | ICH | 36.3% (1 year) | n/a |
| Absolute Contraindications | Relative Contraindications |
|---|---|
| History of malignancy (<2–5 years disease free plus high risk of recurrence) | Age >65 years plus low physiological reserve |
| Significant dysfunction of another major organ system (heart, liver, kidney, brain) | Mechanical ventilation/extracorporeal life support |
| Uncorrected coronary artery disease | Controlled coronary artery disease |
| Unstable medical condition | Significant osteoporosis |
| Uncorrectable bleeding | Extensive prior chest surgery |
| Poorly controlled infection/resistant microbes | Colonization with resistant microbes |
| Inadequate social support | Infectious liver cirrhosis |
| Severe thorax deformity | HIV infection (unless treated adequately) |
| BMI ≥35 kg/m2 | BMI 30–35 kg/m2 |
| Nonadherence to medical therapy (recent & history) | Significant malnutrition |
| Inability to comply with therapy | Specific infections [55] |
| Active tuberculosis/contraindications to immunosuppression | Poorly controlled diabetes, hypertension, epilepsy, peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux, or central venous obstruction |
| History of illicit substance abuse | |
| Inability to participate in rehabilitation |
| Study | Age Defining “Elderly” | No. of Patients Included Total | Hospital Mortality in the “Elderly” |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mendiratta et al. 2014 [58] | >65 | 368 | 59% |
| Karagiannidis et al. 2016 [8] | >80 | 1944 | 76% |
| Deatrick et al. 2020 [61] | >65 >55 | 182 | 83% 43% |
| Giani et al. 2021 [62] | >65 | 144 | 56% |
| Study | Disease State | ICU Mortality | Hospital Mortality | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cawcutt et al. 2014 [65] | HIV/AIDS | 40% | 60% | n/a |
| Schmidt et al. 2018 [66] | Mixed | 66% | n/a | n/a |
| Huprikar et al. 2019 [67] | Acute leukemia | n/a | 50% | n/a |
| Study | Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Pranikoff et al. 1997 [69] | 50% mortality after 5 days on ventilator (90% after 12 days) |
| Mols et al. 2000 [70] | No differences between groups |
| Hemmila et al. 2004 [71] | OR 1.20 (1.09, 1.31) (3.2 vs. 4.5 days) (OR 5.53 if > 8 days) |
| Beiderlinden et al. 2006 [72] | OR 1.064 (1.008, 1.123) (5.3 vs. 8.7 days) |
| Patroniti et al. 2011 [73] | OR 1.291 (29% increase each day) |
| Schmidt et al. 2013 [74] | p = 0.0008 between groups (3 vs. 7 days), OR 1.07 |
| Enger et al. 2014 [75] | p = 0.013 between groups (2 vs. 5 days) |
| Mendiratta et al. 2014 [58] | p = 0.049 between groups (1.19 vs. 1.73 days) |
| Wohlfarth et al. 2014 [76] | p = 0.17 between groups (1 vs. 3 days) |
| Schmidt et al. 2015 [77] | OR 1.15 (1.06, 1.26) (2 vs. 4 days) |
| Klinzing et al. 2015 [78] | p = 0.14 between groups (1 vs. 4 days) |
| Cheng et al. 2016 [79] | p < 0.001 between groups (1 vs. 6 days), OR 4.71 (1.98, 11.23) |
| Choi et al. 2016 [80] | p = 0.11 between groups (4.5 vs. 4.77 days) |
| Huang et al. 2016 [81] | p = 0.093 between groups (0.5 vs. 1.8 days) |
| Hsin et al. 2016 [82] | p < 0.001 between groups (1 vs. 6 days) |
| Lee et al. 2016 [83] | p = 0.114 between groups (2.3 vs. 4.2 days) |
| Serpa Neto et al. 2016 [84] | p = 0.061 between groups (2 vs. 3 days) |
| Wu et al. 2016 [85] | p = 0.005 between groups (2.75 vs. 6.92 days) |
| Hilder et al. 2017 [86] | p = 0.140 between groups (1.08 vs. 1.67 days) |
| Kon et al. 2017 [87] | OR 0.998 (0.997–0.999), p = 0.001 |
| Wu et al. 2017 [88] | p < 0.001 between groups (1 vs. 6 days) |
| Schmidt et al. 2018 [66] | p = 0.004 between groups (2 vs. 3 days) |
| Posluszny et al. 2020 [89] | p = 0.028 between groups (2.33 vs. 3.25 days) |
| Giraud et al. 2021 [90] | p = 0.01 between groups (3.79 vs. 8.67 days) |
