Role of the Membrane Transport Mechanism in Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction Experiments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. N117 Membrane Protonation and ZP Cleaning
- Soaked in MilliQ for 1 h at 90 °C;
- Soaked in H2O2 3% wt for 1 h at 90 °C and rinsed in MilliQ at R.T;
- Soaked in H2SO4 0.5 M for 3 h at 90 °C and rinsed in MilliQ at R.T;
- Soaked in MilliQ for 1 h at 90 °C and finally rinsed in MilliQ at R.T;
- Finally, the membrane was stored in a closed vial for 1 h.
2.3. Ammonia Absorption/Releasing Test
2.4. Ammonia Diffusing Process/Migration from Membrane
2.5. Ammonia Quantification
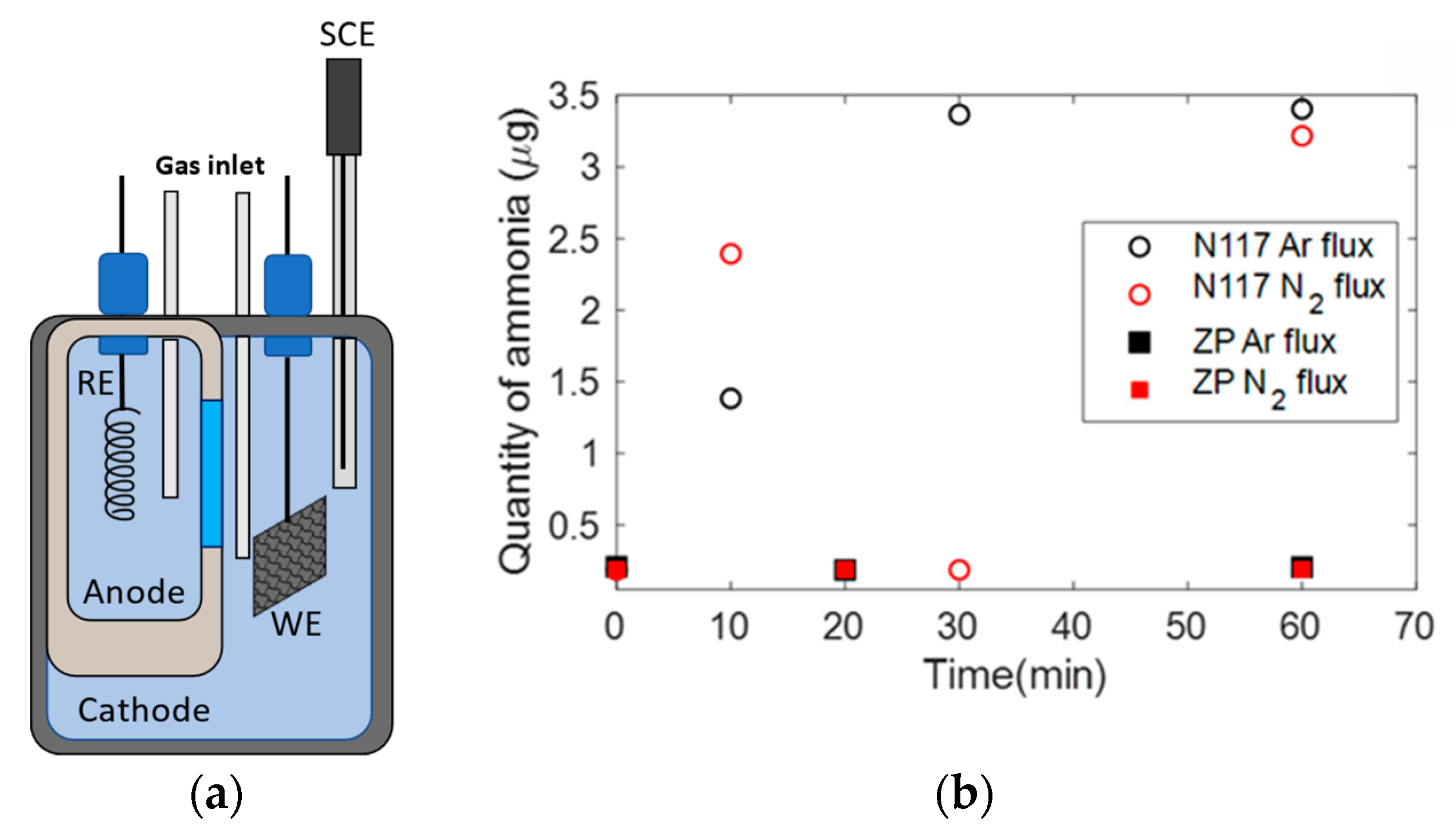
2.6. NRR Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
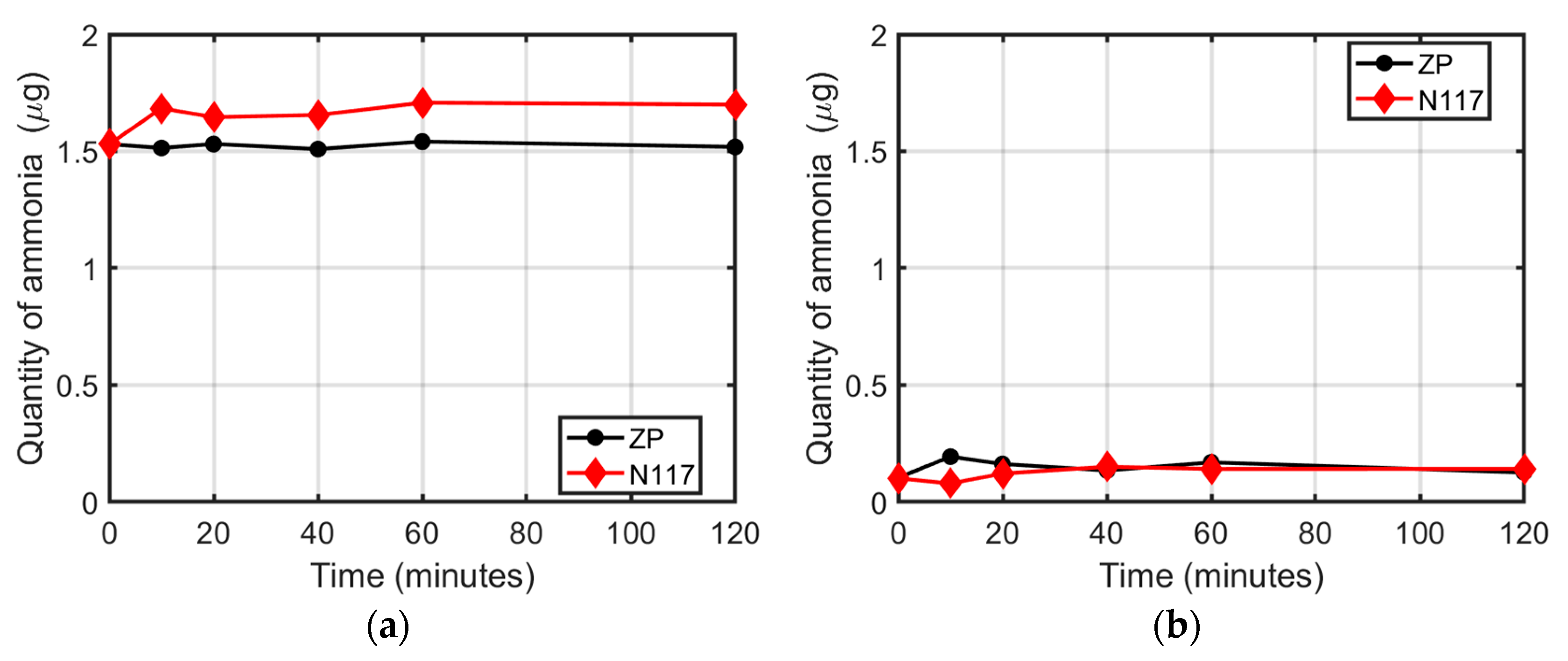
3.1. Membranes in Water Ammonium Solution
3.2. Membranes in Na2SO4 Ammonium Solution
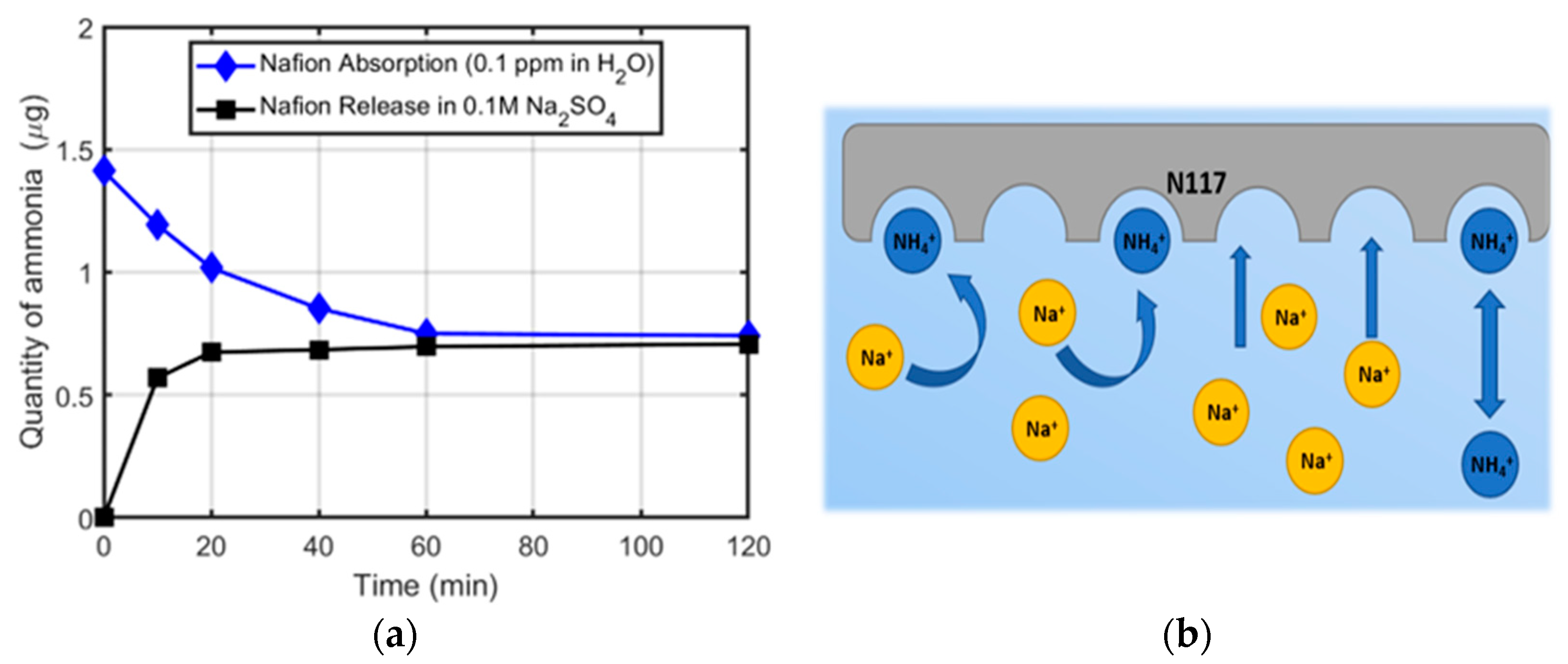
3.3. Absorption in Water Ammonium Solution and Release in Na2SO4
3.4. Ammonium Ion Migration through the ZP Membrane
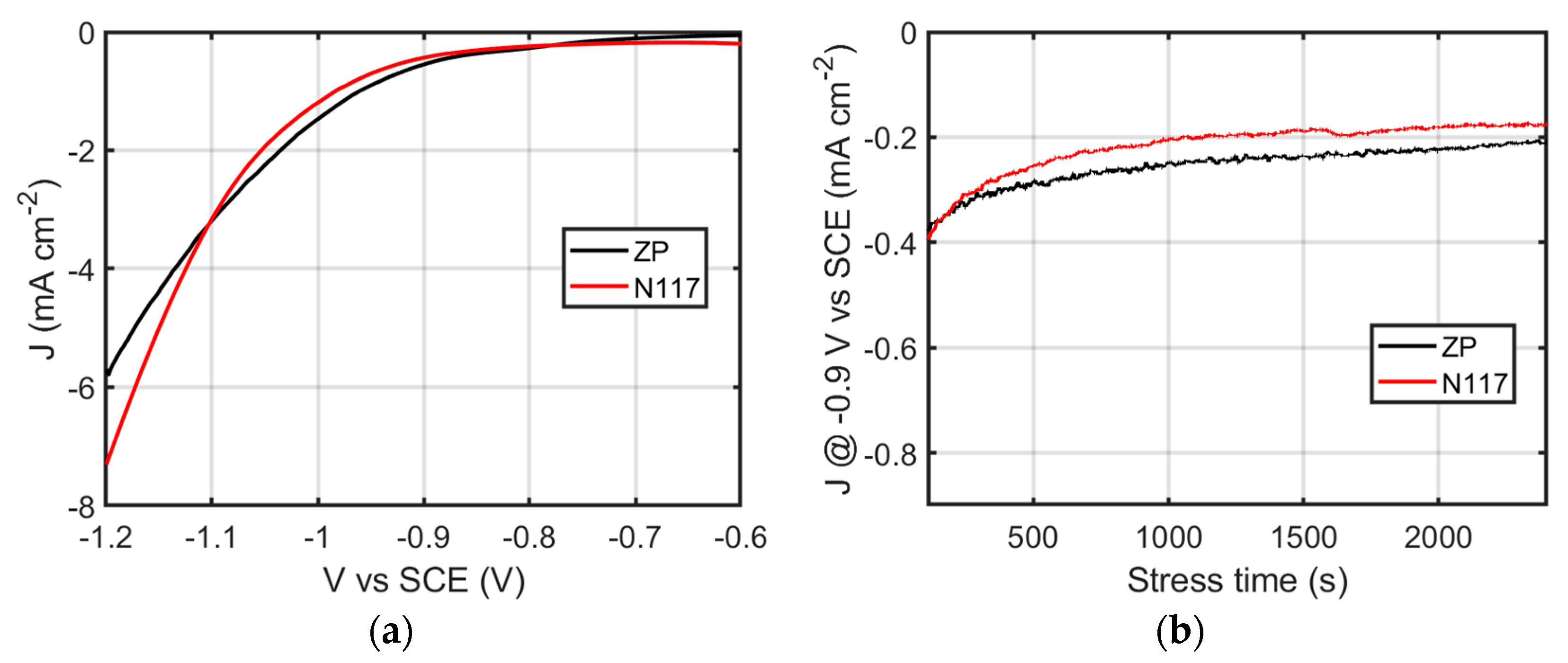
3.5. NRR Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.G.; Crooks, R.M.; Seefeldt, L.C.; Bren, K.L.; Bullock, R.M.; Darensbourg, M.Y.; Holland, P.L.; Hoffman, B.; Janik, M.J.; Jones, A.K.; et al. Beyond fossil fuel–driven nitrogen transformations. Science 2018, 360, 6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shipman, M.A.; Symes, M.D. Recent progress towards the electrosynthesis of ammonia from sustainable resources. Catal. Today 2017, 286, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suryanto, B.H.R.; Du, H.-L.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Simonov, A.N.; MacFarlane, D.R. Challenges and prospects in the catalysis of electroreduction of nitrogen to ammonia. