Determination of Single-Ion Partition Coefficients between Water and Plasticized PVC Membrane Using Equilibrium-Based Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
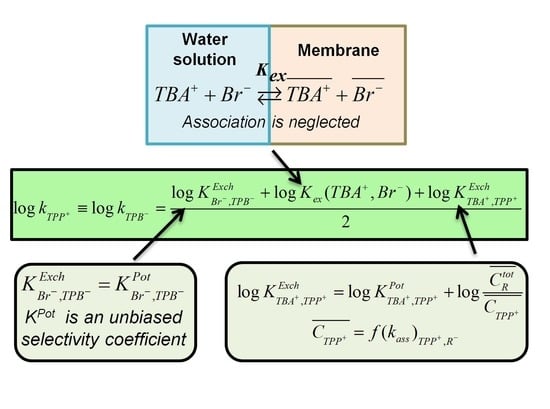
2. Brief Theoretical Background
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
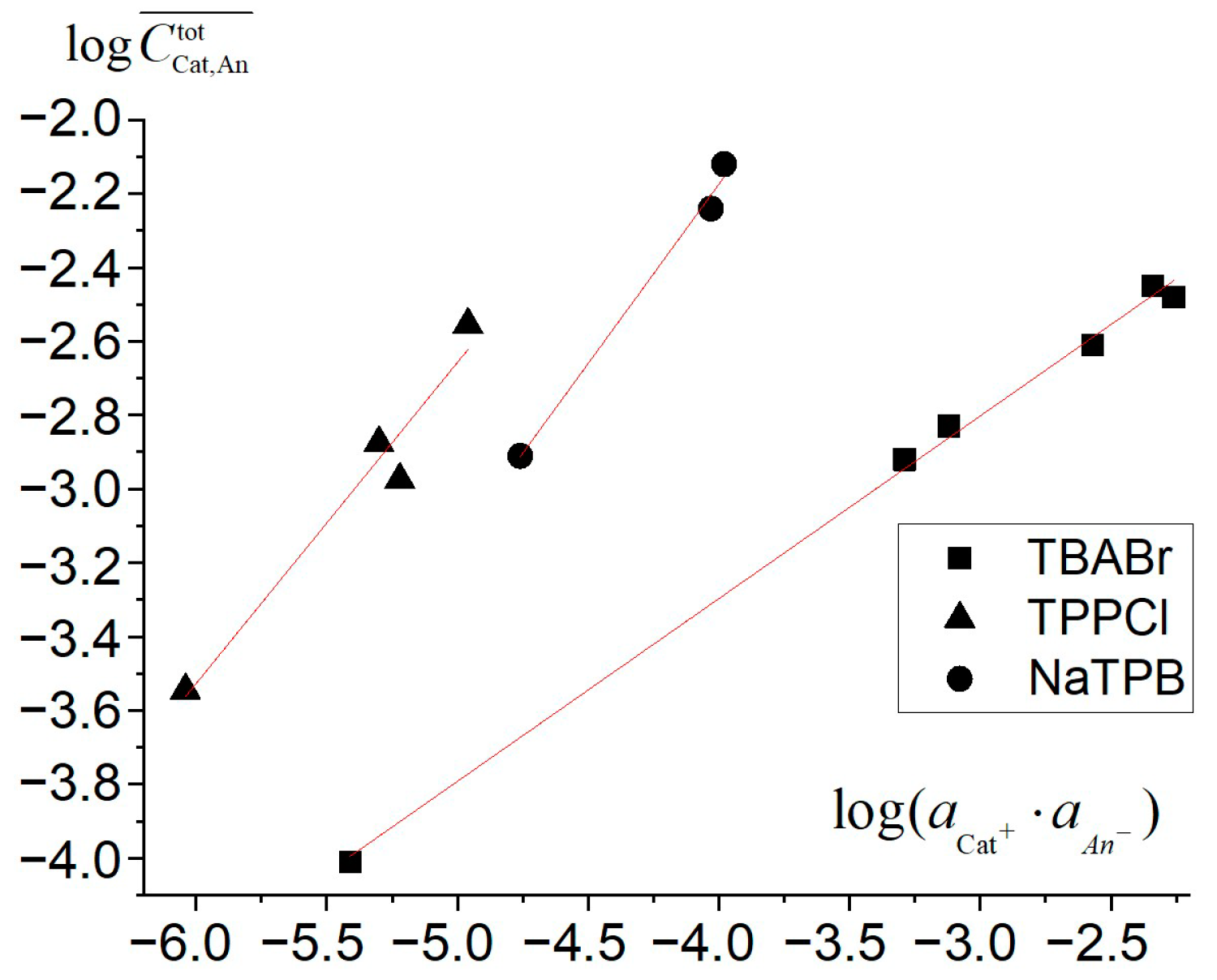
Appendix A. The TBABr: TPPCl, NaTPB Coextraction Constants and TPPCl, NaTPB Association Constants Determination from Distribution Studies
| a(NaBr) aq | 0.688 | 0.688 | 0.0858 | 0.101 | 0.688 | 0.113 |
| a(TBABr) aq | 7.46 × 10−4 | 7.95 × 10−3 | 8.86 × 10−3 | 2.69 × 10−2 | 5.62 × 10−6 | 4.04 × 10−2 |
| C(TBABr) membrane | 1.34 × 10−3 | 3.68 × 10−3 | 1.65 × 10−3 | 2.73 × 10−3 | 1.09 × 10−4 | 3.92 × 10−3 |
| Kex | 3.51 × 10−3 | 2.45 × 10−3 | 3.56 × 10−3 | 2.74 × 10−3 | 3.07 × 10−3 | 3.36 × 10−3 |
| a(NaCl) aq | 0 | 0.658 | 0.0778 |
| a(NaTPB) aq | 9.63 × 10−3 | 1.59 × 10−4 | 2.24 × 10−4 |
| C(NaTPB) membr | 6.36 × 10−3 | 7.63 × 10−3 | 1.37 × 10−3 |
| kass(1) | 1.2 × 104 | ||
| Kex | 5.08 × 10−3 | 5.47 × 10−3 | 5.09 × 10−3 |
| kass(2) | 2.0 × 104 | ||
| Kex | 3.14 × 10−3 | 3.36 × 10−3 | 3.25 × 10−3 |
| a(NaCl) aq | 0 | 0.658 | 0.0778 | 0.147 |
| a(TPPCl) aq | 9.58 × 10−4 | 1.68 × 10−5 | 7.80 × 10−5 | 3.42 × 10−5 |
| C(TPPCl) membr | 3.16 × 10−4 | 3.08 × 10−3 | 1.17 × 10−3 | 1.49 × 10−3 |
| Kex | 5.86 × 10−3 | 5.69 × 10−3 | 3.73 × 10−3 | 5.81 × 10−3 |
Appendix B. Ion Association Constant Determination from Potentiometric Data
Appendix C. TBA+, TPP+ and TPB− Concentration Determination in Aqueous Phase by Direct Potentiometry
Appendix D. TBA+, TPP+ and TPB− Activity Coefficients Determination
| Background Sample (10−4 M) | Time | None | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.2 M NaCl | 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl | 0.1 M NaBr | 0.5 M NaBr | 1 M NaBr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPPCl | 1 min | 121.9 | 121.5 | 123.5 | 128.8 | 131.4 | - | - | - |
| 2 min | 122.6 | 122.1 | 124.4 | 129.8 | 132.6 | ||||
| NaTPB | 1 min | 200.9 | 201.0 | - | 193.6 | 187.4 | - | - | - |
| 2 min | 200.4 | 199.9 | 194.4 | 186.6 | |||||
| TBABr | 1 min | 191.0 | 192.0 | - | - | 204.0 | 188.7 | 186.4 | 186.5 |
| 2 min | 191.6 | 192.3 | 202.0 | 189.4 | 187.3 | 186.8 |
| Ion | 0.1 M NaCl | 0.2 M NaCl | 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl | 0.1 M NaBr | 0.5 M NaBr | 1 M NaBr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPP+ | 0.979 | 1.079 | 1.36 | 1.53 | - | - | - |
| TPB− | 1.021 | - | 1.29 | 1.75 | - | - | - |
| TBA+ | 1.03 | - | - | 1.52 | 0.913 | 0.841 | 0.823 |
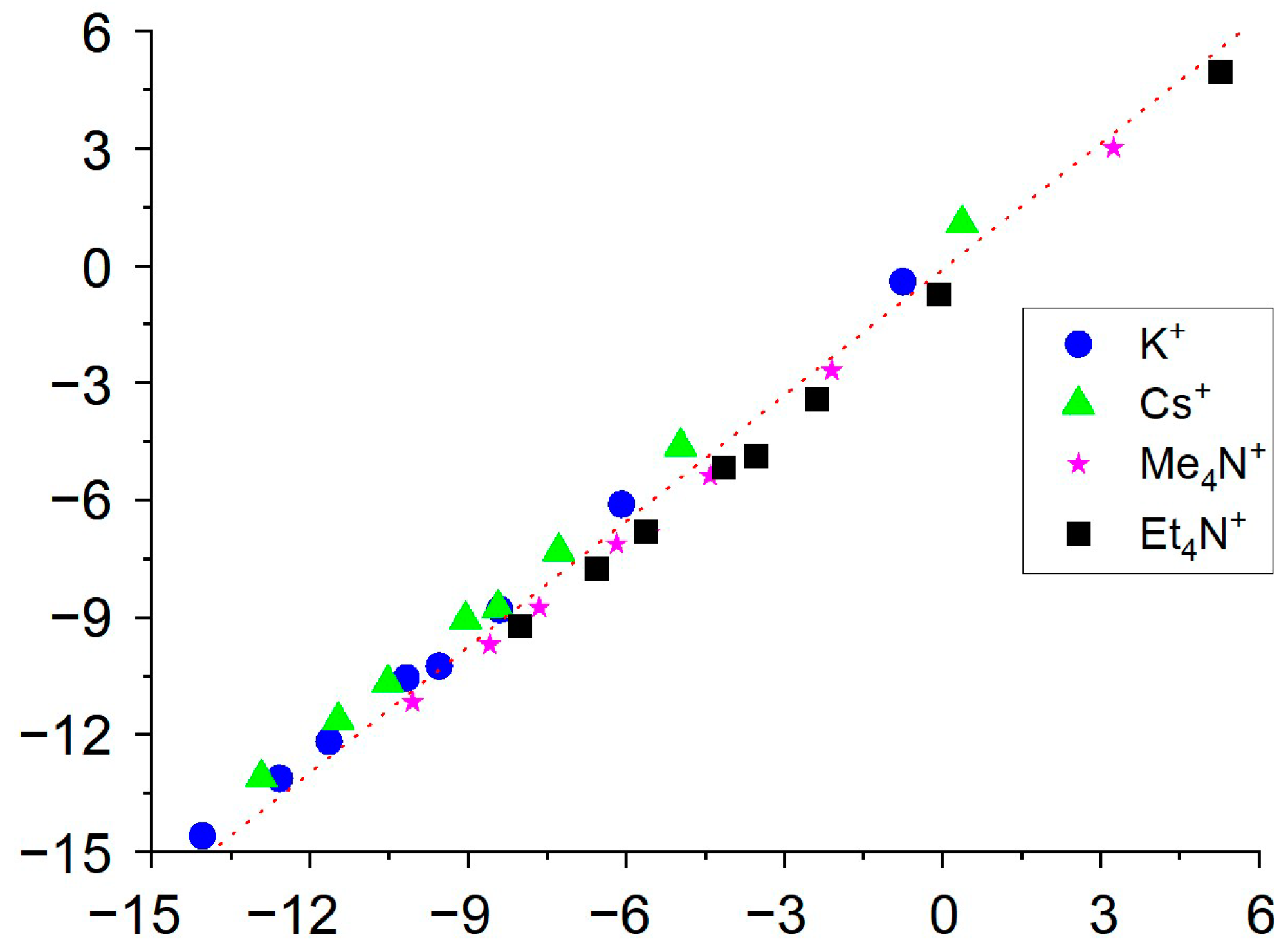
Appendix E. Determinations of Unbiased Potentiometric Selectivity Coefficients
| Cation | Concentration Range, M | Slope, mV | lg KPot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | 0.1–1.0 | 59.4 | −0.80 ± 0.05 |
| Na+ | 0.01–1.0 | 59.8 | ≡0 |
| K+ | 0.01–1.0 | 58.0 | 1.72 ± 0.05 |