| Supady et al. 2021 [91] | p = 0.006 between groups (3 vs. 6 days) |
| Study | Vasopressors Survivors | Vasopressors Nonsurvivors | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benoit et al. 2003 [111] | 29.8% | 70.2% | 0.001 |
| Beiderlinden et al. 2006 [72] | 0.4 µg/kg/min | 0.7 µg/kg/min | 0.16 |
| Brogan et al. 2009 [183] | 57% | 53% | 0.16 |
| Patroniti et al. 2011 [73] | 61% | 63% | n.s. |
| Schmidt et al. 2013 [137] | 73% | 66% | 0.40 |
| Azoulay et al. 2014 [113] | 66.2% | 76.6% | 0.0004 |
| Mendiratta et al. 2014 [58] | 67% | 72% | 0.20 |
| Wohlfarth et al. 2014 [76] | 100% | 100% | n.s. |
| Klinzing et al. 2015 [78] | 54% | 46% | 0.81 |
| Lee et al. 2016 [83] | 73% | 85% | 0.321 |
| Wohlfarth et al. 2017 [119] | 71% | 80% | 0.63 |
| Zayat et al. 2020 [184] | 88.9% | 88% | 1.0 |
| Study | BMI | ICU Mortality | Hospital Mortality | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Soufi et al. 2013 [189] | Quartile 1 Quartile 2 Quartile 3 | n/a | 33.2% 40.4% 33.3% | 0.82 (0.60, 1.11) 0.93 (0.69, 1.25) 0.69 (0.50, 0.96) |
| Swol et al. 2014 [190] | 50% | 50% | 1.05 (0.29, 3.77) | |
| Lazzeri et al. 2016 [94] | 31.5% | n/a | 0.51 (0.26, 0.99) | |
| Kon et al. 2015 [191] | <40 >40 >50 | n/a | 42% 33% 0% | n/a |
| Soubani et al. 2015 [192] | 25–30 30–40 >40 | n/a | n/a | 0.89 (0.696, 1.13) 0.81 (0.62, 1.06) 1.1 (0.72, 1.695) |
| Lazzeri et al. 2017 [193] | 25–30 30–40 >40 | 40.5% 28% 9.1% | n/a | 0.41 (0.17, 1.01) 0.24 (0.08, 0.68) 0.06 (0.01, 0.47) |
| Swol et al. 2017 [194] | 25–30 30–35 >35 | 38.7% 66.7% 52.4% | 42% 78% 52.4% | 1.01 (0.27, 3.78)/1.16 (0.31, 4.35) 3.20 (0.79, 13.02)/3.89 (0.94, 16.1) 1.60 (0.39, 6.63)/1.60 (0.39, 6.63) |
| Salna et al. 2018 [195] | All <30 30–40 >40 | n/a | 34.4% 33.6% 44.4% 17.9% | n/a |
| Keyser et al. 2020 [196] | <35 | n/a | 34% | n/a |
| Galvagno et al. 2020 [197] | 25–30 30–35 35–40 >40 | n/a | 19.1% 32.7% 22.7% 19.5% | n/a |
| Study | ICU Mortality | Hospital Mortality | Odds Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cordell-Smith et al. 2006 [220] | n/a | 28.52% | n/a |
| Arlt et al. 2010 [161] | n/a | 40% | n/a |
| Guirand et al. 2014 [210] | n/a | 23.5% | n/a |
| Bosarge et al. 2016 [203] | n/a | 13% | 0.01 (0.06, 0.36) |
| Ull et al. 2017 [207] (review) | 34.7% | 30.6% | 0.14 (0.06, 0.36)/0.22 (0.09, 0.52) |
| Grant et al. 2018 [204] | 36% | 45% | n/a |
| Strumwasser et al. 2018 [206] | n/a | 60% | n/a |
| Ainsworth et al. 2018 [221] | 29% | 43% | n/a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harnisch, L.-O.; Moerer, O. Contraindications to the Initiation of Veno-Venous ECMO for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Practical Approach Based on the Current Literature. Membranes 2021, 11, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080584
Harnisch L-O, Moerer O. Contraindications to the Initiation of Veno-Venous ECMO for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Practical Approach Based on the Current Literature. Membranes. 2021; 11(8):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080584
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarnisch, Lars-Olav, and Onnen Moerer. 2021. "Contraindications to the Initiation of Veno-Venous ECMO for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Practical Approach Based on the Current Literature" Membranes 11, no. 8: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080584
APA StyleHarnisch, L.-O., & Moerer, O. (2021). Contraindications to the Initiation of Veno-Venous ECMO for Severe Acute Respiratory Failure in Adults: A Systematic Review and Practical Approach Based on the Current Literature. Membranes, 11(8), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080584