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, S.Z.; Čolić, V.; Yang, S.; Schwalbe, J.A.; Nielander, A.C.; McEnaney, J.M.; Enemark-Rasmussen, K.; Baker, J.G.; Singh, A.R.; Rohr, B.A.; et al. A rigorous electrochemical ammonia synthesis protocol with quantitative isotope measurements. Nature 2019, 570, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Qiao, S.-Z. How to explore ambient electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reliably and insightfully. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3166–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakou, V.; Garagounis, I.; Vasileiou, E.; Vourros, A.; Stoukides, M. Progress in the Electrochemical Synthesis of Ammonia. Catal. Today 2017, 286, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ham, C.J.M.; Koper, M.T.M.; Hetterscheid, D.G.H. Challenges in reduction of dinitrogen by proton and electron transfer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5183–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.-C.; Guo, Y.; Chen, L.-W.; Shu, M.; Wang, X.-Y.; Bu, T.-A.; Gao, W.-Y.; Zhang, N.; Su, X.; Feng, X.; et al. Promoting nitrogen electroreduction to ammonia with bismuth nanocrystals and potassium cations in water. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Iriawan, H.; Yang, F.; Luo, L.; Shen, S.; Shao-Horn, Y.; Zhang, J. Interaction of Ammonia with Nafion and Electrolyte in Electrocatalytic Nitrogen Reduction Study. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 6861–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongsirikarn, K.; Goodwin, J.G.; Greenway, S.; Creager, S. Influence of ammonia on the conductivity of Nafion membranes. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pasaogullari, U.; Molter, T. Influence of ammonia on membrane-electrode assemblies in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 9188–9194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, C.; Tan, X.; Han, X.; Huang, H.; Huang, H.; Qiu, J. Is It Appropriate to Use the Nafion Membrane in Electrocatalytic N2 Reduction? Small Methods 2019, 3, 1900474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J. The removal of inevitable NOx species in catalysts and the selection of appropriate membrane for measuring electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis accurately. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 49, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.; Adriansens, W.; Moreels, J.P.; Leysen, R. Evaluation of the Zirfon® separator for use in alkaline water electrolysis and Ni-H2 batteries. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 1998, 23, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Xie, X.Y.; Qiu, J.; Fang, W.H.; Liang, R.; Ren, X.; Ji, X.; Cui, G.; Asiri, A.M.; Cui, G.; et al. High-performance artificial nitrogen fixation at ambient conditions using a metal-free electrocatalyst. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Li, T.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Q.; Qiu, W.; Guo, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, P.; Asiri, A.M.; Chen, L.; et al. Boosted Electrocatalytic N2 Reduction to NH3 by Defect-Rich MoS2 Nanoflower. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Ruther, R.E.; Hamers, R.J. Photo-illuminated diamond as a solid-state source of solvated electrons in water for nitrogen reduction. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guijarro, N.; Luo, J. The pitfalls in electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction for ammonia synthesis. J. Energy Chem. 2021, 61, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifpour, F.; Sveinbjörnsson, A.; Canales, C.P.; Skúlason, E.; Flosadóttir, H.D. Preparation of Nafion Membranes for Reproducible Ammonia Quantification in Nitrogen Reduction Reaction Experiments. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22938–22942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Xie, G.; Gorseth, O.; Kjelstrup, S.; Nakamura, N.; Arimura, T. Ion and water transport characteristics of Nafion membranes as electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 3741–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Garzon, F.H. Ionic Transport and Water Vapor Uptake of Ammonium Exchanged Perfluorosulfonic Acid Membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, B265–B269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Møller-Holst, S.; Gorseth, O.; Kjelstrup, S. Transport and equilibrium properties of Nafion® membranes with H+ and Na+ ions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 442, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, M.T.; Vreman, A.W. Ohmic resistance in zero gap alkaline electrolysis with a Zirfon diaphragm. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 369, 137684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslau, B.R.; Miller, I.F. A Hydrodynamic Model for Electroosmosis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 2002, 10, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.-D.; Paddison, S.J.; Spohr, E.; Schuster, M. Transport in Proton Conductors for Fuel-Cell Applications: Simulations, Elementary Reactions, and Phenomenology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4637–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peighambardoust, S.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Amjadi, M. Review of the proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 9349–9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, G.F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Comprehensive Understanding of the Thriving Ambient Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Yin, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, H. Rigorous and reliable operations for electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 278, 119325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorante, M.J.; Reynoso, C.Y.; Franco, J.I. Water electrolysis with Zirfon® as separator and NaOH as electrolyte. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 56, 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.; Moreels, J.P.; Claes, A.; Beckers, H. Electrode diaphragm electrode assembly for alkaline water electrolysers. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 9305–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, S. Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials. In Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials; Kobayashi, S., Müllen, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leonardi, M.; Tranchida, G.; Corso, R.; Milazzo, R.G.; Lombardo, S.A.; Privitera, S.M.S. Role of the Membrane Transport Mechanism in Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction Experiments. Membranes 2022, 12, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100969
Leonardi M, Tranchida G, Corso R, Milazzo RG, Lombardo SA, Privitera SMS. Role of the Membrane Transport Mechanism in Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction Experiments. Membranes. 2022; 12(10):969. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100969
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeonardi, Marco, Giuseppe Tranchida, Roberto Corso, Rachela G. Milazzo, Salvatore A. Lombardo, and Stefania M. S. Privitera. 2022. "Role of the Membrane Transport Mechanism in Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction Experiments" Membranes 12, no. 10: 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100969
APA StyleLeonardi, M., Tranchida, G., Corso, R., Milazzo, R. G., Lombardo, S. A., & Privitera, S. M. S. (2022). Role of the Membrane Transport Mechanism in Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction Experiments. Membranes, 12(10), 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100969