| Rb+ | 0.01–1.0 | 55.9 | 2.29 ± 0.06 |
| Cs+ | 0.01–1.0 | 56.0 | 2.90 ± 0.05 |
| TMA+ | 10−3–10−1 | 57.5 | 5.02 ± 0.05 |
| TEA+ | 10−4–10−2 | 58.7 | 6.95 ± 0.05 |
| TBA+ | 10−4–10−2 | 54.5 | 10.96 ± 0.08 |
| TPP+ | 10−4–10−2 | 59.7 | 12.64 ± 0.05 |
| Anion | Concentration Range, M | Slope, mV | lg KPot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl− | 0.01–1.0 | 57.1 | ≡0.00 |
| Br− | 0.01–0.1 | 54.8 | 1.45 ± 0.07 |
| NO3− | 0.01–1.0 | 53.1 | 2.39 ± 0.08 |
| I− | 0.01–1.0 | 58.5 | 3.87 ± 0.04 |
| SCN− | 0.01–1.0 | 57.0 | 4.48 ± 0.05 |
| ClO4− | 0.01–0.1 | 54.3 | 5.64 ± 0.07 |
| TPB− | 10−4–10−3 | 60.0 | 13.28 ± 0.05 |
References
- Sandblom, J.P.; Eisenman, G. Membrane Potentials at Zero Current: The Significance of a Constant Ionic Permeability Ratio. Biophys. J. 1967, 7, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Xu, A.; Pretsch, E. Optimum composition of neutral carrier based pH electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 295, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, V.V.; Lushchik, Y.F.; Sin’kevich, Y.V. Electrode based on neutral carriers of the amine type and selective to H+ ions: A simple quantitative description of the operation limits. Russ. J. Electrochem. 1998, 34, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Dekina, D.I.; Kalinichev, A.V.; Pokhvishcheva, N.V.; Peshkova, M.A.; Mikhelson, K.N. Effects of quantitative composition of the sensing phase in the response of ionophore-based optical sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 277, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinichev, A.V.; Frosinyuk, A.; Peshkova, M.A.; Mikhelson, K.N. The impact of ion association in the optode phase to the dynamic range and the sensitivity of the response of ion-selective bulk optodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.J.; Soda, Y.; Bakker, E. Recent improvements to the selectivity of extraction-based optical ion sensors. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 4279–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, M.M.; Stefanova, O.K.; Mokrov, S.B.; Mikhelson, K.N. Potentiometric Estimation of the Stability Constants of Ion−Ionophore Complexes in Ion-Selective Membranes by the Sandwich Membrane Method: Theory, Advantages, and Limitations. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, E.; Willer, M.; Lerchi, M.; Seiler, K.; Pretsch, E. Determination of complex formation constants of neutral cation-selective ionophores in solvent polymeric membranes. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- And, M.T.-D.; Bakker, E. Effect of Lipophilic Ion-Exchanger Leaching on the Detection Limit of Carrier-Based Ion-Selective Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5582–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.D.; Bachas, L.G. Ionophore-based ion-selective potentiometric and optical sensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühlmann, P.; Amemiya, S.; Yajima, A.S.; Umezawa, Y. Co-Ion Interference for Ion-Selective Electrodes Based on Charged and Neutral Ionophores: A Comparison. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4291–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morf, W.E. The Principles of Ion-Selective Electrodes and of Membrane Transport; Pungor, E., Simon, W., Inczedy, J., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Budapest, Hungary, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Morf, W.E.; Badertscher, M.; Zwickl, T.; de Rooij, N.F.; Pretsch, E. Effects of Ion Transport on the Potential Response of Ionophore-Based Membrane Electrodes: A Theoretical Approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 11346–11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasielec, J.J.; Mousavi, Z.; Granholm, K.; Sokalski, T.; Lewenstam, A. Sensitivity and Selectivity of Ion-Selective Electrodes Interpreted Using the Nernst-Planck-Poisson Model. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9644–9649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawara, S.; Carey, I.J.L.; Zou, X.U.; Bühlmann, P. Donnan Failure of Ion-Selective Electrodes with Hydrophilic High-Capacity Ion-Exchanger Membranes. ACS Sens. 2015, 1, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhoff, M.; Opdycke, W.N. Ion-Selective Electrodes. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Spiegel, H.E., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; Volume 25, pp. 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinichev, A.V.; Pokhvishcheva, N.V.; Peshkova, M.A. Influence of Electrolyte Coextraction on the Response of Indicator-Based Cation-Selective Optodes. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3558–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiullin, T.M.; Pokhvishceva, N.; Kalinichev, A.V.; Peshkova, M.A. Evaluation of Ionic Liquids Based on Amino Acid Anions for Use in Liquid-junction Free Reference Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Beriet, C.; Girault, H.H. Amperometric detection of alkali metal ions on micro-fabricated composite polymer membranes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 453, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Bakker, E. Voltammetric and Amperometric Transduction for Solvent Polymeric Membrane Ion Sensors. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3657–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Bakker, E. Evaluation of the Separate Equilibrium Processes That Dictate the Upper Detection Limit of Neutral Ionophore-Based Potentiometric Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3134–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapkiewicz, J.; Czapkiewicz-Tutaj, B. Relative scale of free energy of transfer of anions from water to 1,2-dichloroethane. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1980, 76, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladkov, V.; Guillou, V.; Peulon, S.; L’Her, M. Voltammetry of tetraalkylammonium picrates at water∣nitrobenzene and water∣dichloroethane microinterfaces; influence of partition phenomena. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 573, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Namor, A.F.D.; Hill, T.; Sigstad, E. Free energies of transfer of 1:1 electrolytes from water to nitrobenzene. Partition of ions in the water + nitrobenzene system. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1983, 79, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samec, Z.; Langmaier, J.; Trojánek, A. Polarization phenomena at the water|o-nitrophenyl octyl ether interface. Part 1. Evaluation of the standard Gibbs energies of ion transfer from the solubility and voltammetric measurements. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1996, 409, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, F.; Gulaboski, R.; Caban, K. The determination of standard Gibbs energies of transfer of cations across the nitrobenzene|water interface using a three-phase electrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koryta, J. Ion Transfer Across Water/Organic Phase Boundaries and Analytical Applications. In Ion-Selective Electrode Reviews; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 5, pp. 131–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, S.; Zerihun, T. Standard Gibbs energies of ion transfer across the water∣2-nitrophenyl octyl ether interface. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 515, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, O.; Koryta, J.; Panoch, M. Voltammetric study of ion transfer across the water/o-nitrophenyloctyl ether interface. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1987, 226, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabela, A.; Mareček, V.; Samec, Z.; Fuoco, R. Standard Gibbs energies of transfer of univalent ions from water to 1,2-dichloroethane. Electrochim. Acta 1992, 37, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Harashima, K.; Hiyoshi, K.; Takagi, J.; Katsuta, S.; Takeda, Y. Extraction of Some Univalent Salts into 1,2-Dichloroethane and Nitrobenzene: Analysis of Overall Extraction Equilibrium Based on Elucidating Ion-pair Formation and Evaluation of Standard Potentials for Ion Transfers at the Interfaces between Their Diluents and Water. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrisstoffels, L.A.J.; de Jong, F.; Reinhoudt, D.N. Facilitated Transport of Salts by Neutral Anion Carriers. Chem. A Eur. J. 2000, 6, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.H.; Acree, W.E.; Liu, X. Partition of Neutral Molecules and Ions from Water to o-Nitrophenyl Octyl Ether and of Neutral Molecules from the Gas Phase to o-Nitrophenyl Octyl Ether. J. Solut. Chem. 2018, 47, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Mi, Y.; Bakker, E. Determination of complex formation constants of 18 neutral alkali and alkaline earth metal ionophores in poly(vinyl chloride) sensing membranes plasticized with bis(2-ethylhexyl)sebacate and o-nitrophenyloctylether. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 421, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Bakker, E. Determination of Complex Formation Constants of Lipophilic Neutral Ionophores in Solvent Polymeric Membranes with Segmented Sandwich Membranes. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 5279–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, V.V.; Lyaskovski, P.L.; Il’Inchik, I.V.; Soroka, V.V.; Nazarov, V.A. Estimation of Ion-Pairing Constants in Plasticized Poly(vinyl chloride) Membranes Using Segmented Sandwich Membranes Technique. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E. Determination of Unbiased Selectivity Coefficients of Neutral Carrier-Based Cation-Selective Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peshkova, M.A.; Korobeynikov, A.I.; Mikhelson, K.N. Estimation of ion-site association constants in ion-selective electrode membranes by modified segmented sandwich membrane method. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5819–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, U.; Bakker, E.; Spichiger, U.E.; Pretsch, E. Ionic additives for ion-selective electrodes based on electrically charged carriers. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhman’ko, E.M.; Leschev, S.M.; Starobinets, G.L. The influence of medium effects on extractional separation of quaternary ammonium bases from primary-tertiary amines. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. BSSR 1978, 22, 1006–1009. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rakhman’ko, E.M.; Starobinets, G.L.; Leschev, S.M. The microimpurities of higher amines determination in higher quaternary ammonium salts. J. Anal. Chem. 1979, 34, 2244–2247. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovich, V.A.; Havin, Z.Y. Ultimate Chemist’s Book; Kotz, W.A., Tomarchenko, S.L., Myasnikova, L.B., Eds.; Chemistry: Leningrad, Russia, 1991; p. 432. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Parker, A. Solvation of ions—Enthalpies, entropies and free energies of transfer. Electrochim. Acta 1976, 21, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Abraham, M.H. Octanol/Water Partition of Ionic Species, Including 544 Cations. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 2633–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhman’Ko, E.M.; Starobinets, G.L.; Yegorov, V.V.; Gulevich, A.L.; Lestchev, S.M.; Borovski, E.S.; Tsyganov, A.R. Analytical application of high-molecular quaternary ammonium salts. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 1989, 335, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, I. Solvation and complex formation in strongly solvating solvents. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiuftiakov, N.Y.; Kalinichev, A.V.; Rudenko, I.V.; Bessonova, E.A.; Kartsova, L.A.; Peshkova, M.A. pH-dependent distribution of the indicator dye tetrabromophenolphthalein ethyl ester between aqueous solution and plasticized polymeric phase: Predicting the lifetime of ion-selective optical sensors. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2020, 37, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincze, A.; Horvai, G. The design of reference electrodes without liquid junction. Electrochem. Soc. Proc. 1997, 97, 550. [Google Scholar]
- Stashkova, A.E.; Peshkova, M.A.; Mikhelson, K.N. Single-ion activity: Optical sensing vs. electrochemical sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siamionau, A.V.; Ragoyja, E.G.; Egorov, V.V. A feasible, fast and reliable method for estimating ion-site association constants in plasticized PVC ion-selective electrode membranes. Anal. Chim. Acta, 2022; submitted, but not yet accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Sokalski, T.; Ceresa, A.; Zwickl, A.T.; Pretsch, E. Large Improvement of the Lower Detection Limit of Ion-Selective Polymer Membrane Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11347–11348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, V.V. Ion-selective liquid electrodes: Problems of description and experimental determination of selectivity. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2008, 78, 2455–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cation | *** | Anion | , ** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | 13.44 ± 0.05 | 13.99 * | Cl− | 13.28 ± 0.05 |
| Na+ | 12.64 ± 0.05 | 13.19 | Br− | 11.83 ± 0.07 |
| K+ | 10.92 ± 0.05 | 11.49 | C6H5SO3− | 10.90 ± 0.06 |
| Rb+ | 10.35 ± 0.06 | 10.94 | NO3− | 10.89 ± 0.08 |
| Cs+ | 9.74 ± 0.05 | 10.37 | I− | 9.41 ± 0.04 |
| TMA+ | 7.62 ± 0.05 | 7.50 | SCN− | 8.80 ± 0.05 |
| TEA+ | 5.69 ± 0.05 | 5.47 | ClO4− | 7.64 ± 0.07 |
| TBA+ | 1.68 ± 0.08 | 1.46 | Pic− | 5.34 ± 0.06 |
| TPP+ | ≡0 | ≡0 | TPB− | ≡0 |
| Ion | , Water—o−NPOE * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Paper | [25] a | [25] b | [29] | [32] | [28] | |
| Li+ | −8.62 | |||||
| Na+ | −7.82 | −6.36 | ||||
| K+ | −6.12 | −5.81 | ||||
| Rb+ | −5.57 | |||||
| Cs+ | −5.00 | −4.03 | −3.68 | −4.32 | ||
| TMA+ | −2.13 | −1.88 | 3.29 | −1.89 | −2.39 | |
| TEA+ | −0.10 | −0.46 | −0.46 | −0.46 | −0.82 | −0.44 |
| TPA+ | 1.52 | 1.37 | 1.58 | |||
| TBA+ | 3.91 | 4.08 | 3.15 | |||
| TPP+ | 5.37 | 4.35 | ||||
| TPAs+ | 5.31 | 5.40 | ||||
| TPB− | 5.37 | 5.31 | 5.52 | 4.35 | 5.40 | |
| Pic− | 0.03 | 0.65 | −0.66 | −0.30 | ||
| ClO4− | −2.28 | −2.70 | − 2.33 | −2.65 | −1.86 | −2.99 |
| SCN− | −3.43 | −3.36 | −4.44 | |||
| I− | −4.05 | −3.70 | −4.74 | |||
| NO3− | −5.52 | −3.82 | −6.36 | |||
| C6H5SO3− | −5.53 | −6.16 | ||||
| Br− | −6.46 | −5.92 | −7.31 | |||
| Cl− | −7.92 | −7.55 | −8.78 | |||
| Li+ | Na+ | K+ | Cs+ | TMA+ | TEA+ | TBA+ | TPP+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPB− | −3.25 | −2.45 −2.01 [32] | −0.75 −0.41 [28] | 0.37 1.28 [25] a 1.84 [25] b 1.08 [28] | 3.24 3.64 [25] b 2.46 [32] 3.01 [28] | 5.27 4.85 [25] a 5.06 [25] b 3.53 [32] 4.96 [28] | 9.28 9.39 [25] a 7.50 [32] | 10.74 8.70 [32] |
| Pic− | −8.59 | −7.79 | −6.09 −6.11 [28] | −4.97 −3.03 [25] b −4.62 [28] | −2.10 −1.23 [25] b −2.63 [29] −2.69 [28] | −0.07 0.19 [25] b −1.12 [29] −0.74 [28] | 3.94 | 5.4 |
| ClO4− | −10.9 | −10.10 −8.22 [32] −8.4 [21] | −8.40 −8.80 [28] −7.2 [21] | −7.28 −6.73 [25] a −6.01 [25] b −7.31 [28] | −4.41 −4.21 [25] b −0.64 [29] −3.75 [32] −5.38 [28] | −2.38 −3.16 [25] a −2.79 [25] b −3.11 [29] −2.68 [32] −3.43 [28] | 1.63 1.38 [25] a 1.29 [32] | 3.09 2.49 [32] |
| SCN− | −12.05 | −11.25 −9.72 [32] −9.8 [21] | −9.55 −10.25 [28] −8.6 [21] | −8.43 −8.76 [28] | −5.56 −5.25 [32] −6.83 [28] | −3.53 −4.18 [32] −4.88 [28] | 0.48 −0.21 [32] | 1.94 0.99 [32] |
| I− | −12.67 | −11.87 −10.2 [21] | −10.17 −10.55 [28] −9.0 [21] | −9.05 −9.06 [28] | −6.18 −5.59 [32] −7.13 [28] | −4.15 −4.52 [32] −5.18 [28] | −0.14 −0.55 [32] | 1.32 0.65 [32] |
| NO3− | −14.14 | −13.34 −10.18 [32] −11.5 [21] | −11.64 −12.17 [28] −10.3 [21] | −10.52 −10.68 [28] | −7.65 −5.71 [32] −8.75 [28] | −5.62 −4.64 [32] −6.80 [28] | −1.61 −0.67 [32] | −0.15 0.53 [32] |
| Br− | −15.08 | −14.28 −12.28 [32] −12.4 [21] | −12.58 −13.12 [28] −11.2 [21] | −11.46 −11.63 [28] | −8.59 −7.81 [32] −9.70 [28] | −6.56 −6.74 [32] −7.75 [28] | −2.55 −2.77 [32] | −1.09 −1.57 [32] |
| Cl− | −16.54 | −15.74 −13.91 [32] −13.6 [21] | −14.04 −14.59 [28] −12.4 [21] | −12.92 −13.10 [28] | −10.05 −9.44 [32] −11.17 [28] | −8.02 −8.37 [32] −9.22 [28] | −4.01 −4.40 [32] | −2.55 −3.20 [32] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siamionau, A.V.; Egorov, V.V. Determination of Single-Ion Partition Coefficients between Water and Plasticized PVC Membrane Using Equilibrium-Based Techniques. Membranes 2022, 12, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101019
Siamionau AV, Egorov VV. Determination of Single-Ion Partition Coefficients between Water and Plasticized PVC Membrane Using Equilibrium-Based Techniques. Membranes. 2022; 12(10):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101019
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiamionau, Andrei V., and Vladimir V. Egorov. 2022. "Determination of Single-Ion Partition Coefficients between Water and Plasticized PVC Membrane Using Equilibrium-Based Techniques" Membranes 12, no. 10: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101019
APA StyleSiamionau, A. V., & Egorov, V. V. (2022). Determination of Single-Ion Partition Coefficients between Water and Plasticized PVC Membrane Using Equilibrium-Based Techniques. Membranes, 12(10), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12101019